1993 DODGE TRUCK ignition
[x] Cancel search: ignitionPage 323 of 1502

8A
- 2
ELECTRICAL
•
MALFUNCTION
INDICATOR
LAMP
DIAGNOSTIC SCAN
TOOL
POWERTRAIN CONTROL
MODULE
GENERATOR
BATTERY
J938A-23
Fig.
2
Charging
System
Components—Typical
BATTERY TEST
PROCEDURES
INDEX
page
Battery
Charging
6
Battery
Load Test
5
Battery
Open
Circuit
Voltage Test
.............
4
Causes
of
Battery
Discharging
3
GENERAL
INFORMATION
The battery stores, stabilizes,
and
produces electri
cal current.
A
battery must
be
able
to
accept
a
charge
and
produce high-amperage current over
an
extended period.
A
chemical reaction takes place
be
tween sulfuric acid solution (electrolyte)
and
lead + /-
plates
in
each cell
of the
battery.
As the
battery discharges,
the
plates collect acid from
the
electro
lyte.
When
the
charging system charges
the
battery,
water
is
converted
to
sulfuric acid
in the
battery.
The
amount
of
acid (specific gravity)
in the
electrolyte
can
be
measured with
a
hydrometer.
A
factory
in
stalled battery
has a
built-in test indicator
to
help
determine state-of-charge.
The
factory installed bat
tery
is
also nonrefillable, water
can not be
added.
The battery
is
vented
to
release gases that
are cre-
page
General
Information
2
Ignition
Off
Draw (IOD)
4
State
of
Charge Test Using Test
Indicator
.......
3
Test
Indicator
3
ated when
the
battery
is
being charged.
The
battery
top,
posts,
and
terminals should
be
cleaned when other underhood maintenance
is
performed (Fig.
3).
WARNING:
DO
NOT
ATTEMPT
TO
ASSIST BOOST, CHARGE,
OR
TEST BATTERY WHEN ELECTROLYTE LEVEL IS BELOW THE TOP
OF
THE PLATES
(YELLOW
OR
BRIGHT COLOR
IS
VISIBLE). PER
SONAL
INJURY
MAY
OCCUR.
When
the
electrolyte level
is
below
the top of the
plates (yellow
or
bright indicator),
the
battery must
be replaced.
The
battery must
be
completely charged (green indicator)
and the top,
posts,
and
terminals
should
be
properly cleaned before diagnostic proce
dures
are
performed. Refer
to
Group
8B -
Battery/ Starter Service,
for
additional information.
Page 324 of 1502
•
ELECTRICAL
8A - 3
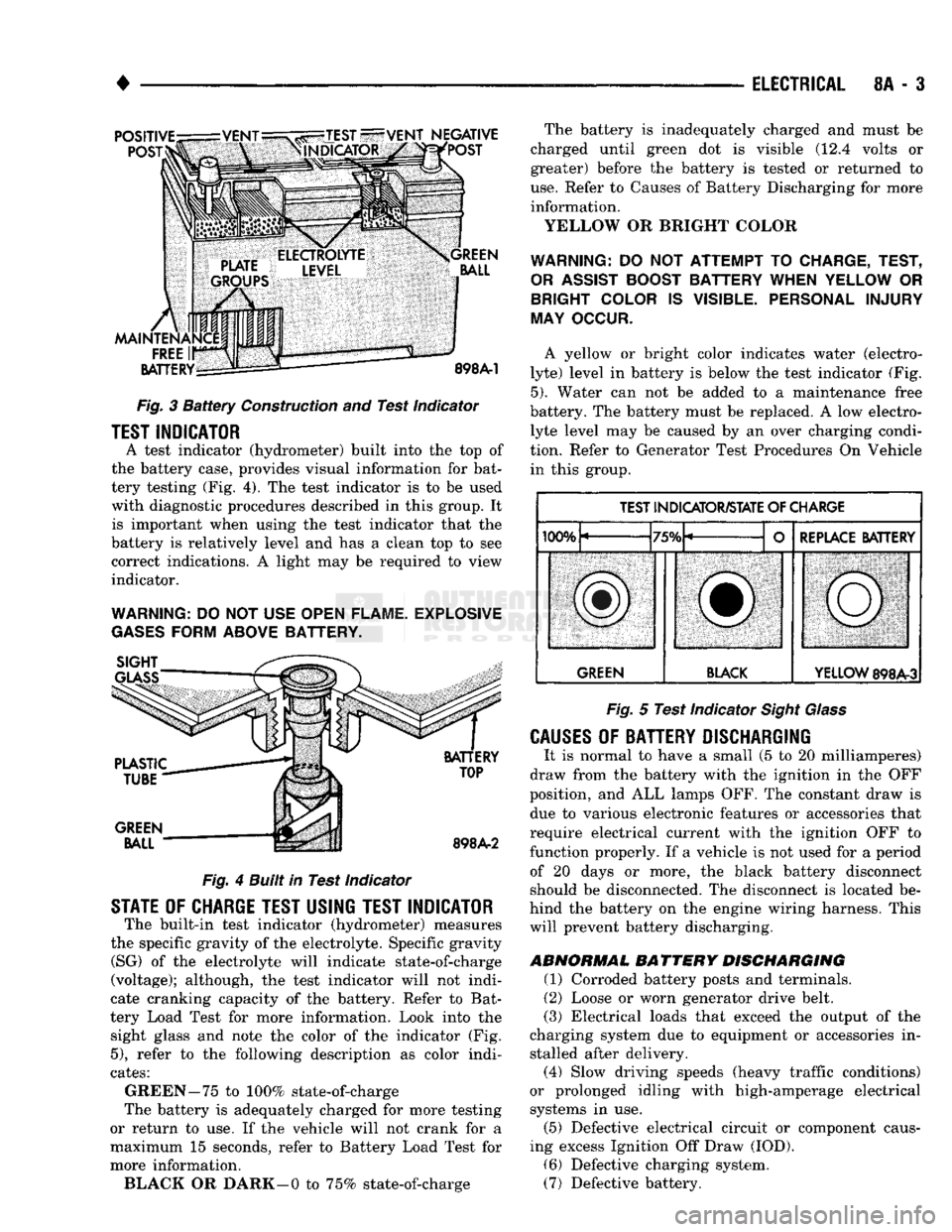
Fig.
3
Battery
Construction
and
Test Indicator
TEST INDICATOR
A test indicator (hydrometer) built into
the top of
the battery case, provides visual information
for
bat
tery testing (Fig.
4). The
test indicator
is to be
used with diagnostic procedures described
in
this group.
It
is important when using
the
test indicator that
the
battery
is
relatively level
and has a
clean
top to see
correct indications.
A
light
may be
required
to
view
indicator.
WARNING:
DO
NOT USE
OPEN FLAME. EXPLOSIVE
GASES
FORM ABOVE BATTERY.
Fig.
4
Built in Test Indicator
STATE
OF
CHARGE TEST USING TEST INDICATOR
The built-in test indicator (hydrometer) measures
the specific gravity
of
the electrolyte. Specific gravity (SG)
of the
electrolyte will indicate state-of-charge
(voltage); although,
the
test indicator will
not
indi
cate cranking capacity
of the
battery. Refer
to
Bat
tery Load Test
for
more information. Look into
the
sight glass
and
note
the
color
of the
indicator
(Fig.
5),
refer
to the
following description
as
color indi
cates:
GREEN-75
to
100% state-of-charge
The battery
is
adequately charged
for
more testing
or return
to use. If the
vehicle will
not
crank
for a
maximum
15
seconds, refer
to
Battery Load Test
for
more information. BLACK
OR
DARK—0
to
75% state-of-charge The battery
is
inadequately charged
and
must
be
charged until green
dot is
visible
(12.4
volts
or
greater) before
the
battery
is
tested
or
returned
to
use.
Refer
to
Causes
of
Battery Discharging
for
more information.
YELLOW
OR
BRIGHT COLOR
WARNING:
DO NOT
ATTEMPT
TO
CHARGE, TEST,
OR
ASSIST
BOOST BATTERY WHEN YELLOW
OR
BRIGHT COLOR
IS
VISIBLE. PERSONAL INJURY
MAY OCCUR.
A yellow
or
bright color indicates water (electro
lyte) level
in
battery
is
below
the
test indicator
(Fig.
5).
Water
can not be
added
to a
maintenance free
battery.
The
battery must
be
replaced.
A low
electro lyte level
may be
caused
by an
over charging condi
tion. Refer
to
Generator Test Procedures
On
Vehicle in this group.
TEST INDICATOR/STATE
OF
CHARGE
IfVW,
"TCfV
REPLACE BATTERY
lUUTu
/Otu L
f
REPLACE BATTERY
SBl
ill,
iMMiMMMMSMM^MM
GREEN BLACK
YELLOW
898A-3
Fig.
5
Test Indicator
Sight Glass
CAUSES
OF
BATTERY DISCHARGING
It
is
normal
to
have
a
small
(5 to 20
milliamperes)
draw from
the
battery with
the
ignition
in the OFF
position,
and ALL
lamps OFF.
The
constant draw
is
due
to
various electronic features
or
accessories that
require electrical current with
the
ignition
OFF to
function properly.
If a
vehicle
is not
used
for a
period of
20
days
or
more,
the
black battery disconnect
should
be
disconnected.
The
disconnect
is
located
be
hind
the
battery
on the
engine wiring harness. This will prevent battery discharging.
ABNORMAL
BATTERY
DISCHARGING
(1) Corroded battery posts
and
terminals.
(2) Loose
or
worn generator drive belt.
(3) Electrical loads that exceed
the
output
of the
charging system
due to
equipment
or
accessories
in
stalled after delivery. (4) Slow driving speeds (heavy traffic conditions)
or prolonged idling with high-amperage electrical systems
in use.
(5) Defective electrical circuit
or
component caus
ing excess Ignition
Off
Draw (IOD).
(6) Defective charging system.
(7) Defective battery.
Page 325 of 1502

8A
- 4
ELECTRICAL
•
IGNITION
OFF
DRAW
(IOD)
Ignition off draw refers to power being drained
from the battery with the ignition turned off. A nor
mal vehicle electrical system will draw from 5 to 20
milliamps. A vehicle that has not been operated for
an extended period of time (approximately 20 days)
may discharge the battery to an inadequate level.
Battery drain should not exceed approximately 20
MA (20 milliamps = 0.020 amps). The 20 MA are needed to supply PCM memory,
digital clock memory, and ETR (electronically tuned
radio) memory. Excessive battery drain is caused by items left
turned on, internally shorted generator, or intermit
tent short in wiring.
If the IOD is excessive (over 20 milliamperes), the
defect must be found and corrected before replacing a
battery. In most cases the battery can be charged and returned to service.
TEST PROCEDURE Testing for higher amperage IOD must be per
formed first to prevent damage to most milliamp
meters.
Verify that all electrical accessories are OFF. Turn
off all lights, remove ignition key, and close all
doors.
If the vehicle is equipped with electronic acces
sories (illuminated entry, high line radio), allow the
systems to automatically shut off (time out), up to 3
minutes.
(1) After determining that the underhood lamp is
operating properly then disconnect bulb. (2) Disconnect negative cable from battery.
(3) Connect a typical 12 volt test light (low watt
age bulb) between the negative cable clamp and the
battery negative terminal. The test light may light brightly for up to 3 min
utes or may not light at all (depending on the elec
trical equipment). The term brightly being used
throughout the following tests, implies the bright ness of the test light will be the same as if it were
connected across the battery.
The test light must be securely clamped to the neg
ative cable and battery terminal. If the test light be
comes disconnected during any of the IOD test, the electronic timer function will be activated and all
tests must be repeated.
(4) After 3 minutes, the test light should turn OFF
or be DIMLY lit (depending on the electrical equip
ment).
If the test light remains brightly lit do not
disconnect it. Remove each fuse or circuit breaker (refer to Group 8 - Wiring Diagrams) until test light
is either OFF or DIMLY lit. This will eliminate the
higher amperage draw.
If test light is still bright after disconnecting each
fuse and circuit breaker, disconnect the wiring har ness from the generator. Refer to Generator Testing
in this group. Do not disconnect the test light. After higher amperage IOD has been corrected, low
amperage IOD may be checked.
It is now safe to install milliamp meter to check for
low amperage IOD.
(5) With test light still connected, securely clamp
an ammeter between battery negative terminal and
negative battery cable.
If the test light or the milliamp meter circuit is
broken the various timer circuits will start. Do
not open any doors or turn on any electrical ac cessories with the test light disconnected or the
meter may be damaged.
(6) Disconnect test light. The current draw should
not exceed 0.020 amp. If it exceeds 20 milliamps iso
late each circuit by removing circuit breakers and
fuses.
The meter reading drops once the high current
problem is found. Repair this section of the circuit,
whether it is a wiring short or component failure.
BATTERY
OPEN CIRCUIT VOLTAGE TEST
A battery voltage (no load) test will indicate the
state of charge of a battery that will pass the Battery
Load Test described in this section. Before proceed
ing with this test or the Battery Load Test the
battery must be completely charged as de scribed in Battery Charging in this section. If a battery has a no load voltage reading of 12.4
volts or greater but will not endure a load test, it is
defective and should be replaced. Refer to Group 8B,
Battery/Starter Service for instructions. To test bat
tery no load voltage, perform the following operation: (1) Before measuring open circuit voltage, the sur
face charge must be removed from plates. Turn head lights on for 15 seconds then allow up to 5 minutes
for voltage to stabilize. (2) Remove both battery cables, negative first.
(3) Using a voltmeter connected to the battery
posts,
see instructions provided with voltmeter, mea sure open circuit voltage (Fig. 6). This voltage reading will indicate state of charge,
but will not reveal cranking capacity. Refer to Bat
tery Open Circuit Voltage chart.
BATTERY OPEN CIRCUIT VOLTAGE
Open
Circuit
Volts
Percent
Chang©
11.7
volts
or
less
0%
12.0 25%
12.2 50%
12.4 75%
12.6
or more 100%
918A-3
Page 329 of 1502
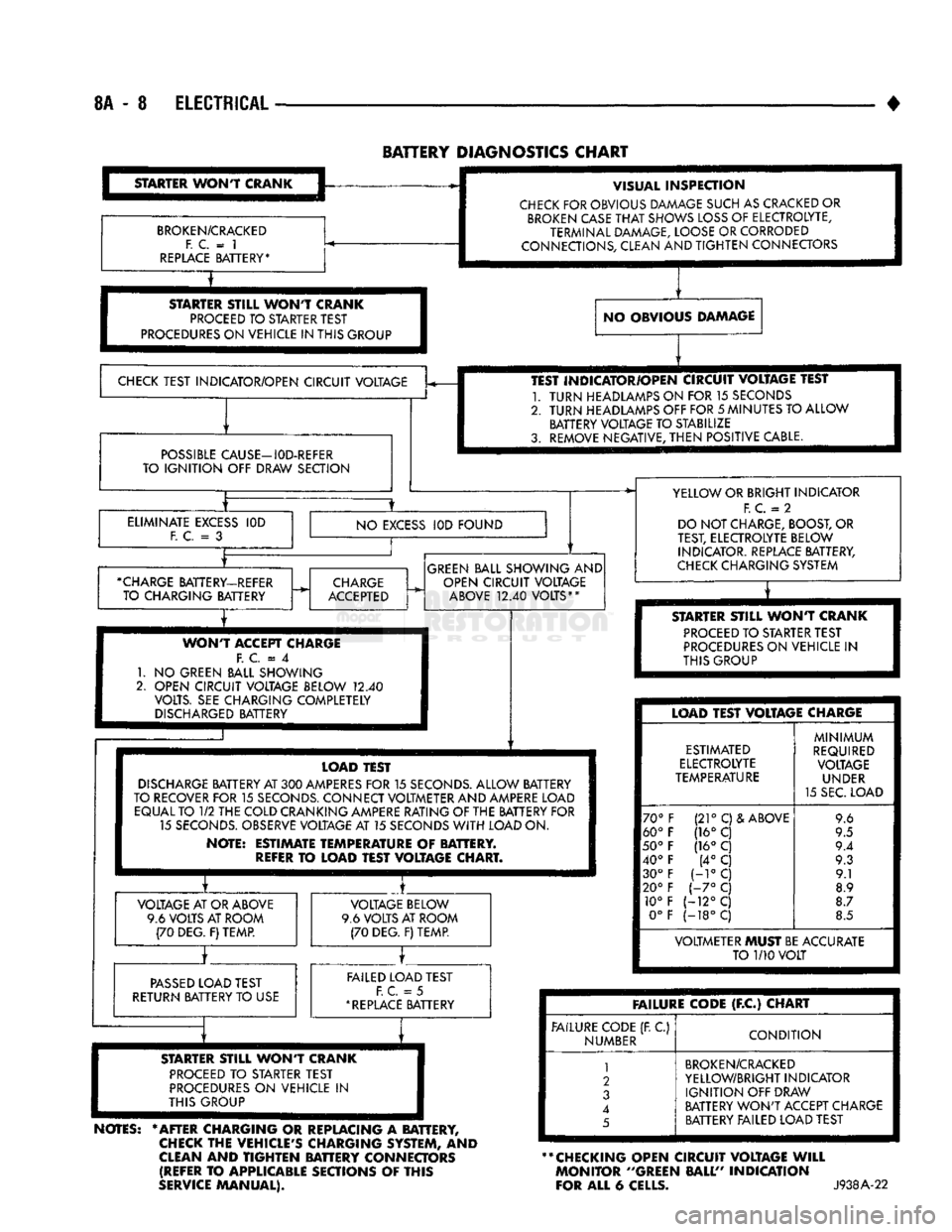
8A
- 8
ELECTRICAL
BATTERY
DIAGNOSTICS
CHART
STARTER
WONT
CRANK
BROKEN/CRACKED
F. C.
= 1
REPLACE
BATTERY* VISUAL
INSPECTION
CHECK
FOR OBVIOUS DAMAGE SUCH AS CRACKED OR
BROKEN
CASE
THAT
SHOWS
LOSS
OF ELECTROLYTE,
TERMINAL DAMAGE, LOOSE OR CORRODED
CONNECTIONS, CLEAN AND
TIGHTEN
CONNECTORS
STARTER
STILL
WONT
CRANK
PROCEED
TO STARTER TEST
PROCEDURES
ON VEHICLE IN THIS GROUP NO OBVIOUS DAMAGE
CHECK
TEST INDICATOR/OPEN CIRCUIT VOLTAGE
POSSIBLE
CAUSE—I0D-REFER
TO
IGNITION
OFF DRAW SECTION TEST INDICATOR/OPEN CIRCUIT VOLTAGE TEST
1.
TURN
HEADLAMPS ON FOR 15 SECONDS
2.
TURN
HEADLAMPS OFF FOR
5
MINUTES TO ALLOW BATTERY VOLTAGE TO STABILIZE
3. REMOVE NEGATIVE,
THEN
POSITIVE CABLE.
ELIMINATE
EXCESS
F. C.
= 3
IOD
NO
EXCESS
IOD FOUND
•CHARGE
BATTERY-REFER TO CHARGING BATTERY
CHARGE
ACCEPTED
GREEN
BALL SHOWING AND
OPEN CIRCUIT VOLTAGE
ABOVE
12.40
VOLTS**
WONT
ACCEPT CHARGE F.
C = 4
1.
NO
GREEN BALL SHOWING
2. OPEN CIRCUIT VOLTAGE BELOW
12.40
VOLTS. SEE CHARGING COMPLETELY
DISCHARGED
BATTERY YELLOW OR BRIGHT INDICATOR
F.
C.
= 2
DO NOT CHARGE, BOOST, OR
TEST, ELECTROLYTE BELOW INDICATOR. REPLACE BATTERY,
CHECK
CHARGING SYSTEM
T
STARTER
STILL
WONT
CRANK
PROCEED
TO STARTER TEST
PROCEDURES
ON VEHICLE
IN
THIS GROUP LOAD TEST
DISCHARGE
BATTERY AT
300
AMPERES
FOR
15
SECONDS.
ALLOW BATTERY
TO RECOVER FOR
15
SECONDS.
CONNECT VOLTMETER AND AMPERE LOAD EQUAL TO
1/2
THE COLD CRANKING AMPERE RATING OF THE BATTERY FOR 15
SECONDS.
OBSERVE VOLTAGE AT 15 SECONDS
WITH
LOAD ON.
NOTE: ESTIMATE TEMPERATURE
OF
BATTERY.
REFER
TO
LOAD TEST VOLTAGE CHART. VOLTAGE AT OR ABOVE
9.6 VOLTS AT ROOM (70 DEG. F) TEMP. VOLTAGE BELOW
9.6 VOLTS AT ROOM (70 DEG. F) TEMP.
PASSED
LOAD TEST
RETURN BATTERY TO USE FAILED LOAD TEST
F. C.
= 5
*
REPLACE
BATTERY LOAD TEST VOLTAGE CHARGE
ESTIMATED
ELECTROLYTE
TEMPERATURE
70°
60°
50°
40° 30°
20° 10° 0° (21°
C)& ABOVE
(16° C
(16°
C (4°
C
H°C
1-7°
C
(-12°C
(-18°C
MINIMUM
REQUIRED VOLTAGE UNDER
15 SEC. LOAD 9.6
9.5
9.4 9.3 9.1
8.9
8.7
8.5 VOLTMETER MUST BE ACCURATE
TO
1/10
VOLT
STARTER
ST8LL
WONT
CRANK
PROCEED
TO
STARTER TEST
PROCEDURES
ON
VEHICLE
IN
THIS GROUP
NOTES:
* AFTER CHARGING
OR
REPLACING
A
BATTERY,
CHECK
THE VEHICLE'S CHARGING SYSTEM,
AND
CLEAN
AND
TIGHTEN
BATTERY CONNECTORS (REFER
TO
APPLICABLE SECTIONS
OF
THIS
SERVICE
MANUAL). FAILURE CODE
(F.C)
CHART
FAILURE CODE (R
C)
NUMBER
CONDITION
1
2
3
4
5
BROKEN/CRACKED
YELLOW/BRIGHT INDICATOR
IGNITION
OFF DRAW
BATTERY
WON'T
ACCEPT CHARGE BATTERY FAILED LOAD TEST
** CHECKING OPEN CIRCUIT VOLTAGE
WILL
MONITOR ''GREEN BALL" INDICATION
FOR ALL
6
CELLS.
J938A-22
Page 330 of 1502
•
ELECTRICAL
8A - 9
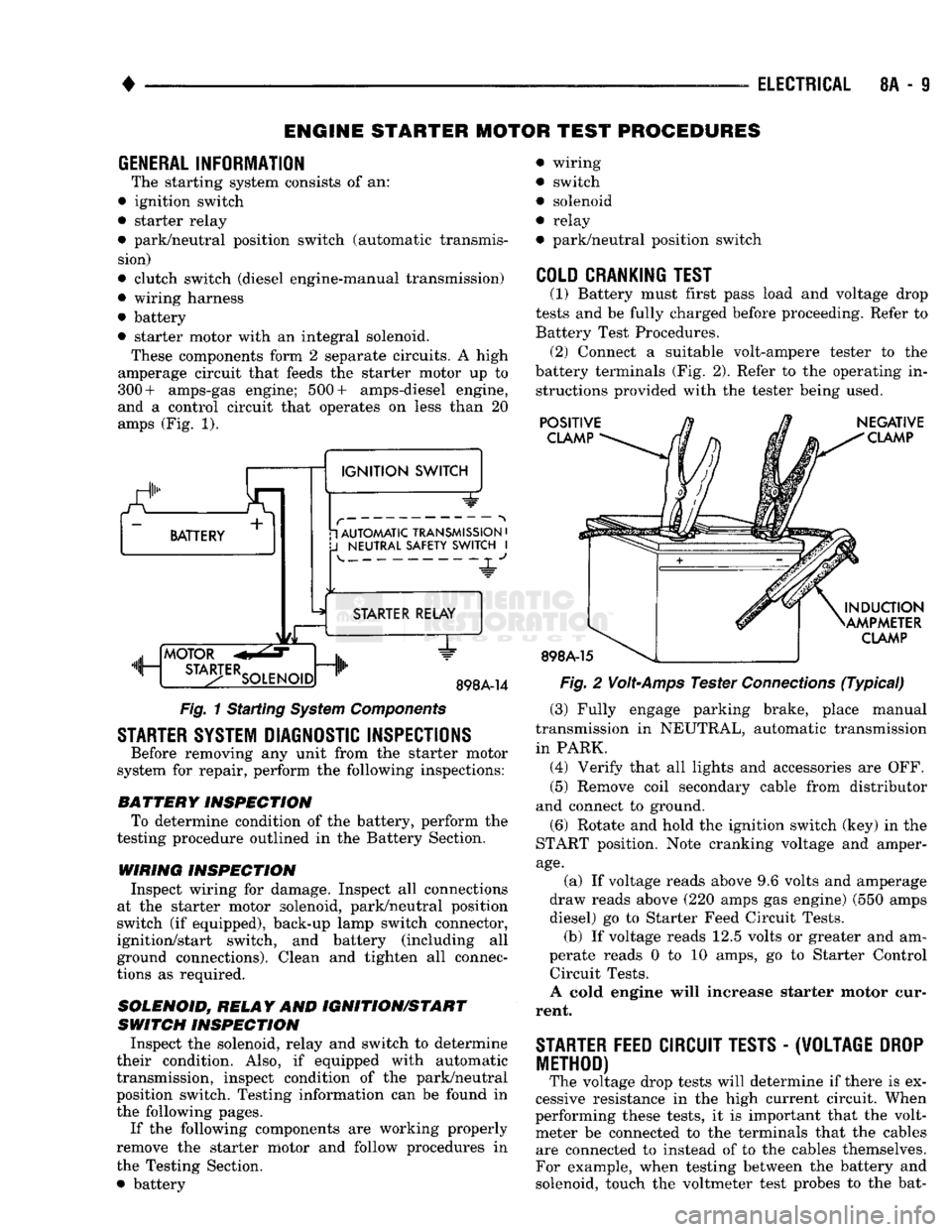
ENGINE STARTER MOTOR TEST PROCEDURES
GENERAL INFORMATION
The starting system consists of an:
• ignition switch
• starter relay
• park/neutral position switch (automatic transmis sion)
• clutch switch (diesel engine-manual transmission)
• wiring harness
• battery
• starter motor with an integral solenoid. These components form 2 separate circuits. A high
amperage circuit that feeds the starter motor up to
300+ amps-gas engine; 500+ amps-diesel engine,
and a control circuit that operates on less than 20
amps (Fig. 1).
a.
BATTERY +
1
IGNITION
SWITCH 1 AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION
•
J
NEUTRAL SAFETY SWITCH
I 4-
"JL"
MOTOR
m, ...
STA3-TERSOLENO,Dnlh
STARTER RELAY
1"
898A-14
Fig.
1 Starting
System
Components
STARTER SYSTEM DIAGNOSTIC INSPECTIONS
Before removing any unit from the starter motor
system for repair, perform the following inspections:
BATTERY
INSPECTION
To determine condition of the battery, perform the
testing procedure outlined in the Battery Section.
WIRING INSPECTION
Inspect wiring for damage. Inspect all connections
at the starter motor solenoid, park/neutral position
switch (if equipped), back-up lamp switch connector,
ignition/start switch, and battery (including all
ground connections). Clean and tighten all connec
tions as required.
SOLENOID, RELAY
AND
IGNITION/START
SWITCH
INSPECTION
Inspect the solenoid, relay and switch to determine
their condition. Also, if equipped with automatic
transmission, inspect condition of the park/neutral position switch. Testing information can be found in
the following pages.
If the following components are working properly
remove the starter motor and follow procedures in
the Testing Section. • battery wiring
switch
solenoid
relay
park/neutral position switch
COLD CRANKING TEST
(1) Battery must first pass load and voltage drop
tests and be fully charged before proceeding. Refer to Battery Test Procedures. (2) Connect a suitable volt-ampere tester to the
battery terminals (Fig. 2). Refer to the operating in structions provided with the tester being used.
POSITIVE
CLAMP
898A-15
NEGATIVE
CLAMP
INDUCTION
AMPMETER
CLAMP
Fig.
2
Volt-Amps
Tester
Connections
(Typical)
(3) Fully engage parking brake, place manual
transmission in NEUTRAL, automatic transmission
in PARK. (4) Verify that all lights and accessories are OFF. (5) Remove coil secondary cable from distributor
and connect to ground.
(6) Rotate and hold the ignition switch (key) in the
START position. Note cranking voltage and amper
age.
(a) If voltage reads above 9.6 volts and amperage
draw reads above (220 amps gas engine) (550 amps
diesel) go to Starter Feed Circuit Tests. (b) If voltage reads 12.5 volts or greater and am-
perate reads 0 to 10 amps, go to Starter Control Circuit Tests.
A cold engine will increase starter motor cur
rent.
STARTER
FEED
CIRCUIT TESTS
-
(W0LTAGE
DROP
METHOD)
The voltage drop tests will determine if there is ex
cessive resistance in the high current circuit. When
performing these tests, it is important that the volt meter be connected to the terminals that the cables are connected to instead of to the cables themselves.
For example, when testing between the battery and
solenoid, touch the voltmeter test probes to the bat-
Page 331 of 1502
8A
- 10
ELECTRICAL
•
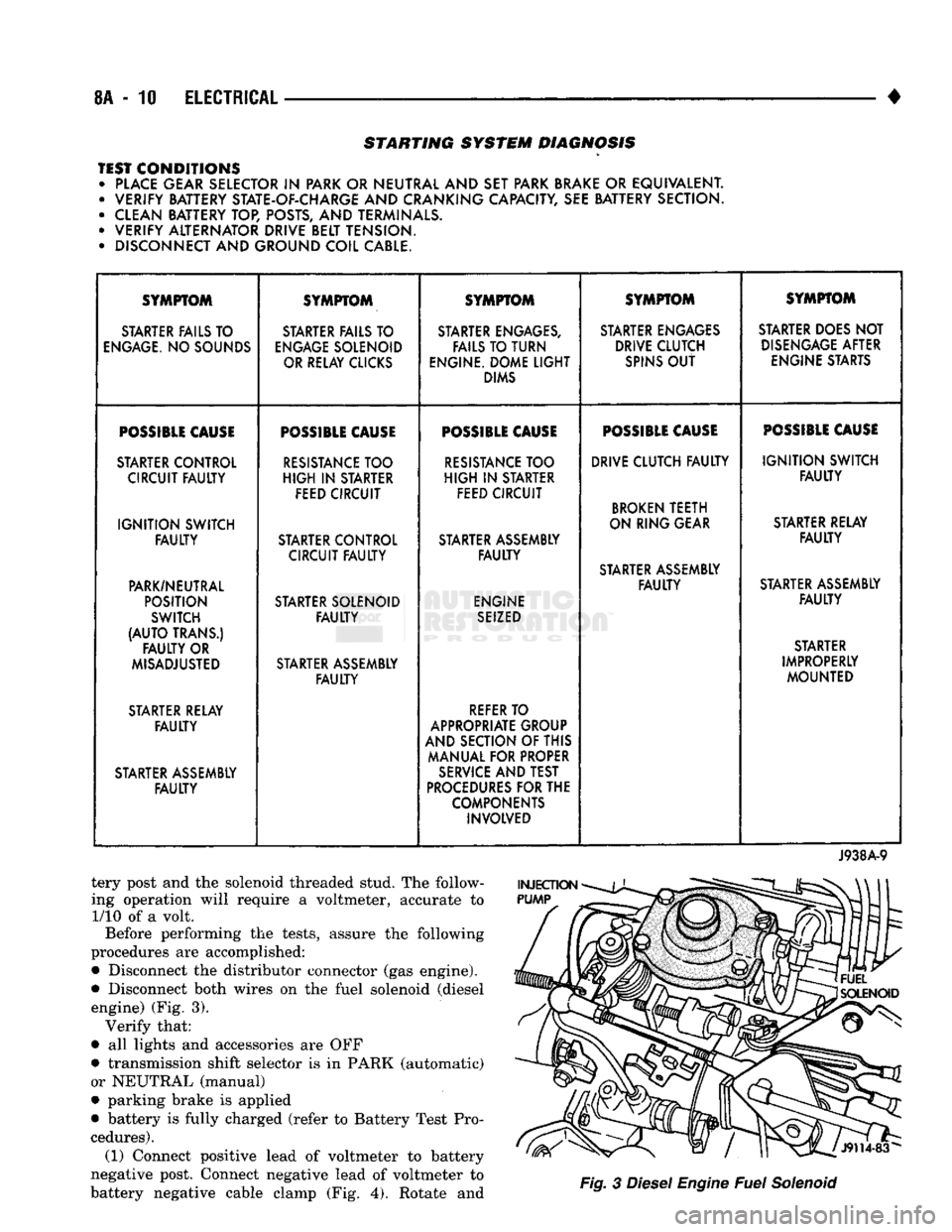
STARTING SYSTEM DIAGNOSIS
TEST CONDITIONS • PLACE GEAR SELECTOR
IN
PARK OR NEUTRAL AND SET PARK BRAKE
OR
EQUIVALENT. • VERIFY BATTERY STATE-OF-CHARGE AND CRANKING CAPACITY, SEE BATTERY SECTION.
• CLEAN BATTERY TOP, POSTS, AND TERMINALS.
• VERIFY ALTERNATOR DRIVE BELT TENSION.
• DISCONNECT AND GROUND COIL CABLE. SYMPTOM
SYMPTOM SYMPTOM SYMPTOM SYMPTOM
STARTER FAILS TO STARTER FAILS TO STARTER ENGAGES, STARTER ENGAGES STARTER DOES NOT
ENGAGE.
NO SOUNDS
ENGAGE
SOLENOID FAILS TO TURN DRIVE CLUTCH
DISENGAGE
AFTER
OR RELAY CLICKS ENGINE. DOME
LIGHT
SPINS
OUT
ENGINE STARTS
DIMS
POSSIBLE
CAUSE
POSSIBLE
CAUSE
POSSIBLE
CAUSE
POSSIBLE
CAUSE
POSSIBLE
CAUSE
STARTER CONTROL
RESISTANCE
TOO
RESISTANCE
TOO DRIVE CLUTCH
FAULTY
IGNITION
SWITCH
CIRCUIT
FAULTY
HIGH
IN
STARTER
HIGH
IN
STARTER
FAULTY
FEED CIRCUIT FEED CIRCUIT
BROKEN
TEETH
IGNITION
SWITCH ON RING GEAR
STARTER RELAY
FAULTY
STARTER CONTROL STARTER ASSEMBLY
FAULTY
CIRCUIT
FAULTY FAULTY
STARTER ASSEMBLY
PARK/NEUTRAL
FAULTY
STARTER ASSEMBLY
POSITION STARTER SOLENOID ENGINE
FAULTY
SWITCH
FAULTY
SEIZED
(AUTO
TRANS.) STARTER
FAULTY
OR STARTER
MISADJUSTED STARTER ASSEMBLY IMPROPERLY
FAULTY
MOUNTED
STARTER RELAY
REFER
TO
FAULTY
APPROPRIATE GROUP
AND SECTION OF THIS
MANUAL FOR PROPER
STARTER ASSEMBLY
SERVICE
AND TEST
FAULTY
PROCEDURES
FOR THE
COMPONENTS INVOLVED
J938A-9
tery post and the solenoid threaded stud. The follow
ing operation will require a voltmeter, accurate to 1/10 of a volt.
Before performing the tests, assure the following
procedures are accomplished:
•
Disconnect the distributor connector (gas engine).
•
Disconnect both wires on the fuel solenoid (diesel engine) (Fig. 3). Verify that:
•
all lights and accessories are OFF
•
transmission shift selector is in PARK (automatic)
or NEUTRAL (manual)
•
parking brake is applied
•
battery is fully charged (refer to Battery Test Pro
cedures). (1) Connect positive lead of voltmeter to battery
negative post. Connect negative lead of voltmeter to
battery negative cable clamp (Fig. 4). Rotate and
Fig.
3
Diesel
Engine
Fuel
Solenoid
Page 332 of 1502
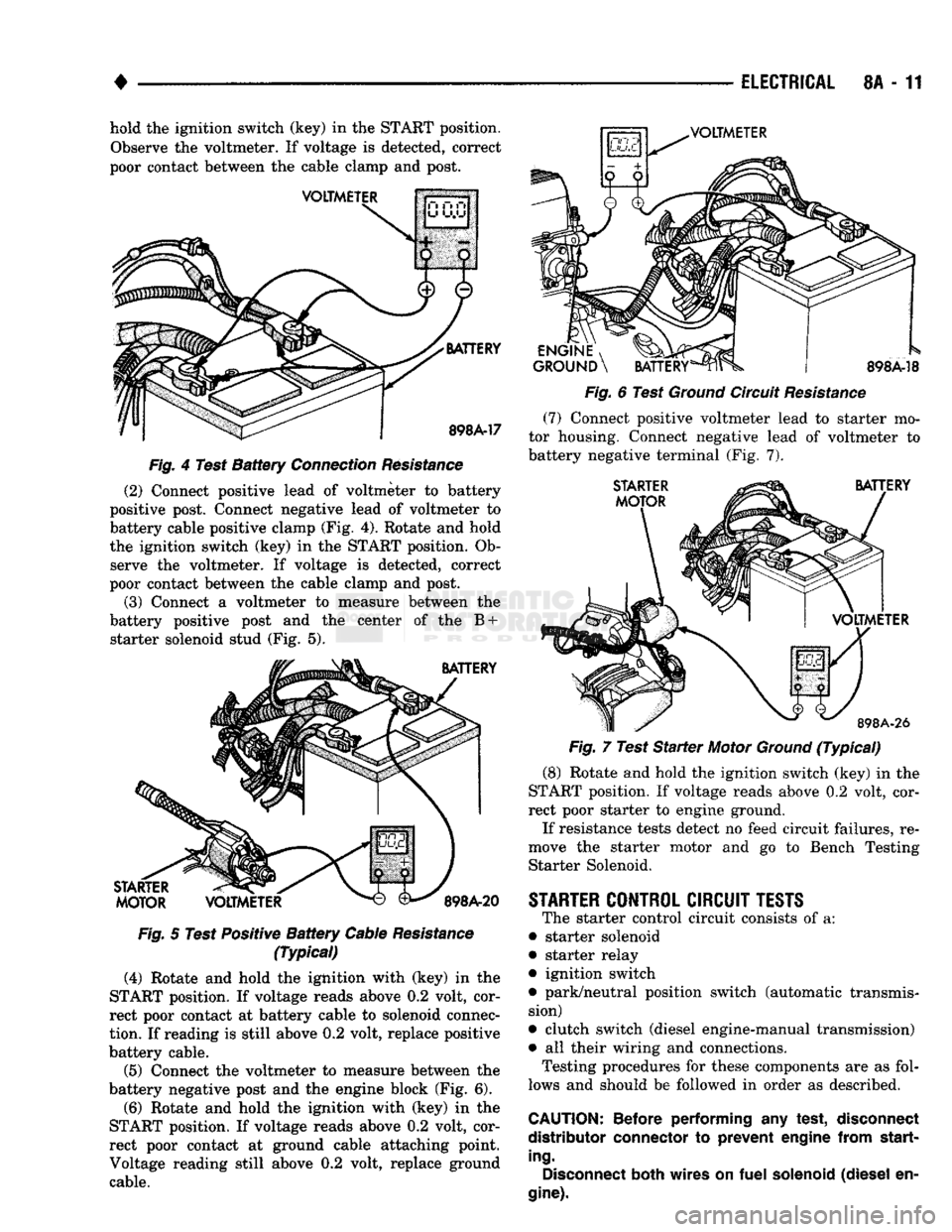
•
ELECTRICAL
8A - 11 hold the ignition switch (key) in the START position.
Observe the voltmeter. If voltage is detected, correct
poor contact between the cable clamp and post.
VOLTMETER
VOLTMETER
BATTERY
898A-17
Fig.
4 Test
Battery
Connection
Resistance
(2) Connect positive lead of voltmeter to battery
positive post. Connect negative lead of voltmeter to
battery cable positive clamp (Fig. 4). Rotate and hold
the ignition switch (key) in the START position. Ob serve the voltmeter. If voltage is detected, correct
poor contact between the cable clamp and post.
(3) Connect a voltmeter to measure between the
battery positive post and the center of the B + starter solenoid stud (Fig. 5).
BATTERY
STARTER
MOTOR
VOLTMETER
898A-20
Fig.
5 Test Positive
Battery
Cable
Resistance
(Typical)
(4) Rotate and hold the ighition with (key) in the
START position. If voltage reads above 0.2 volt, cor
rect poor contact at battery cable to solenoid connec
tion.
If reading is still above 0.2 volt, replace positive
battery cable.
(5) Connect the voltmeter to measure between the
battery negative post and the engine block (Fig. 6).
(6) Rotate and hold the ignition with (key) in the
START position. If voltage reads above 0.2 volt, cor
rect poor contact at ground cable attaching point.
Voltage reading still above 0.2 volt, replace ground cable.
ENGINE
, ^J^P
GROUND
\
BATTERY
898A-18
Fig.
6 Test
Ground
Circuit
Resistance
(7)
Connect positive voltmeter lead to starter mo
tor housing. Connect negative lead of voltmeter to
battery negative terminal (Fig. 7).
STARTER
MOTOR
BATTERY
VOLTMETER
898A-26
Fig.
7 Test
Starter
Motor
Ground
(Typical)
(8) Rotate and hold the ignition switch (key) in the
START position. If voltage reads above 0.2 volt, cor
rect poor starter to engine ground.
If resistance tests detect no feed circuit failures, re
move the starter motor and go to Bench Testing Starter Solenoid.
STARTER
CONTROL
CIRCUIT
TESTS
The starter control circuit consists of a:
• starter solenoid
• starter relay
• ignition switch
• park/neutral position switch (automatic transmis sion)
• clutch switch (diesel engine-manual transmission)
• all their wiring and connections.
Testing procedures for these components are as fol
lows and should be followed in order as described.
CAUTION:
Before
performing
any
test,
disconnect
distributor
connector
to
prevent
engine
from
start
ing.
Disconnect
both
wires
on
fuel
solenoid
(diesel
en
gine).
Page 333 of 1502
8A
- 12
ELECTRICAL
•
ENGINE
STARTER
RELAY
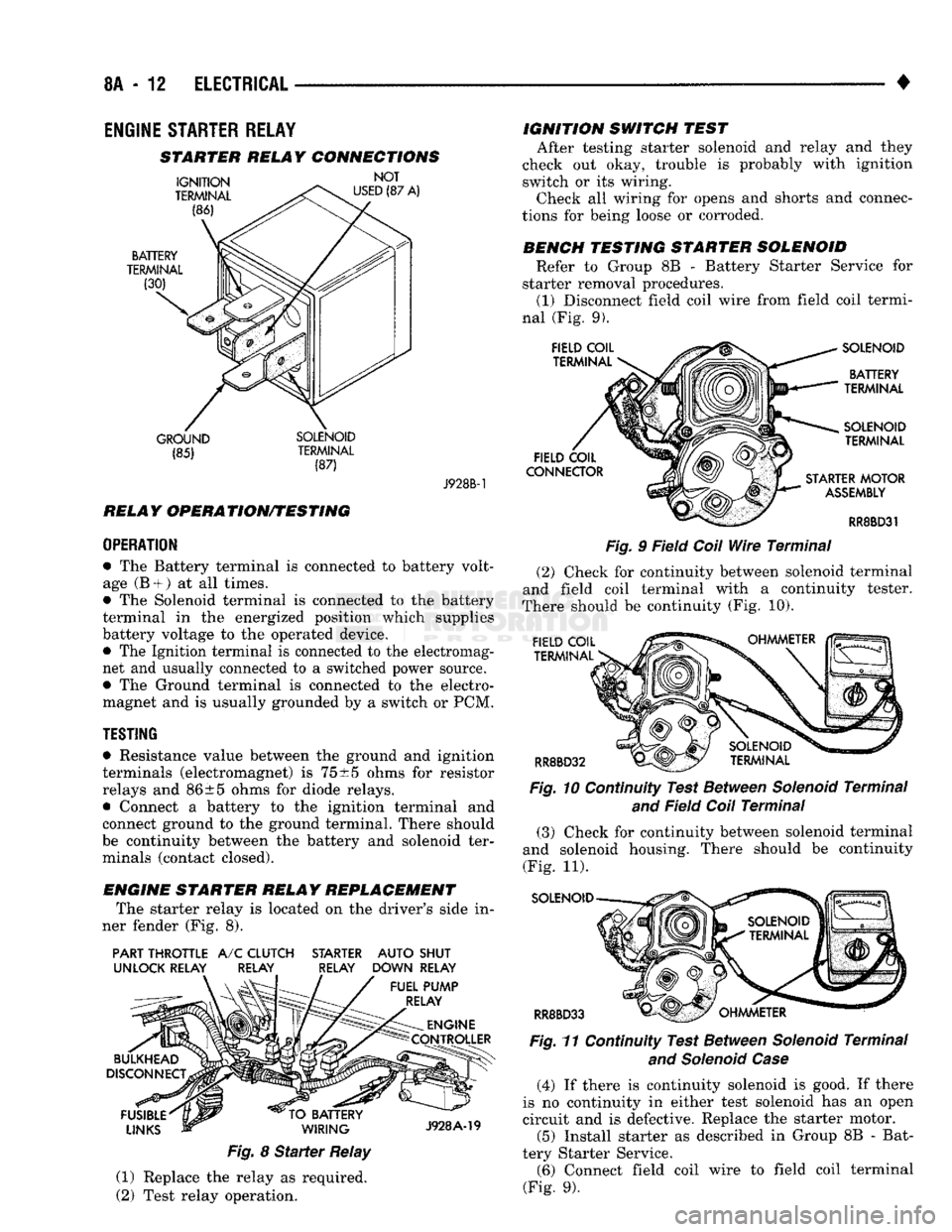
STARTER RELAY CONNECTIONS
GROUND SOLENOID (85) TERMINAL
(87) J928B-1
RELAY OPERATION/TESTING
OPERATION
• The Battery terminal is connected to battery volt
age (B +
)
at all times.
• The Solenoid terminal is connected to the battery
terminal in the energized position which supplies
battery voltage to the operated device. • The Ignition terminal is connected to the electromag
net and usually connected to a switched power source.
• The Ground terminal is connected to the electro
magnet and is usually grounded by a switch or PCM.
TESTING
• Resistance value between the ground and ignition
terminals (electromagnet) is
75
±5 ohms for resistor
relays and 86±5 ohms for diode relays.
• Connect a battery to the ignition terminal and
connect ground to the ground terminal. There should
be continuity between the battery and solenoid ter minals (contact closed).
ENGINE STARTER RELAY REPLACEMENT The starter relay is located on the driver's side in
ner fender (Fig. 8).
PART THROTTLE
A/C
CLUTCH STARTER AUTO SHUT
UNLOCK RELAY RELAY RELAY DOWN RELAY
Fig.
8
Starter
Relay
(1) Replace the relay as required.
(2) Test relay operation. IGNITION SWITCH TEST
After testing starter solenoid and relay and they
check out okay, trouble is probably with ignition
switch or its wiring. Check all wiring for opens and shorts and connec
tions for being loose or corroded.
BENCH TESTING STARTER SOLENOID Refer to Group 8B - Battery Starter Service for
starter removal procedures. (1) Disconnect field coil wire from field coil termi
nal (Fig. 9).
Fig.
9 Field
Coil
Wire
Terminal
(2) Check for continuity between solenoid terminal
and field coil terminal with a continuity tester.
There should be continuity (Fig. 10).
Fig.
10 Continuity Test Between
Solenoid
Terminal
and
Field
Coil
Terminal
(3) Check for continuity between solenoid terminal
and solenoid housing. There should be continuity
(Fig. 11).
SOLENOID
RR8BD33 Fig.
11 Continuity Test Between
Solenoid
Terminal
and Solenoid Case
(4) If there is continuity solenoid is good. If there
is no continuity in either test solenoid has an open
circuit and is defective. Replace the starter motor. (5) Install starter as described in Group 8B - Bat
tery Starter Service. (6) Connect field coil wire to field coil terminal
(Fig. 9).