1993 CHEVROLET PLYMOUTH ACCLAIM check engine
[x] Cancel search: check enginePage 1618 of 2438
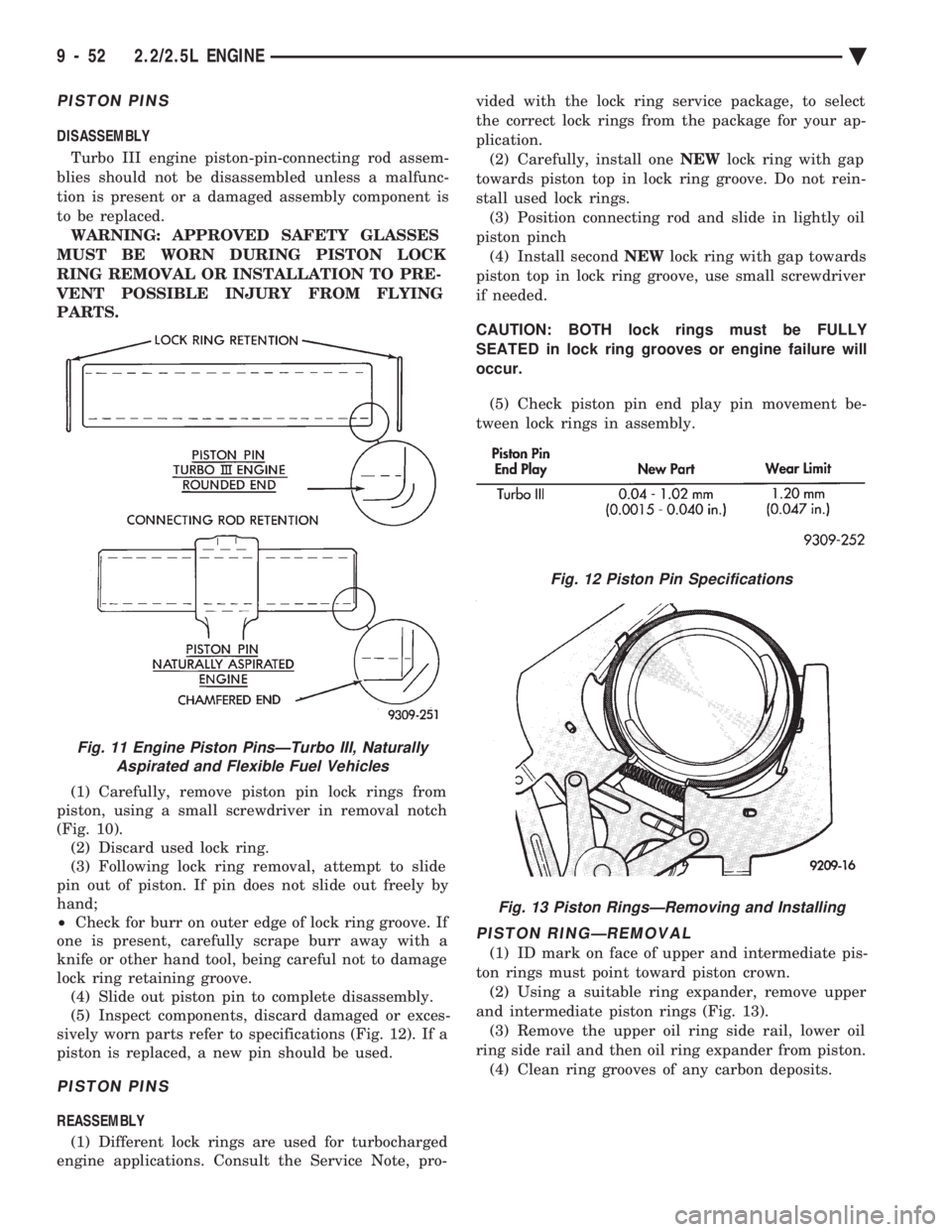
PISTON PINS
DISASSEMBLY Turbo III engine piston-pin-connecting rod assem-
blies should not be disassembled unless a malfunc-
tion is present or a damaged assembly component is
to be replaced. WARNING: APPROVED SAFETY GLASSES
MUST BE WORN DURING PISTON LOCK
RING REMOVAL OR INSTALLATION TO PRE-
VENT POSSIBLE INJURY FROM FLYING
PARTS.
(1) Carefully, remove piston pin lock rings from
piston, using a small screwdriver in removal notch
(Fig. 10). (2) Discard used lock ring.
(3) Following lock ring removal, attempt to slide
pin out of piston. If pin does not slide out freely by
hand;
² Check for burr on outer edge of lock ring groove. If
one is present, carefully scrape burr away with a
knife or other hand tool, being careful not to damage
lock ring retaining groove. (4) Slide out piston pin to complete disassembly.
(5) Inspect components, discard damaged or exces-
sively worn parts refer to specifications (Fig. 12). If a
piston is replaced, a new pin should be used.
PISTON PINS
REASSEMBLY
(1) Different lock rings are used for turbocharged
engine applications. Consult the Service Note, pro- vided with the lock ring service package, to select
the correct lock rings from the package for your ap-
plication.
(2) Carefully, install one NEWlock ring with gap
towards piston top in lock ring groove. Do not rein-
stall used lock rings. (3) Position connecting rod and slide in lightly oil
piston pinch (4) Install second NEWlock ring with gap towards
piston top in lock ring groove, use small screwdriver
if needed.
CAUTION: BOTH lock rings must be FULLY
SEATED in lock ring grooves or engine failure will
occur.
(5) Check piston pin end play pin movement be-
tween lock rings in assembly.
PISTON RINGÐREMOVAL
(1) ID mark on face of upper and intermediate pis-
ton rings must point toward piston crown. (2) Using a suitable ring expander, remove upper
and intermediate piston rings (Fig. 13). (3) Remove the upper oil ring side rail, lower oil
ring side rail and then oil ring expander from piston. (4) Clean ring grooves of any carbon deposits.
Fig. 11 Engine Piston PinsÐTurbo III, Naturally Aspirated and Flexible Fuel Vehicles
Fig. 12 Piston Pin Specifications
Fig. 13 Piston RingsÐRemoving and Installing
9 - 52 2.2/2.5L ENGINE Ä
Page 1619 of 2438
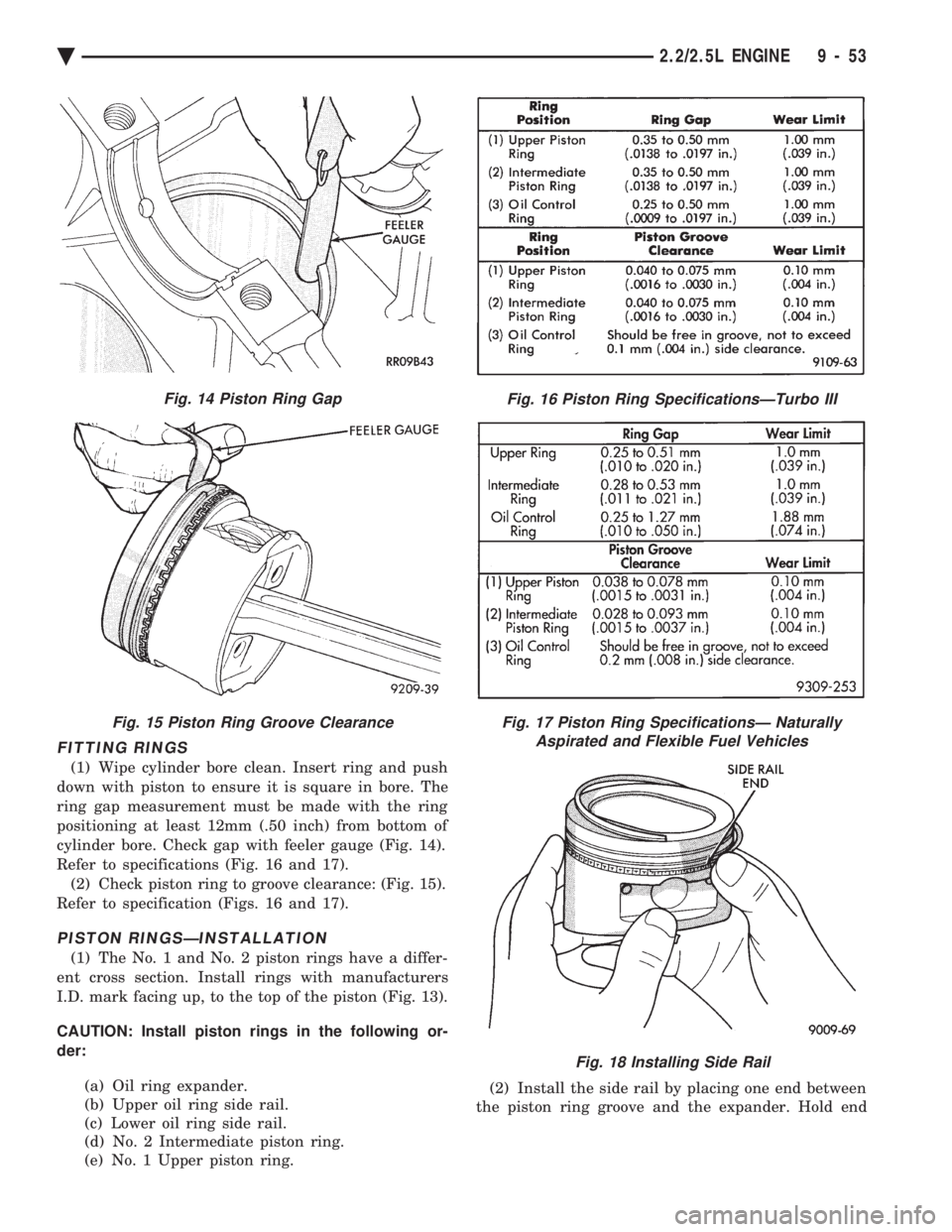
FITTING RINGS
(1) Wipe cylinder bore clean. Insert ring and push
down with piston to ensure it is square in bore. The
ring gap measurement must be made with the ring
positioning at least 12mm (.50 inch) from bottom of
cylinder bore. Check gap with feeler gauge (Fig. 14).
Refer to specifications (Fig. 16 and 17). (2) Check piston ring to groove clearance: (Fig. 15).
Refer to specification (Figs. 16 and 17).
PISTON RINGSÐINSTALLATION
(1) The No. 1 and No. 2 piston rings have a differ-
ent cross section. Install rings with manufacturers
I.D. mark facing up, to the top of the piston (Fig. 13).
CAUTION: Install piston rings in the following or-
der:
(a) Oil ring expander.
(b) Upper oil ring side rail.
(c) Lower oil ring side rail.
(d) No. 2 Intermediate piston ring.
(e) No. 1 Upper piston ring. (2) Install the side rail by placing one end between
the piston ring groove and the expander. Hold end
Fig. 16 Piston Ring SpecificationsÐTurbo III
Fig. 17 Piston Ring SpecificationsÐ Naturally Aspirated and Flexible Fuel Vehicles
Fig. 18 Installing Side Rail
Fig. 14 Piston Ring Gap
Fig. 15 Piston Ring Groove Clearance
Ä 2.2/2.5L ENGINE 9 - 53
Page 1620 of 2438

firmly and press down the portion to be installed un-
til side rail is in position. Do not use a piston ring
expander. (Fig. 19).
(3) Install upper side rail first and then the lower
side rail. (4) Install No. 2 piston ring and then No. 1 piston
ring (Fig. 8). (5) Position piston ring end gaps as shown in (Fig.
19). (6) Position oil ring expander gap at least 45É from
the side rail gaps but noton the piston pin center or
on the thrust direction. Staggering ring gap is impor-
tant for oil control.
PISTON AND CONNECTING ROD ASSEMBLY INSTALLATION
(1) Before installing pistons and connecting rod as-
semblies into the bore, besure that compression ring
gaps are staggered so that neither is in line with oil
ring rail gap. (2) Before installing the ring compressor, make
sure the oil ring expander ends are butted and the
rail gaps located as shown in (Fig. 19).
(3) Immerse the piston head and rings in clean en-
gine oil, slide the ring compressor, over the piston and tighten with the special wrench (Fig. 20).
Be sure
position of rings does not change during this
operation .
(4) The valve cut should be toward the manifold side
of the engine (Fig. 21). (5) Install connecting rod bolt protectors on rod bolts
(Fig. 4). (6) Rotate crankshaft so that the connecting rod
journal is on the center of the cylinder bore. Insert rod
and piston into cylinder bore and guide rod over the
crankshaft journal. (7) Tap the piston down in cylinder bore, using a
hammer handle. At the same time, guide connecting
rod into position on connecting rod journal. (8) Install rod caps. Install nuts on cleaned and oiled
rod bolts and tighten nuts to 54 N Im (40 ft. lb.) Plus 1/4
turn for N/A engines and 68 N Im (50 ft. lbs.) for turbo
III engines.
Fig. 19 Piston Ring End Gap Position
Fig. 20 Installing Piston
Fig. 21 Piston Markings
Fig. 22 Checking Connecting Rod Bearing Clear- ance
9 - 54 2.2/2.5L ENGINE Ä
Page 1621 of 2438

CONNECTING RODS
(1) Follow procedure specified in the Standard Ser-
vice Procedures Section for Measuring Main Bearing
Clearance and Connecting Rod Bearing Clearance
(Fig. 22). Refer to specifications (Fig. 25).
CAUTION: Do not rotate crankshaft or the Plastic-
Gage may be smeared.
The rod bearing bolts should be examined be-
fore reuse. If the threads are necked down the
bolts should be replaced (Fig. 23). Necking can be checked by holding a scale or straight
edge against the threads. If all the threads do not
contact the scale the bolt should be replaced.
(2) Before installing the nuts the threads should be
oiled with engine oil.
(3) Install nuts on each bolt finger tight than alter-
nately torque each nut to assemble the cap properly.
(4) Tighten the nuts to 54 N Im PLUS 1/4 turn (40 ft.
lbs. PLUS 1/4 turn) for N/A engines Do not use a
torque wrench for last step. and 68 NIm (50 ft. lbs.)
for Turbo III engines. (5) Using a feeler gauge, check connecting rod side
clearance (Fig. 24). Refer to connecting rod specifica-
tions (Fig. 25).
ENGINE CORE PLUGS
REMOVAL
Using a blunt tool such as a drift or a screwdriver
and a hammer, strike the bottom edge of the cup plug
(Fig. 26). With the cup plug rotated, grasp firmly with
pliers or other suitable tool and remove plug (Fig. 26).
CAUTION: Do not drive cup plug into the casting as
restricted cooling can result and cause serious en-
gine problems.
INSTALLATION
Thoroughly clean inside of cup plug hole in cylinder
block or head. Be sure to remove old sealer. Lightly coat
inside of cup plug hole with sealer. Make certain the
new plug is cleaned of all oil or grease. Using proper
drive plug, drive plug into hole so that the sharp edge of the plug is at least 0.5mm
(.020 inch) inside the lead-in chamfer (Fig. 26).
It is in not necessary to wait for curing of the seal-
ant. The cooling system can be refilled and the vehi-
cle placed in service immediately.
Fig. 24 Checking Connecting Rod Side Clearance
Fig. 25 Connecting Rod Specifications
Fig. 26 Core Hole Plug Removal
Fig. 23 Checking Bolts for Stretching (Necked)
Ä 2.2/2.5L ENGINE 9 - 55
Page 1624 of 2438

OIL PAN
A formed steel oil pan provides lower engine pro-
tection as well as serving as the engine oil reservoir
(Fig. 1). Pan side flanges to block are sealed with
gaskets. The oil pickup tube for some 2.2L engines
have a circular strainer and cover. The 2.5L engine
pickup is also unsupported and the lower end has a
box type strainer (Fig. 4).
PRESSURE LUBRICATION
Oil drawn up through the pickup tube is pressur-
ized by the pump and routed through the full flow
filter to the main oil gallery running the length of
the cylinder block (Fig. 2). Modified oil pickup, pump
and check valve provide increased oil flow to the
main oil gallery.
MAIN/ROD BEARINGS
A diagonal hole in each bulkhead feeds oil to each
main bearing. Drilled passages within the crankshaft
route oil from main bearing journals to crankpin
journals.
ACCESSORY SHAFT
Two separate holes supply the accessory shaft for
the N/A engines. For Turbo III engines there is a slot
in the rear shaft bushing that squirts oil onto the
oil pump drive gears (Fig. 2).
BALANCE SHAFTS
The engine balance shafts are lubricated by an ad-
ditional hole that interconnects a passage in one leg
of the balance shaft carrier to route oil down to the
carrier oil gallery. This gallery directly supplies the
balance shafts front bearings and internal machined
passages in the shafts routes oil from front to rear
shaft bearing journals.
TURBOCHARGER (WHERE EQUIPPED)
If turbocharger equipped, pressurized oil from the
main gallery to sending unit hex fitting is piped from
the fitting to the turbocharger bearing housing.
From the housing a hose and tube connection to a
machined hole in the block provides drainback.
CAMSHAFT/HYDRAULIC LIFTERS
A vertical hole at the number five bulkhead routes
pressurized oil through a restrictor up past a cylinder
head bolt to an oil gallery running the length of the
cylinder head. For 2.2/2.5L and 2.5L FFV engines
hydraulic adjusters are supplied directly from this
gallery while diagonal holes supply oil to the cam-
shaft journals. The camshaft journals are partially
slotted to allow a predetermined amount of pressur-
ized oil to pass into the bearing cap cavities with
small holes directed to spray lubricate the camshaft
lobes. For Turbo III engines oil is supplied thru oil
galleries in the head to the camshafts and rocker arm shafts which feed oil to the lash adjusters. Oil is
feed thru the rocker arms to lubricate the rollers and
the camshaft lobes.
SPLASH LUBRICATION
Oil returning to the pan from pressurized compo-
nents supplies lubrication to the valve stems. Cylinder
bores and wrist pins are splash lubricated from di-
rected holes in the connecting rods.
OIL PAN
REMOVAL
(1) Drain engine oil and remove oil pan.
(2) Clean oil pan and all gasket surfaces.
OIL PAN RAIL TO BLOCK SEALING
For all engines side gaskets (Fig. 1) are employed for
rail sealing.
INSTALLATION
(1) Apply Mopar Silicone Rubber Adhesive Sealant
or equivalent at the front seal retainer parting line
(Fig. 3). (2) Install the oil pan side gaskets to the block. Use
heavy grease or Mopar Silicone Rubber Adhesive Seal-
ant or equivalent to hold in place. (3) Apply Mopar Silicone Rubber Adhesive Sealant
or equivalent to ends of new oil pan end seals at
junction of cylinder block pan rail gasket (Fig. 3). (4) Install pan and tighten to (12) M8 screws to 23
N Im (200 in. lbs.) and 1 M6 screws to 12 N Im (105 in.
lbs.).
OIL PUMP SERVICE
OIL PICKUP
(1) Remove screw on pump cover holding oil pick-up
tube to oil pump (Fig. 4). (2) Remove oil pick-up tube. When reinstalling
make sure to use a new O-Ring on pickup tube .
Fig. 3 Sealing, Front and Rear End Seals
9 - 58 2.2/2.5L ENGINE Ä
Page 1626 of 2438

CAUTION: Pump must be held in fully seated posi-
tion (described above) while installing screws. (6) Tighten screws to 23 N Im (200 in. lbs.).
INSPECTION
(1) Check rotor end clearance with feeler gauge as
shown in (Fig. 8). (2) Limits:
² 0.03mm (.001 inch) minimum.
² 0.09mm (.0035 inch) maximum.
(3) Thickness: 23.96mm (.9435 inch) minimum.
Outer Diameter: 62.7mm (2.469 inch) minimum (Fig.
9). (4) Install with large chamfered edge in pump
body (Fig. 9).
Clearance: 0.20mm (.008 inch) maximum (Fig. 10). Clearance: 0.35mm (.014 inch) maximum (Fig. 11).
Clearance: 0.076mm (.003 inch) maximum (Fig.
12). Oil pressure relief valve spring: Free length:
49.5mm (1.95 inch). Load: 89 N at 34mm. Load: (20
lbs. at 1.34 inch) (Fig. 13). Thickness: 23.96mm (.9435 inch) Minimum (Fig.
14).
CHECKING ENGINE OIL PRESSURE
(1) Remove pressure sending unit and install Spe-
cial Tool S-94 with gauge assembly C-3292 (Fig. 15). (2) Warm engine at high idle until thermostat
opens.
CAUTION: If oil pressure is 0 at idle, Do Not Run
engine at 3000 RPM
Fig. 8 Checking Rotor End Clearance
Fig. 9 Measuring Outer Rotor
Fig. 10 Clearance Between Rotors
Fig. 11 Outer Rotor Clearance
9 - 60 2.2/2.5L ENGINE Ä
Page 1627 of 2438

(3) Oil Pressure: Curb Idle25 kPa (4 psi) mini-
mum 3000 RPM 170-550 kPa (25-80 psi).
OIL FILTER
ANTI-DRAIN BACK VALVE
Installation: Apply liquid (Teflon Type) sealant to
valve-to-block threads (Fig. 16). Tighten assembly to
55 N Im (40 ft. lbs.).
FILTER
CAUTION: When servicing the oil filter (Fig. 16)
avoid deforming the filter can by installing the re-
move/install tool band strap against the can-to-base
lockseam. The lockseam joining the can to the base
is reinforced by the base plate.
(1) Turn counter clockwise to remove.
(2) To install, lubricate new filter gasket. Check
filter mounting surface. The surface must be smooth,
flat and free of debris or old pieces of rubber. Screw
filter on until gasket contacts base. Tighten to 3/4 to
1 turn.
Fig. 12 Oil Pump Cover
Fig. 13 Oil Pressure Relief Valve
Fig. 14 Measuring Inner Rotor Thickness
Fig. 15 Checking Oil Pump PressureÐTypical
Fig. 16 Engine Oil Filter and Antidrain Back Valve
Ä 2.2/2.5L ENGINE 9 - 61
Page 1632 of 2438

3.0L ENGINE INDEX
page page
Accessory Drive Belt Service ................ 70
Auto Lash Adjuster ....................... 75
Camshaft Service ........................ 76
Checking Engine Oil Pressure ............... 93
Crankshaft and Cylinder Block, Assembly Service . 86
Cylinder Block ........................... 89
Cylinder Head ........................... 78
Cylinder Head and Camshaft Service ......... 75
Engine Assembly ......................... 69
Engine Lubrication System ................. 91
Engine Mounts .......................... 68 Engine Specifications
..................... 95
General Information ....................... 66
Oil Filter and Bracket ..................... 94
Oil Pan ................................ 92
Oil Pump Service ........................ 92
Piston and Connecting Rod Assembly Service . . . 82
Timing Belt InspectionÐIn Vehicle ............ 72
Timing Belt Service ....................... 72
Valve Service ........................... 80
GENERAL INFORMATION
ENGINE IDENTIFICATION NUMBER OR CODE
The engine identification number is located on the
rear of the cylinder block just below the cylinder
head (Fig. 1). BLOCK: The cylinder block is a light weight de-
sign created by reducing thickness in many parts
and a short 10 mm (3/8 inch) block skirt. High rigid-
ity is provided with ribs cast in the outer wall, a full
length water jacket, and a monoblock or beam type, main bearing cap. This single unit four bearing cap
is designed to control vibration of the cylinder block
partition walls.
CRANKSHAFT: A six throw, five weight crank-
shaft is supported by four main bearings with num-
ber three being the thrust bearing. The six separate
connecting rod throws pins reduce torque fluctua-
tions while a torsional vibration damper is used to
control torsion caused vibration of the crankshaft.
Rubber lipped seals are used at front and rear. The
front seal is retained in the oil pump case and the
rear is retained in a block-mounted housing.
3.0L ENGINE
9 - 66 3.0L ENGINE Ä