Page 3362 of 4087
Cold Start Injector Circuit
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
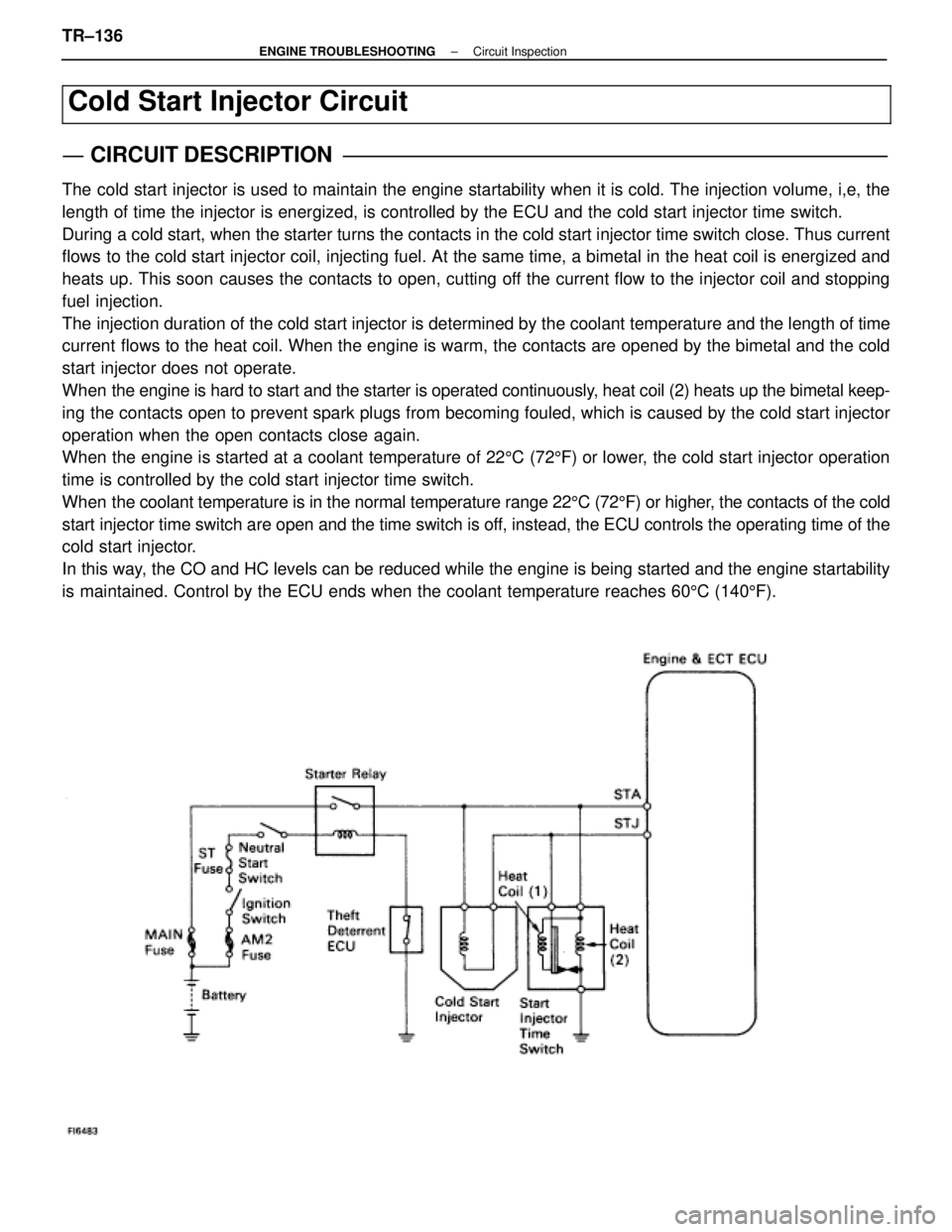
The cold start injector is used to maintain the engine startability when it\
is cold. The injection volume, i,e, the
length of time the injector is energized, is controlled by the ECU and t\
he cold start injector time switch.
During a cold start, when the starter turns the contacts in the cold start inj\
ector time switch close. Thus current
flows to the cold start injector coil, injecting fuel. At the same time, a bi\
metal in the heat coil is energized and
heats up. This soon causes the contacts to open, cutting off the current flow to the injector coil and stopping
fuel injection.
The injection duration of the cold start injector is determined by the cool\
ant temperature and the length of time
current flows to the heat coil. When the engine is warm, the contacts are opened by the bimetal and the cold
start injector does not operate.
When the engine is hard to start and the starter is operated continuously, heat coil (2) heats up the bimetal keep-
ing the contacts open to prevent spark plugs from becoming fouled, which is\
caused by the cold start injector
operation when the open contacts close again.
When the engine is started at a coolant temperature of 225C (72 5F) or lower, the cold start injector operation
time is controlled by the cold start injector time switch.
When the coolant temperature is in the normal temperature range 22 5C (72 5F) or higher, the contacts of the cold
start injector time switch are open and the time switch is off, instead, the ECU controls the operating time of the
cold start injector.
In this way, the CO and HC levels can be reduced while the engine is being started \
and the engine startability
is maintained. Control by the ECU ends when the coolant temperature reac\
hes 60 5C (140 5F).
TR±136±
ENGINE TROUBLESHOOTING Circuit Inspection
WhereEverybodyKnowsYourName
Page 3366 of 4087
ISC Valve Circuit
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
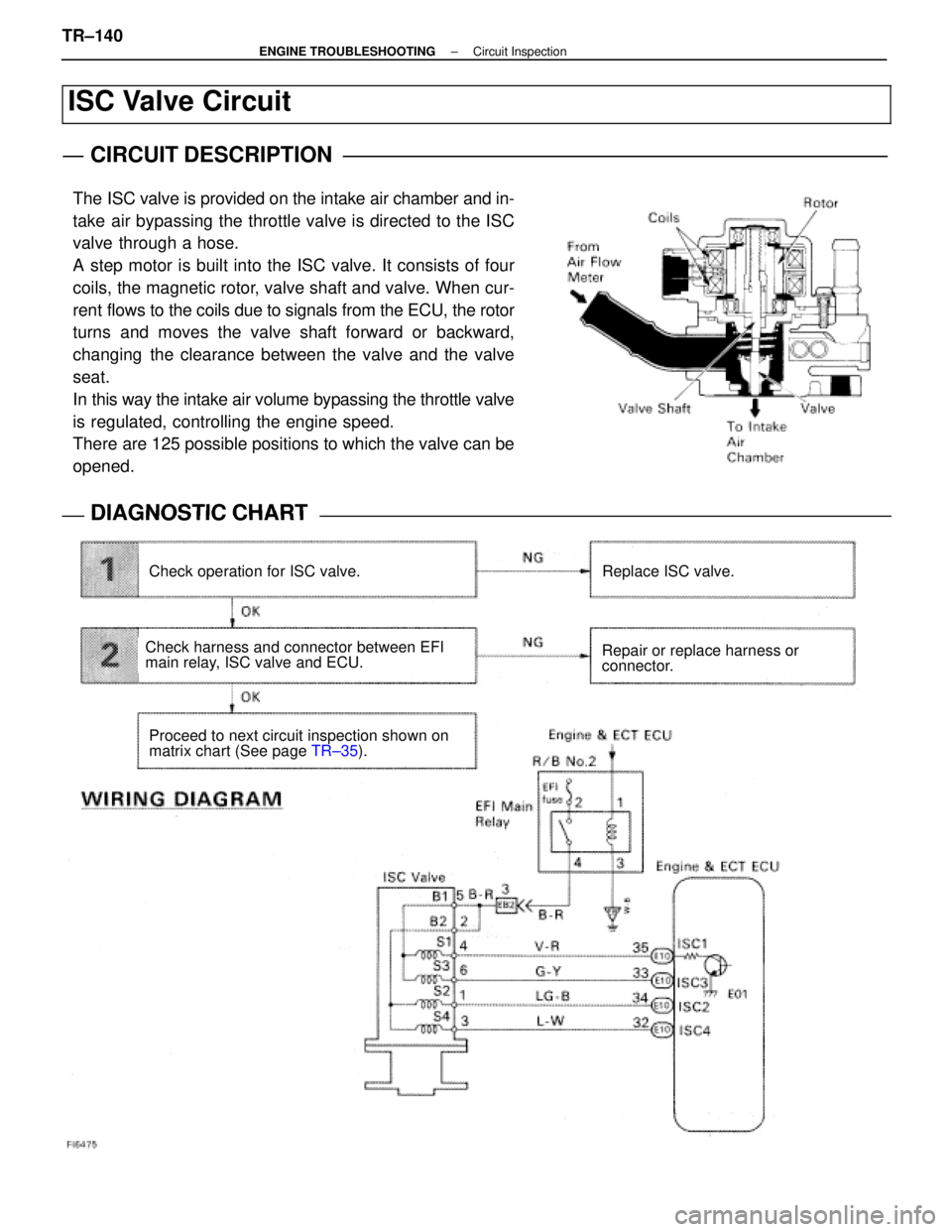
The ISC valve is provided on the intake air chamber and in-
take air bypassing the throttle valve is directed to the ISC
valve through a hose.
A step motor is built into the ISC valve. It consists of four
coils, the magnetic rotor, valve shaft and valve. When cur-
rent flows to the coils due to signals from the ECU, the rotor
turns and moves the valve shaft forward or backward,
changing the clearance between the valve and the valve
seat.
In this way the intake air volume bypassing the throttle valve
is regulated, controlling the engine speed.
There are 125 possible positions to which the valve can be
opened.
DIAGNOSTIC CHARTDIAGNOSTIC CHART
Check operation for ISC valve.Replace ISC valve.
Repair or replace harness or
connector.
Proceed to next circuit inspection shown on
matrix chart (See page TR±35).
Check harness and connector between EFI
main relay, ISC valve and ECU.
TR±140±
ENGINE TROUBLESHOOTING Circuit Inspection
WhereEverybodyKnowsYourName
Page 3397 of 4087
YESNO
NOYES
YES
NO
OKNG
BASIC INSPECTION
When the normal code is displayed in the diagnostic code check, troubleshoot\
ing should be performed in the
order for all possible circuits to be considered as the causes of the pr\
oblems.
In many cases, by carrying out the basic engine check shown in the follo\
wing flow chart, the location causing
the problem can be found quickly and ef ficiently. Therefore, use of this check is essential in engine troubleshoot-
ing.
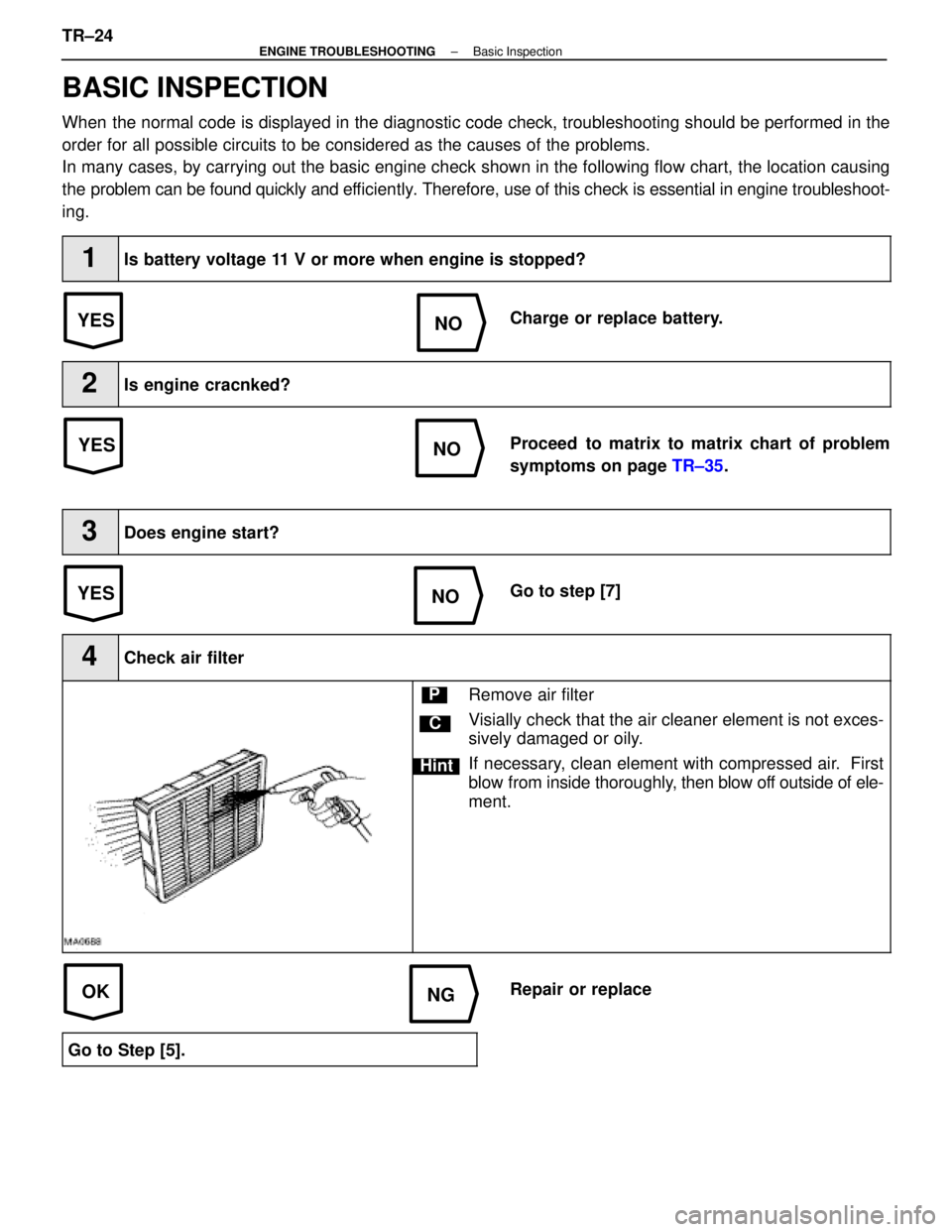
1Is battery voltage 11 V or more when engine is stopped?
Charge or replace battery.
2Is engine cracnked?
Proceed to matrix to matrix chart of problem
symptoms on page TR±35.
3Does engine start?
Go to step [7]
4Check air filter
C
Hint
PRemove air filter
Visially check that the air cleaner element is not exces-
sively damaged or oily.
If necessary, clean element with compressed air. First
blow from inside thoroughly, then blow off outside of ele-
ment.
Repair or replace
Go to Step [5].
TR±24±
ENGINE TROUBLESHOOTING Basic Inspection
WhereEverybodyKnowsYourName
Page 3398 of 4087
OKNG
OKNG
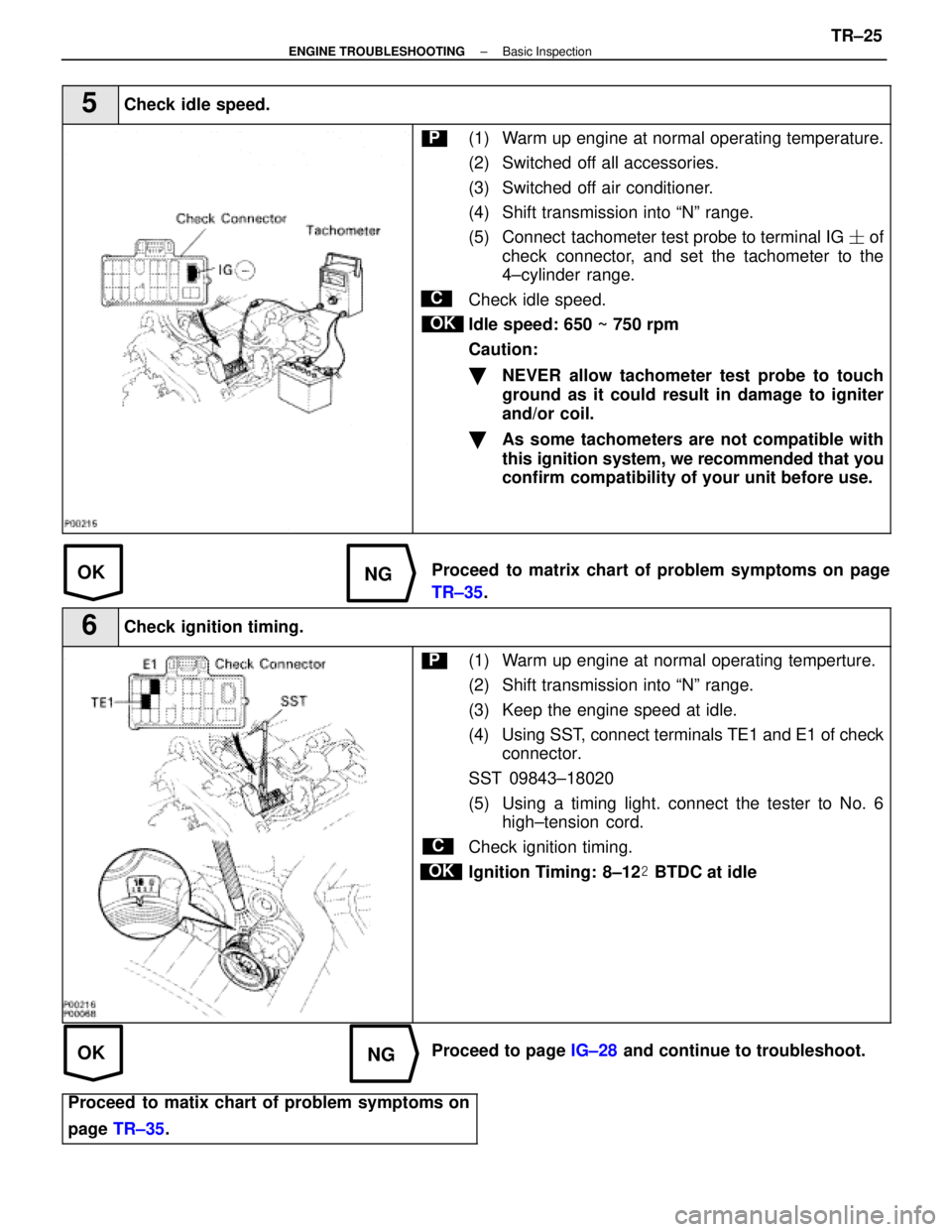
5Check idle speed.
C
OK
P(1) Warm up engine at normal operating temperature.
(2) Switched off all accessories.
(3) Switched off air conditioner.
(4) Shift transmission into ªNº range.
(5) Connect tachometer test probe to terminal IG � of
check connector, and set the tachometer to the
4±cylinder range.
Check idle speed.
Idle speed: 650 ~ 750 rpm
Caution:
�NEVER allow tachometer test probe to touch
ground as it could result in damage to igniter
and/or coil.
�As some tachometers are not compatible with
this ignition system, we recommended that you
confirm compatibility of your unit before use.
Proceed to matrix chart of problem symptoms on page
TR±35 .
6Check ignition timing.
C
OK
P(1) Warm up engine at normal operating temperture.
(2) Shift transmission into ªNº range.
(3) Keep the engine speed at idle.
(4) Using SST, connect terminals TE1 and E1 of check
connector.
SST 09843±18020
(5) Using a timing light. connect the tester to No. 6 high±tension cord.
Check ignition timing.
Ignition Timing: 8±12 � BTDC at idle
Proceed to page IG±28 and continue to troubleshoot.
Proceed to matix chart of problem symptoms on
page TR±35 .
±
ENGINE TROUBLESHOOTING Basic InspectionTR±25
WhereEverybodyKnowsYourName
Page 3437 of 4087
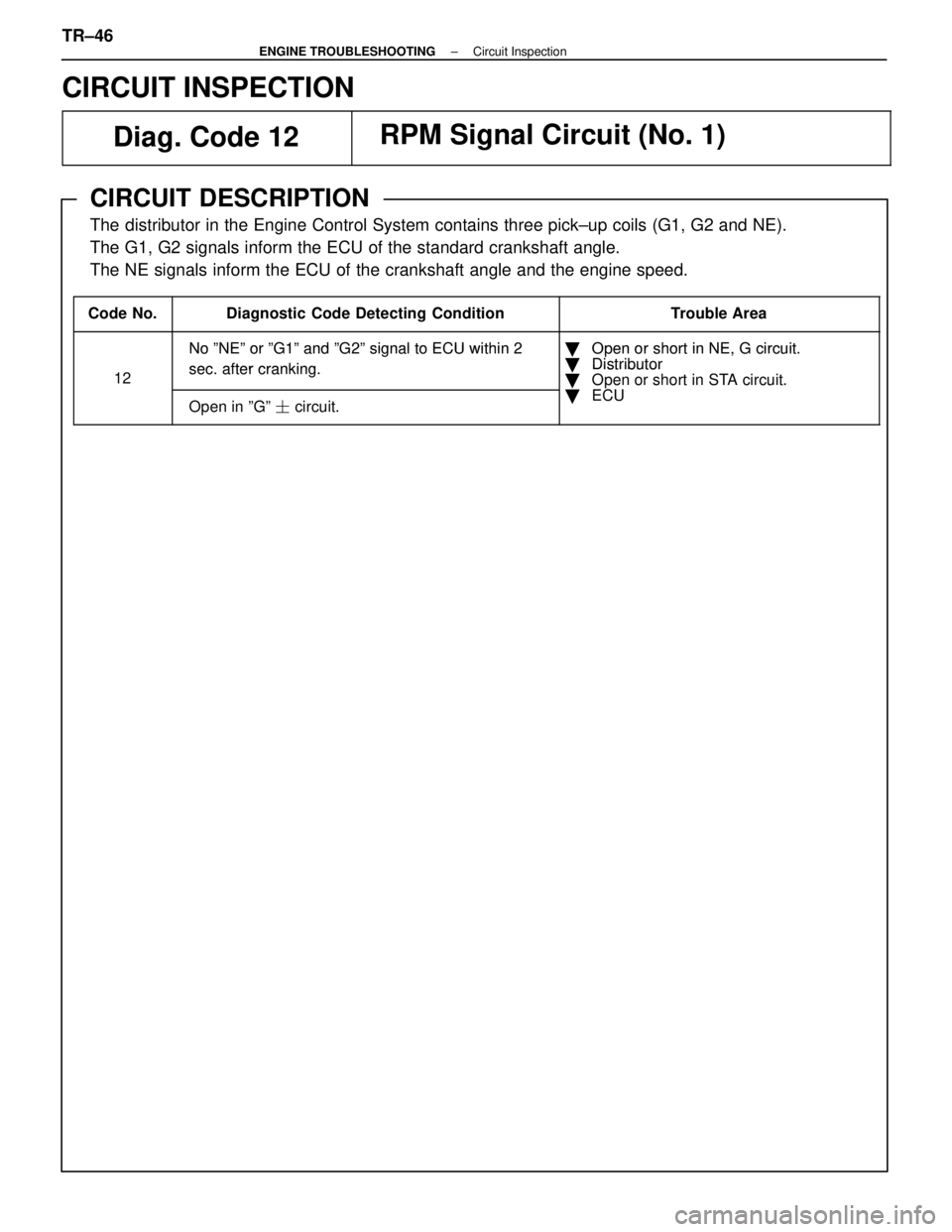
CIRCUIT INSPECTIONDiag. Code 12
RPM Signal Circuit (No. 1)
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
The distributor in the Engine Control System contains three pick±up coil\
s (G1, G2 and NE).
The G1, G2 signals inform the ECU of the standard crankshaft angle.
The NE signals inform the ECU of the crankshaft angle and the engine spe\
ed.
����� �����Code No.����������������� �����������������Diagnostic Code Detecting Condition�������������� ��������������Trouble Area
����� ���������������������� �����������������
NoºNEºorºG1ºandºG2ºsignal to ECU within 2
�������������� ��������������
�Open or short in NE G circuit����� ���������������������� �����������������No ºNEº or ºG1º and ºG2º signal to ECU within 2
sec after cranking�������������� ��������������� Open or short in NE, G circuit.
� Distributor
����� �����12����������������� �����������������sec. after cranking.�������������� ��������������� Distributor
� Open or short in STA circuit.
ECU����� ���������������������� �����������������Open in ºGº � circuit.�������������� ��������������
Oen or short in STA circuit.
� ECU
TR±46±
ENGINE TROUBLESHOOTING Circuit Inspection
WhereEverybodyKnowsYourName
Page 3438 of 4087
DIAGNOSTIC CHART
WIRING DIAGRAM
Check resistance of each pickup coils in
distributor
Check for open and short in harness and
connector between ECU and distributor.
Check air gap.
Check and replace ECU.
Replace distributor.
Repair or rep lace harness or connector.
Replace distributor
±
ENGINE TROUBLESHOOTING Circuit InspectionTR±47
WhereEverybodyKnowsYourName
Page 3439 of 4087
Disconnect distributor connector.
Measure resistance between each terminal shown in
table below.
Check resistance of each picup coils in distributor.
�During cranking or idling, check between terminals G1,
G2, NE and G � of engine (&ECT) ECU.
HINT: The correct waveforms appears as shown in the illustration on the left.
Replace distributor.
Check for open and short in harness and connector between engine
(&ECT) ECU and distributor (See page IN±27
Repair or replace harness or connector.
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
TR±48±
ENGINE TROUBLESHOOTING Circuit Inspection
WhereEverybodyKnowsYourName
Page 3440 of 4087
Remove distributor cap & rotor.
Using SST (G1 and G2 pickups) and a thikness gauge
(NE pickup). measure the air gap between the signal
rotor projection and pickup coil.
SST 09240±00020 fro G1 and G2 pickups
Air gap: 0.2±0.4 mm (0.008±0.016 in.)
Replace distributor.
Check and replace engine (& ECT) ECU.
±
ENGINE TROUBLESHOOTING Circuit InspectionTR±49
WhereEverybodyKnowsYourName