1991 ACURA NSX turn signal
[x] Cancel search: turn signalPage 228 of 1640

PGM-FI System
System Description
PGM-FI System
The PGM-FI system on this model is a sequential multiport fuel injection system.
Fuel Injector Timing and Duration
The ECM contains memories for the basic discharge durations at various engine speeds and manifold pressures. The
basic discharge duration, after being read out from the memory, is further modified by signals sent from various sensors
to obtain the final discharge duration.
Throttle Valve Control
The ECM controls the throttle valve control motor based on accelerator pedal position, TCS control unit and various sig-
nals. The ECM also controls the idle control function, cruise control function, and other functions with the throttle valve
control.
Ignition Timing Control
• The ECM contains memories for basic ignition timing at various engine speeds and manifold pressures. Ignition timing
is also adjusted for engine coolant temperature.
• A knock control system is also used. When detonation is detected by the knock sensor (KS), the ignition timing is
retarded.
Other Control Functions
1. Starting Control
When the engine is started, the ECM provides a rich mixture by increasing fuel injector duration.
2. Fuel Pump Control
• When the ignition switch is initially turned on, the ECM supplies ground to the PGM-FI main relay that supplies
current to the fuel pump for two seconds to pressurize the fuel system.
• When the engine is running, the ECM supplies ground to the PGM-FI main relay that supplies current to the fuel pump.
• When the engine is not running and the ignition is on, the ECM cuts ground to the PGM-FI main relay which cuts
current to the fuel pump.
• Excellent engine performance is achieved through the use of VTEC (Variable Valve Timing and Valve Lift Electronic
Control System), intake air bypass control and discharge volume control of the fuel pump.ProCarManuals.com
Page 230 of 1640
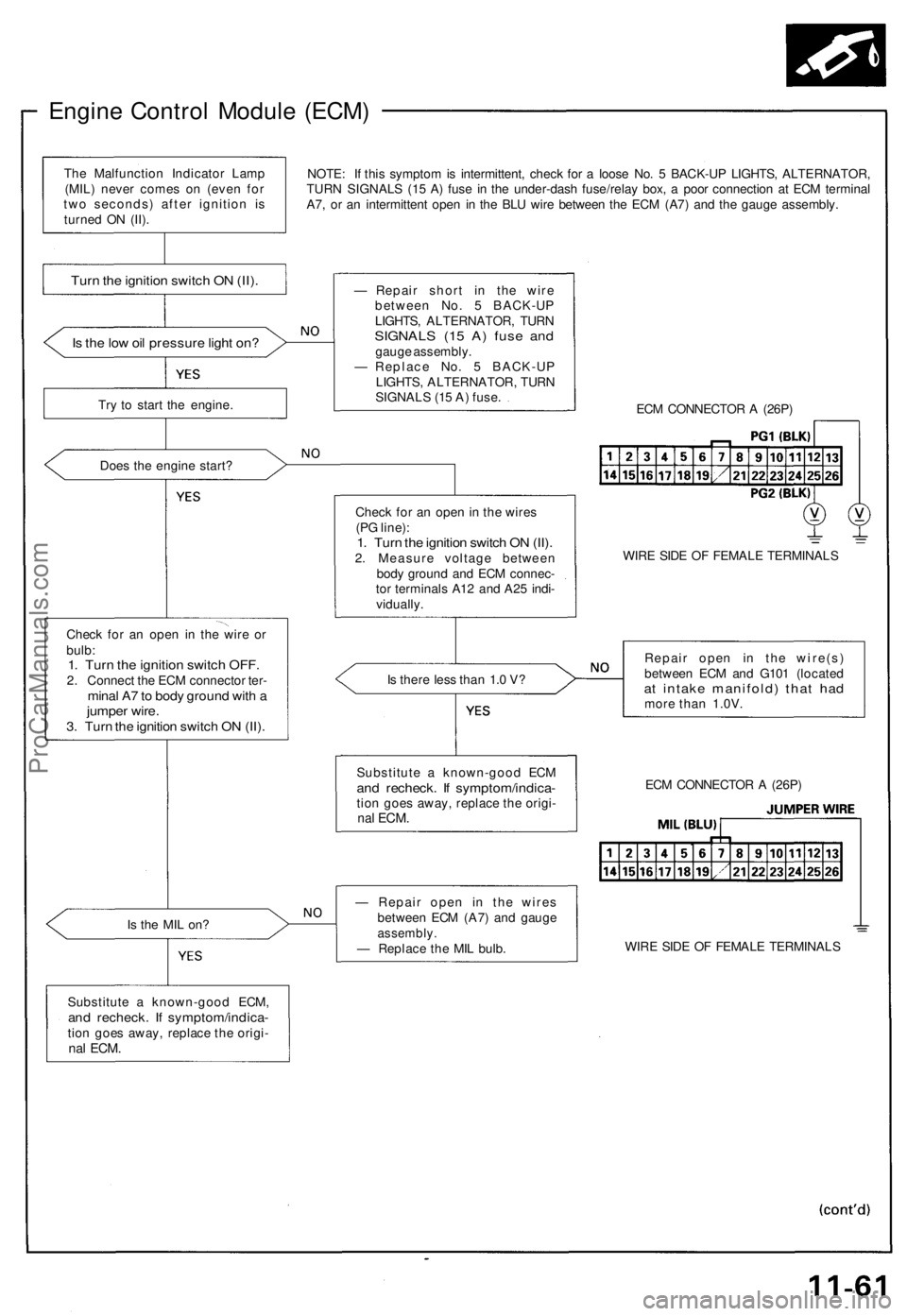
Engine Control Module (ECM)
NOTE: If this symptom is intermittent, check for a loose No. 5 BACK-UP LIGHTS, ALTERNATOR,
TURN SIGNALS (15 A) fuse in the under-dash fuse/relay box, a poor connection at ECM terminal
A7, or an intermittent open in the BLU wire between the ECM (A7) and the gauge assembly.
Is the low oil pressure light on?
Try to start the engine.
Does the engine start?
Check for an open in the wire or
bulb:
1. Turn the ignition switch OFF.
2. Connect the ECM connector ter-
minal A7 to body ground with a
jumper wire.
3. Turn the ignition switch ON (II).
Is the MIL on?
Substitute a known-good ECM,
and recheck. If symptom/indica-
tion goes away, replace the origi-
nal
ECM.
— Repair short in the wire
between No. 5 BACK-UP
LIGHTS, ALTERNATOR, TURN
SIGNALS (15 A) fuse and
gauge assembly.
— Replace No. 5 BACK-UP
LIGHTS, ALTERNATOR, TURN
SIGNALS (15 A) fuse.
ECM CONNECTOR A (26P)
Check for an open in the wires
(PG line):
1. Turn the ignition switch ON (II).
2. Measure voltage between
body ground and ECM connec-
tor terminals A12 and A25 indi-
vidually.
WIRE SIDE OF FEMALE TERMINALS
Is there less than 1.0 V?
Repair open in the wire(s)
between ECM and G101 (located
at intake manifold) that had
more than 1.0V.
— Repair open in the wires
between ECM (A7) and gauge
assembly.
— Replace the MIL bulb.
WIRE SIDE OF FEMALE TERMINALS
ECM CONNECTOR A (26P)
Substitute a known-good ECM
and recheck. If symptom/indica-
tion goes away, replace the origi-
nal
ECM.
Turn the ignition switch ON (II).
The Malfunction Indicator Lamp
(MIL) never comes on (even for
two seconds) after ignition is
turned ON (II).ProCarManuals.com
Page 238 of 1640
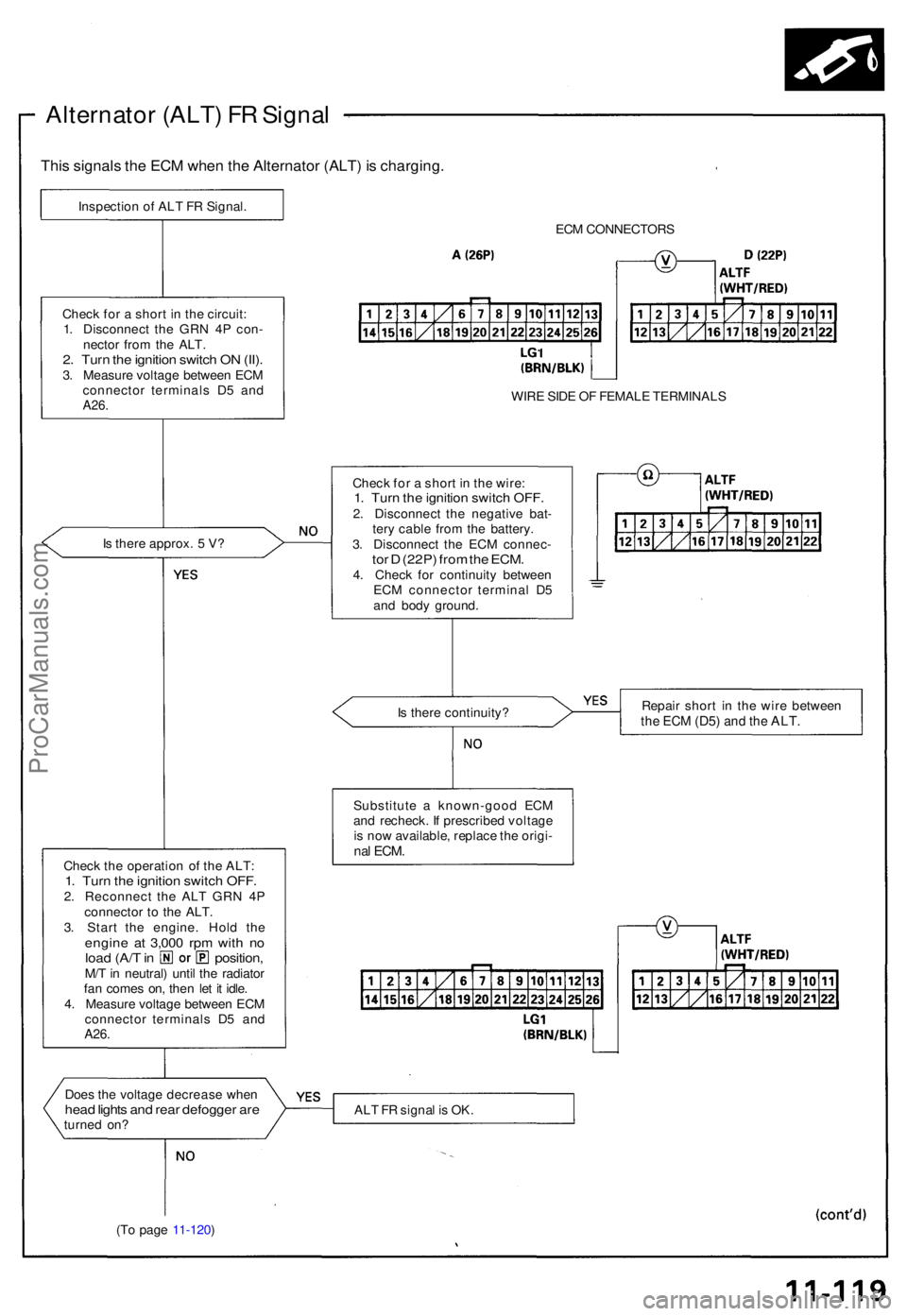
Alternator (ALT ) F R Signa l
This signal s th e EC M whe n th e Alternato r (ALT ) i s charging .
Inspection o f AL T F R Signal .
ECM CONNECTOR S
WIR E SID E O F FEMAL E TERMINAL S
Chec k fo r a shor t i n th e wire :
1. Tur n th e ignitio n switc h OFF .2. Disconnec t th e negativ e bat -
ter y cabl e fro m th e battery .
3 . Disconnec t th e EC M connec -
tor D (22P ) fro m th e ECM .4. Chec k fo r continuit y betwee n
EC M connecto r termina l D 5
an d bod y ground .
I
s ther e approx . 5 V ?
Chec
k fo r a shor t i n th e circuit :
1 . Disconnec t th e GR N 4 P con -
necto r fro m th e ALT .
2. Tur n th e ignitio n switc h O N (II) .3. Measur e voltag e betwee n EC M
connecto r terminal s D 5 an d
A26 .
Is ther e continuity ? Repai
r shor t i n th e wir e betwee nthe EC M (D5 ) and th e ALT .
Substitut e a known-goo d EC M
an d recheck . I f prescribe d voltag e
i s no w available , replac e th e origi -
nal ECM .Chec k th e operatio n o f th e ALT :1. Tur n th e ignitio n switc h OFF .2. Reconnec t th e AL T GR N 4 P
connecto r t o th e ALT .
3 . Star t th e engine . Hol d th e
engin e a t 3,00 0 rp m wit h n oloa d (A/ T in position ,M/T in neutral ) unti l th e radiato r
fa n come s on , the n le t i t idle .
4 . Measur e voltag e betwee n EC M
connecto r terminal s D 5 an d
A26.
Doe s th e voltag e decreas e whe nhead light s an d rea r defogge r ar eturne d on ? AL
T F R signa l i s OK .
(T o pag e 11-120 )
ProCarManuals.com
Page 268 of 1640
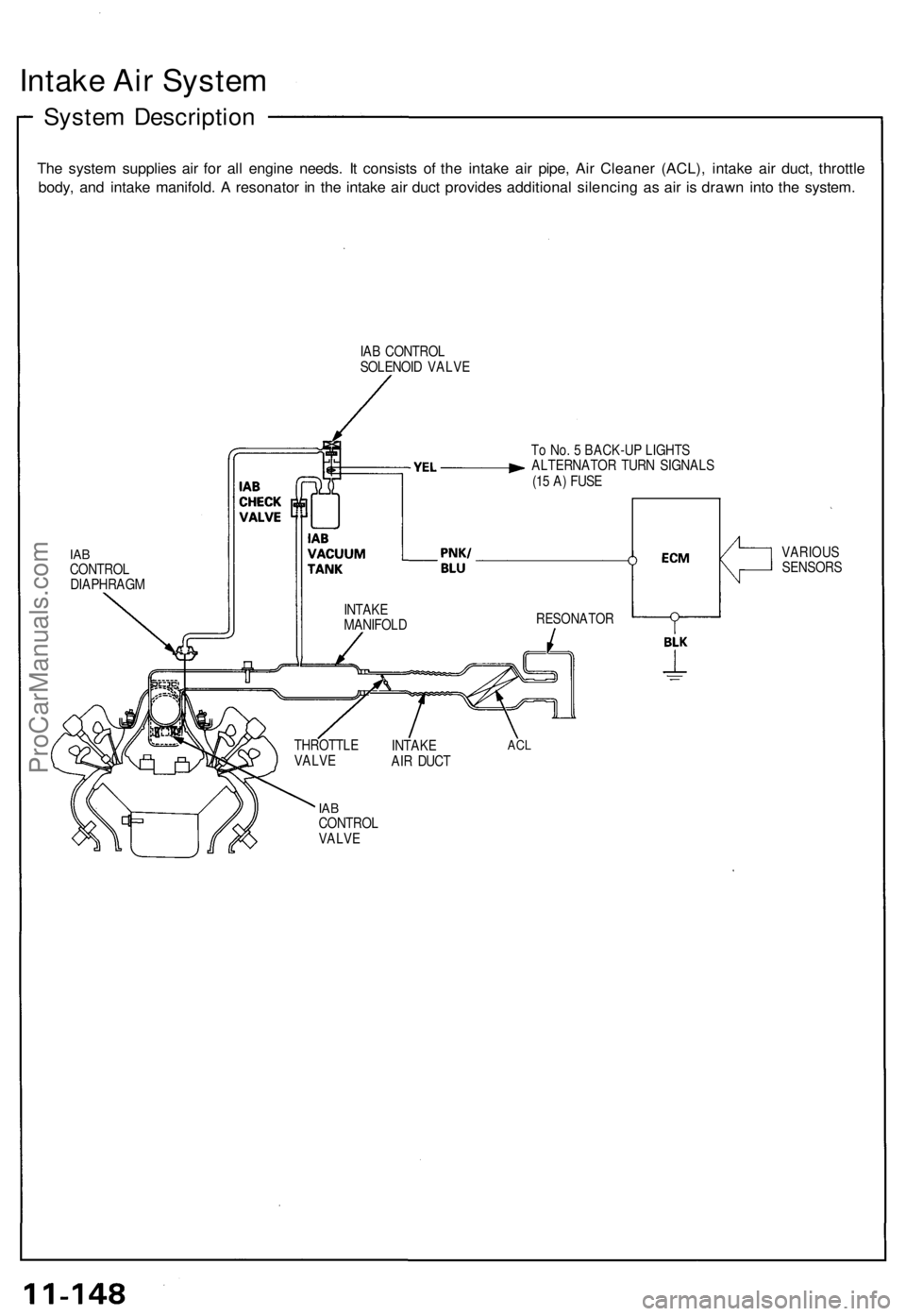
Intake Air System
System Description
The system supplies air for all engine needs. It consists of the intake air pipe, Air Cleaner (ACL), intake air duct, throttle
body, and intake manifold. A resonator in the intake air duct provides additional silencing as air is drawn into the system.
IAB CONTROL
SOLENOID VALVE
To No. 5 BACK-UP LIGHTS
ALTERNATOR TURN SIGNALS
(15 A) FUSE
IAB
CONTROL
DIAPHRAGM
IAB
CONTROL
VALVE
THROTTLE
VALVE
INTAKE
AIR DUCT
ACL
RESONATOR
VARIOUS
SENSORS
INTAKE
MANIFOLDProCarManuals.com
Page 274 of 1640
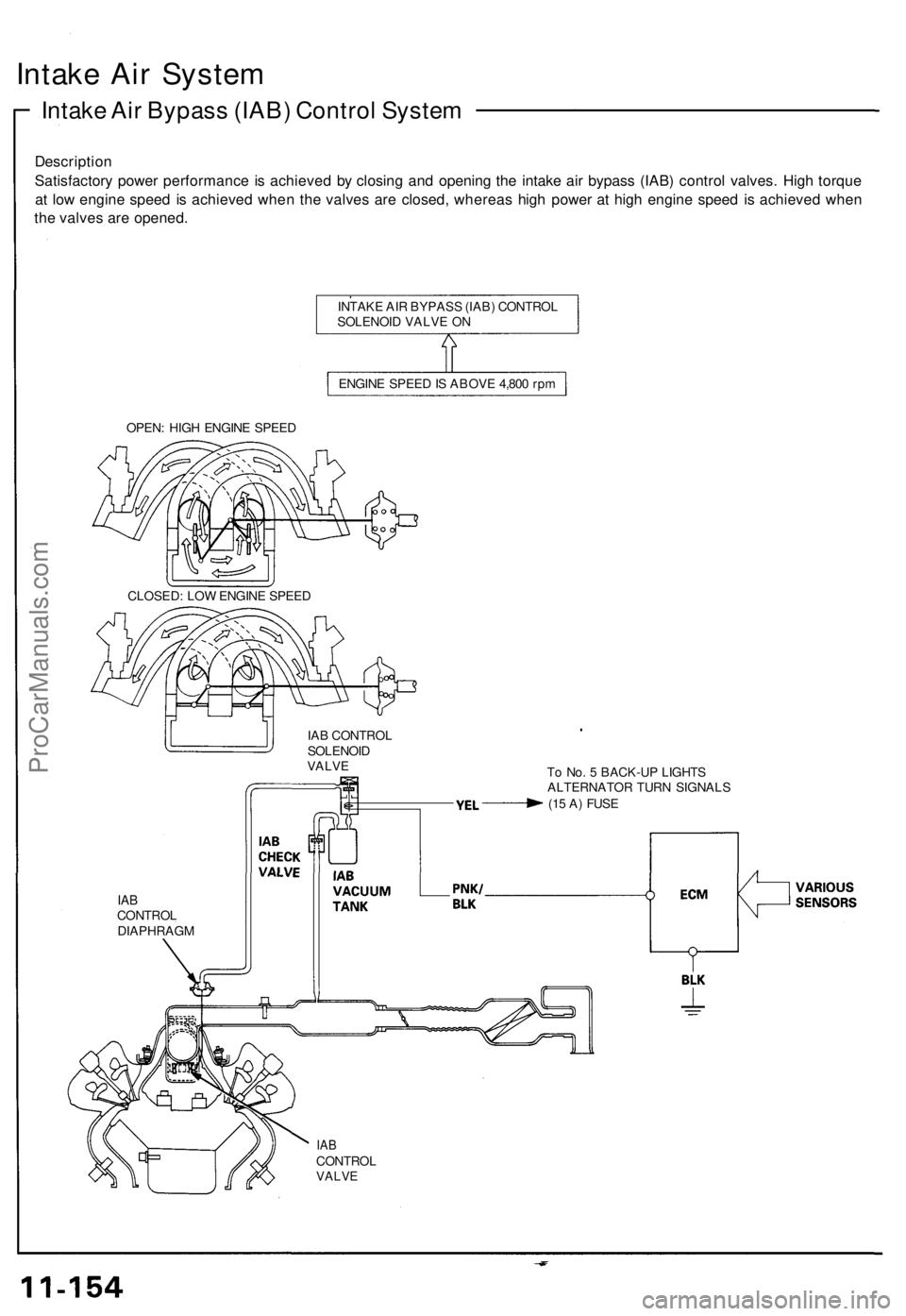
Intake Air System
Intake Air Bypass (IAB) Control System
Description
Satisfactory power performance is achieved by closing and opening the intake air bypass (IAB) control valves. High torque
at low engine speed is achieved when the valves are closed, whereas high power at high engine speed is achieved when
the valves are opened.
INTAKE AIR BYPASS (IAB) CONTROL
SOLENOID VALVE ON
ENGINE SPEED IS ABOVE 4,800 rpm
OPEN: HIGH ENGINE SPEED
IAB CONTROL
SOLENOID
VALVE
To No. 5 BACK-UP LIGHTS
ALTERNATOR TURN SIGNALS
(15 A) FUSE
IAB
CONTROL
DIAPHRAGM
IAB
CONTROL
VALVE
CLOSED: LOW ENGINE SPEEDProCarManuals.com
Page 280 of 1640
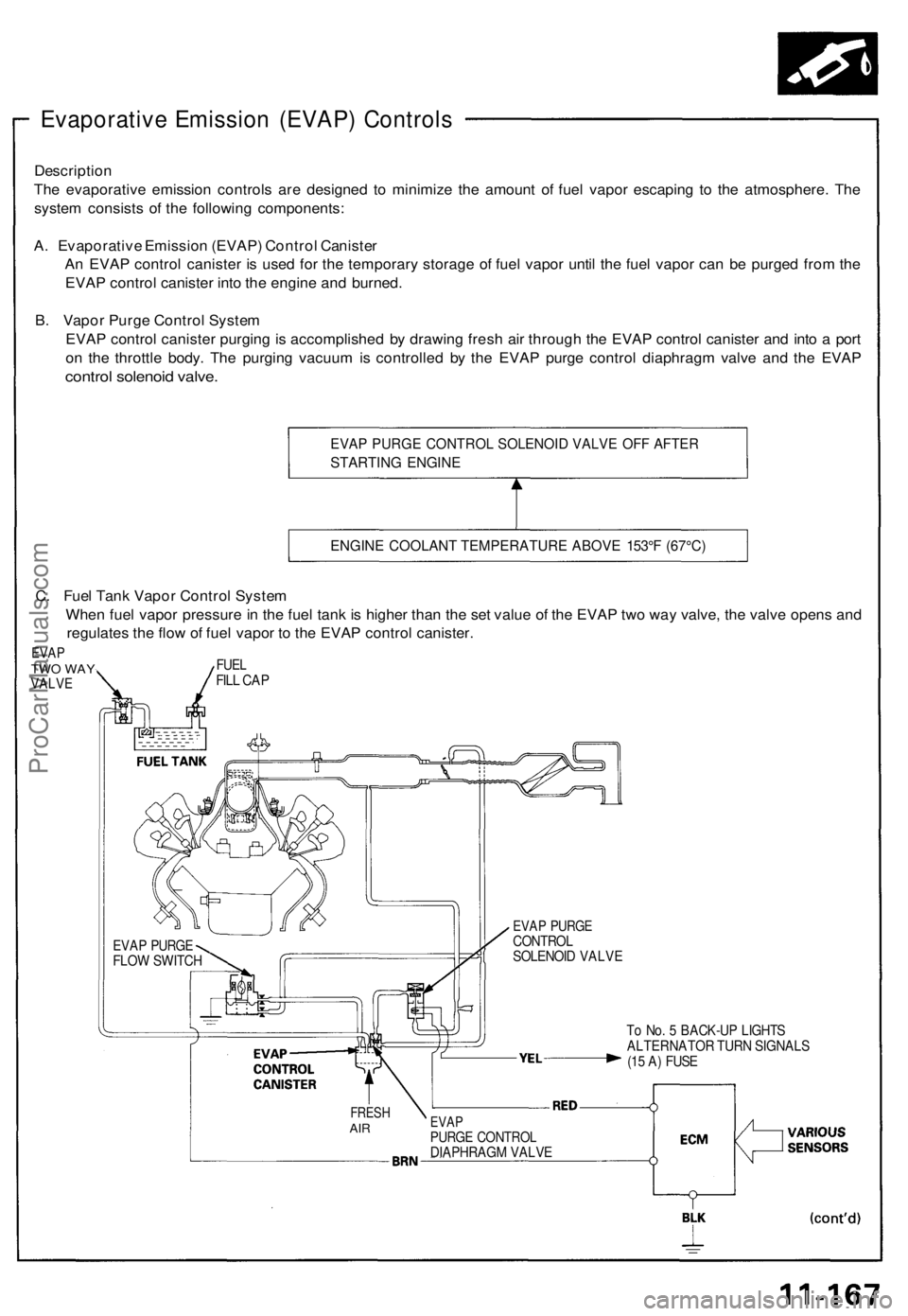
Evaporative Emission (EVAP) Controls
Description
The evaporative emission controls are designed to minimize the amount of fuel vapor escaping to the atmosphere. The
system consists of the following components:
A. Evaporative Emission (EVAP) Control Canister
An EVAP control canister is used for the temporary storage of fuel vapor until the fuel vapor can be purged from the
EVAP control canister into the engine and burned.
B. Vapor Purge Control System
EVAP control canister purging is accomplished by drawing fresh air through the EVAP control canister and into a port
on the throttle body. The purging vacuum is controlled by the EVAP purge control diaphragm valve and the EVAP
control solenoid valve.
EVAP PURGE CONTROL SOLENOID VALVE OFF AFTER
STARTING ENGINE
ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE ABOVE 153°F (67°C)
To No. 5 BACK-UP LIGHTS
ALTERNATOR TURN SIGNALS
(15 A) FUSE
FRESH
AIR
EVAP
PURGE CONTROL
DIAPHRAGM VALVE
EVAP PURGE
CONTROL
SOLENOID VALVE
EVAP PURGE
FLOW SWITCH
C. Fuel Tank Vapor Control System
When fuel vapor pressure in the fuel tank is higher than the set value of the EVAP two way valve, the valve opens and
regulates the flow of fuel vapor to the EVAP control canister.
EVAP
TWO WAY
VALVE
FUEL
FILL CAPProCarManuals.com
Page 410 of 1640
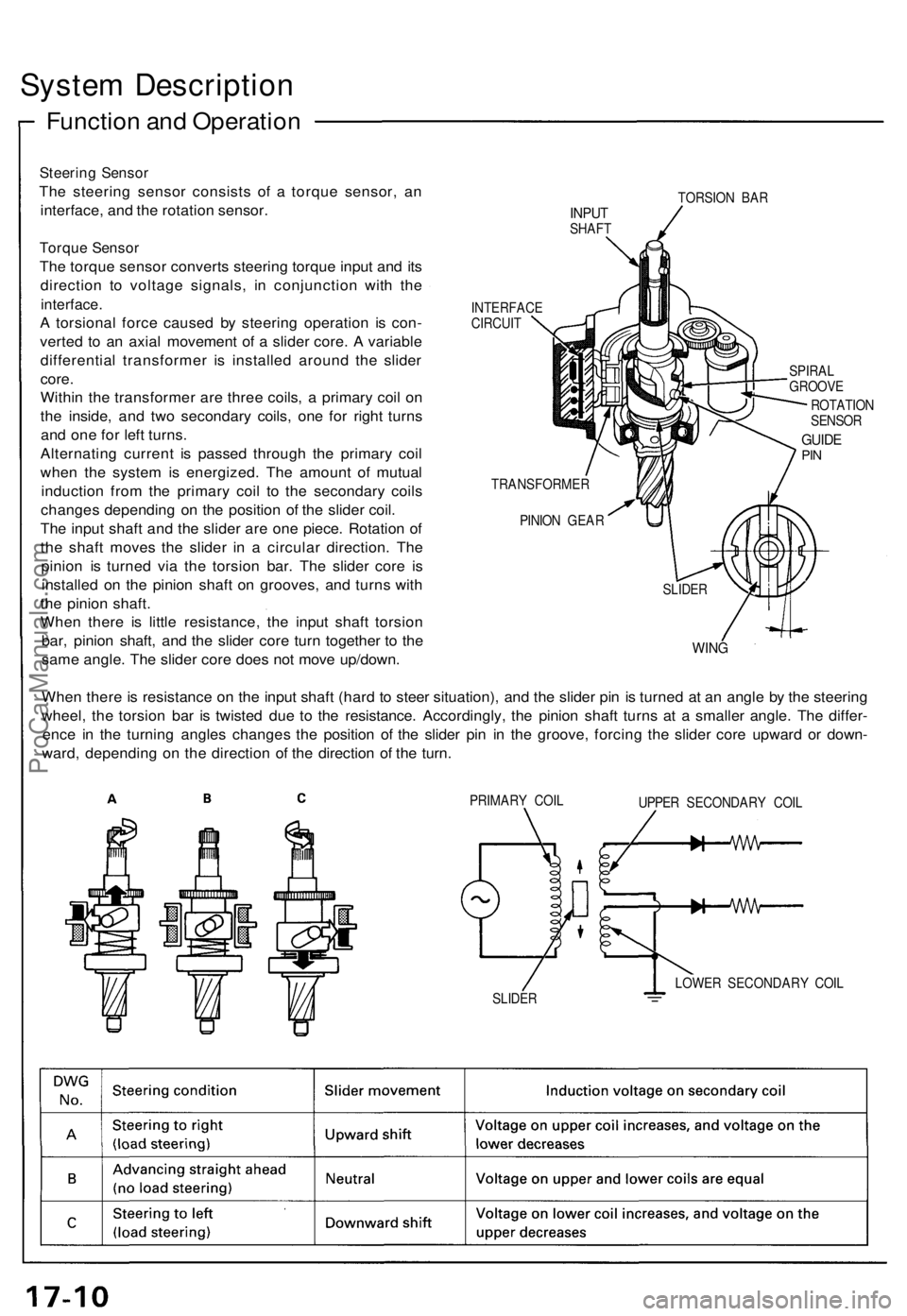
System Description
Function and Operation
Steering Sensor
The steering sensor consists of a torque sensor, an
interface, and the rotation sensor.
Torque Sensor
The torque sensor converts steering torque input and its
direction to voltage signals, in conjunction with the
interface.
A torsional force caused by steering operation is con-
verted to an axial movement of a slider core. A variable
differential transformer is installed around the slider
core.
Within the transformer are three coils, a primary coil on
the inside, and two secondary coils, one for right turns
and one for left turns.
Alternating current is passed through the primary coil
when the system is energized. The amount of mutual
induction from the primary coil to the secondary coils
changes depending on the position of the slider coil.
The input shaft and the slider are one piece. Rotation of
the shaft moves the slider in a circular direction. The
pinion is turned via the torsion bar. The slider core is
installed on the pinion shaft on grooves, and turns with
the pinion shaft.
When there is little resistance, the input shaft torsion
bar, pinion shaft, and the slider core turn together to the
same angle. The slider core does not move up/down.
TORSION BAR
INPUT
SHAFT
INTERFACE
CIRCUIT
SPIRAL
GROOVE
ROTATION
SENSOR
GUIDE
PIN
TRANSFORMER
PINION GEAR
WING
When there is resistance on the input shaft (hard to steer situation), and the slider pin is turned at an angle by the steering
wheel, the torsion bar is twisted due to the resistance. Accordingly, the pinion shaft turns at a smaller angle. The differ-
ence in the turning angles changes the position of the slider pin in the groove, forcing the slider core upward or down-
ward, depending on the direction of the direction of the turn.
PRIMARY COIL
UPPER SECONDARY COIL
LOWER SECONDARY COIL
SLIDER
SLIDERProCarManuals.com
Page 411 of 1640
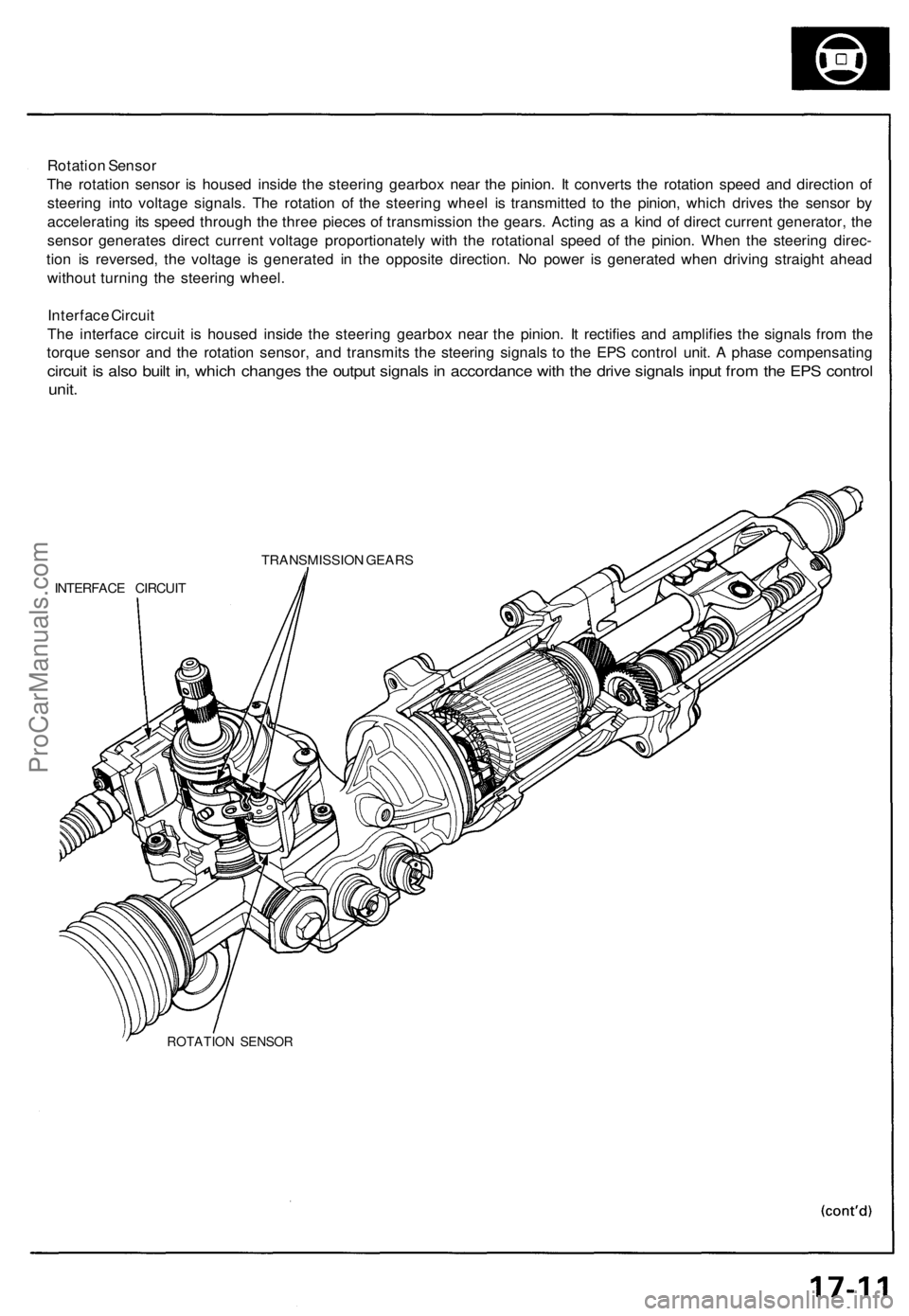
Rotation Sensor
The rotation sensor is housed inside the steering gearbox near the pinion. It converts the rotation speed and direction of
steering into voltage signals. The rotation of the steering wheel is transmitted to the pinion, which drives the sensor by
accelerating its speed through the three pieces of transmission the gears. Acting as a kind of direct current generator, the
sensor generates direct current voltage proportionately with the rotational speed of the pinion. When the steering direc-
tion is reversed, the voltage is generated in the opposite direction. No power is generated when driving straight ahead
without turning the steering wheel.
Interface Circuit
The interface circuit is housed inside the steering gearbox near the pinion. It rectifies and amplifies the signals from the
torque sensor and the rotation sensor, and transmits the steering signals to the EPS control unit. A phase compensating
circuit is also built in, which changes the output signals in accordance with the drive signals input from the EPS control
unit.
TRANSMISSION GEARS
INTERFACE CIRCUIT
ROTATION SENSORProCarManuals.com