1990 MITSUBISHI SPYDER transmission
[x] Cancel search: transmissionPage 1148 of 2103

AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
ENGINE (NON-TURBO)> Troubleshootihg
Code Scan tool 31Hydraulic pressure switch: ODProbable
No.General scan tool
Pressure switch falls to respond within specified time for given temperature range.
l Low/high fluid level in transaxle
l Malfunction of pressure switch assembly
l Internal transaxle problem
OKNGHydraulic pressure check Check the following Repair
l Measure the overdrive clutch pressure
l
l engine
l Disconnect the solenoid and pressure switchOK
assembly connector and apply system voltage
between terminals (6) (8).
WARNING: FRONT WHEELS MUST BE OFFReplace the solenoid and pressure switch bly.
THE GROUND BEFORE PRO-CEEDING.
NOTE: Step on the brake pedal so the wheels won’t rotate.
l Select lever: Increase the engine speed slightly.
S t a n d a r d
(75-95 psi)
every 3 seconds
Check the transmission fluid level.
NG
Repair
l Solenoid and pressure switch assembly
Internal transaxle failure. (Refer to
Code Scan tool 32 Hydraulic pressure switch: 2-4 Probable cause
No.General scan tool
TSB Revision
Pressure switch falls to respond within specified t
ime for given temperature range.l
Low/high fluid level in transaxle
l Malfunction of pressure switch assembly
l Internal transaxle problem
Hydraulic pressure check
l Measure the 2-4 clutch pressure
Start engine
following connector
WARNING: FRONT WHEELS MUST BE OFF THE GROUND BEFORE PRO-
CEEDING. on the brake pedal so that wheels
won’t rotate.
l Select lever:
l increase the engine speed slightly.
S t a n d a r d
(75-95 psi)
everv 3 seconds
NGOK
NG Repair
OK
the solenoid and pressure switch assem-
Check the transmission fluid level.
NG
Possible causes:
l Solenoid and pressure switch assembly
linternal transaxle failure. (Refer to
Page 1149 of 2103

AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
ENGINE (NON-TURBO)> Troubleshooting
Code Scan tool 33Hydraulicpressureswitch:
No.General scan tool
Pressure switch falls to respond within specified t ime for given temperature range.
l Low/high fluid level in transaxle Malfunction Internal transaxle problem
,l Carry out the inspection procedure for code No. 31. (Refertol Carry out the inspection procedure for code No. 32. (Refer
to
Code Scan tool 35 Check level . Probable cause No.General scan tool
No pressure is present for any element.l fluid level in l
Malfunction of oil filter
l Missing O-ring
l Malfunction of transmission fluid cooler
Code Scan tool 38
Fault immediately after a shift Probable cause
No.General scan tool
Fault happened within 1.3 second of a shift (This code is not stored alone. It if
a speed error (codes through 58) is detected immediately after a l Internal transaxle problem
(Refer to Speed errors) I
Code
Scan tool 37 Solenoid switch valve latched in
No.General scan tool the LU position
Three unsuccessful attempts shift gear.
Probable
l
Internal transaxle problemlRefer to Inspection for diagnostic trouble
code. (Internal transaxle problem
Lock-up control out of rangeProbable cause
Electronically Modulated Converter Clutch (EMCC) op eration is inhibitedl L o w / h i g h f l u i d l e v e l i n I n t e r n a l p r o b l e m
checkNGI -..< .
l - Measure the torque converter clutch offcontrol valves.
l‘Use the scan tool to erase diagnostic troublecodes.l Drive the vehicle in overdrive until it is fully
warmed up.
lDrive in gear overdrive for a minimum of10 seconds.NOTEl The vehicle speed must be greater than 80 (50 mph).lThrottle must be open greater than 6 degrees.
Standard value: Less than 69 (10 psi)
ROAD TESTOK: Code 38 set. Check the transmission fluid level.OK
NG Repair
Replacethetorqueconverterandtransmissionfluid
cooler.
Possible cause:lInternal transaxle failure. (Refer to
TSB Revision
Page 1156 of 2103

AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
ENGINE (NON-TURBO)> Troubleshooting
NGCheck the installation condition of the input speed sensor Repair
OK
NGCheck the installation Repair
NG Repair
l
OK
SCAN TOOL Data list lCarry out the inspection procedure for code No. 56.
44 Transaxle input speed
Check the transmission fluid level.
OK
SCAN TOOL Data list
44 Transaxle input speed l Raise the vehicle’s drive wheels off the ground
NG Repair
1. NG
The 2-4 clutch or clutch may be slipping.
l Start the engine and step on the brake so the wheel s won’t
rotate.1. Selector lever: 2
l the throttle to 30%
Caution Do not test any gear range for longer than 5 secon ds
l Use the scan tool ‘to monitor the input RPM.
Allow the engne to return to idle. OK: 0 rpm l
The reverse clutch or low/reverse clutch may be sli pping.
2. Select lever:
l Open the throttle to 30%
l Use the scan tool to monitor the input RPM.
Allow the enaine to return to idle.
OK: 0 rpm
Transaxle overhaul
l If code No. 50 is set:
Reverse clutch or
clutch may be slipping
l If code No. 51 is set:
UD clutch may be slipping
l If code No. 52 is set:
2-4 clutch or UD clutch may be slipping
l If code No. 53 is set:
OD clutch may be slipping
l If code No. 54 is set:
OD clutch may be slipping
OK
Check trouble symptom.
NG
Check the following connectors: Replace the TCM.
N G
TSBRevision
Repair
Page 1159 of 2103
AUTOMATIC .
.
Code Scan tool 58 S p e e d s e r r o r :
No.General scan toolground
After a reset in Neutral and input shaft speed/outp
ut shaft speed of input
gear teeth to output teeth of 2.50.
A hard fault is considered to exist when the fault counter has matured to a value of 255.
An intermittent fault is considered present when th e fault counter is greater than or equal
to 6 and less than 255. No fault is considered to exist when the fault coun ter is less than 6.
.
. , ,
. .
ground open-circuited
OKNGMeasure at the TCM connector Check the following Repair
l Disconnect the connector and
l
measure at the harness side.Resistance value between (12) andOKl
(53).lResistance value between (53) andReplace the . (54).O K :.
Less than
Code Scan tool 60, 61, inadequate element volume: Probable
No. 62LR, 2-4, OD
General scan tool
.
The updated learned volume is below a threshold val ue..The volumes of the transmission fluid needed to app
ly the friction elements are continuouslymonitored and learned for adaptive controls. As the friction material wears, the volume Ofcode. (Internal transaxle problem fluid needed to apply the element increases. The fo llowing are the typical clutch volumes
beyond which the clutches might be damaged:
L R : 3 5 - 8 3 O D :
2-4: UD:
Code Scan tool 73Worn out/burnt transmission fluid Probable cause
No.General scan tool
With the clutch engaged, clutch fully on, partial lock failure counter greaterl
Degraded fluid
than equal to and the turbine acceleration out of range. l
Wheels severely out of alignment
Theory of operation: l
Internal transaxle problem
While in gear Fully electronically modulated converter clut ch (FEMCC) and just beforethe clutch engages, the PCM requests the TCM to moment arily establish Partial
electronically modulated converter clutch (PEMCC) o peration. If the turbine acceleration is
out of range during the FEMCC to PEMCC transition, a counter is incremented. When the
count is 20 or more, the trouble code is set. This code does not cause the code is set,
FEMCC to PEMCC operation before the A/C clutch enga gement will be disabled.
TSB Revision
Page 1167 of 2103

AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
ENGINE (NON-TURBO)>
.
to GROU’P 00
RefertoGROUP 00 Maintenance Service.
TCM RESETTING
(1) Disconnect the negative battery cable from the
before replacing the transaxle out overhaul.
(2) After work has been completed, check
trouble codes (DTC). If DTC 12 (“Battery power was
disconnected since last power has been
generated, this DTC must be cleared. Furthermore, select “Special function” on the scan tool
and then set the scan tool to Quick Learn mode (car ry
out this operation from the scan tool screen). Then input
the clutch volume index into the
PINION FACTOR WRITING PROCEDURE
REPLACEMENT OR TIRE SIZE
NOTE
With transmissions, the TCM uses the rotation speed
of the transaxle output shaft to calculate the vehicle speed
and cumulative distance
Because of this, it is
necessary to input (or update) the tire size coeffi cient into
the TCM memory after the TCM has been replaced or t he
tire size has been changed.
(1) Select “Special function” on the scan
and then set
the scan tool to Pinion Factor mode (carry out this operation from the scan tool screen). Then input (o r
update) the tire size coefficient the TCM memory.
Note that new
do not a tire size
already input.
TSB Revision
Page 1174 of 2103
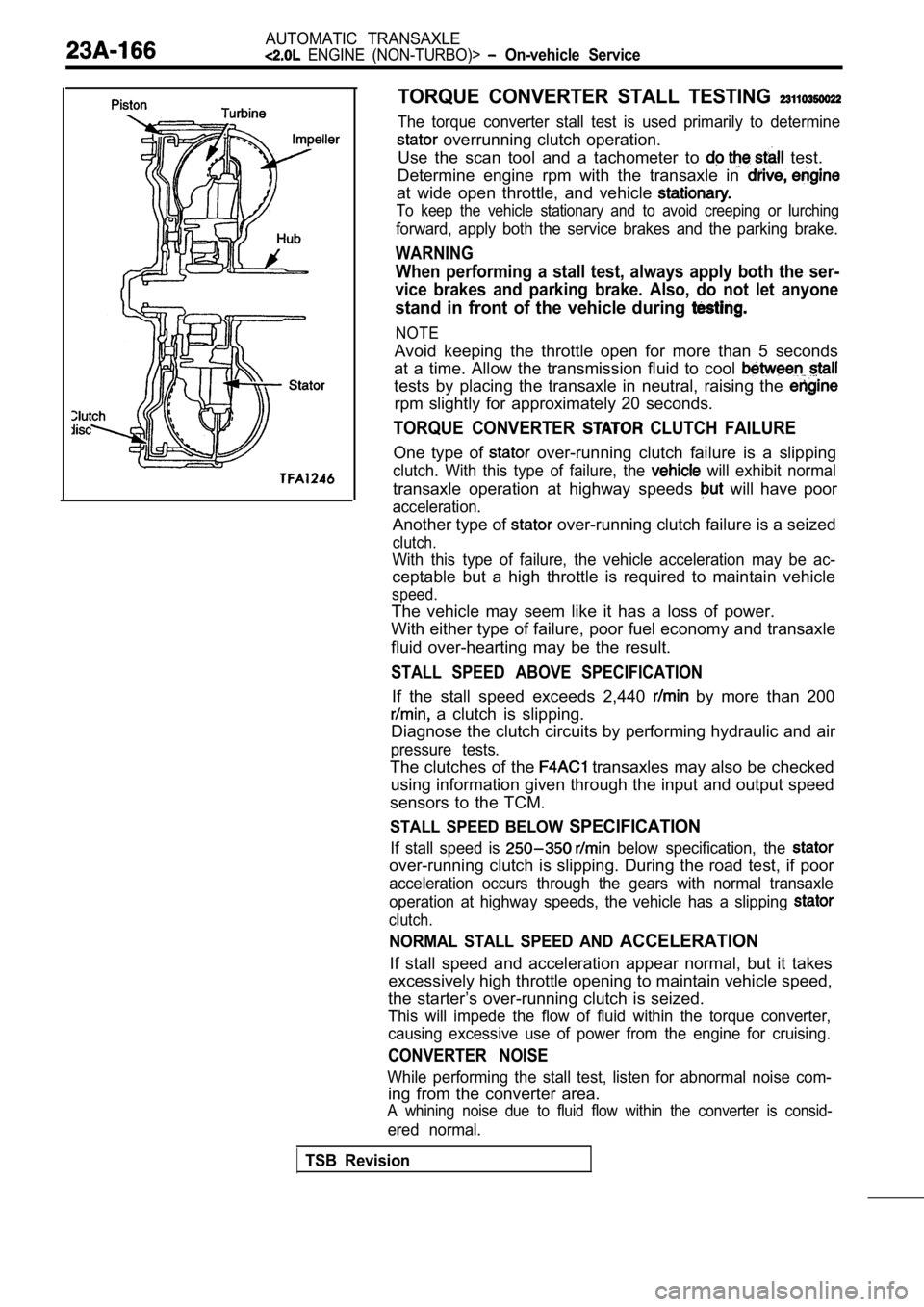
AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
ENGINE (NON-TURBO)> On-vehicle Service
TORQUE CONVERTER STALL TESTING
The torque converter stall test is used primarily to determine
overrunning clutch operation.
Use the scan tool and a tachometer to
test.
Determine engine rpm with the transaxle in
at wide open throttle, and vehicle
To keep the vehicle stationary and to avoid creepin g or lurching
forward, apply both the service brakes and the parking brake.
WARNING
When performing a stall test, always apply both the ser-
vice brakes and parking brake. Also, do not let any one
stand in front of the vehicle during
NOTE
Avoid keeping the throttle open for more than 5 seconds
at a time. Allow the transmission fluid to cool
tests by placing the transaxle in neutral, raising the
rpm slightly for approximately 20 seconds.
TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH FAILURE
One type of over-running clutch failure is a slipping
clutch. With this type of failure, the will exhibit normal
transaxle operation at highway speeds will have poor
acceleration.
Another type of over-running clutch failure is a seized
clutch.
With this type of failure, the vehicle acceleration may be ac-
ceptable but a high throttle is required to maintai n vehicle
speed.
The vehicle may seem like it has a loss of power.
With either type of failure, poor fuel economy and transaxle
fluid over-hearting may be the result.
STALL SPEED ABOVE SPECIFICATION
If the stall speed exceeds 2,440 by more than 200
a clutch is slipping.
Diagnose the clutch circuits by performing hydrauli c and air
pressure tests.
The clutches of the transaxles may also be checked
using information given through the input and outpu t speed
sensors to the TCM.
STALL SPEED BELOW SPECIFICATION
If stall speed is below specification, the
over-running clutch is slipping. During the road te st, if poor
acceleration occurs through the gears with normal t ransaxle
operation at highway speeds, the vehicle has a slip ping
clutch.
NORMAL STALL SPEED AND ACCELERATION
If stall speed and acceleration appear normal, but it takes
excessively high throttle opening to maintain vehic le speed,
the starter’s over-running clutch is seized.
This will impede the flow of fluid within the torqu e converter,
causing excessive use of power from the engine for cruising.
CONVERTER NOISE
While performing the stall test, listen for abnormal noise com-
ing from the converter area.
A whining noise due to fluid flow within the conver ter is consid-
ered normal.
TSB Revision
Page 1203 of 2103
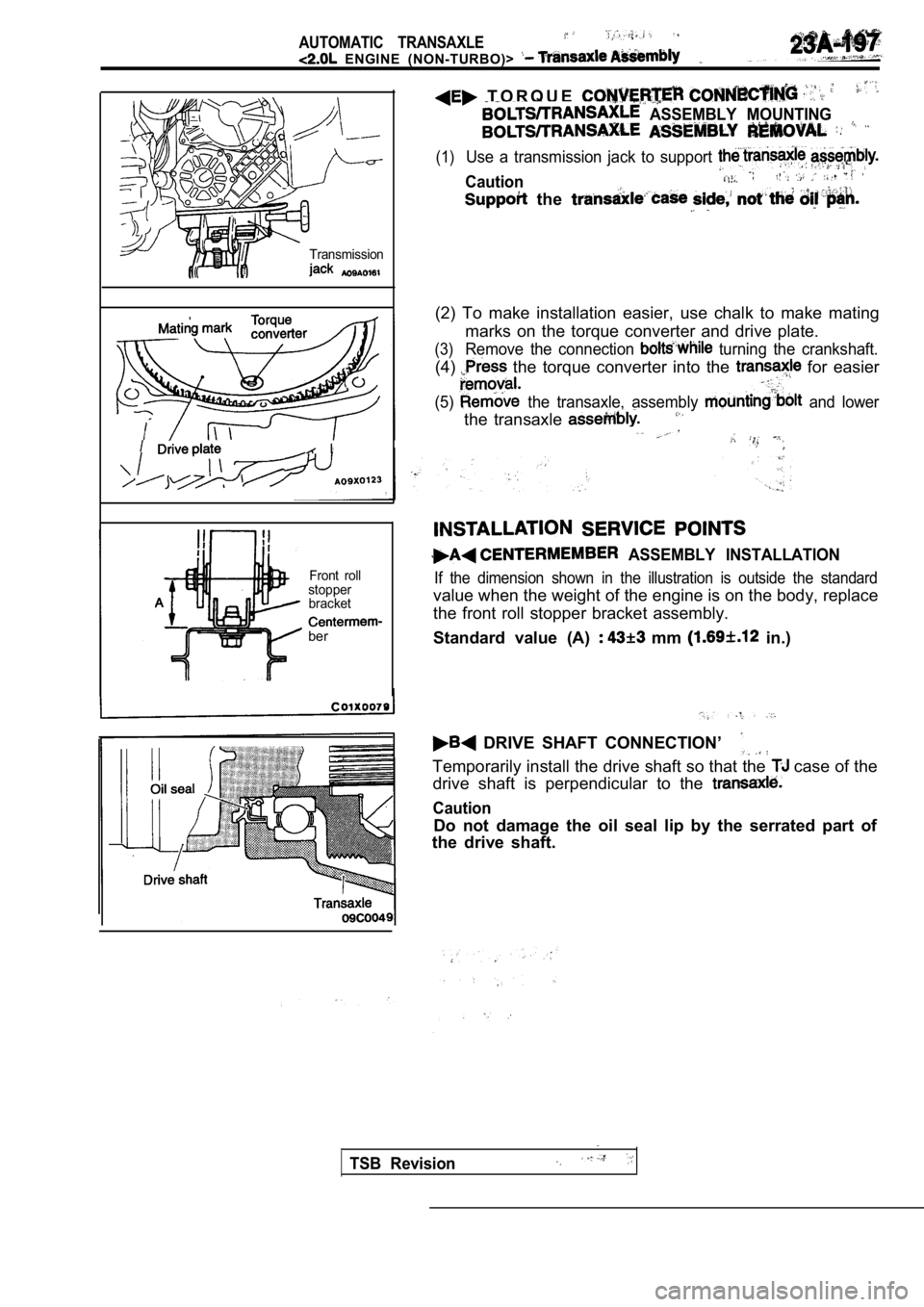
AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
ENGINE (NON-TURBO)>
Transmission
I
Front roll
stopper bracket
ber
T O R Q U E
ASSEMBLY MOUNTING
(1)Use a transmission jack to support
Caution
the
(2) To make installation easier, use chalk to make mating
marks on the torque converter and drive plate.
(3)Remove the connection turning the crankshaft.
(4) the torque converter into the for easier
(5) the transaxle, assembly and lower
the transaxle
ASSEMBLY INSTALLATION
If the dimension shown in the illustration is outsi de the standard
value when the weight of the engine is on the body, replace
the front roll stopper bracket assembly.
Standard value (A)
mm in.)
DRIVE SHAFT CONNECTION’
Temporarily install the drive shaft so that the case of the
drive shaft is perpendicular to the
Caution
Do not damage the oil seal lip by the serrated part of
the drive shaft.
TSB Revision
Page 1208 of 2103
AUTOMATIC TRANSAXLE
OVERHAUL General Information
GENERAL INFORMATION
Precautions to be taken when disassembling and the
l
Because the automatic transaxle is composed of component parts high degree of
precision, these parts should be very carefully han dled during disassembly andassembly so as not
to scar or scratch them.
A rubber mat should be placed on the workbench, it should kept clean.
During disassembly, cloth gloves or shop towels sho uld not be used. If
items must be used,
either use articles made of nylon, or use paper tow els.
All disassembled parts must be thoroughly cleaned.
Metal parts may be cleaned with ordinary detergents , but must be thoroughly air dried.
Clean the clutch disc, resin thrust plate and rubber parts by using transmission fluid),
being very careful that dust, dirt, etc. do not adhere to them.
Do not reuse gaskets, oil seals, or rubber parts.
Replace such parts with new ones at every reassembl y. The’ O-ring of the oil level gauge need not
be replaced.
Do not use grease other than petrolatum jelly.
Apply ATF to friction components, rotating parts, a nd sliding parts before installation.
A new clutch disc should be immersed in ATF for at least two hours before installation.
Do not apply sealer or adhesive to gaskets.
When a bushing
be replaced, replace the assembly in which incorporated.
If the transaxle main unit is damaged, also disasse mble and clean the cooler system.
TSBRevision