1988 PONTIAC FIERO fuse
[x] Cancel search: fusePage 737 of 1825

Starting Mode
When the ignition is first turned "ON," the ECM
will turn "ON" the fuel pump relay for two seconds,
and the fuel pump will build up pressure. The ECM
then checks the coolant temperature sensor, throttle
position sensor, and determines the proper airlfuel
ratio for starting. This ranges from 1.5
: 1 at -36°C (-
33°F ) to 14.7 : 1 at 94°C ( 201°F ). The ECM controls
the amount of fuel delivered in the STARTING mode
by changing how long the injectors are pulsed "ON".
The cold start valve (Figure C2-2) not controlled
by the ECM is used to provide additional fuel during
the starting mode to improve cold start-ups. This
circuit is important when the engine coolant
temperature is very low because the other injectors
would not be pulsed "ON" long enough to provide the
needed amount of fuel to start. The cold start valve is
somewhat different from the other injectors in that it
causes the fuel to be vaporized for a better combustible
mixture.
101 TUBE AND BODY ASSEMBLY
102 O-RING SEAL
- VALVE
103 O-RING SEAL
- BODY
104 O-RING SEAL
- TUBE
Figure C2-2 Cold Start Valve
The circuit is activated only in the crank mode.
The power is supplied directly from the starter
solenoid and is protected by the crank fuse. The
system is controlled by
a cold start fuel injection
switch which provides
a ground path for the valve
during cranking whenever engine coolant is below 35"
C (95°F).
Clear Flood Mode
If the engine floods, clear it by pushing the
accelerator pedal down all the way. The
ECM then
will turn "OFF" the fuel to the injectors. The
ECM
holds this injector rate as long as the throttle stays
wide open, and the engine rpm is below
600. If the
throttle position becomes less than
80%, the ECM
returns to the STARTING mode.
Run Mode
The RUN mode has two conditions called "Open
Loop" and "Closed Loop".
When the engine is first started, and rpm is above
400 rpm, the system goes into "Open Loop" operation.
In "Open Loop," the ECM will ignore the signal from
the oxygen
(02) sensor, and calculate the airlfuel ratio
based on inputs
from the coolant and MAF sensors.
The system will stay in "Open Loop" until the
following conditions are met:
1. The
O2 sensor has varying voltage output,
showing that it is hot enough to operate properly.
(This depends on temperature.)
2. The coolant sensor is above a specified
temperature about 25°C
(77°F).
3. A specific amount of time has elapsed after
starting the engine.
The specific values for the above conditions vary
with different engines, and are stored in the PROM or
Mem-Cal. When these conditions are met, the system
goes into "Closed Loop" operation. In "Closed Loop",
the ECM will calculate the airlfuel ratio (injector on-
time) based on the signal from the
O2 sensor. This
allows the airlfuel ratio to stay very close to 14.7: 1.
Acceleration Mode
The ECM looks at rapid changes in throttle
position and air flow, and provides extra fuel.
Deceleration Mode
The ECM looks at changes in throttle position and
air flow to reduce the amount of fuel. When
deceleration is very fast, the ECM can cut off fuel
completely for short periods.
The cold start fuel injection switch contains a
bimetal switch which opens the circuit at specified
Battery Voltage Correction Mode
coolant temperature. This bimetal is also heated by
the winding in the switch which would allow the valve When battery
voltage is low, the ECM can
to stay "ON" 8 seconds at -20°C or below. The time compensate
for the weak spark delivered by the
the switch stays closed varies inversely with coolant distributor
by:
temperature. In other words, as the coolant
@ Increasing the amount of fuel delivered;
temperature goes up the maximum cold start valve
@ Increasing the idle rpm; and
"ON" time goes down. Increasing ignition
dwell time.
Page 794 of 1825
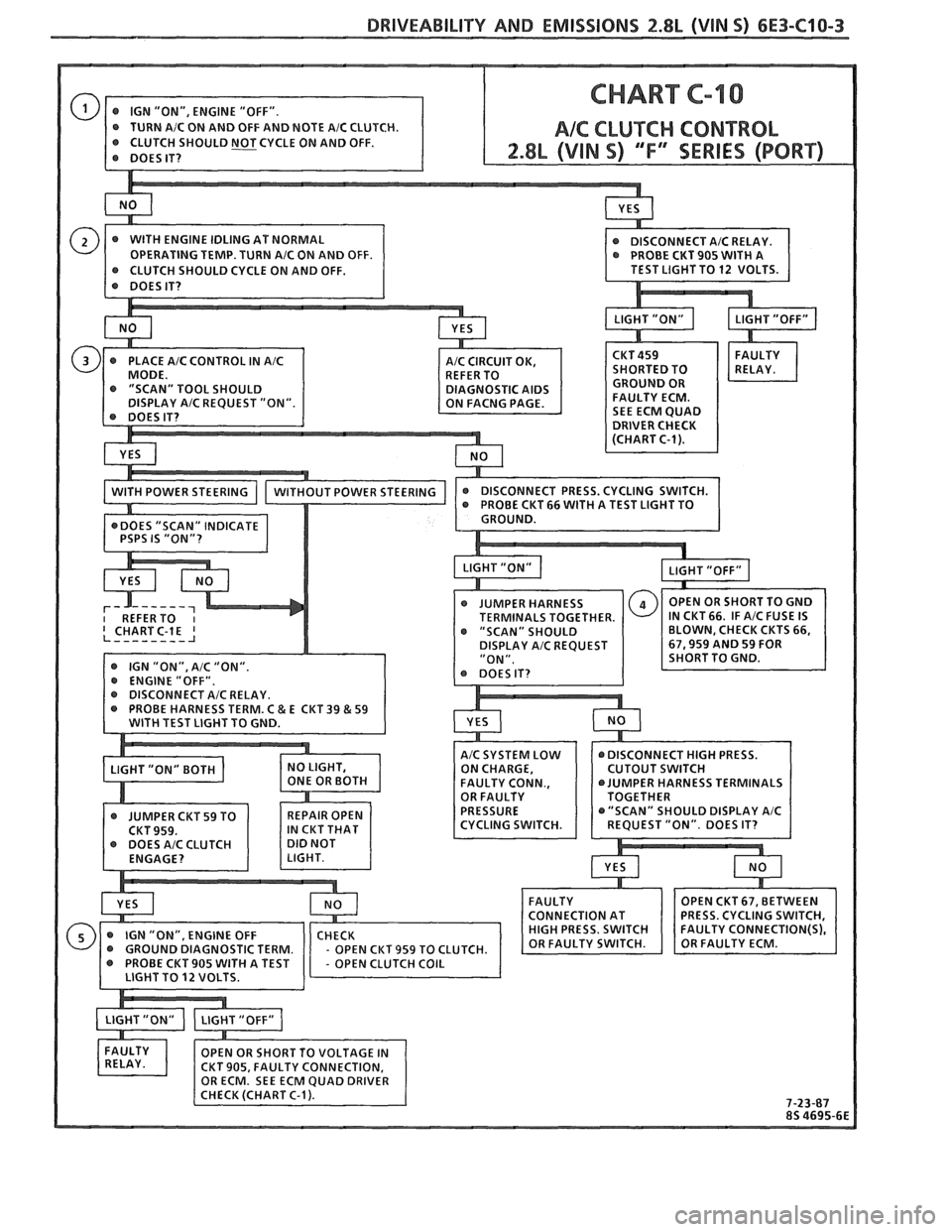
DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 2.8L (VIN S) 6E3-C10-3
@ DISCONNECT AIC RELAY.
PROBE CKT 905 WITH A
IN CKT66. IF AIC FUSE IS
BLOWN, CHECK CKTS 66,
Page 805 of 1825
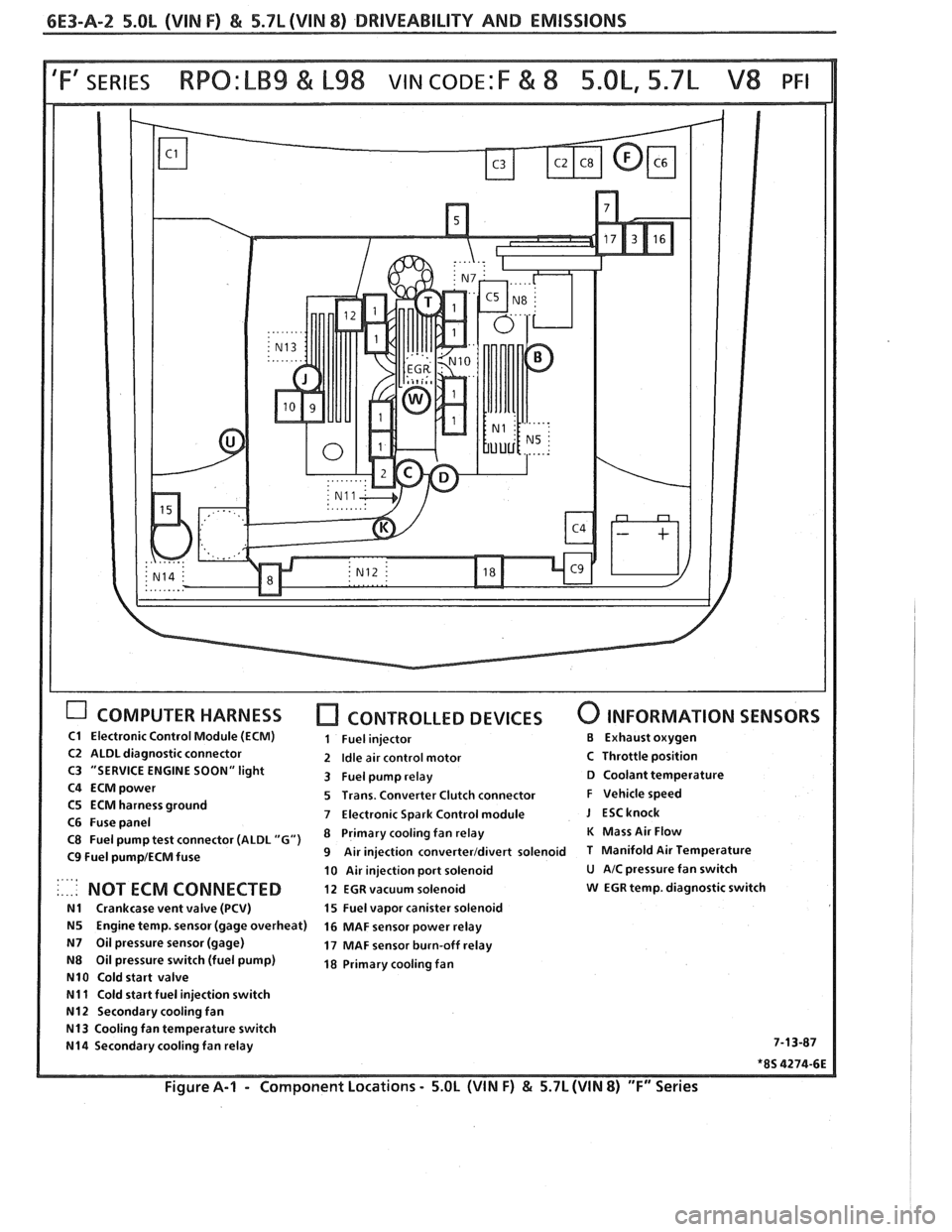
6E3-A-2 5.OL (VIN F) & 5.7L(VIN 8) DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
COMPUTER HARNESS [7 CONTROLLED DEVICES 0 INFORMATION SENSORS
C1 Electronic Control Module (ECM) 1 Fuel injector €3 Exhaust oxygen
C2 ALDL diagnostic connector 2 Idle air control motor C Throttle position
C3 "SERVICE ENGINE SOON" light
3 Fuel pump relay D Coolant temperature
C4
ECMpower 5 Trans. Converter Clutch connector F Vehicle speed
C5 ECM harness ground
7 Electronic Spark Control module J ESCknock C6 Fuse panel
C8 Fuel pump test connector (ALDL "G") Primary fan relay K Mass Air Flow
C9 Fuel pump1ECM fuse 9 Air injection converterldivert solenoid T Manifold Air Temperature
10 Air injection port solenoid
U AIC pressure fan switch . ., .. .. NOT ECM CONNECTED 12 EGR vacuum solenoid w EGR temp. diagnostic switch
N1 Crankcase vent valve (PCV) 15 Fuel vapor canister solenoid
N5 Engine temp. sensor (gage overheat)
16 MAF sensor power relay
N7 Oil pressure sensor (gage) 17 MAF sensor burn-off relay
N8 Oil pressure switch (fuel pump) 18 Primary cooling fan
N10 Cold start valve
N11 Cold start fuel injection switch
N12 Secondary cooling fan
N13 Cooling fan temperature switch
N14 Secondary cooling fan relay 7-13-87
*8S 4274-6E
Figure A-I - Component
Locations - 5.OL (WIN F) & 5.7L (WIN 8) "F" Series
Page 813 of 1825
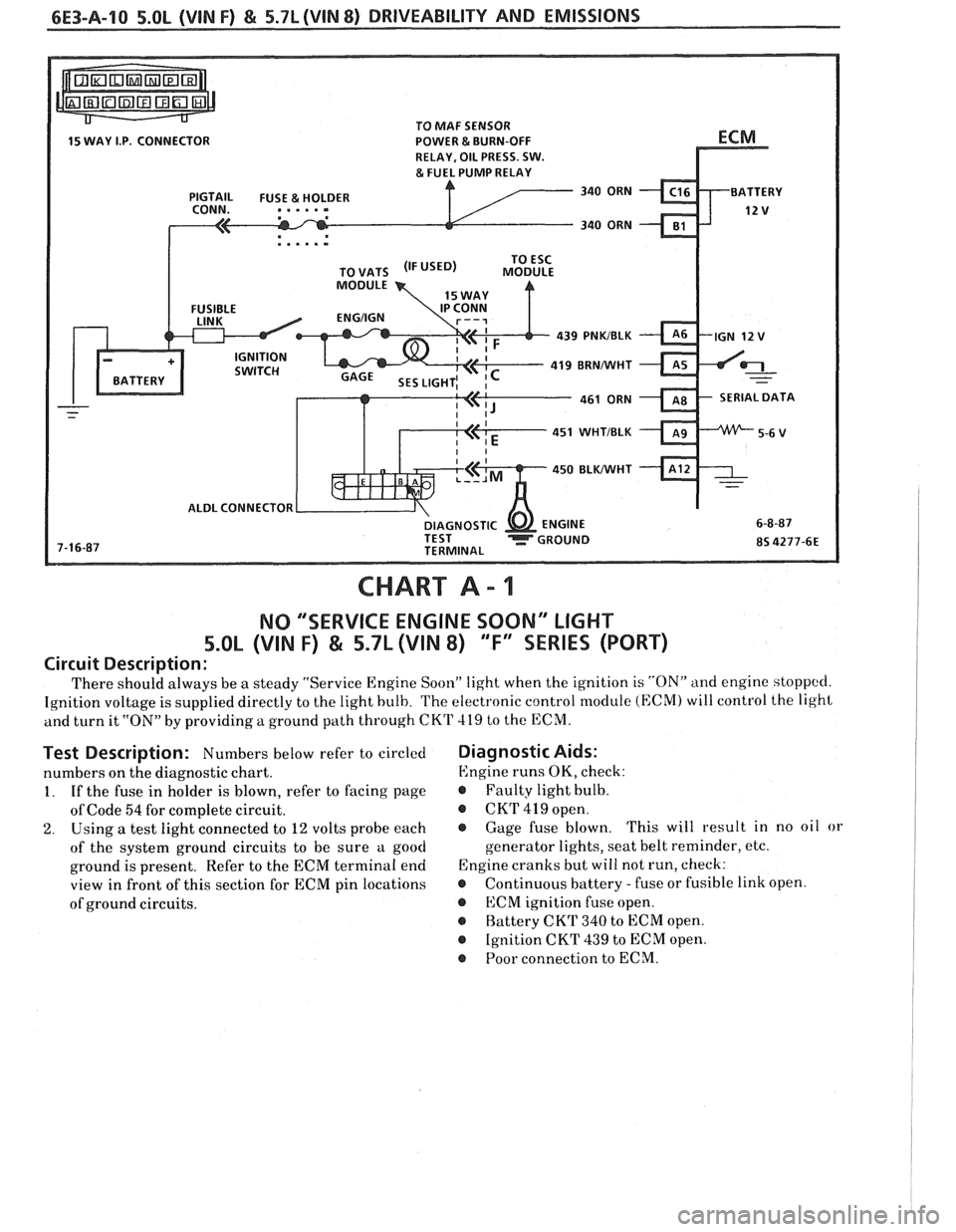
TO MAF SENSOR
POWER & BURN-OFF
RELAY, OIL PRESS. SW.
.....-
439 PNKIBLK
419 BRNNVHT
SERIAL DATA
451 WHTIBLK
450
BLWHT
ALDL CONNECTOR
CHART A - 1
NO "'SERVICE ENGINE SOON" LIGHT
5.OL (VIN F) & 5.7L (VIN 8) "F'XSEBIE'S (PORT)
Circuit Description:
There should always be a steady "Service Engine Soon" light when the ignition is "ON" and engine stoppccl.
Ignition voltage is supplied directly to the light bulb. The electronic control module (ECM) will control the light
and turn it
"ON" by providing a ground path through CKT 419 to the ECM.
Test Description: Numbers below refer to circled
numbers on the diagnostic chart.
1. If the fuse in holder is blown, refer to facing page
of Code
54 for complete circuit.
2. Using a test light connected to 12 volts probe each
of the system ground circuits to be sure a good
ground is present. Refer to the ECM terminal end
view in front of this section for ECM pin locations
of ground circuits.
Diagnostic Aids:
Engine runs OK, check:
r Faulty light bulb.
@ CKrI' 419 open.
@ Gage fuse blown. This
will result in no oil or
generator lights, seat belt reminder, etc.
Engine cranks but will not run, check:
r Continuous battery - fuse or fusible link open.
@ ECM ignition fuse open.
r Battery CKT 340 to ECM open.
@ Ignition CKT 439 to ECM open.
@ Poor connection to ECM.
Page 814 of 1825
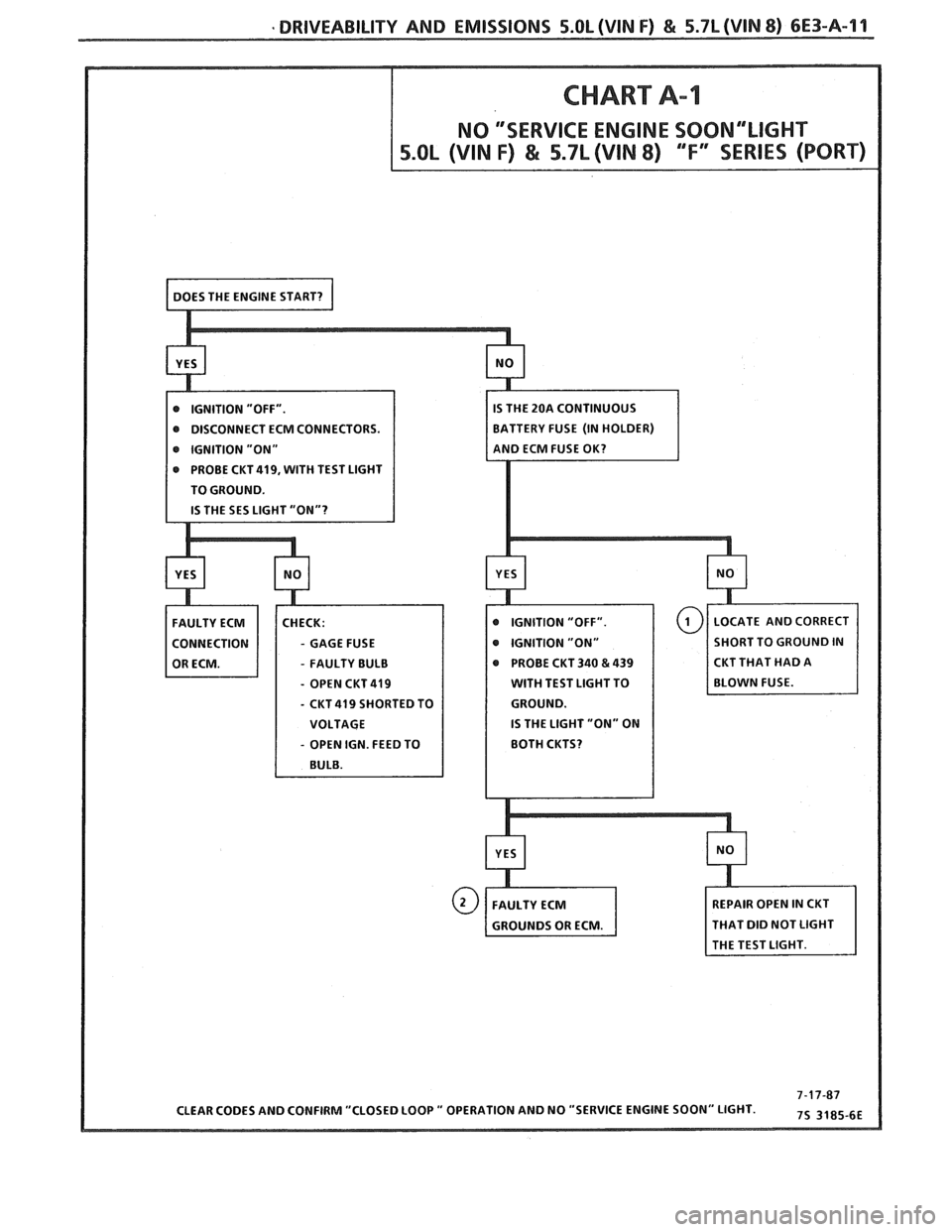
DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 5.0L (VIN F) & 5.7L (WIN 8) 6E3-A-11
@ DISCONNECT ECM CONNECTORS.
e IGNITION "ON"
PROBE
CKT419, WITH TEST LIGHT
TO GROUND.
- GAGE FUSE
- FAULTY BULB PROBE
CKT 340 & 439 CKT
THAT HAD A
- OPEN CKT 419 WITH TEST LIGHT TO
- CKT 419 SHORTED TO
IS THE LIGHT "ON" ON
- OPEN IGN. FEED TO
HAT DID NOT LIGHT
Page 817 of 1825
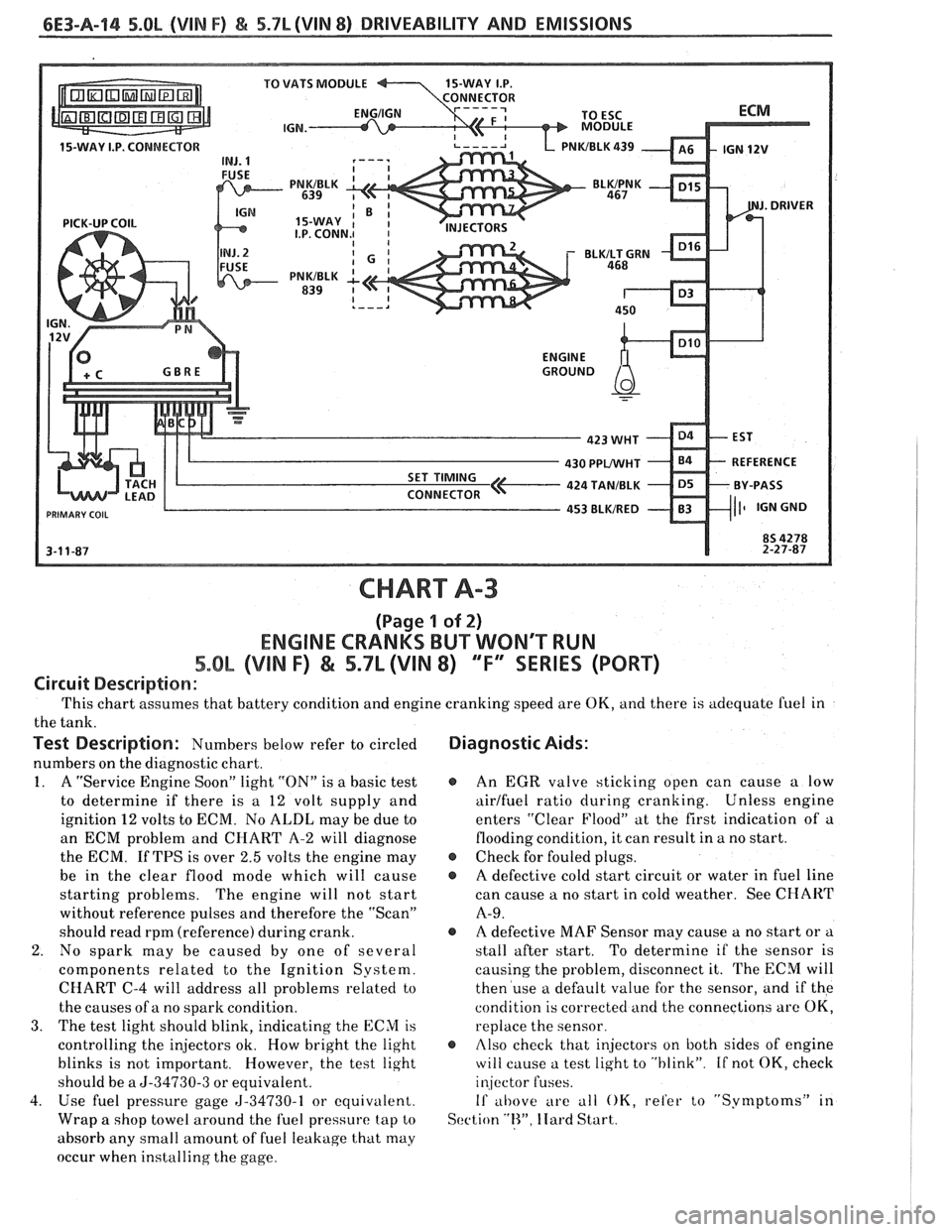
6E3-A-14 5.0L (VIN F) & 5.7L (VIN 8) DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
CHART A-3
(Page 1 of 2)
ENGINE CRANKS BUT WON'T RUN
5.OL (VIN F) & 5.7L (VIN 8) "F" SRIES (PORT)
Circuit Description :
This chart assumes that battery condition and engine cranking speed are OK, and there is adequate fuel in
the tank.
Test Description: Numbers below refer to circled Diagnostic Aids:
numbers on the diagnostic chart.
1. A "Service Engine Soon" light "ON" is a basic test @ An EGR valve sticking open can cause a low
to determine if there is a
12 volt supply and airlfuel ratio during cranking. Unless
engine
ignition
12 volts to ECM. No ALDL may be due to enters
"Clear Flood" at the first indication of a
an ECM problem and CHART
A-2 will diagnose flooding
condition, it can result in a no start.
the ECM. If TPS is over
2.5 volts the engine may @ Check for fouled plugs.
be in the clear flood mode which will cause
@ A defective cold start circuit or water in fuel line
starting problems. The engine
will not start can
cause a no start in cold weather. See
CHART
without reference pulses and therefore the "Scan" A-9.
should read rpm (reference) during crank. @ A defective MAF Sensor may cause a no start or a
2. No spark may be caused by one of several stall
after start. To determine if the sensor is
components related to the Ignition System. causing
the problem, disconnect it. The
ECM will
CHART C-4 will address all problems related to then
use a default value for the sensor, and if the
the causes of a no spark condition. condition
is corrected and the connections are
OK,
3. The test light should blink, indicating the ECM is replace the sensor.
controlling the injectors ok. How bright the light
@ rllso check that injectors on both sides of engine
blinks is not important. However, the test light
will cause a test light to "blink". If not OK, check
should be a
5-34730-3 or equivalent. injector fuses.
4. Use fuel
pressure gage 5-34730-1 or equivalent. If al~ove are all OK, refer to "Symptoms" it1
Wrap a shop towel around the fuel pressure tap to Scction "R". Ilard Start.
absorb any small amount of fuel leakage that may
occur when installing the gage.
Page 825 of 1825
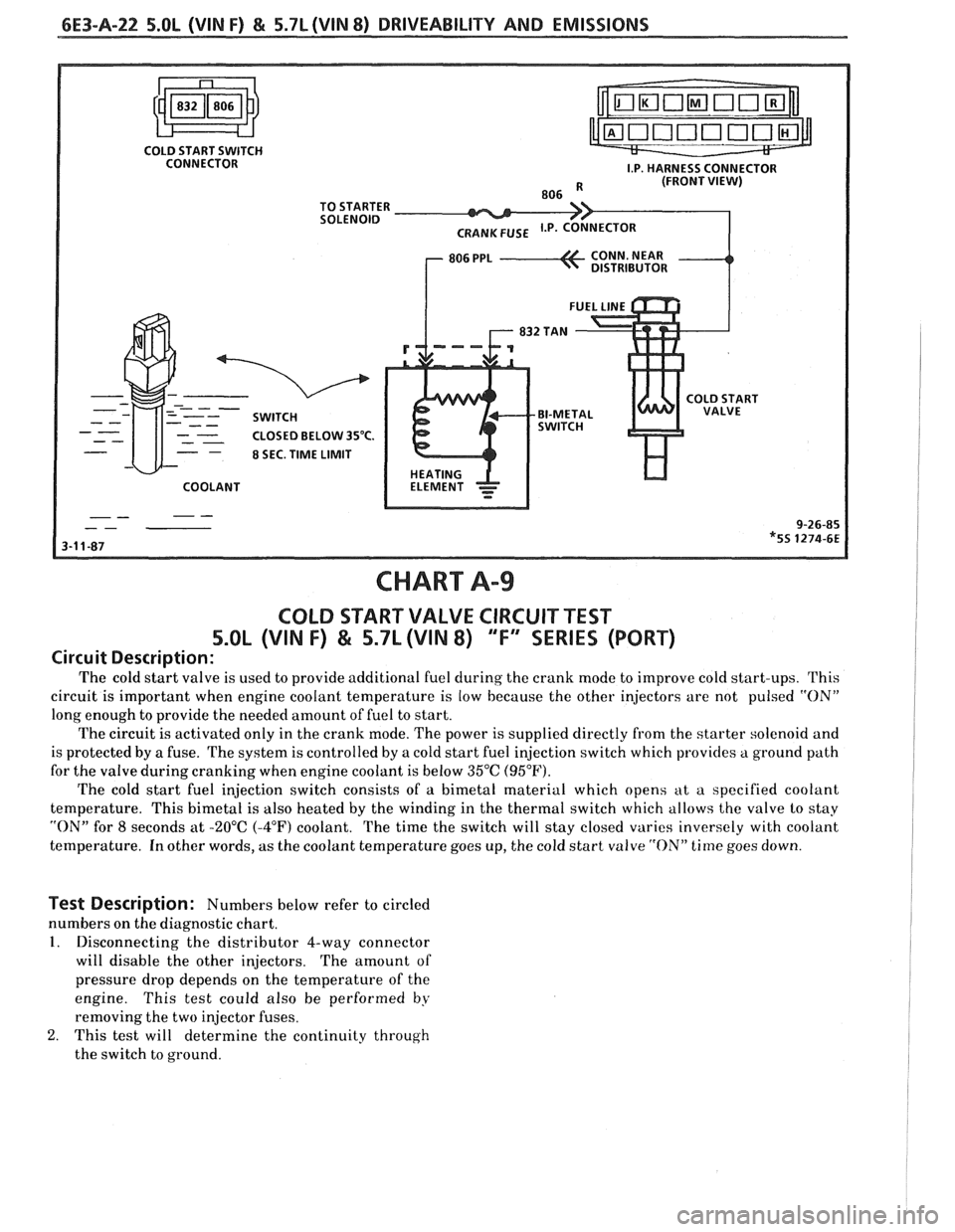
6E3-A-22 5.OL (VIN F) & 5.7L (VIN 8) DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
COLD START SWITCH
CONNECTOR
CLOSED BELOW
3S°C.
8 SEC. TIME LIMIT
COOLANT
CHART A99
COLD START VALVE CIRCUIT TEST
5.OL (VIN F) & 5.7L (VIN 8) "F" SERIES (PORT)
Circuit Description:
The cold start valve is used to provide additional fuel cluring the crank mode to improve cold start-ups. This
circuit is important when engine coolant temperature is low because the other injectors are not pulsed
"ON"
long enough to provide the needed amount of fuel to start.
The circuit is activated only in the crank mode. The power is supplied directly from the starter solenoid and
is protected by a fuse. The system is controlled by a cold start fuel injection switch which provides a ground path
for the valve during cranking when engine coolant is below 35°C (95°F).
The cold start fuel injection switch consists of a bimetal material which opens at a specified coolant
temperature. This bimetal is also heated by the winding in the thertnal switch which allows the valve lo stay
"ON" for 8 seconds at -20°C (-4°F) coolant. The time the switch will stay closed varies inversely with coolant
temperature. In other words, as the coolant temperature goes up, the cold start valve
"ON" time goes down.
Test Description: Numbers below refer to circled
numbers on the diagnostic chart.
1. Disconnecting the distributor 4-way connector
will disable the other injectors. The amount of
pressure drop depends on the temperature of the
engine. This test could also be performed
by
removing the two injector fuses.
2. This test will determine the continuity through
the switch to ground.
Page 867 of 1825

6E3-B-2 5.OL (VIN F) & 5.7L (VIN 8) DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Problem may or may not turn "ON" the "Service Engine Soon" light, or store a code.
DO NOT use the Trouble Code Charts in
An intermittent "Service Engine Soon" light
Section A for intermittent problems. The fault must
with no stored code may be caused by:
be present to locate the problem. If a fault is
@ Ignition coil shorted to ground and arcing at
intermittent, use of Trouble Code Charts
may result
spark plug wires or plugs.
in replacement of good parts.
"Service Engine Soon" light wire to
ECM
@ Most intermittent problems are caused by
shorted to ground. (CKT 419).
faulty electrical connections or wiring. Perform
Diagnostic "Test" Terminal wire to ECM,
careful check as described at start of Section
shorted to
ground.(CKT 451)
"B". Check for:
@ ECM power grounds. See ECSI wiring
@ Poor mating of the connector halves, or diagrams.
terminals not fully seated in the connector
@ Loss of trouble code memory. To check,
body (backed out). disconnect TPS and idle engine until "Service
@ Improperly formed or damaged terminals.
Engine Soon" light comes on. Code 22 should be
All connector terminals in problem circuit
stored, and kept in memory when ignition is
should be carefully reformed or replaced to turned "OFF". If not, the ECM is faulty.
insure proper contact tension.
@ Check for an electrical system interference
@ Poor terminal to wire connection. This caused by a defective relay, ECM driven
requires removing the terminal from the
solenoid, or switch. They can cause a sharp
connector body to check. See "Introduction"
electrical surge. Normally, the problem will
to Section
"6E". occur when the faulty component is operated.
@ If a visual check does not find the cause of the @ Check for improper installation of electrical
problem, the car can be driven with a voltmeter
options, such as lights,
%way radios, etc.
connected to
a suspected circuit. A "Scan" tool
EST wires should be kept away from spark plug
can also be used for monitoring input signals to wires, distributor wires, distributor housing,
the ECM to help detect intermittent conditions. coil, and generator. Wire from
ECM to
An abnormal voltage, or "Scan" reading, when distributor
(CKT 453) should be a good
the problem occurs, indicates the problem
may connection.
be in that circuit. If the wiring and connectors
@ Check for open diode across AIC compressor
check OK and a Trouble Code was stored for a
clutch, and for other open diodes (see wiring
circuit having a sensor, except for Codes
43, 44, diagrams).
and 45, substitute a known good sensor and
recheck.
HARD START
Definition: Engine cranks OK, but does not start for a long
time. Does eventually run, or may start but immediately dies.
Perform careful check as described at start of
Section
"B".
@ Make sure driver is using correct starting
procedure.
@ CHECK:
- TPS for sticking or binding or a high TPS
voltage with the throttle closed (should read
less than
.700 volts).
- High resistance in coolant sensor circuit or
sensor itself. See Code 15 chart or with
a
"Scan" tool compare coolant temperature with
ambient temperature on a cold engine.
- Fuel pressure CHART A-7.
- Water contaminated fuel.
- EGR operation. Be sure valve seats properly and
is not staying open. See CHART C-7.
- Both injector fuses (visually inspect).
- Ignition system - Check distributor for:
Proper Output with ST-125.
Worn shaft.
Bare and shorted wires.
Pickup coil resistance and connections.
Loose ignition coil ground.
Moisture in distributor cap.
@ If problem exists in cold weather, check cold start
valve. See CHART A-9.