1988 PONTIAC FIERO oil
[x] Cancel search: oilPage 390 of 1825
V-8 ENGINE BA3-11
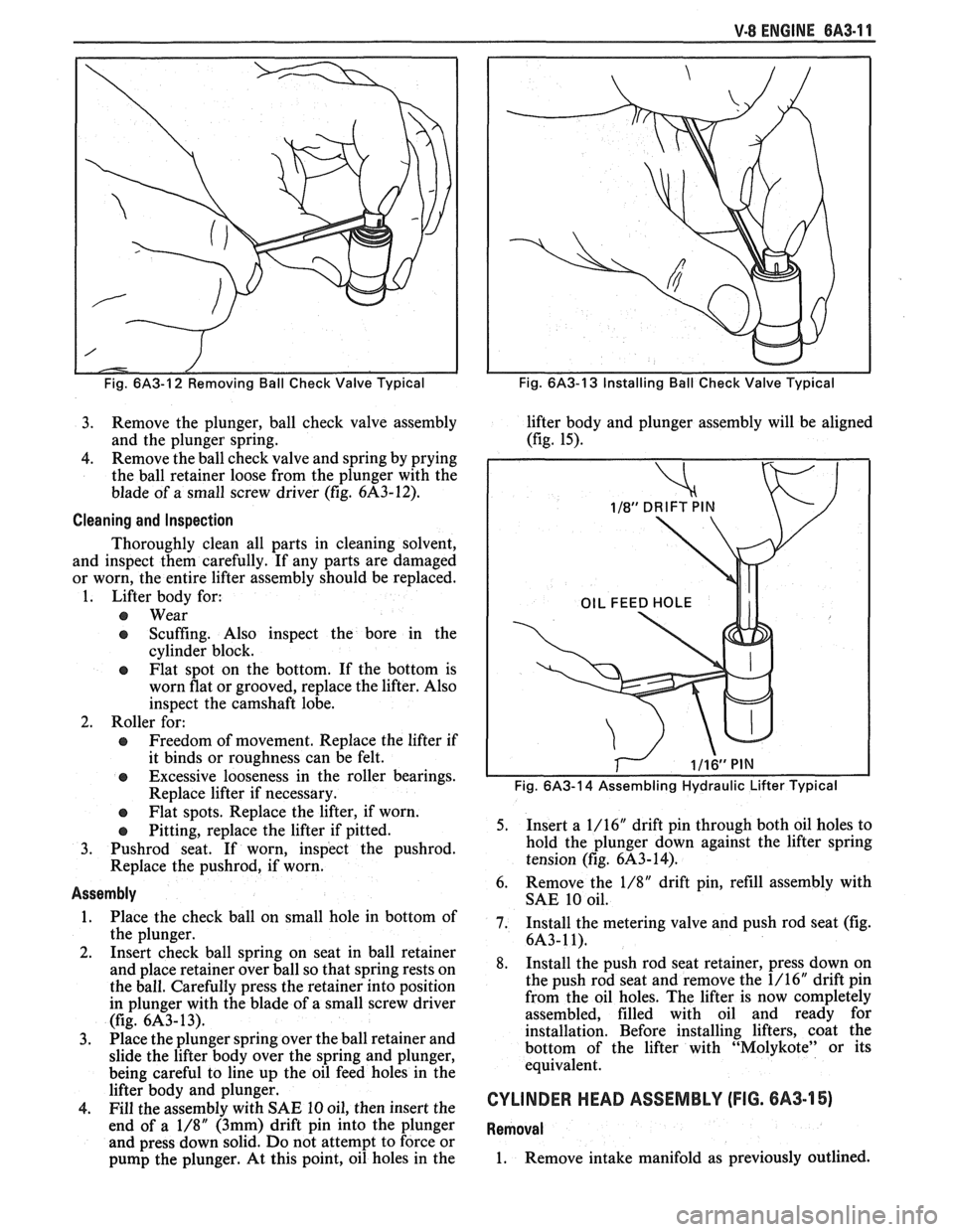
Fig. 6/43-12 Removing Ball Check Valve Typical
3. Remove the plunger, ball check valve assembly
and the plunger spring.
4. Remove
the ball check valve and spring by prying
the ball retainer loose from the plunger with the
blade of a small screw driver (fig.
6A3-12).
Cleaning and Inspection
Thoroughly clean all parts in cleaning solvent,
and inspect them carefully. If any parts are damaged
or worn, the entire lifter assembly should be replaced.
1. Lifter body for:
@ Wear
e Scuffing. Also inspect the bore in the
cylinder block.
@ Flat spot on the bottom. If the bottom is
worn flat or grooved, replace the lifter. Also
inspect the camshaft lobe.
2. Roller for:
@ Freedom of movement. Replace the lifter if
it binds or roughness can be felt.
@ Excessive looseness in the roller bearings.
Replace lifter if necessary.
e Flat spots. Replace the lifter, if worn.
e Pitting, replace the lifter if pitted.
3.
Pushrod seat. If worn, inspect the pushrod.
Replace the pushrod, if worn.
Assembly
1. Place the check ball on small hole in bottom of
the plunger.
2. Insert check ball spring on seat in ball retainer
and place retainer over ball so that spring rests on
the ball. Carefully press the retainer into position
in plunger with the blade of a small screw driver
(fig.
6A3- 13).
3. Place the
plunger spring over the ball retainer and
slide the lifter body over the spring and plunger,
being careful to line up the oil feed holes in the
lifter body and plunger.
4. Fill the assembly with SAE 10 oil, then insert the
end of a
1/8" (3mm) drift pin into the plunger
and press down solid. Do not attempt to force or
pump the plunger. At this point, oil holes in the
Fig. 6A3-13 Installing Ball Check Valve Typical
lifter body and plunger assembly will be aligned
(fig. 15).
Fig. 6A3-14 Assembling Hydraulic Lifter Typical
5. Insert a
1/16" drift pin through both oil holes to
hold the plunger down against the lifter spring
tension (fig.
6A3-14).
6. Remove
the 1/8" drift pin, refill assembly with
SAE 10 oil.
7. Install the metering valve and push rod seat (fig.
6A3-11).
8. Install the push rod seat retainer, press down on
the push rod seat and remove the 1/16" drift pin
from the oil holes. The lifter is now completely
assembled, filled with oil and ready for
installation. Before installing lifters, coat the
bottom of the lifter with "Molykote" or its
equivalent.
CYLINDER HEAD ASSEMBLY (FIG. 6A3-15)
Removal
1. Remove intake manifold as previously outlined.
Page 391 of 1825
6A3-12 V-8 ENGINE
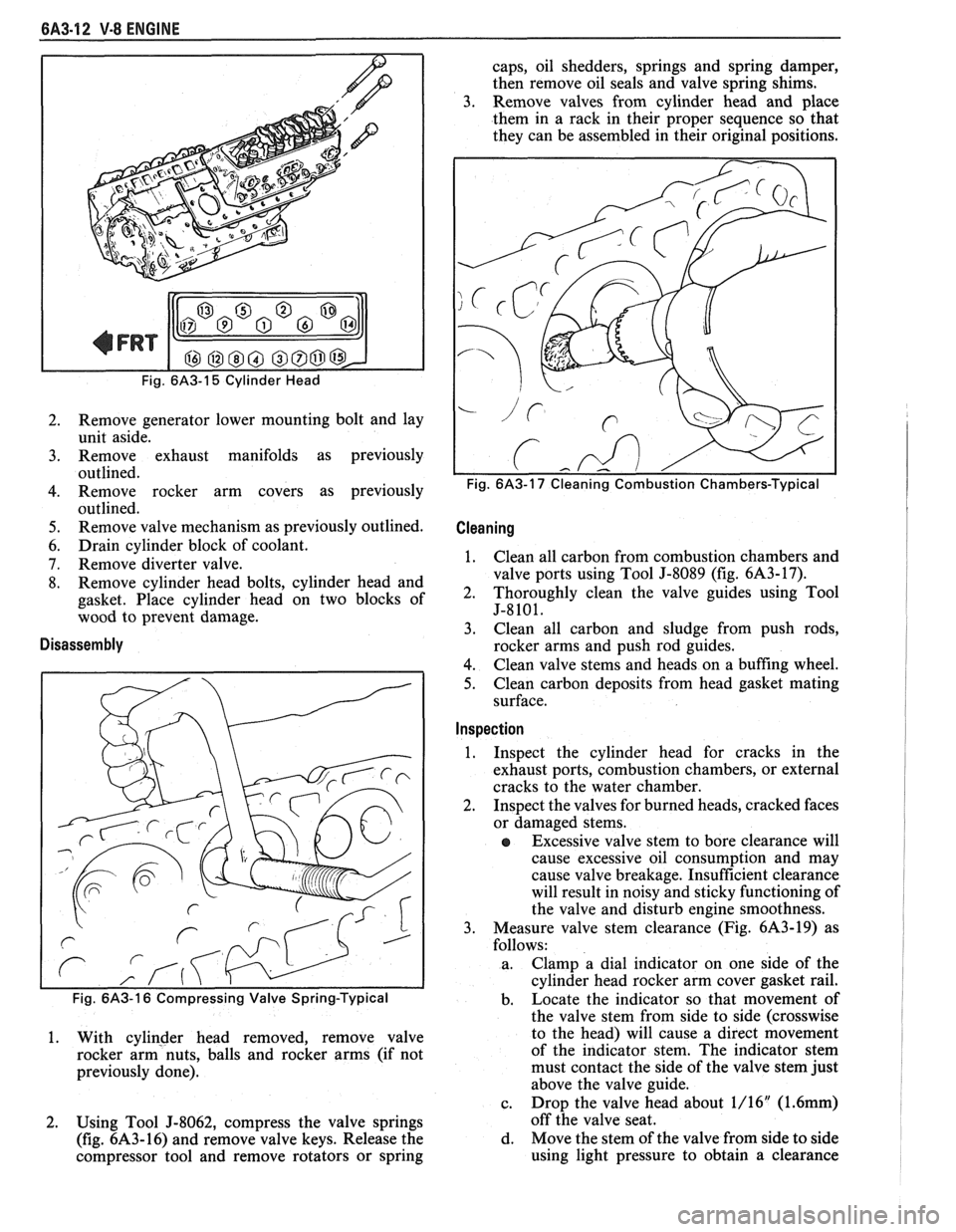
Fig. 6A3-15 Cylinder Head
2. Remove generator lower mounting bolt and lay
unit aside.
3. Remove exhaust manifolds as previously
outlined.
4. Remove rocker arm covers as previously
outlined.
5. Remove valve mechanism as previously outlined.
6. Drain cylinder block of coolant.
7. Remove diverter valve.
8. Remove cylinder head bolts, cylinder head and
gasket. Place cylinder head on two blocks of
wood to prevent damage.
Disassembly
1. With cylinder head removed, remove valve
rocker arm nuts, balls and rocker arms (if not
previously done).
2. Using Tool
5-8062, compress the valve springs
(fig.
6A3-16) and remove valve keys. Release the
compressor tool and remove rotators or spring caps, oil shedders,
springs and spring damper,
then remove oil seals and valve spring shims.
3. Remove valves from cylinder head and place
them in a rack in their proper sequence so that
they can be assembled in their original positions.
Cleaning I
1. Clean all carbon from combustion chambers and
valve ports using Tool J-8089 (fig.
6A3-17).
2. Thoroughly clean the valve guides using Tool
5-8101.
3. Clean
all carbon and sludge from push rods,
rocker arms and push rod guides.
4. Clean valve stems and heads on a buffing wheel.
5. Clean carbon deposits from head gasket mating
surface.
Inspection I
1. Inspect
the cylinder head for cracks in the
exhaust ports, combustion chambers, or external
cracks to the water chamber.
2. Inspect the valves for burned heads, cracked faces
or damaged stems.
e Excessive valve stem to bore clearance will
cause excessive oil consumption and may
cause valve breakage. Insufficient clearance
will result in noisy and sticky functioning of
the valve and disturb engine smoothness.
3. Measure valve stem clearance (Fig. 6A3-19) as
follows:
a. Clamp a dial indicator
on one side of the
cylinder head rocker arm cover gasket rail.
b. Locate
the indicator so that movement of
the valve stem from side to side (crosswise
to the head) will cause a direct movement
of the indicator stem. The indicator stem
must contact the side of the valve stem just
above the valve guide.
c. Drop
the valve head about 1/16"
(1.6mm)
off the valve seat.
d. Move the stem of the valve from side to side
using light pressure to obtain a clearance
Page 392 of 1825

V-8 ENGINE 6A3-13
reading. If clearance exceeds specifications,
it will be necessary to ream valve guides for
oversize valves.
e Service valves are available in standard,
.003", .015" and .030n oversize.
4. Check valve spring tension with Tool
5-8056
spring tester (fig. 6143-19). Springs should be
compressed to the specified height and checked
against the specifications chart. Springs should be
replaced if not within 10 lbs. (44
N) of the
specified load (without dampers).
5. Inspect rocker arm studs for wear of damage.
Assembly
1. Insert a
valve in the proper port.
2. Assemble the valve spring and related parts as
follows:
a. Set
the valve spring shim, valve spring (with
damper), oil shedder and valve cap or
rotator in place.
b. Compress the spring with Tool J-8062. c.
Install oil seal in the lower groove of the
stem, making sure that the seal is flat and
not twisted.
d. Install the valve locks and release the
compressor tool making sure that the locks
seat properly in the upper groove of the
valve stem. Grease may be used to hold the
locks in place while releasing the
compressor tools.
Fig. 6A3-20 Checking Valve Stem Oil Seals
3. Install the remaining valves.
4. Check each
valve stem oil seal by placing Valve
Seal Leak Detector
(Too01 9-23994) over the end
of the valve stem and against the cap. Operate the
vacuum pump and make sure no air leaks past the
seal (fig.
6A3-20).
Fig. 6A3-2 1 Cutaway Scale
5. Check the installed height of the valve springs,
using a narrow thin scale. A cutaway scale will
help (fig.
6A3-21). Measure from the top of the
shim or the spring seat to the top of the oil
shedder. If this is found to exceed the specified
height, install a valve spring seat shim
approximately 1/16"
(1.6mm) thick. At no time
should the spring be shimmed to give an installed
height under the minimum specified.
Page 394 of 1825
V-8 ENGINE 6A3-15
engine to deliver the power and performance built into
it.
Another important factor is the cooling of the
valve heads. Good contact between each valve and its
seat in the head is imperative to insure that the heat in
the valve head will be properly carried away.
Several different types of equipment are available
for reseating valves seats. The recommendations of the
manufacturer of the equipment being used should be
carefully followed to attain proper results.
Regardless of what type of equipment is used,
however, it is essential that valve guide bores be free
from carbon or dirt to ensure proper centering of pilot
in the guide. Valve seats should be concentric to within
,002" total indicator reading.
VALVES
Valves that are pitted can be refaced to the proper
angle, insuring correct relation between the head and
stem on a valve
refacing mechanism. Valve stems
which show excessive wear, or valves that are warped
excessively should be replaced. When a valve head
which is warped excessively is
refaced, a knife edge will
be ground on part or all of the valve head due to the
amount of metal that must be removed to completely
reface. Knife edges lead to breakage, burning or
pre-ignition due to heat localizing on this knife edge.
If the edge of the valve head is less than 1/32"
(.08mm)
thick after grinding, replace the valve. Several different
types of equipment are available for
refacing valves.
The recommendation of the manufacturer of the
equipment being used should be carefully followed to
attain proper results.
TORSIONAL DAMPER
Removal
1.
Remove drive belts and pulley.
2. Raise vehicle.
3. Remove crankshaft pulley, then remove damper
retaining bolt.
4. Install Tool J-23523 on damper then, turning
puller screw, remove damper.
Installation
NOTICE: The inertial weight section of the
torsional damper is assembled to the hub with a
rubber type material. The installation procedures
(with proper tool) must be followed or movement
of the inertia weight section on the hub will
destroy the tuning of the torsional damper.
1. Inspect the cover seal contact area surface (on
damper) for damage or grooving and coat front
cover seal with engine oil.
2. Place damper in position over key on crankshaft.
3. Pull damper onto crankshaft as follows:
a. Install appropriate threaded end of Tool
J-23523 into crankshaft. Install tool in
crankshaft so that at least
1/2" (13mm) of
thread engagement is obtained.
Fig. 6A3-26 Installing Torsional Damper
b.
Install plate, thrust bearing and nut to
complete tool installation.
c. Pull damper into position as shown in
Figure 6A3-26.
d. Remove tool from crankshaft then install
damper retaining bolt and torque to
specifications.
4. Install crankshaft pulley.
5. Lower vehicle.
6. Install drive belts and adjust to specifications.
CRANKCASE FRONT COVER (FIG. 6A3-27)
Removal
1.
Remove torsional damper as previously outlined.
2. Remove oil pan.
3. Remove water pump as outlined in Section
6B.
4. Remove crankcase front cover attaching screws
and remove front cover and gasket, then discard
gasket.
lnstallation
1. Clean gasket surface on block and crankcase
front cover.
Page 395 of 1825
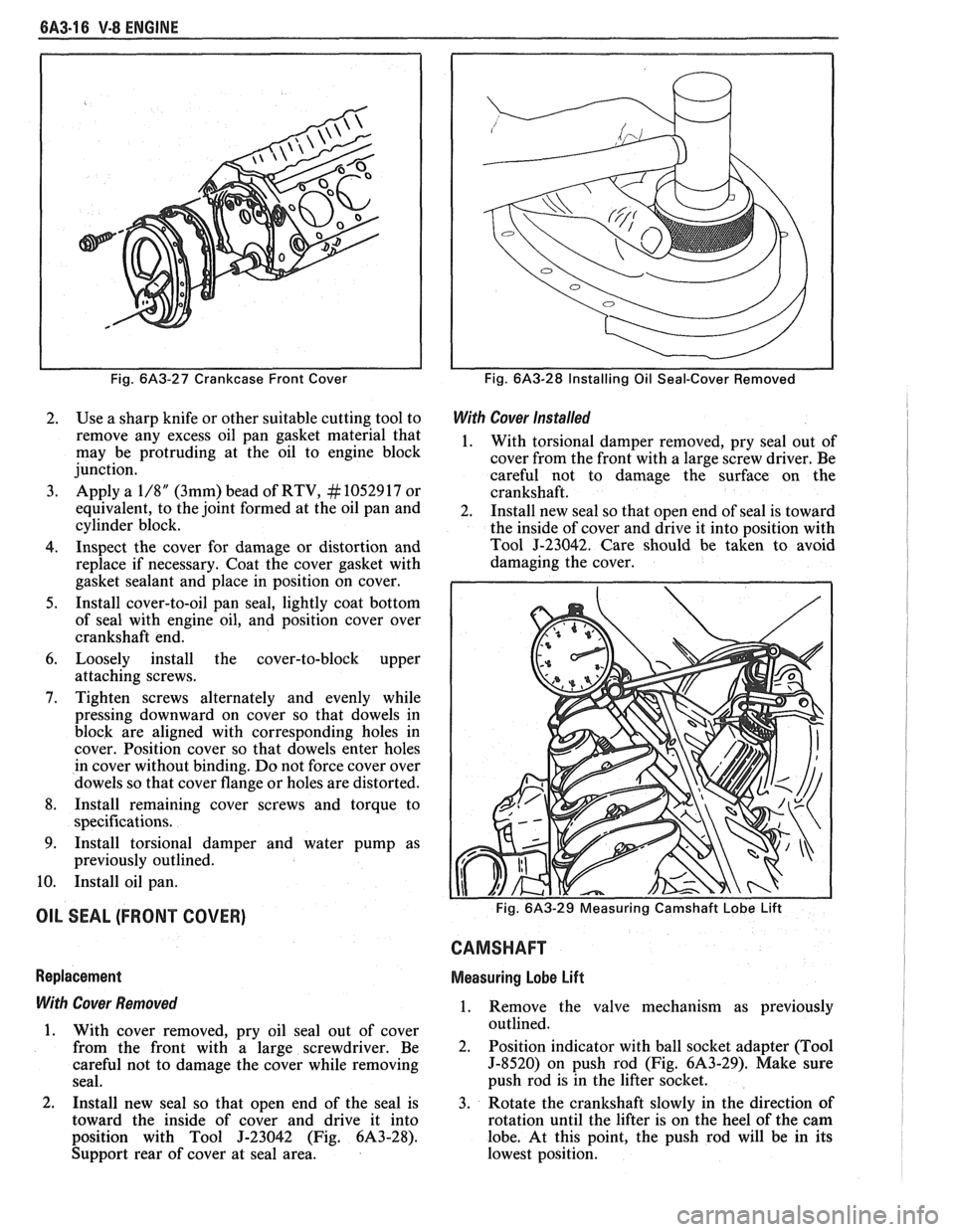
6A3-16 V-8 ENGINE
Fig. 6A3-27 Crankcase Front Cover
2. Use a sharp knife or other suitable cutting tool to
remove any excess oil pan gasket material that
may be protruding at the oil to engine block
junction.
3. Apply a 1/8" (3mm) bead of RTV, # 10529 17 or
equivalent, to the joint formed at the oil pan and
cylinder block.
4. Inspect the cover for damage or distortion and
replace if necessary. Coat the cover gasket with
gasket sealant and place in position on cover.
5. Install cover-to-oil pan seal, lightly coat bottom
of seal with engine oil, and position cover over
crankshaft end.
6. Loosely install the cover-to-block upper
attaching screws.
7. Tighten screws alternately and evenly while
pressing downward on cover so that dowels in
block are aligned with corresponding holes in
cover. Position cover so that dowels enter holes
in cover without binding.
Do not force cover over
dowels so that cover flange or holes are distorted.
8. Install remaining cover screws and torque to
specifications.
9. Install torsional damper and water pump as
previously outlined.
10. Install oil pan.
OIL SEAL (FRONT COVER)
Replacement
With Cover Removed
1. With cover removed, pry oil seal out of cover
from the front with a large screwdriver. Be
careful not to damage the cover while removing
seal.
2. Install new seal so that open end of the seal is
toward the inside of cover and drive it into
position with Tool
J-23042 (Fig. 6A3-28).
Support rear of cover at seal area.
Fig. 6A3-28 Installing Oil Seal-Cover Removed
With Cover Installed
1. With torsional damper removed, pry seal out of
cover from the front with a large screw driver. Be
careful not to damage the surface on the
crankshaft.
2. Install new seal so that open end of seal is toward
the inside of cover and drive it into position with
Tool
J-23042. Care should be taken to avoid
damaging the cover.
CAMSHAFT
Measuring Lobe Lift
1. Remove the valve mechanism as previously
outlined.
2. Position indicator with ball socket adapter (Tool
5-8520) on push rod (Fig. 6A3-29). Make sure
push rod is in the lifter socket.
3. Rotate the crankshaft slowly in the direction of
rotation until the lifter is on the heel of the cam
lobe. At this point, the push rod will be in its
lowest position.
Page 396 of 1825
V-8 ENGINE 6A3.17
4. Set dial indicator on zero, then rotate the
crankshaft slowly, or attach an auxiliary starter
switch and "bump" the engine over, until the
push rod is fully raised position.
e Whenever the engine is cranked remotely at
the started, with a special jumper cable or
other means, the distributor primary lead
should be disconnected from the distributor
(coil).
5. Compare the total lift recorded from the dial
indicator with specifications.
6. If camshaft readings for all lobes are within
specifications, remove dial indicator assembly.
7. Install and adjust valve mechanism as outlined.
Removal
Fig. 6A3-30 Removing Camshaft
1.
Remove valve lifters as previously outlined.
2. Remove crankcase front cover as previously
outlined.
3. Remove grille.
4. Remove fuel pump push rod as outlined in
Section 6C.
5. Complete camshaft removal as follows:
e Sprocket is a light fit on camshaft. If
sprocket does not come off easily a light
blow on the lower edge of the sprocket (with
a plastic mallet) should dislodge the
sprocket.
6. Install two 5/16" - 18 x 4" bolts in camshaft bolt
holes then remove camshaft (fig. 6A3-30).
NOTICE: All camshaft journals are the same
diameter and care must be used in removing
camshaft to avoid damage to bearings.
Inspection
The camshaft bearing journals should be
measured with a micrometer for an out-of-round
condition. If the journals exceed
.001" out-of-round,
the camshaft should be replaced.
Installation
When a new camshaft is installed coat camshaft
lobes with "Molykote" or its equivalent. When a new
camshaft is installed, replacement of all valve lifters is
recommended to insure durability of the camshaft
lobes and lifter feet.
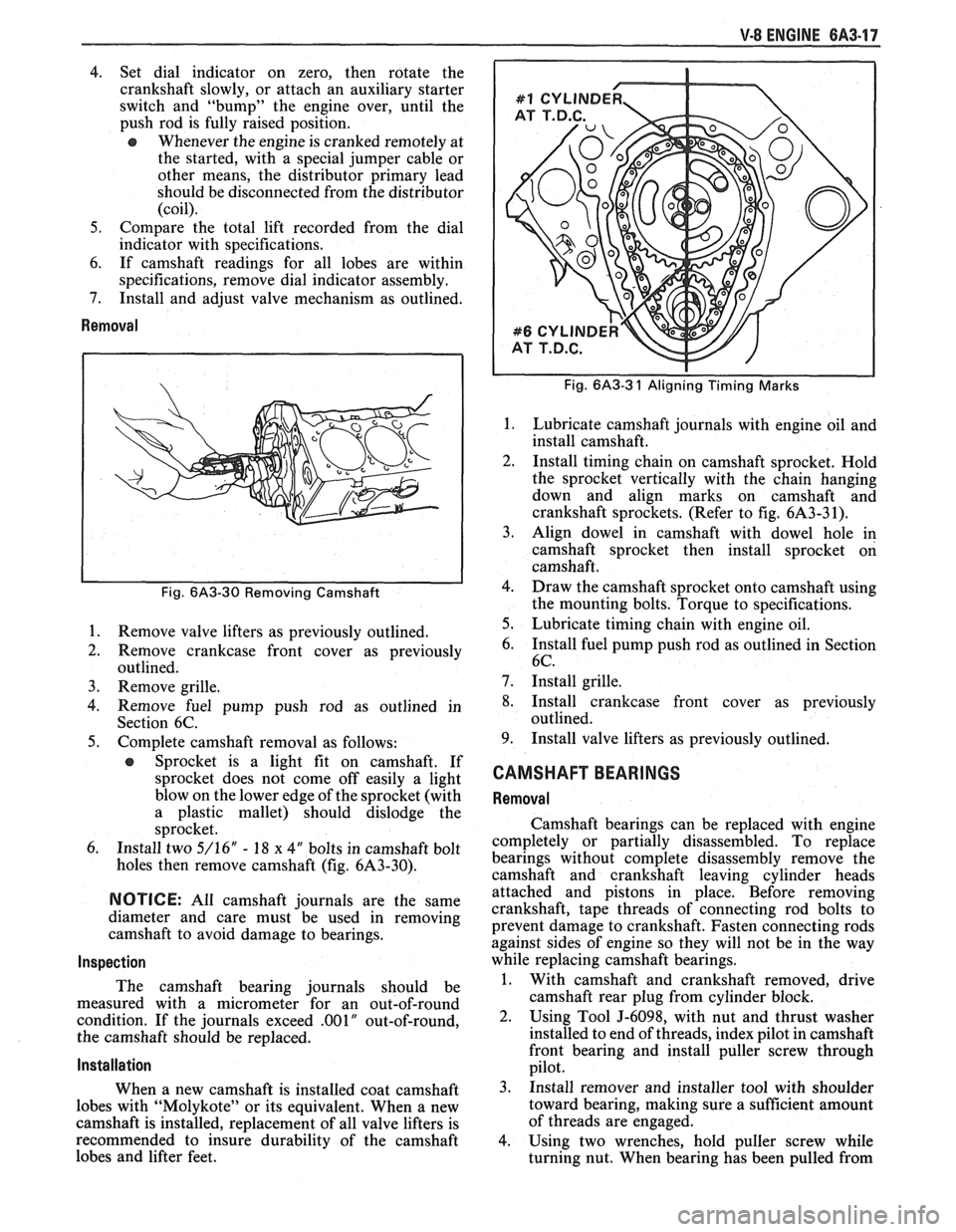
Fig. 6A3-3 1 Aligning Timing Marks
Lubricate camshaft journals with engine oil and
install camshaft.
Install timing chain on camshaft sprocket. Hold
the sprocket vertically with the chain hanging
down and align marks on camshaft and
crankshaft sprockets. (Refer to fig. 6A3-3 1).
Align dowel in camshaft with dowel hole in
camshaft sprocket then install sprocket on
camshaft.
Draw the camshaft sprocket onto camshaft using
the mounting bolts. Torque to specifications.
Lubricate timing chain with engine oil.
Install fuel pump push rod as outlined in Section
6C.
Install grille.
Install crankcase front cover as previously
outlined.
Install valve lifters as previously outlined.
CAMSHAFT BEARINGS
Removal
Camshaft bearings can be replaced with engine
completely or partially disassembled. To replace
bearings without complete disassembly remove the
camshaft and crankshaft leaving cylinder heads
attached and pistons in place. Before removing
crankshaft, tape threads of connecting rod bolts to
prevent damage to crankshaft. Fasten connecting rods
against sides of engine so they will not be in the way
while replacing camshaft bearings.
1. With camshaft and crankshaft removed, drive
camshaft rear plug from cylinder block.
2. Using Tool J-6098, with nut and thrust washer
installed to end of threads, index pilot in camshaft
front bearing and install puller screw through
pilot.
3. Install remover and installer tool with shoulder
toward bearing, making sure a sufficient amount
of threads are engaged.
4. Using two wrenches, hold puller screw while
turning nut. When bearing has been pulled from
Page 397 of 1825
6A3-18 V-8 ENGINE
bore, remove remover and installer tool and
bearing from puller screw.
5. Remove remaining bearings (except front and
rear) in the same manner. It will be necessary to
index pilot in camshaft rear bearing to remove the
rear intermediate bearing.
6. Assemble remover
and installer tool on driver
handle and remove camshaft front and rear
bearings by driving towards center of cylinder
block.
lnstallation
The camshaft front and rear bearings should be
installed first. These bearings will act as guides for the
pilot and center the remaining bearings being pulled
into place.
1. Assemble remover
and installer tool on driver
handle and install camshaft front and rear
bearings by driving towards center of cylinder
block.
2. Using Tool Set J-6098, with nut then thrust
washer installed to end of threads, index pilot in
camshaft front bearing and install puller screw
through pilot.
3. Index camshaft bearing in bore (with oil hole
aligned as outlined below), then install remover
and installer tool on puller screw with shoulder
toward bearing.
e Number one cam bearing oil hole must be
positioned so that oil holes are equidistant
from 6 o'clock position.
e Number two through number four bearing
oil holes must be positioned at 5 o'clock
position (toward left side of engine and at a
position even with bottom of cylinder bore).
e Number five bearing oil hole must be in 12
o'clock position.
4. Using two wrenches, hold puller screw while
turning nut. After bearing has been pulled into
bore, remove the remover and installer tool from
puller screw and check alignment of oil hole in
camshaft bearing.
5. Install remaining bearings in the same manner. It
will be necessary to index pilot in the camshaft
rear bearing to install the rear intermediate
bearing.
6. Coat new camshaft rear plug O.D. with
# 1052080 sealant, or equivalent, and install
flush to 1/32"
(.80mm) deep.
OIL PAN
Removal
1. Disconnect battery negative cable.
2. Remove fan shroud.
3. Remove air cleaner and lay aside if equipped.
4. Remove distributor cap and lay aside.
5. Raise vehicle.
6. Drain crankcase.
7. Disconnect exhaust pipe at manifold.
8. Disconnect AIR pipe clamp.
9. Disconnect converter hanger bolts and allow
exhaust to hang down.
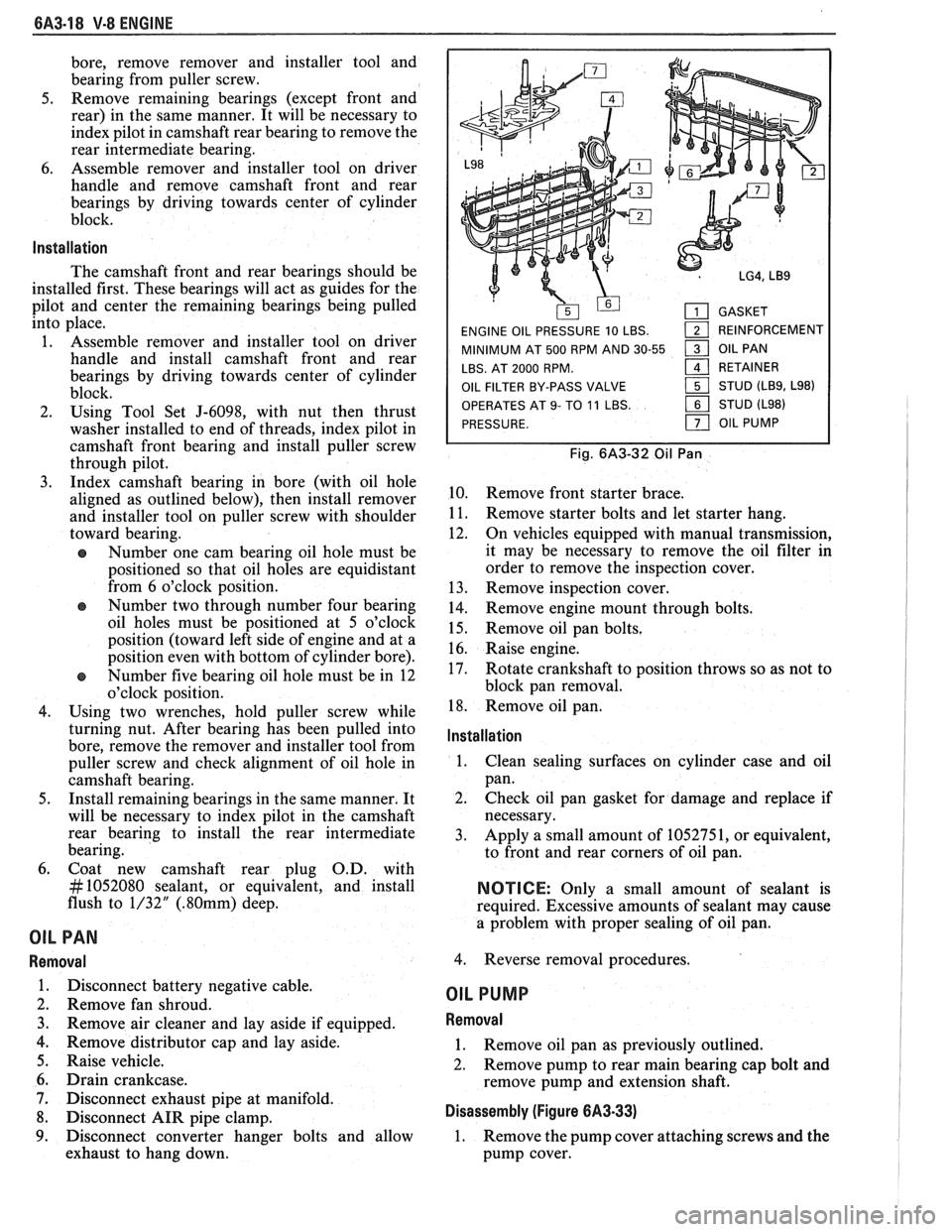
GASKET
ENGINE OIL PRESSURE 10 LBS.
1 REINFORCEMENT
MINIMUM AT 500 RPM AND 30-55
1 OIL PAN
LBS. AT 2000 RPM.
161 RETAINER
OIL FILTER BY-PASS VALVE STUD
(LB9, L98)
OPERATES
AT 9- TO 11 LBS. STUD (L98)
PRESSURE.
OIL PUMP
Fig. 6A3-32 Oil Pan
10. Remove front starter brace.
11. Remove starter bolts and let starter hang.
12. On vehicles equipped with manual transmission,
it may be necessary to remove the oil filter in
order to remove the inspection cover.
13. Remove inspection cover.
14. Remove engine mount through bolts.
15. Remove oil pan bolts.
16. Raise engine.
17. Rotate crankshaft to position throws so as not to
block pan removal.
18. Remove oil pan.
lnstallation
1.
Clean sealing surfaces on cylinder case and oil
pan.
2. Check oil pan gasket for damage and replace if
necessary.
3. Apply a small amount of 1052751, or equivalent,
to front and rear corners of oil pan.
NOTICE: Only a small amount of sealant is
required. Excessive amounts of sealant may cause
a problem with proper sealing of oil pan.
4. Reverse removal procedures.
OIL PUMP
Removal
1. Remove oil pan as previously outlined.
2. Remove pump to rear main bearing cap bolt and
remove pump and extension shaft.
Disassembly (Figure 6A3-33)
1. Remove the pump cover attaching screws and the
pump cover.
Page 398 of 1825
V-8 ENGINE 6A3-19
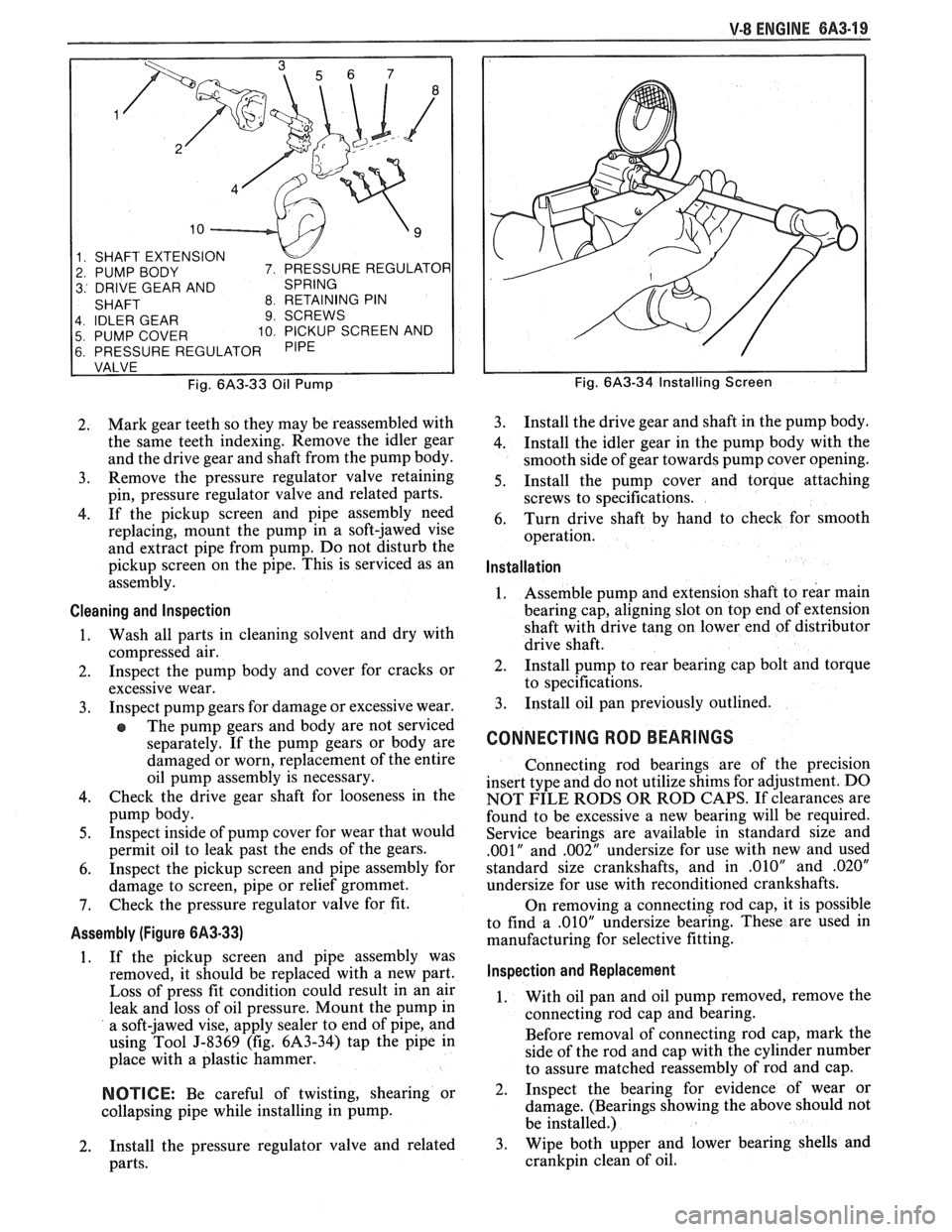
1 SHAFT EXTENSION
2 PUMP BODY
3 DRIVE GEAR AND
4 IDLER GEAR
9 SCREWS
5 PUMP COVER 10 PICKUP SCREEN AND
6 PRESSURE REGULATOR
Fig.
6A3-33 Oil Pump
2. Mark
gear teeth so they may be reassembled with
the same teeth indexing. Remove the idler gear
and the drive gear and shaft from the pump body.
3. Remove
the pressure regulator valve retaining
pin, pressure regulator valve and related parts.
4. If the pickup screen and pipe assembly need
replacing, mount the pump in a soft-jawed vise
and extract pipe from pump. Do not disturb the
pickup screen on the pipe. This is serviced as an
assembly.
Cleaning and lnspection
1. Wash all parts in cleaning solvent and dry with
compressed air.
2. Inspect the pump body and cover for cracks or
excessive wear.
3. Inspect
pump gears for damage or excessive wear.
The pump gears and body are not serviced
separately. If the pump gears or body are
damaged or worn, replacement of the entire
oil pump assembly is necessary.
4. Check the drive gear shaft for looseness in the
pump body.
5. Inspect inside of pump cover for wear that would
permit oil to leak past the ends of the gears.
6. Inspect the pickup screen and pipe assembly for
damage to screen, pipe or relief grommet.
7. Check the pressure regulator valve for fit.
Assembly (Figure 6A3-33)
1. If
the pickup screen and pipe assembly was
removed, it should be replaced with a new part.
Loss of press fit condition could result in an air
leak and loss of oil pressure. Mount the pump in
a soft-jawed vise, apply sealer to end of pipe, and
using Tool J-8369 (fig. 6A3-34) tap the pipe in
place with a plastic hammer.
NOTICE: Be careful of twisting, shearing or
collapsing pipe while installing in pump.
2. Install the
pressure regulator valve and related
parts.
Fig. 6A3-34 Installing Screen
3. Install the drive gear and shaft in the pump body.
4. Install
the idler gear in the pump body with the
smooth side of gear towards pump cover opening.
5. Install the pump cover and torque attaching
screws to specifications.
6. Turn
drive shaft by hand to check for smooth
operation.
Installation
1. Assemble
pump and extension shaft to rear main
bearing cap, aligning slot on top end of extension
shaft with drive tang on lower end of distributor
drive shaft.
2. Install
pump to rear bearing cap bolt and torque
to specifications.
3. Install
oil pan previously outlined.
CONNECTING ROD BEARINGS
Connecting rod bearings are of the precision
insert type and do not utilize shims for adjustment. DO
NOT FILE RODS OR ROD CAPS. If clearances are
found to be excessive a new bearing will be required.
Service bearings are available in standard size and
.001" and ,002" undersize for use with new and used
standard size crankshafts, and in
.010" and .020"
undersize for use with reconditioned crankshafts.
On removing a connecting rod cap, it is possible
to find a
.010" undersize bearing. These are used in
manufacturing for selective fitting.
lnspection and Replacement
1. With
oil pan and oil pump removed, remove the
connecting rod cap and bearing.
Before removal of connecting rod cap, mark the
side of the rod and cap with the cylinder number
to assure matched reassembly of rod and cap.
2. Inspect
the bearing for evidence of wear or
damage. (Bearings showing the above should not
be installed.)
3. Wipe both upper and lower bearing shells and
crankpin clean of oil.