1988 OPEL CALIBRA check oil
[x] Cancel search: check oilPage 90 of 525

HEI (High Energy Ignition)
system
5This comprises of a breakerless distributor
and an electronic switching/amplifier module
along with the coil and spark plugs.
6The electrical impulse that is required to
switch off the low tension circuit is generated
by a magnetic trigger coil in the distributor. A
trigger wheel rotates within a magnetic stator,
the magnetic field being provided by a
permanent magnet. The magnetic field across
the two poles (stator arm and trigger wheel) is
dependent on the air gap between the two
poles. When the air gap is at its minimum, the
trigger wheel arm is directly opposite the
stator arm, and this is the trigger point. As the
magnetic flux between the stator arm and
trigger wheel varies, a voltage is induced in the
trigger coil mounted below the trigger wheel.
This voltage is sensed and then amplified by
the electronic module, and used to switch off
the low tension circuit. There is one trigger arm
and one stator arm for each cylinder.
7The ignition advance is a function of the
distributor, and is controlled both
mechanically and by a vacuum-operated
system. The mechanical governor mechanism
consists of two weights that move out from
the distributor shaft due to centrifugal force as
the engine speed rises. As the weights move
outwards, they rotate the trigger wheel
relative to the distributor shaft and so
advance the spark. The weights are held in
position by two light springs, and it is the
tension of the springs that is largely
responsible for correct spark advancement.
8The vacuum control consists of a
diaphragm, one side of which is connected by
way of a small-bore hose to the carburettor,
and the other side to the distributor.
Depression in the inlet manifold and
carburettor, which varies with engine speed
and throttle position, causes the diaphragm to
move, so moving the baseplate and
advancing or retarding the spark. A fine
degree of control is achieved by a spring in
the diaphragm assembly.
MSTS-i (Microprocessor-
controlled Spark Timing System)
9This system comprises a “Hall-effect”
distributor (or a crankshaft speed/position
sensor on X 16 SZ models), a manifold pressure
sensor, an oil temperature sensor, and a
module, along with the coil and spark plugs.
10On 1.6 litre models, the electrical impulse
that is required to switch off the low tension
circuit is generated by a sensor in the
distributor. A trigger vane rotates in the gap
between a permanent magnet and the sensor.
The trigger vane has four cut-outs, one for
each cylinder. When one of the trigger vane
cut-outs is in line with the sensor, magnetic
flux can pass between the magnet and the
sensor. When a trigger vane segment is in line
with the sensor, the magnetic flux is diverted
through the trigger vane away from thesensor. The sensor senses the change in
magnetic flux, and sends an impulse to the
MSTS-i module, which switches off the low
tension circuit.
11On 1.8 litre models, the electrical impulse
that is required to switch off the low tension
circuit is generated by a crankshaft
speed/position sensor, which is activated by a
toothed wheel on the crankshaft. The toothed
wheel has 35 equally spaced teeth, with a gap
in the 36th position. The gap is used by the
sensor to determine the crankshaft position
relative to TDC (top dead centre) of No 1 piston.
12Engine load information is supplied to the
MSTS-i module by a pressure sensor, which
is connected to the carburettor by a vacuum
pipe. Additional information is supplied by an
oil temperature sensor. The module selects
the optimum ignition advance setting based
on the information received from the sensors.
The degree of advance can thus be constantly
varied to suit the prevailing engine conditions.
Multec, with MSTS-i
13The ignition system is fully electronic in
operation and incorporates the Electronic
Control Unit (ECU) mounted in the driver’s
footwell. A distributor (driven off the camshaft
left-hand end and incorporating the amplifier
module) as well as the octane coding plug,
the spark plugs, HT leads, ignition HT coil and
associated wiring.
14The ECU controls both the ignition system
and the fuel injection system, integrating the
two in a complete engine management
system. Refer to Chapters 4B and 4C for
further information that is not detailed here.
15For ignition the ECU receives information
in the form of electrical impulses or signals
from the distributor (giving it the engine speed
and crankshaft position), from the coolant
temperature sensor (giving it the engine
temperature) and from the manifold absolute
pressure sensor (giving it the load on the
engine). In addition, the ECU receives input
from the octane coding plug (to provide
ignition timing appropriate to the grade of fuel
used) and from, where fitted, the automatic
transmission control unit (to smooth gear
changing by retarding the ignition as changes
are made).
16All these signals are compared by the
ECU with set values pre-programmed
(mapped) into its memory. Considering this
information, the ECU selects the ignition
timing appropriate to those values and
controls the ignition HT coil by way of the
amplifier module accordingly.
17The system is so sensitive that, at idle
speed, the ignition timing may be constantly
changing; this should be remembered if trying
to check the ignition timing.
18The system fitted to C18 NZ models, is
similar to that described above, except that
the amplifier module is separate. The ECU
determines engine speed and crankshaft
position using a sensor mounted in the
right-hand front end of the engine’s cylinderblock; this registers with a 58-toothed disc
mounted on the crankshaft so that the gap left
by the missing two teeth provides a reference
point, so enabling the ECU to recognise TDC.
19Note that this simplifies the distributor’s
function, which is merely to distribute the HT
pulse to the appropriate spark plug; it has no
effect whatsoever on the ignition timing.
DIS (Direct Ignition System)
20On all X16 SZ engines, and on C20 XE
(DOHC) engines from 1993-on, a DIS (Direct
Ignition System) module is used in place of
the distributor and coil. On the X16 SZ engine
the DIS module is attached to the camshaft
housing in the position normally occupied by
the distributor. On the C20 XE engine, a
camshaft phase sensor is attached to the
cylinder head at the non-driven end of the
exhaust camshaft, in the position normally
occupied by the distributor. The DIS module
is attached, by a bracket, to the cylinder head
at the non-driven end of the inlet camshaft.
21The DIS module consists of two ignition
coils and an electronic control module housed
in a cast casing. Each ignition coil supplies
two spark plugs with HT voltage. One spark is
provided in a cylinder with its piston on the
compression stroke, and one spark is
provided to a cylinder with its piston on the
exhaust stroke. This means that a “wasted
spark” is supplied to one cylinder during each
ignition cycle, but this has no detrimental
effect. This system has the advantage that
there are no moving parts (therefore there is
no wear), and the system is largely
maintenance-free.
Motronic M4.1 and M1.5
22This system controls both the ignition and
the fuel injection systems.
23The Motronic module receives information
from a crankshaft speed/position sensor, an
engine coolant temperature sensor mounted
in the thermostat housing. A throttle position
sensor, an airflow meter, and on models fitted
with a catalytic converter, an oxygen sensor
mounted in the exhaust system (Chapter 4C).
24The module provides outputs to control
the fuel pump, fuel injectors, idle speed and
ignition circuit. Using the inputs from the
various sensors, the module computes the
optimum ignition advance, and fuel injector
pulse duration, to suit the prevailing engine
conditions. This system gives very accurate
control of the engine under all conditions,
improving fuel consumption and driveability,
and reducing exhaust gas emissions.
25Further details of the fuel injection system
components are given in Chapter 4B.
Motronic M2.5 and M2.8
26The system is similar to that described for
SOHC models, with the following differences.
27Along with the crankshaft speed/position
sensor, a “Hall-effect” distributor is used
(similar to that described in this Section, with
the MSTS-i system).
Engine electrical systems 5•3
5
Page 91 of 525

28The system also incorporates a separate
ignition amplifier module that transmits
amplified signals from the main system
module to trigger the HT pulse from the
ignition coil. The module is mounted on the
ignition coil’s bracket/baseplate.
29Additionally, the Motronic module
receives information from a cylinder
block-mounted knock sensor, which senses
“knocking” (or pre-ignition) just as it begins to
occur, enabling the module to retard the
ignition timing, thus preventing engine
damage.
Simtec 56.1
30This system uses increased amount of
electronic components instead of mechanical
parts as sensors and actuators with the
Simtec engine management system. This
provides more precise operating data as well
as greater problem free motoring.
31The control unit is equipped with
electronic ignition control. Called ‘Micropro-
cessor Spark Timing System, inductive
triggered’, (or MSTS-i), and means that the
mechanical high voltage distributor is no
longer needed. It is located behind the trim
panel, on the right-hand side footwell (door
pillar).
32The ignition coil is replaced by a dual
spark ignition coil, which is switched directly
by the output stages in the control unit.
33A camshaft sensor will maintain
emergency operation, should the crankshaft
inductive pulse pick-up, malfunction. These
sense TDC (‘Top Dead Centre’), crankshaft
angle and engine speed. The signals are used
by the control unit to calculate ignition point
and for fuel injection.
34The ‘hot film airflow meter’ determines the
mass of air taken in by the engine. The system
uses this information to calculate the correct
amount of fuel needed for injection in the
engine.
35The air inlet temperature sensor (NTC), is
fitted in the air inlet duct between the air
cleaner and the hot mass air flow meter.
36A controlled canister purge valve is
actuated by the system. The tank ventilation is
monitored closely with the Lambda control (or
oxygen sensor) and adaptation by the
computer within the control unit.
37A knock control system is also fitted. This
eliminates the need for octane number
adjustment, as it is performed automatically
through the control unit.
3Electrical system -
precautions
1It is necessary to take extra care when
working on the electrical system, to avoid
damage to semi-conductor devices (diodes
and transistors), and to avoid the risk of
personal injury. Along with the precautions
given in the “Safety first!” Section at the
beginning of this manual, take note of the
following points when working on the system.
2Always remove rings, watches, etc. before
working on the electrical system. Even with
the battery disconnected, discharge could
occur if a component live terminal is earthed
through a metal object. This could cause a
shock or nasty burn.
3Do not reverse the battery connections.
Components such as the alternator, or any
other component having semi-conductor
circuitry, could be irreparably damaged.
4If the engine is being started using jump
leads and a slave battery, connect the
batteries positive to positive and negative to
negative. This also applies when connecting a
battery charger.
5Never disconnect the battery terminals, or
alternator multi-plug connector, when the
engine is running.
6The battery leads and alternator wiring
must be disconnected before carrying out any
electric welding on the vehicle.
7Never use an ohmmeter of the type
incorporating a hand-cranked generator for
circuit or continuity testing.
8Engine management modules are very
sensitive components, and certain
precautions must be taken, to avoid damage
to the module when working on a vehicle
equipped with an engine management
system, as follows.
9When carrying out welding operations on
the vehicle using electric welding equipment,
the battery and alternator should be
disconnected.
10Although underbonnet-mounted modules
will tolerate normal underbonnet conditions,
they can be adversely affected by excess heat
or moisture. If using welding equipment or
pressure washing equipment near the
module, take care not to direct heat, or jets of
water or steam, at the module. If this cannot
be avoided, remove the module from the
vehicle, and protect its wiring plug with a
plastic bag.
11Before disconnecting any wiring, or
removing components, always ensure that the
ignition is switched off.
12Do not attempt to improvise fault
diagnosis procedures using a test lamp or
multimeter, as irreparable damage could be
caused to the module.13After working on ignition/engine
management system components, ensure
that all wiring is correctly reconnected before
reconnecting the battery or switching on the
ignition.
14Any ignition system that uses a
“Hall-effect” generator in the distributor,
cannot be tested. Test equipment that uses
its own power source (e.g. an ohmmeter),
when connected to the distributor or the
“Hall-effect” generator, will be damaged.
4Ignition system testing -
general
3
Note: Refer to Section 3 before proceeding.
Always switch off the ignition before
disconnecting or connecting any component
and when using a multi-meter to check
resistances. Any voltmeter or multi-meter
used to test ignition system components must
have an impedance of 10 meg ohms or
greater
1Electronic ignition system components are
normally very reliable. Most faults are far more
likely to be due to loose or dirty connections,
or to “tracking” of HT voltage due to dirt,
dampness or damaged insulation than to
component failure. Always check all wiring
thoroughly before condemning an electrical
component and work methodically to
eliminate all other possibilities before deciding
that a particular component is faulty.
2The old practice of checking for a spark by
holding the live end of a HT lead a short
distance away from the engine is not
recommended. Not only is there a high risk of
a powerful electric shock, but the ignition coil
or amplifier module will be damaged.
Similarly, never try to “diagnose” misfires by
pulling off one HT lead at a time. Note also
that the ECU is at risk if the system is
triggered with an open (i.e., not properly
earthed) HT circuit; ECU’s are very expensive
to replace, so take care!
3If you are in any doubt as to your skill and
ability to test an ignition system component or
if you do not have the required equipment,
take the vehicle to a suitably equipped
Vauxhall dealer. It is better to pay the labour
charges involved in having the vehicle
checked by an expert than to risk damage to
the system or to yourself.
4If the engine either will not turn over at all,
or only turns very slowly, check the battery
and starter motor. Connect a voltmeter across
the battery terminals (meter positive probe to
battery positive terminal) and disconnect the
ignition coil HT lead from the distributor cap
and earth. Note the voltage reading obtained
while turning over the engine on the starter for
(no more than) ten seconds. If the reading
obtained is less than approximately 9.5 volts,
check the battery, battery connections, starter
motor and charging system.
5•4Engine electrical systems
Warning: The HT voltage
generated by an electronic
ignition system is extremely
high and, in certain
circumstances, could prove fatal. Take
care to avoid receiving electric shocks
from the HT side of the ignition system.
Do not handle HT leads, or touch the
distributor or coil, when the engine is
running. If tracing faults in the HT circuit,
use well-insulated tools to manipulate live
leads
Page 92 of 525

5If the engine turns over at normal speed but
will not start, check the HT circuit by
connecting a timing light and turning the
engine over on the starter motor. If the light
flashes, voltage is reaching the spark plugs,
so these should be checked first. If the light
does not flash, check the HT leads
themselves followed by the distributor cap,
carbon brush and rotor arm.
6If there is a spark, check the fuel system for
faults as far as possible (Chapters 4A or 4B).
7If there is still no spark, check the voltage at
the ignition coil “+” or “15” terminal; it should
be the same as the battery voltage (i.e., at
least 11.7 volts). If the voltage at the coil is
more than 1 volt less than that at the battery,
check the connections back through the
ignition switch to the battery and its earth until
the fault is found. Note, however, that the
ECU controls the coil’s feed; do not attempt
to “test” the ECU with anything other than the
correct test equipment, which will be available
only to a Vauxhall dealer. If any of the wires
are to be checked which lead to the ECU,
always first unplug the relevant connector
from the ECU so that there is no risk of the
ECU being damaged by the application of
incorrect voltages from test equipment.
8If the feed to the ignition coil is sound,
check the coil’s primary and secondary
windings (refer to Section 16). Renew the coil
if faulty, but check the condition of the LT
connections themselves before doing so, to
ensure that the fault is not due to dirty or
poorly fastened connectors.
9If the ignition coil is in good condition, the
fault may be within the amplifier module or the
distributor on the C16 NZ and C16 NZ2
engines, or the amplifier or the crankshaft
speed/position sensor on the C18 NZ engine.
A quick check of these components can be
made by connecting a low-wattage bulb
across the ignition coil’s (disconnected) LT
terminals. If the bulb flickers or flashes when
the engine is turned over, the amplifier and
distributor (C16 NZ and C16 NZ2 engines), or
amplifier and crankshaft speed/position
sensor (C18 NZ engine), are sound.
10If this is the case, the entire LT circuit is in
good condition; the fault, if it lies in the
ignition system, must be in the HT circuit
components. These should be checked
carefully, as outlined above.
11If the indicator or bulb does not flash, the
fault is in either the amplifier or the distributor
(C16 NZ and C16 NZ2 engines), or the
amplifier or crankshaft speed/position sensor
(C18 NZ engine). Owners should note,
however, that by far the commonest cause of
“failure” of either of these is a poor
connection, either between the components
themselves or in the LT circuit wiring
connections. If such a fault is suspected, the
vehicle must be taken to a suitably equipped
Vauxhall dealer for testing; no information is
available to eliminate these components by
other means.12An irregular misfire suggests either a
loose connection or intermittent fault on the
primary circuit, or a HT fault on the coil side of
the rotor arm.
13With the ignition switched off, check
carefully through the system ensuring that all
connections are clean and securely fastened.
If the equipment is available, check the LT
circuit as described in paragraphs 7 to 11
above.
14Check that the HT coil, the distributor cap
and the HT leads are clean and dry. Check the
leads and the spark plugs (by substitution, if
necessary), then check the distributor cap,
carbon brush and rotor arm.
15Regular misfiring is almost certainly due to
a fault in the distributor cap, HT leads or spark
plugs. Use a timing light (paragraph 5, above)
to check whether HT voltage is present at all
leads.
16If HT voltage is not present on any
particular lead, the fault will be in that lead or
in the distributor cap. If HT is present on all
leads, the fault will be in the spark plugs;
check and renew them if there is any doubt
about their condition.
17If no HT voltage is present, check the
ignition coil; its secondary windings may be
breaking down under load.
18If all components have been checked for
signs of obvious faults but the system is still
thought to be faulty, take the vehicle to a
Vauxhall dealer for testing on special
equipment.
5Battery - testing and charging
2
Note: Refer to Section 3 before proceeding.
Testing
1Topping-up and testing of the electrolyte in
each cell is not possible. The condition of the
battery can therefore only be tested by
observing the battery condition indicator.
2The battery condition indicator is fitted in
the top of the battery casing, and indicates
the condition of the battery from its colour. If
the indicator shows green, then the battery is
in a good state of charge. If the indicator turns
darker, eventually to black, then the battery
requires charging, as described later in this
Section. If the indicator shows clear/yellow,
then the electrolyte level in the battery is too
low to allow further use, and the battery
should be renewed.
Charging
3Do not attempt to charge, load or jump start
a battery when the indicator shows
clear/yellow. If the battery is to be charged,
remove it from the vehicle and charge it as
follows.
4The maintenance-free type battery takes
considerably longer to fully recharge than the
standard type, the time taken being
dependent on the extent of discharge.5A constant-voltage type charger is required,
to be set, when connected, to 13.9 to 14.9
volts with a charger current below 25 amps.
6If the battery is to be charged from a fully
discharged state (less than 12.2 volts output),
have it recharged by a Vauxhall dealer or
battery specialist, as the charge rate will be
high and constant supervision during charging
is necessary.
6Battery - removal and refitting
2
Note: Refer to Section 3 before proceeding.
Removal
1The battery is located at the left-hand front
corner of the engine compartment.
2Disconnect the lead(s) at the negative
(earth) terminal by unscrewing the retaining
nut and removing the terminal clamp.
3Disconnect the positive terminal lead(s) in
the same way.
4Unscrew the clamp bolt sufficiently to
enable the battery to be lifted from its
location. Keep the battery in an upright
position, to avoid spilling electrolyte on the
bodywork.
Refitting
5Refitting is a reversal of removal, but smear
petroleum jelly on the terminals when
reconnecting the leads, and always connect
the positive lead first and the negative lead
last.
7Alternator - description
1A Delco-Remy or Bosch alternator may be
fitted, depending on model and engine
capacity. The maximum output of the
alternator varies accordingly.
2The alternator is belt-driven from the
crankshaft pulley. Cooling is provided by a
fan, mounted outside the casing on the end of
the rotor shaft. An integral voltage regulator is
incorporated, to control the output voltage.
3The alternator provides a charge to the
battery even at very low engine speed, and
consists of a coil-wound stator in which a
rotor rotates. The rotor shaft is supported in
ball-bearings, and slip rings are used to
conduct current to and from the field coils
through the carbon brushes.
4The alternator generates ac (alternating
current), which is rectified by an internal diode
circuit to dc (direct current) for supply to the
battery.
5Later models are fitted with a Delco-Remy,
‘compact’ series alternators (see illustration).
They use a ribbed V-belt type drivebelt with
automatic tensioner. They are rigidly mounted
to the engine.
Engine electrical systems 5•5
5
Page 96 of 525

2When the starter switch is operated, current
flows from the battery to the solenoid that is
mounted on the starter body. The plunger in
the solenoid moves inwards, so causing a
centrally pivoted lever to push the drive pinion
into mesh with the starter ring gear. When the
solenoid plunger reaches the end of its travel,
it closes an internal contact and full starting
current flows to the starter field coils. The
armature is then able to rotate the crankshaft,
so starting the engine.
3A special freewheel clutch is fitted to the
starter driven pinion, so that when the engine
fires and starts to operate on its own it does
not drive the starter motor.
4When the starter switch is released, the
solenoid is de-energised, and a spring moves
the plunger back to its rest position. This
operates the pivoted lever to the withdraw the
drive pinion from engagement with the starter
ring.
13Starter motor - testing
3
Note: Refer to Section 3 before proceeding
Testing
1If the starter motor fails to turn the engine
when the switch is operated, and engine
seizure is not the problem, there are several
other possible reasons:
a)The battery is faulty
b)The electrical connections between the
switch, solenoid battery and starter motor
are somewhere failing to pass the
necessary current from the battery
through the starter to earth
c)The solenoid switch is faulty
d)The starter motor is mechanically or
electrically defective
e)The starter motor pinion and/or flywheel
ring gear is badly worn, and in need of
replacement
2To check the battery, switch on the
headlamps. If they dim after a few seconds,
then the battery is in a discharged state. If the
lamps glow brightly, operate the starter switch
and see what happens to the lamps. If theydim, then power is reaching the motor, but
failing to turn it. If the starter turns slowly, go
on to the next check.
3If, when the starter switch is operated, the
lamps stay bright, then insufficient power is
reaching the motor. Disconnect the battery
and the starter/solenoid power connections,
and the engine earth strap, then thoroughly
clean them and refit them. Smear petroleum
jelly around the battery connections to
prevent corrosion. Corroded connections are
the most frequent cause of electrical system
malfunctions.
4If the preceding checks and cleaning tasks
have been carried out without success, a
clicking noise will probably have been heard
each time the starter switch was operated.
This indicates that the solenoid switch was
operating, but it does not necessarily follow
that the main contacts were closing properly
(if no clicking has been heard from the
solenoid, it is certainly defective). The
solenoid can be checked by connecting a
voltmeter across the main cable connection
on the solenoid and earth. When the switch is
operated, these should be a reading on the
voltmeter. If there is no reading, the solenoid
unit is faulty, and should be renewed.
5If the starter motor operates, but does not
turn the engine, then it is likely that the starter
pinion and/or flywheel ring gear are badly
worn. If this is the case, the starter motor will
normally be noisy in operation.
6Finally, if it is established that the solenoid
is not faulty, and 12 volts are reaching the
starter, then the motor itself is faulty, and
should be removed for inspection.
14Starter motor - removal and
refitting
3
Note: Refer to Section 3 before proceeding
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Apply the handbrake, then jack up the front
of the vehicle, and support securely on axle
stands (see “Jacking and Vehicle Support”)
positioned under the body side members.3On DOHC models, remove the engine
undershield, as described in Chapter 11.
4Note the wiring connections on the
solenoid, then disconnect them (see
illustration).
5Where applicable, unscrew the bolt
securing the exhaust bracket and the starter
motor mounting bracket to the cylinder block
(see illustration).
6Unscrew the two starter motor mounting
bolts. Note that the top bolt on some models
are fitted from the transmission side, and
secures a wiring harness bracket (see
illustration).
7Withdraw the starter motor.
Refitting
8Refitting is a reversal of removal, but where
applicable, ensure that the wiring harness
bracket is in place on the top mounting bolt,
and tighten all bolts to the specified torque.
15Starter motor - overhaul
5
If the starter motor is thought to be suspect,
it should be removed from the vehicle and
taken to an auto-electrician for testing. Most
auto-electricians will be able to supply and fit
brushes at a reasonable cost. However, check
on the cost of repairs before continuing as it
may prove more economical to obtain a new
or exchange motor.
16Ignition coil - removal, testing
and refitting
3
Note: Refer to Section 3 before proceeding.
An ohmmeter will be required to test the coil
Removal
1The ignition coil is either a cylindrical metal
canister or a moulded plastic unit. It is
clamped or bolted to the left-hand inner wing
panel, near the suspension strut top mounting
(under the power steering fluid reservoir, on
Engine electrical systems 5•9
14.6 Starter motor securing bolts
(arrowed) - 1.6 litre model
(engine removed)14.5 Starter motor mounting
bracket/exhaust bracket securing bolt
(arrowed) - 1.6 litre model14.4 Starter motor and solenoid viewed
from underneath the vehicle. Solenoid
wiring connections arrowed
5
Page 100 of 525
Inspection
17Examine the distributor cap and rotor arm,
as described in paragraphs 6 and 7. Examine
the O-rings at the rear of the distributor body,
and on the rear of the shaft, and renew if
necessary.
Reassembly
18Reassembly is a reversal of dismantling,
ensuring that the thrustwashers are correctly
located. Note that the drive collar should be
refitted so that the drive peg on the collar is
aligned with the groove in the top of the
distributor shaft (it is possible to fit the drive
collar 180°out of position).
19Refit the distributor as described in
Section 18, and then check and if necessary
adjust the ignition timing, as described in
Section 21.
DOHC models (where
applicable)
20The distributor cap and rotor arm can be
examined as described in paragraphs 6 and 7.
21Ignition timing -checking and
adjustment
4
Note: Refer to Section 3 before proceeding. A
tachometer and a timing light will be required
during this procedure. For details of ignition
timing adjustment required to operate vehicles
on unleaded petrol, refer to Section 22.
14 NV and 16 SV models
Checking
1Start the engine and run it until it reaches
normal operating temperature, then switch
off.
2On 14 NV models, disconnect the vacuum
pipe from the distributor vacuum diaphragm
unit.
3On all models use a spanner applied to the
crankshaft pulley bolt to rotate the crankshaft
clockwise until the notch in the pulley’s
inboard rim aligns with the pointer protruding
from the oil pump housing. On 14 NV models,
where two notches (indicating 10°and 5°
BTDC respectively) are found, rotate the
crankshaft until the second notch (in thedirection of rotation -i.e. 5°BTDC) aligns. Use
white paint or similar to emphasise the pointer
and notch, to make them easier to see.
4Connect a timing light to No 1 cylinder
(nearest the timing belt end of the engine) HT
lead, also a tachometer; follow the equipment
manufacturer’s instructions for connection.
5Start the engine and allow it to idle -the
speed should be between 700 and 1000 rpm.
6On 14 NV models, aim the timing light at the
pointer and check that it is aligned with the
crankshaft pulley notch.
7On early 16 SV models, disconnect the
ignition timing basic adjustment coding plug.
This can be identified by a length of Black
wire joining Brown/Red and Brown/Yellow
wires in a connector plug clipped to the wiring
or heater/cooling system hoses beneath the
battery/ignition coil (see illustration, 16.1). This
causes the MSTS-i module to adopt its basic
adjustment mode, sending a constant firing
signal corresponding to 10°BTDC and
eliminating any advance below 2000 rpm. Aim
the timing light at the pointer and check that it
is aligned with the crankshaft pulley notch.
8On later 16 SV, C 16 NZ and C 16 NZ2
models, the coding plugs are no longer fitted.
For accurate checking, special Vauxhall test
equipment must be used which causes the
MSTS module to adopt its basic adjustment
mode.
9Without access to such equipment, it is
possible to check and adjust the ignition
timing, accurate results cannot be
guaranteed. Owners are therefore advised to
have this work carried out by a suitably
equipped Vauxhall dealer; at the very least,
make the initial setting yourself and then have
it checked as soon as possible.
10If you do attempt to check the ignition
timing yourself, note that the fixed reference
mark is now an extended line embossed on
the timing belt lower outer cover.
Adjustment
11If the notch and pointer are not aligned,
loosen the distributor clamp nut and turn the
distributor body slightly in the required
direction to align.
12Tighten the distributor clamp nut, and
check that the notch and pointer are still
aligned. 13Stop the engine, and disconnect the
timing light and tachometer.
14On 16 SV models, reconnect the basic
adjustment coding plug. On 14 NV models,
reconnect the vacuum pipe to the distributor
vacuum diaphragm unit.
Other models
15No adjustment of the ignition timing is
possible on 1.8 and 2.0 litre models, as the
adjustment is carried out automatically by the
electronic control module.
16The ignition timing can be checked by a
Vauxhall dealer using specialist dedicated test
equipment, if a fault is suspected.
22Ignition timing -adjustment
for use with unleaded petrol
3
14 NV models
1All models with the 14 NV engine have the
ignition timing adjusted for use with 95 RON
unleaded petrol before they leave the factory,
and no further adjustment is required.
2Leaded petrol (98 RON) can be used if
desired, with no adverse effects.
1.6, 1.8 and 2.0 SOHC models
Note: Models equipped with a catalytic
converter must be operated on 95 R0N
unleaded petrol at all times, and although an
octane coding plug may be fitted, it should
not be tampered with
3Models, other than 14 NV, are equipped
with an octane coding plug, which is located
Engine electrical systems 5•13
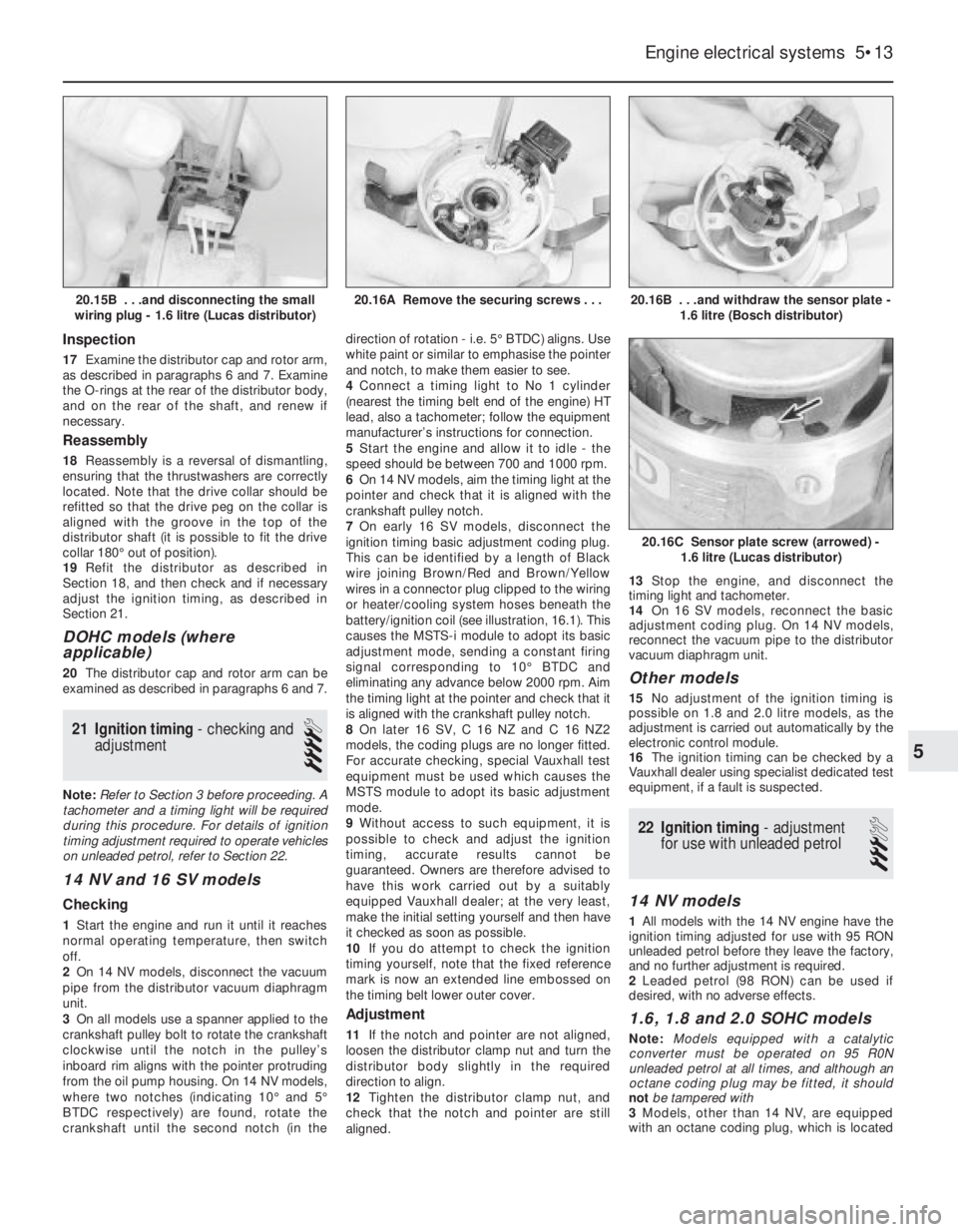
20.16B . . .and withdraw the sensor plate -
1.6 litre (Bosch distributor)
20.16C Sensor plate screw (arrowed) -
1.6 litre (Lucas distributor)
20.16A Remove the securing screws . . .20.15B . . .and disconnecting the small
wiring plug - 1.6 litre (Lucas distributor)
5
Page 105 of 525

wax-based underbody protective coating, it is
a good idea to have the whole of the
underframe of the vehicle steam cleaned,
engine compartment included, so that a
thorough inspection can be carried out to see
what minor repairs and renovations are
necessary. Steam cleaning is available at
many garages and is necessary for removal of
the accumulation of oily grime that sometimes
is allowed to become thick in certain areas.
The dirt can then be simply hosed off. Note
that these methods should not be used on
vehicles with wax-based underbody
protective coating or the coating will be
removed. Such vehicles should be inspected
annually, preferably just before winter, when
the underbody should be washed down and
any damage to the wax coating repaired.
Ideally, a completely fresh coat should be
applied. It would also be worth considering
the use of such wax-based protection for
injection into door panels, sills, box sections,
etc., as an additional safeguard against rust
damage where such protection is not
provided by the vehicle manufacturer.
After washing paintwork, wipe off with a
chamois leather to give an unspotted clear
finish. A coat of clear protective wax polish,
will give added protection against chemical
pollutants in the air. If the paintwork sheen
has dulled or oxidised, use a cleaner/polisher
combination to restore the brilliance of the
shine. This requires a little effort, but such
dulling is usually caused because regular
washing has been neglected. Care needs to
be taken with metallic paintwork, as special
non-abrasive cleaner/polisher is required to
avoid damage to the finish.
Always check that the door and ventilator
opening drain holes and pipes are completely
clear so that water can be drained out. Bright
work should be treated in the same way as
paint work. Windscreens and windows can be
kept clear of the smeary film that often
appears, by using a glass cleaner. Never use
any form of wax or other body or chromium
polish on glass.
3Upholstery and carpets -
maintenance
1
Mats and carpets should be brushed or
vacuum cleaned regularly to keep them free of
grit. If they are badly stained remove them
from the vehicle for scrubbing or sponging
and make quite sure they are dry before
refitting. Seats and interior trim panels can be
kept clean by wiping with a damp cloth. If they
do become stained (which can be more
apparent on light coloured upholstery) use a
little liquid detergent and a soft nail brush to
scour the grime out of the grain of the
material. Do not forget to keep the headlining
clean in the same way as the upholstery.
When using liquid cleaners inside the vehicle
do not over-wet the surfaces being cleaned.Excessive damp could get into the seams and
padded interior causing stains, offensive
odours or even rot. If the inside of the vehicle
gets wet accidentally it is worthwhile taking
some trouble to dry it out properly, particularly
where carpets are involved. Do not leave oil or
electric heaters inside the vehicle for this
purpose.
4Minor body damage - repair
3
Repairs of minor scratches in
bodywork
If the scratch is very superficial, and does
not penetrate to the metal of the bodywork,
repair is very simple. Lightly rub the area of
the scratch with a paintwork renovator, to
remove loose paint from the scratch and to
clear the surrounding bodywork of wax polish.
Rinse the area with clean water.
Apply touch-up paint to the scratch using a
fine paint brush; continue to apply fine layers
of paint until the surface of the paint in the
scratch is level with the surrounding
paintwork. Allow the new paint at least two
weeks to harden: then blend it into the
surrounding paintwork by rubbing the scratch
area with a paintwork renovator or a very fine
cutting paste and apply wax polish.
Where the scratch has penetrated right
through to the metal of the bodywork, causing
the metal to rust, a different repair technique
is required. Remove any loose rust from the
bottom of the scratch with a penknife, then
apply rust inhibiting paint, to prevent the
formation of rust in the future. Using a rubber
or nylon applicator fill the scratch with
bodystopper paste. If required, this paste can
be mixed with cellulose thinners to provide a
very thin paste that is ideal for filling narrow
scratches. Before the stopper-paste in the
scratch hardens, wrap a piece of smooth
cotton rag around the top of a finger. Dip the
finger in cellulose thinners and then quickly
sweep it across the surface of the
stopper-paste in the scratch; this will ensure
that the surface of the stopper-paste is
slightly hollowed. The scratch can now be
painted over as described earlier in this
Section.
Repair of dents in bodywork
When deep denting of the vehicle’s
bodywork has taken place, the first task is to
pull the dent out, until the affected bodywork
almost attains its original shape. There is little
point in trying to restore the original shape
completely, as the metal in the damaged area
will have stretched on impact and cannot be
reshaped fully to its original contour. It is
better to bring the level of the dent up to a
point that is about 8 in (3 mm) below the level
of the surrounding bodywork. In cases where
the dent is very shallow anyway, it is not worthtrying to pull it out at all. If the underside of the
dent is accessible, it can be hammered out
gently from behind, using a mallet with a
wooden or plastic head. Whilst doing this,
hold a block of wood firmly against the
outside of the panel to absorb the impact
from the hammer blows and thus prevent a
large area of the bodywork from being
“belled-out”.
Should the dent be in a section of the
bodywork that has a double skin or some
other factor making it inaccessible from
behind, a different technique is called for. Drill
several small holes through the metal inside
the area particularly in the deeper section.
Then screw long self-tapping screws into the
holes just sufficiently for them to gain a good
purchase in the metal. Now the dent can be
pulled out by pulling on the protruding heads
of the screws with a pair of pliers.
The next stage of the repair is the removal
of the paint from the damaged area, and from
an inch or so of the surrounding “sound”
bodywork. This is accomplished most easily
by using a wire brush or abrasive pad on a
power drill, although it can be done just as
effectively by hand using sheets of abrasive
paper. To complete the preparation for filling,
score the surface of the bare metal with a
screwdriver or the tang of a file, or
alternatively, drill small holes in the affected
area. This will provide a good “key” for the
filler paste.
To complete the repair see the Section on
filling and re-spraying.
Repair of rust holes or gashes in
bodywork
Remove all paint from the affected area and
from an inch or so of the surrounding “sound”
bodywork, using an abrasive pad or a wire
brush on a power drill. If these are not
available a few sheets of abrasive paper will
do the job just as effectively. With the paint
removed you will be able to gauge the severity
of the corrosion and therefore decide whether
to renew the whole panel (if this is possible) or
to repair the affected area. New body panels
are not as expensive as most people think
and it is often quicker and more satisfactory
to fit a new panel than to attempt to repair
large areas of corrosion.
Remove all fittings from the affected area
except those which will act as a guide to the
original shape of the damaged bodywork (e.g.
headlamp shells, etc.). Then, using tin snips or
a hacksaw blade, remove all loose metal and
any other metal badly affected by corrosion.
Hammer the edges of the hole inwards to
create a slight depression for the filler paste.
Wire brush the affected area to remove the
powdery rust from the surface of the
remaining metal. Paint the affected area with
rust inhibiting paint. If the back of the rusted
area is accessible treat this also.
Before filling can take place it will be
necessary to block the hole in some way. This
can be achieved by using aluminium or plastic
mesh, or aluminium tape.
11•2Bodywork and fittings
Page 108 of 525

to be refitted, tie a length of string to the end
of the wiring. Then feed the wiring through the
boot lid and untie the string, leaving it in
position in the boot lid to assist refitting.
3Mark the position of the hinges on the boot
lid.
4With the help of an assistant, support the
weight of the boot lid, then unscrew the
securing bolts from the hinges, and lift the
boot lid from the vehicle. If the boot lid is to be
refitted, rest it carefully on rags or cardboard,
to avoid damaging the paint.
5If a new boot lid is to be fitted, transfer all
the serviceable fittings (rubber buffers, lock
mechanism, etc.), to it.
6If desired, the boot lid hinge counter-
balance springs can be removed, but before
unhooking them from the vehicle body, note
their position so that they can be refitted in
their original positions (see illustration). Use
a lever to unhook the springs.
Refitting
7Refitting is a reversal of removal,
remembering the following points.
8Align the hinges with the precisely made
marks on the boot lid.
9Where applicable, draw the central locking
solenoid wiring through the boot lid, using the
string.
10If necessary, adjust the hinge bolts and
the rubber buffer until a good fit is obtained
with the boot lid shut.
11If necessary, adjust the position of the
lock striker on the body, to achieve
satisfactory lock operation.
10Boot lid lock (Saloon
models) - removal and
refitting
2
Removal
1Open the boot lid fully.
2Unscrew the two securing screws, then
withdraw the lock and disconnect the
operating rod.
Refitting
3Refitting is a reversal of removal, but if
necessary adjust the position of the lock
striker on the body, to achieve satisfactory
lock operation.
11Boot lid lock cylinder
(Saloon models) - removal
and refitting
2
Removal
1Open the boot lid fully.
2Unscrew the two securing nuts, then
withdraw the lock cylinder complete with the
housing, and disconnect the operating rods(s).
3To remove the lock cylinder from the
housing, insert the key into the lock, then
extract the circlip and the operating lever
assembly from the end of the lock cylinder,
and withdraw the cylinder from the housing.
Refitting
4Refitting is a reversal of removal, but check
the operations of the lock on completion (see
illustration).
12Tailgate (Hatchback models)
-removal and refitting
2
Removal
1Open the tailgate fully.
2Disconnect the battery negative lead.
3Remove the securing screws, and withdraw
the tailgate trim panels.
4Disconnect all the relevant wiring now
exposed, and disconnect the washer fluid
hose.5If the original tailgate is to be refitted, tie
string to the ends of all the relevant wires, and
if necessary the washer fluid hose, then feed
the wiring and the hose through the top edge
of the tailgate. Untie the string, leaving it in
position in the tailgate to assist refitting.
6Prise off the rear roof trim panel, taking care
not to break the securing clips, and lower the
rear of the headlining slightly for access to the
tailgate hinge securing screws (see
illustrations). Mark the hinge positions on the
body.
7Have an assistant support the weight of the
tailgate, then disconnect the tailgate struts
from their mounting balljoints, with reference
to Section 15.
8Ensure that the tailgate is adequately
supported, then remove the hinge securing
screws and withdraw the tailgate from the
vehicle. If the tailgate is to be refitted, rest it
carefully on rags or cardboard, to avoid
damaging the paint.
9If desired, the hinges can be removed from
the tailgate by driving out the hinge pins.
10If the tailgate can be moved up and down
on its hinges due to wear in the hinge pins or
their holes, it may be possible to drill out the
holes and fit slightly oversize pins. Consult a
Vauxhall dealer for further advice.
11If a new tailgate is to be fitted, transfer all
serviceable components to it.
Refitting
12Refitting is a reversal of removal,
remembering the following points.
13Align the hinges with the previously made
marks on the body.
Bodywork and fittings 11•5
12.6B . . . for access to the tailgate hinge
screws12.6A Prise off the rear roof trim panel . . .
11.4 Boot lid/tailgate lock cylinder
components
1 Lock cylinder
2 Housing
3 Operating lever assembly
4 Circlip
9.6 Boot lid hinge counterbalance spring
locations - Saloon models
1 Position for basic boot lid
2 Position for boot lid with outer plastic
trim panel or spoiler
3 Position for boot lid with outer plastic
trim panel and spoiler
11
Page 127 of 525

2Exhaust gas recirculation
(EGR) system - general
The system reintroduces small amounts of
exhaust gas into the combustion cycle to
reduce the generation of oxides of nitrogen
(NOx).
On C16 NZ, C16 NZ2 and C18 NZ engines,
the volume of exhaust gas reintroduced is
governed by manifold vacuum, through the
EGR valve mounted on the inlet manifold.
When the valve is opened small amounts of
exhaust gas are allowed to enter the inlet
tract, passing through ports in the cylinder
head.
On X16 SZ engines the EGR valve is
operated by an EGR module, mounted on the
left-hand side of the engine compartment
behind the battery. This module amplifies
signals received from the fuel system ECU
and operates the EGR valve electronically
providing precise control of exhaust gas
recirculation under all engine conditions.
3EGR valve (Multec system
models) - testing, removal and
refitting
2
Testing
1On C16 NZ, C16 NZ2 and C18 NZ engines,
it is recommended that the system is checked
annually, by checking the movement of the
valve’s diaphragm carrier plate as follows.
Note that the carrier plate is visible only
through the apertures in the underside of the
valve, so a battery-operated torch and small
mirror may be useful. On X16 SZ engines,
Vauxhall test equipment is necessary to check
the EGR system.
2With the engine fully warmed up to normal
operating temperature and idling, briefly open
and close the throttle. The carrier plate should
move upwards as the manifold vacuum
changes. When the engine is idling smoothly
again, press the carrier plate upwards (do this
very carefully, so that the plate is not distorted or
the diaphragm damaged). The idle speed should
drop significantly (approximately 100 rpm).
3If the valve does not respond as described,
it must be cleaned.
Removal
4Pull off the hose from the valve, then unbolt
the valve and remove it (see illustrations).
Clean away all carbon using a wire brush and
a pointed tool, but take care not to damage
the valve seat. Renew the valve gasket to
prevent induction leaks.
Refitting
5Refit the valve and reconnect the hose,
then recheck the system’s performance; if
there is no improvement, the valve must be
renewed.
4EGR valve (Simtec system) -
testing, removal and refitting
3
Note: A new gasket will be required when
refitting the valve.
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Remove wiring harness and vacuum hose.
3Mark position of the valve, to ensure
correct relocation.
4Undo the 3 bolts, and remove the valve
from the dual spark ignition coil’s coolant
flange.
Refitting
5Clean the sealing surfaces of the valve and
flange.
6Refit the valve with a new gasket and line
up the marks made before removal (see
illustration).
5EGR module (X16 SZ
models) - removal and
refitting
2
Removal
1Disconnect the knock module from its
bracket (refer to Chapter 4B, if necessary),
and place to one side.
2Remove wiring plug from module. Remove
module from bracket.
Refitting
3Refitting is a reversal of removal.
6AIR pump assembly (Simtec
system) - removal and refitting
3
Removal
1Chock the rear wheels, jack up the front of
the vehicle and support it on axle stands
placed under the body side members (see
“Jacking and Vehicle Support”)
2Remove the left hand front wheel and inner
wheel arch lining.
3Loosen the hose clamp and remove the air
duct hose from the pump.
4Disconnect the battery negative lead.
5Undo the securing nuts and remove the
pump assembly from its location. Disconnect
the wiring plug.
6Remove the wiring plug from the pump’s
bracket.
7Mark the position of the pump on it’s
bracket before separating.
8Remove the fixing bolts and disconnect the
pump from it’s insulator.
9The insulator can also be checked by
removing the 3 nuts, securing the protective
shield. Before removing, mark the shield and
insulator. Replace if necessary.
10Check the pump’s air cleaner for damage.
Refitting
11Refitting is a reversal of removal. Ensure
correct alignment of the components.
7AIR cut-off valve - removal,
testing and refitting
3
Removal
1Before removal, mark on the cut-off valve,
the direction of flow towards the non-return
valve (see illustration).
2Disconnect and remove the air duct and
vacuum hoses.
3Undo the switchover valve’s bolts and
move to one side.
4C•2Fuel and exhaust systems - exhaust and emissions
3.4 Disconnecting the vacuum hose from
the exhaust gas recirculation valve
4.6 EGR valve
1 Valve 2 Gasket
3.4B Withdrawing the exhaust gas
recirculation valve