1988 OPEL CALIBRA change time
[x] Cancel search: change timePage 4 of 525

4Unscrew the two securing bolts, and
withdraw the pump from the camshaft
housing (see illustration).
5Recover the plastic insulating block.
Refitting
6Refitting is a reversal of removal, but ensure
that the fuel hoses are reconnected to their
correct locations as noted during removal,
and tighten the securing bolts to the specified
torque.
7Run the engine and check for leaks on
completion. If leakage is evident, stop the
engine immediately and rectify the problem
without delay. Note that the engine may take
a longer time than usual to start when the
pump has been removed, as the pump refills
with fuel.
7Fuel tank - removal,
examination and refitting
4
Note: Refer to Section 2 before proceeding
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Siphon out any remaining fuel in the tank
through the filler pipe. Siphon the fuel into a
clean metal container that can be sealed.
3Chock the front wheels, then jack up the
rear of the vehicle, and support securely on
axle stands (see “Jacking and Vehicle
Support”) placed under the body side
members.
4Disconnect the exhaust system front
flexible joint. Suspend the front section of the
exhaust system with wire or string from the
underbody.
5Disconnect the rear section of the exhaust
system from its rubber mountings, and allow it
to rest on the rear suspension torsion beam. It
is advisable to support the rear section of the
exhaust at its front end, with wire or string
from the underbody, to avoid straining the
system.
6Unclip the handbrake cable from the
bracket on the left-hand fuel tank securing
strap.
7Disconnect the fuel hoses from the fuel
level sender unit located in the right-hand side
of the fuel tank. Make a note of the hosepositions for use when refitting. Be prepared
for fuel spillage, and take adequate fire
precautions. Plug the open ends of the hoses,
to prevent dirt ingress and further fuel loss.
8Disconnect the wiring plug from the fuel
level sender unit.
9Disconnect the filler and vent hoses from
the rear of the fuel tank.
10Support the weight of the fuel tank on a
jack with an interposed block of wood.
11Unscrew the securing bolts from the tank
mounting straps, then remove the straps and
lower the tank sufficiently to enable the
disconnection of the remaining vent hose.
12With the aid of an assistant, withdraw the
tank sideways from the right-hand side of the
vehicle. Note that as the tank is withdrawn,
some residual fuel may be released.
Examination
13If the tank contains sediment or water, it
may be cleaned out using two or three rinses
with clean fuel. Shake vigorously using
several changes of fuel, but before doing so,
remove the fuel level sender unit, as
described in Section 8. This procedure should
be carried out in a well-ventilated area, and it
is vital to take adequate fire precautions -
refer to the “Safety first!” Section at the
beginning of this manual for further details.
14Any repairs to the fuel tank should be
carried out by a professional. Do not under
any circumstances attempt to weld or solder a
fuel tank. Removal of all residual fuel vapour
requires several hours of specialist cleaning.
Refitting
15Refitting is a reversal of removal, ensuring
that all hoses are reconnected to their correct
locations as noted during removal.
16On completion, fill the fuel tank, then run
the engine and check for leaks. If leakage is
evident, stop the engine immediately and
rectify the problem without delay. Note that
the engine may take a longer time than usual
to start when the fuel tank has been removed,
as the pump refills with fuel.
8Fuel level sender unit -
removal and refitting
3
Note: Refer to Section 2 before proceeding
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Siphon out any remaining fuel in the tank
through the filler pipe. Siphon the fuel into a
clear metal container that can be sealed.
3Chock the front wheels, then jack up the rear
of the vehicle, and support securely on axle
stands (see “Jacking and Vehicle Support”)
placed under the body side members.
4The sender unit is located in the right-hand
side at the fuel tank.
5Make alignment marks on the sender unit
and the fuel tank, so that the sender unit can
be refitted in its original position.6Disconnect the fuel hoses from the sender
unit. Be prepared for fuel spillage, and take
adequate fire precautions. Plug the open ends
of the hoses, to prevent dirt ingress and
further fuel loss.
7Disconnect the wiring plug from the fuel
level sender unit.
8To remove the sender unit, engage a flat
piece of metal as a lever between two of the
slots on the sender unit rim, and turn it anti-
clockwise.
9Withdraw the unit carefully, to avoid
bending the float arm.
10Recover the sealing ring.
Refitting
11Refitting is a reversal of removal,
remembering the following points.
12Examine the condition of the sealing ring,
and renew if necessary.
13Ensure that the marks made on the
sender unit and fuel tank before removal are
aligned.
14Ensure that the hoses are reconnected to
their correct locations as noted during
removal.
15On completion, fill the fuel tank, then run
the engine and check for leaks. Also check
that the fuel gauge reads correctly. If leakage
is evident, stop the engine immediately and
rectify the problem without delay. Note that
the engine may take a longer time than usual
to start when the sender unit has been
removed, as the fuel pump refills with fuel.
9Fuel vapour separator (1.6
and 1.8 litre models) -
removal and refitting
3
Note: Refer to Section 2 before proceeding
Removal
1The fuel vapour separator is located on a
bracket attached to the side of the
carburettor.
2Note the locations of the three fuel hoses,
labelling them if necessary for use when
refitting, then disconnect the hoses from the
vapour separator. Be prepared for fuel
spillage, and take adequate fire precautions.
Plug the open ends of the hoses, to prevent
dirt ingress and further fuel spillage.
3Remove the two securing screws, and lift
the vapour separator from its bracket.
4Check the body of the separator for cracks
or leaks before refitting, and renew if
necessary.
Refitting
5Refitting is a reversal of removal, but ensure
that the three fuel hoses are connected to
their correct locations as noted during
removal.
6Run the engine and check the hose
connections for leaks on completion. If
leakage is evident, stop the engine
immediately and rectify the problem without
delay.
4A•4Fuel and exhaust systems - carburettor models
6.4 Withdrawing the fuel pump and plastic
insulating block - 1.6 litre model
Page 96 of 525

2When the starter switch is operated, current
flows from the battery to the solenoid that is
mounted on the starter body. The plunger in
the solenoid moves inwards, so causing a
centrally pivoted lever to push the drive pinion
into mesh with the starter ring gear. When the
solenoid plunger reaches the end of its travel,
it closes an internal contact and full starting
current flows to the starter field coils. The
armature is then able to rotate the crankshaft,
so starting the engine.
3A special freewheel clutch is fitted to the
starter driven pinion, so that when the engine
fires and starts to operate on its own it does
not drive the starter motor.
4When the starter switch is released, the
solenoid is de-energised, and a spring moves
the plunger back to its rest position. This
operates the pivoted lever to the withdraw the
drive pinion from engagement with the starter
ring.
13Starter motor - testing
3
Note: Refer to Section 3 before proceeding
Testing
1If the starter motor fails to turn the engine
when the switch is operated, and engine
seizure is not the problem, there are several
other possible reasons:
a)The battery is faulty
b)The electrical connections between the
switch, solenoid battery and starter motor
are somewhere failing to pass the
necessary current from the battery
through the starter to earth
c)The solenoid switch is faulty
d)The starter motor is mechanically or
electrically defective
e)The starter motor pinion and/or flywheel
ring gear is badly worn, and in need of
replacement
2To check the battery, switch on the
headlamps. If they dim after a few seconds,
then the battery is in a discharged state. If the
lamps glow brightly, operate the starter switch
and see what happens to the lamps. If theydim, then power is reaching the motor, but
failing to turn it. If the starter turns slowly, go
on to the next check.
3If, when the starter switch is operated, the
lamps stay bright, then insufficient power is
reaching the motor. Disconnect the battery
and the starter/solenoid power connections,
and the engine earth strap, then thoroughly
clean them and refit them. Smear petroleum
jelly around the battery connections to
prevent corrosion. Corroded connections are
the most frequent cause of electrical system
malfunctions.
4If the preceding checks and cleaning tasks
have been carried out without success, a
clicking noise will probably have been heard
each time the starter switch was operated.
This indicates that the solenoid switch was
operating, but it does not necessarily follow
that the main contacts were closing properly
(if no clicking has been heard from the
solenoid, it is certainly defective). The
solenoid can be checked by connecting a
voltmeter across the main cable connection
on the solenoid and earth. When the switch is
operated, these should be a reading on the
voltmeter. If there is no reading, the solenoid
unit is faulty, and should be renewed.
5If the starter motor operates, but does not
turn the engine, then it is likely that the starter
pinion and/or flywheel ring gear are badly
worn. If this is the case, the starter motor will
normally be noisy in operation.
6Finally, if it is established that the solenoid
is not faulty, and 12 volts are reaching the
starter, then the motor itself is faulty, and
should be removed for inspection.
14Starter motor - removal and
refitting
3
Note: Refer to Section 3 before proceeding
Removal
1Disconnect the battery negative lead.
2Apply the handbrake, then jack up the front
of the vehicle, and support securely on axle
stands (see “Jacking and Vehicle Support”)
positioned under the body side members.3On DOHC models, remove the engine
undershield, as described in Chapter 11.
4Note the wiring connections on the
solenoid, then disconnect them (see
illustration).
5Where applicable, unscrew the bolt
securing the exhaust bracket and the starter
motor mounting bracket to the cylinder block
(see illustration).
6Unscrew the two starter motor mounting
bolts. Note that the top bolt on some models
are fitted from the transmission side, and
secures a wiring harness bracket (see
illustration).
7Withdraw the starter motor.
Refitting
8Refitting is a reversal of removal, but where
applicable, ensure that the wiring harness
bracket is in place on the top mounting bolt,
and tighten all bolts to the specified torque.
15Starter motor - overhaul
5
If the starter motor is thought to be suspect,
it should be removed from the vehicle and
taken to an auto-electrician for testing. Most
auto-electricians will be able to supply and fit
brushes at a reasonable cost. However, check
on the cost of repairs before continuing as it
may prove more economical to obtain a new
or exchange motor.
16Ignition coil - removal, testing
and refitting
3
Note: Refer to Section 3 before proceeding.
An ohmmeter will be required to test the coil
Removal
1The ignition coil is either a cylindrical metal
canister or a moulded plastic unit. It is
clamped or bolted to the left-hand inner wing
panel, near the suspension strut top mounting
(under the power steering fluid reservoir, on
Engine electrical systems 5•9
14.6 Starter motor securing bolts
(arrowed) - 1.6 litre model
(engine removed)14.5 Starter motor mounting
bracket/exhaust bracket securing bolt
(arrowed) - 1.6 litre model14.4 Starter motor and solenoid viewed
from underneath the vehicle. Solenoid
wiring connections arrowed
5
Page 143 of 525
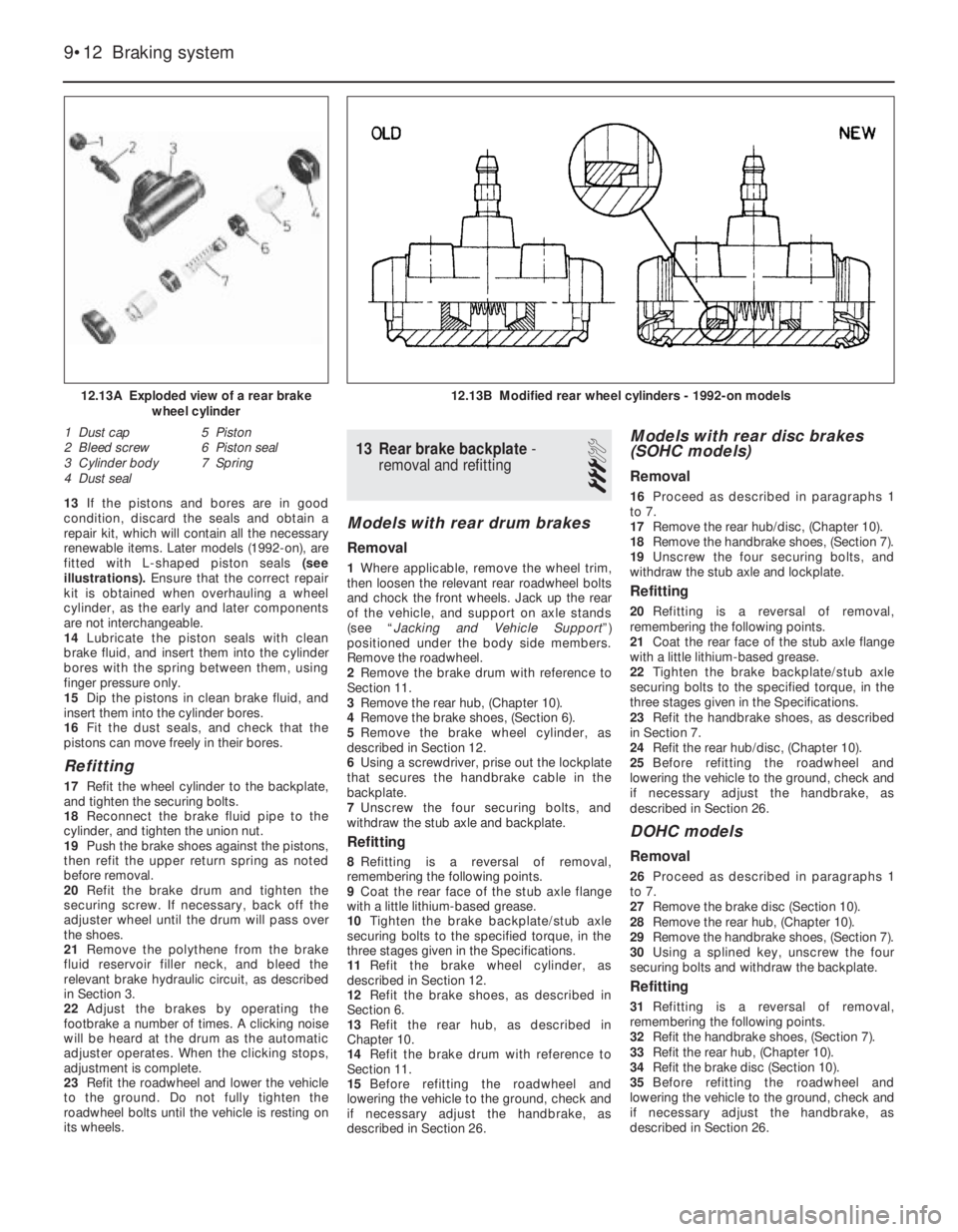
13If the pistons and bores are in good
condition, discard the seals and obtain a
repair kit, which will contain all the necessary
renewable items. Later models (1992-on), are
fitted with L-shaped piston seals (see
illustrations). Ensure that the correct repair
kit is obtained when overhauling a wheel
cylinder, as the early and later components
are not interchangeable.
14Lubricate the piston seals with clean
brake fluid, and insert them into the cylinder
bores with the spring between them, using
finger pressure only.
15Dip the pistons in clean brake fluid, and
insert them into the cylinder bores.
16Fit the dust seals, and check that the
pistons can move freely in their bores.
Refitting
17Refit the wheel cylinder to the backplate,
and tighten the securing bolts.
18Reconnect the brake fluid pipe to the
cylinder, and tighten the union nut.
19Push the brake shoes against the pistons,
then refit the upper return spring as noted
before removal.
20Refit the brake drum and tighten the
securing screw. If necessary, back off the
adjuster wheel until the drum will pass over
the shoes.
21Remove the polythene from the brake
fluid reservoir filler neck, and bleed the
relevant brake hydraulic circuit, as described
in Section 3.
22Adjust the brakes by operating the
footbrake a number of times. A clicking noise
will be heard at the drum as the automatic
adjuster operates. When the clicking stops,
adjustment is complete.
23Refit the roadwheel and lower the vehicle
to the ground. Do not fully tighten the
roadwheel bolts until the vehicle is resting on
its wheels.
13Rear brake backplate -
removal and refitting
3
Models with rear drum brakes
Removal
1Where applicable, remove the wheel trim,
then loosen the relevant rear roadwheel bolts
and chock the front wheels. Jack up the rear
of the vehicle, and support on axle stands
(see “Jacking and Vehicle Support”)
positioned under the body side members.
Remove the roadwheel.
2Remove the brake drum with reference to
Section 11.
3Remove the rear hub, (Chapter 10).
4Remove the brake shoes, (Section 6).
5Remove the brake wheel cylinder, as
described in Section 12.
6Using a screwdriver, prise out the lockplate
that secures the handbrake cable in the
backplate.
7Unscrew the four securing bolts, and
withdraw the stub axle and backplate.
Refitting
8Refitting is a reversal of removal,
remembering the following points.
9Coat the rear face of the stub axle flange
with a little lithium-based grease.
10Tighten the brake backplate/stub axle
securing bolts to the specified torque, in the
three stages given in the Specifications.
11Refit the brake wheel cylinder, as
described in Section 12.
12Refit the brake shoes, as described in
Section 6.
13Refit the rear hub, as described in
Chapter 10.
14Refit the brake drum with reference to
Section 11.
15Before refitting the roadwheel and
lowering the vehicle to the ground, check and
if necessary adjust the handbrake, as
described in Section 26.
Models with rear disc brakes
(SOHC models)
Removal
16Proceed as described in paragraphs 1
to 7.
17Remove the rear hub/disc, (Chapter 10).
18Remove the handbrake shoes, (Section 7).
19Unscrew the four securing bolts, and
withdraw the stub axle and lockplate.
Refitting
20Refitting is a reversal of removal,
remembering the following points.
21Coat the rear face of the stub axle flange
with a little lithium-based grease.
22Tighten the brake backplate/stub axle
securing bolts to the specified torque, in the
three stages given in the Specifications.
23Refit the handbrake shoes, as described
in Section 7.
24Refit the rear hub/disc, (Chapter 10).
25Before refitting the roadwheel and
lowering the vehicle to the ground, check and
if necessary adjust the handbrake, as
described in Section 26.
DOHC models
Removal
26Proceed as described in paragraphs 1
to 7.
27Remove the brake disc (Section 10).
28Remove the rear hub, (Chapter 10).
29Remove the handbrake shoes, (Section 7).
30Using a splined key, unscrew the four
securing bolts and withdraw the backplate.
Refitting
31Refitting is a reversal of removal,
remembering the following points.
32Refit the handbrake shoes, (Section 7).
33Refit the rear hub, (Chapter 10).
34Refit the brake disc (Section 10).
35Before refitting the roadwheel and
lowering the vehicle to the ground, check and
if necessary adjust the handbrake, as
described in Section 26.
9•12Braking system
12.13A Exploded view of a rear brake
wheel cylinder
1 Dust cap
2 Bleed screw
3 Cylinder body
4 Dust seal5 Piston
6 Piston seal
7 Spring
12.13B Modified rear wheel cylinders - 1992-on models
Page 221 of 525

23Cylinder head - inspection
and renovation
4
Note: Refer to a dealer for advice before
attempting to carry out valve grinding or valve
seat reciting operations, as these operations
may not be possible for the DIY mechanic.
This is due to the fitment of hardened valve
seats for use with unleaded petrol
Inspection
1Remember that the cylinder head is of light
alloy construction and is easily damaged, use
a blunt scraper or rotary wire brush to clean all
traces of carbon deposits from the
combustion spaces and the ports. The valve
stems and valve guides should also be freed
from any carbon deposits. Wash the
combustion spaces and ports down with
paraffin and scrape the cylinder head surface
free of any foreign matter with the side of a
steel rule, or a similar article.
2If the engine is installed in the car, clean the
pistons and the top of the cylinder bores. If
the pistons are still in the block, it is essential
that great care is taken to ensure that no
carbon gets into the cylinder bores. This could
scratch the cylinder walls or cause damage to
the pistons and rings. To ensure this does not
happen, first turn the crankshaft so that two of
the pistons are at the top of their bores. Insert
rag into the other two bores or seal them off
with paper and masking tape. The waterways
should also be covered with small pieces of
masking tape, to prevent particles of carbon
entering the cooling system and damaging the
coolant pump.
3Press a little grease into the gap between
the cylinder walls and the two pistons that are
to be worked on. With a blunt scraper,
carefully scrape away the carbon from the
piston crown, taking great care not to scratch
the aluminium. Also scrape away the carbon
from the surrounding lip of the cylinder wall.
When all carbon has been removed, scrape
away the grease that will now be
contaminated with carbon particles, taking
care not to press any into the bores. To assist
prevention of carbon build-up, the piston
crown can be polished with a metal polish.
Remove the rags or masking tape from the
other two cylinders, and turn the crankshaft
so that the two pistons that were at thebottom are now at the top. Place rag or
masking tape in the cylinders that have been
decarbonised, and continue as just described.
4Examine the heads of the valves for pitting
and burning, especially the heads of the
exhaust valves. The valve seatings should be
examined at the same time. If the pitting on
the valve and seat is very slight, the marks
can be removed by grinding the seats and
valves together with coarse, and then fine,
valve grinding paste.
5Where bad pitting has occurred to the valve
seats, it will be necessary to recut them and fit
new valves. This latter job should be entrusted
to the local dealer or engineering works. In
practice it is very seldom that the seats are so
badly worn. Normally it is the valve that is too
badly worn for refitting, and the owner can
easily buy a new set of valves and match
them to the seats by valve grinding.
Renovation
6Valve grinding is carried out as follows.
Smear a trace of coarse carborundum paste
on the seat face and apply a suction grinder
tool to the valve head. With a semi-rotary
motion, grind the valve head to its seat, lifting
the valve occasionally to redistribute the
grinding paste. When a dull matt even surface
is produced on both the valve seat and the
valve, wipe off the paste and repeat the
process with fine carborundum paste, lifting
and turning the valve to redistribute the paste
as before. A light spring placed under the
valve head will greatly ease this operation.
When a smooth unbroken ring of light grey
matt finish is produced, on both valve and
valve seat faces, the grinding operation is
complete. Carefully clean away every trace of
grinding compound, taking great care to leave
none in the ports or in the valve guides. Clean
the valves and valve seats with a
paraffin-soaked rag, then with a clean rag,
and finally, if an air line is available, blow the
valves, valve guides and valve ports clean.
7Check that all valve springs are intact. If any
one is broken, all should be renewed. Check
the free height of the springs against new
ones. If some springs are not long enough,
replace them all. Springs suffer from fatigue
and it is a good idea to renew them even if
they look serviceable. 8The cylinder head can be checked for
warping either by placing it on a piece of plate
glass or using a straight-edge and feeler
blades. If there is any doubt or if its block face
is corroded, have it re-faced by your dealer or
motor engineering works.
9On 1.8 and 2.0 litre, always renew the
sealing ring between the cylinder head and
the thermostat housing when the head is
removed for overhaul (see illustration).
Reference to Chapter 21 will show that a
considerable amount of work is involved if it is
wished to renew the sealing ring with the
cylinder head installed.
10If the oil pressure regulating valve in the
cylinder head is to be renewed, access is
gained through the circular plug covering the
end of the valve (see illustration). The old
valve must be crushed, then its remains
extracted, and a thread (M10) cut in the valve
seat to allow removal using a bolt. A new
valve and plug can then be driven into
position. In view of the intricacies of this
operation, it is probably best to have the valve
renewed by a Vauxhall dealer if necessary.
24Hydraulic valve lifters -
inspection
4
Inspection
1On engines that have covered a high
mileage, or for which the service history
(particularly oil changes) is suspect, it is
possible for the valve lifters to suffer internal
contamination. In extreme cases this may
result in increased engine top end noise and
wear. To minimise the possibility of problems
occurring later in the life of the engine, it is
advisable to dismantle and clean the hydraulic
valve lifters as follows whenever the cylinder
head is overhauled. Note that no spare parts
are available for the valve lifters, and if any of
the components are unserviceable, the
complete assembly must be renewed (see
illustration).
2With the cylinder head removed and
dismantled as described in Sections 21 and
23, first inspect the valve lifter bores in the
2A•24SOHC engine procedures
23.10 Oil pressure regulating valve (1) and
plug (2) - 2.0 litre engine23.9 Renewing the thermostat housing
sealing ring - 2.0 litre engine
Warning: The exhaust valves
fitted to 20 XEJ and C 20 XE
(DOHC) models are fitted with
sodium to improve their heat
transfer. Sodium is a highly reactive
metal, which will ignite or explode
spontaneously on contact with water
(including water vapour in the air). These
must NOT be disposed of with ordinary
scrap. Seek advice from a Vauxhall dealer
or your Local Authority, if the valves are to
be disposed of.
Page 231 of 525

5Note that the rubber plug located next to
the bellhousing flange on the cylinder block
covers the aperture for the installation of a
diagnostic TDC sensor. The sensor, when
connected to a monitoring unit, indicates TDC
from the position of the pins set into the
crankshaft balance weight.
37Examination and renovation
-general
4
General
1With the engine completely stripped, clean all
components and examine them for wear. Each
component should be checked, and where
necessary renewed or renovated, as described
in the relevant Sections of this Chapter.
2Renew main and big-end bearing shells as
a matter of course, unless it is known that
they have had little wear, and are in perfect
condition.
3If in doubt whether to renew a component
that is still just serviceable, consider the time
and effort that will be incurred should the
component fail at an early date after rebuild.
Obviously, the age and expected life of the
vehicle must influence the standards applied.4Gaskets, oil seals and O-rings must all be
renewed as a matter of routine. Flywheel,
cylinder head, and main and big-end bearing
cap bolts must be renewed, because of the
high stress to which they are subjected.
5Renew the engine core plugs while they are
easily accessible, if they show signs of
leakage. Knock out the old plugs with a
hammer and chisel or punch. Clean the plug
seats, smear the new plugs with sealing
compound, and tap them squarely into
position.
38Initial start-up after major
overhaul or repair
2
1Make a final check to ensure that
everything has been reconnected to the
engine, and that no rags or tools have been
left in the engine compartment.
2Check that oil and coolant levels are
correct.
3Start the engine. This may take a little longer
than usual, as fuel is pumped to the engine.
4Check that the oil pressure warning lamp
goes out when the engine starts. This may
take a few seconds as the new oil filter fills
with oil.5Run the engine at a fast tickover, and check
for leaks of oil, fuel and coolant. If a new
camshaft has been fitted, pay careful
attention to the running-in procedure given in
Section 18, paragraphs 17 and 18. Where
applicable, check the power steering and/or
automatic transmission fluid cooler unions for
leakage. Some smoke and odd smells may be
experienced, as assembly lubricants and
sealers burn off the various components.
6Bring the engine to normal operating
temperature. Check the ignition timing, idle
speed and the mixture (where applicable), as
described in Chapter 4A or 4B.
7Allow the engine to cool, then recheck the
oil and coolant levels. Top-up if necessary
8If new bearings, pistons, etc., have been
fitted, the engine should be run-in at reduced
speeds and loads for the first 500 miles (800
km) or so. It is beneficial to change the engine
oil and filter after this mileage.
2A•34SOHC engine procedures
Page 234 of 525

level in the expansion tank, and top-up if
necessary. Note that the system must be cold
before an accurate level is indicated in the
expansion tank. If the expansion tank cap is
removed while the engine is still warm, cover
the cap with a thick cloth and unscrew the
cap slowly, to gradually relieve the system
pressure. Take care to avoid scalding by
steam or coolant escaping from the
pressurised system.
9On DOHC models, refit the engine
undershield on completion.
5Coolant mixture -general
1It is important to use an antifreeze mixture
in the cooling system all year round, to
prevent corrosion of the alloy engine
components. The coolant mixture should be
made up from clean, preferably soft, tap
water, and a good quality antifreeze
containing corrosion inhibitor. Ensure that the
antifreeze is ethylene glycol based, as the
cheaper methanol based types evaporate
over a period of time.
2The proportions of water and antifreeze
used will depend on the degree of protection
required. A coolant mixture containing 25%
antifreeze should be regarded as the
minimum strength required to maintain good
anti-corrosion properties. Details of the
degree of protection provided against freezing
will be supplied with the antifreeze by the
manufacturers. For absolute protection, use a
50% antifreeze mixture.
3The coolant mixture should be renewed
every two years, as the corrosion inhibitors
will deteriorate with time.
4Before filling the system with fresh coolant,
drain and flush the system, as described in
Sections 2 and 3, and check that all hoses are
secure and that the clips are tight. Antifreeze
has a searching action, and will leak morerapidly than plain water.
5Refill the system as described in Section 4.
All future topping-up should be carried out
using a coolant mixture of the same
proportions as that used to initially fill the
system.
6Do not use antifreeze in the windscreen
wash system, as it will attack the vehicle
paintwork. Note that antifreeze is poisonous,
and must be handled with due care.
6Radiator (manual
transmission) -removal and
refitting
3
Removal
1The radiator can be removed complete with
the coolant fan and shroud if there is no need
to disturb the fan. If desired, the fan and its
shroud can be removed from the radiator,
with reference to Section 12.
2Drain the cooling system, as described in
Section 2.
3Disconnect the radiator top hose and the
expansion tank at the radiator.
4Disconnect the battery negative lead, then
disconnect the wiring from the cooling fan
switch, located at the bottom right-hand side
of the radiator.5Disconnect the cooling fan wiring
connector, noting its location for use when
refitting.
6Compress and remove the two radiator
securing clips, located at the top corners of
the radiator (see illustration).
7Pull the top of the radiator back towards the
engine to free it from the top mountings, then
lift the radiator to disengage the lower
securing lugs. Move the radiator clear of the
vehicle, taking care not to damage the cooling
fins (see illustrations).
Refitting
8The radiator can be inspected and cleaned
as described in Section 8.
9Refitting is a reversal of removal, bearing in
mind the following points.
10Ensure that the radiator rubber mountings
are in good condition and renew if necessary,
and ensure that the lower securing lugs
engage correctly as the radiator is refitted.
11Refill the cooling system, (Section 4).
7Radiator (automatic
transmission) -removal and
refitting
3
Removal
1On models with automatic transmission,
the radiator left-hand side tank incorporates a
heat exchanger to cool the transmission fluid.
It is connected to the transmission by a pair of
flexible hoses, with a metal pipe at each end.
2When removing the radiator, either clamp
the transmission fluid cooler flexible hoses, or
slacken their clamps, work them off their
unions and swiftly plug or cap each hose end
and union to minimise the loss of fluid and to
prevent the entry of dirt.
Refitting
3On refitting, reverse the removal procedure
and do not forget to check the transmission
fluid level, topping-up as necessary to replace
the lost fluid, as described in Chapter 7B.
Cooling, heating and ventilation systems 3•3
6.7B Withdrawing the radiator -
2.0 litre SOHC model6.7A Radiator freed from top right-hand mounting -
1.6 litre model
6.6 Compressing a radiator securing clip -
2.0 litre SOHC model
3