1982 CHEVROLET CAMARO wheel torque
[x] Cancel search: wheel torquePage 82 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 82
Avoid inhaling any dust from
any brake surface! When cleaning brake surfaces,
use a commercially available brake cleaning fluid.
1. Remove
2/3 of the brake fluid from the mast er cylinder. Raise the vehicle and
remove the wheel.
2. Place a C-clamp across the caliper, positioned on the brake pads. Tighten it
until the piston is forced into its bore.
3. Remove the C-clamp. Remove the bolt holding the brake hose to the caliper.
4. Remove the Allen head caliper mounting bolts. Inspect them for corrosion
and replace them if necessary. Remove the caliper.
To install:
5. Position the caliper with the brake pad installed and install Allen head caliper
mounting bolts. Mounting bo lt torque is 21-35 ft. lbs. (28-47 Nm.) for the
caliper.
6. Install the bolt holding the brake hos e to the caliper and tighten to 18-30 ft.
lbs. (24-40 Nm.).
7. Fill the master cylinder with brake fluid.
8. Install the wheels and lower the vehicle.
CAUTION - Before moving the vehicle, pump the brakes several times to seat
the brake pad against the rotor
OVERHAUL
Some vehicles may be equipped dual piston calipers. The procedure to
overhaul the caliper is e ssentially the same with t he exception of multiple
pistons, O-rings and dust boots.
1. Remove the caliper from the ve hicle and place on a clean workbench.
CAUTION - NEVER place your finger s in front of the pistons in an attempt to
catch or protect the pistons when applying compressed air. This could result in
personal injury!
Depending upon the vehicle, there are two different ways to remove the piston
from the caliper. Refer to the brake pad replacement procedure to make sure
you have the correct procedure for your vehicle.
2. The first method is as follows: a. Stuff a shop towel or a block of wood into the caliper to catch the piston.
b. Remove the caliper piston using co mpressed air applied into the caliper
inlet hole. Inspect the piston for scor ing, nicks, corrosion and/or worn or
damaged chrome plating. The piston mu st be replaced if any of these
conditions are found.
Page 102 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 102
CAUTION
- Brake shoes may contain asbest os, which has been determined to
be a cancer causing agent. Never clean the brake surfaces with compressed
air! Avoid inhaling any dust from any brake surface! When cleaning brake
surfaces, use a commercially available brake cleaning fluid.
1. Raise and support the car. Remove t he wheel. Remove the brake shoes by
following the Brake Shoe R eplacement procedure.
2. Remove dirt from ar ound the wheel cylinder inle t and pilot. Disconnect the
inlet tube.
3. Using 2 awls,
1/8 in. (3mm) in diameter, or J29839, remove the wheel
cylinder retainer. Insert the awls in to the access slots between the wheel
cylinder pilot and retainer. Simultaneous ly, bend both tabs away from each
other. Remove the wheel cylinder.
To install:
4. Place wheel cylinder into position and place a block of wood between it and
the axle flange. Install a new retainer over the end of the wheel cylinder.
Using a 1
1/8 in. 12-point socket with an extensi on, drive the new retainer into
position.
5. Connect the inlet tube and torque 120-280 inch lbs. (13.6-20 Nm). Complete
installation by reversing the remova l procedure. Bleed the brakes.
OVERHAUL
Wheel cylinder overhaul kits may be available, but often at little or no savings
over a reconditioned wheel cylinder. It often makes sense with these
components to substitute a new or re conditioned part instead of attempting an
overhaul.
If no replacement is availabl e, or you would prefer to overhaul your wheel
cylinders, the following procedure may be used. When rebuilding and installing
wheel cylinders, avoid getting any cont aminants into the system. Always use
clean, new, high quality brake fluid. If di rty or improper fluid has been used, it
will be necessary to drain the entire syst em, flush the system with proper brake
fluid, replace all rubber components , then refill and bleed the system.
1. Remove the wheel cylinder from the vehicle and place on a clean
workbench.
2. First remove and discard the old r ubber boots, then withdraw the pistons.
Piston cylinders are equipped with seals and a spring assembly, all located
behind the pistons in the cylinder bore.
Page 113 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 113
1. Remove 2/3 of the brake fluid from the ma
ster cylinder. Raise the car.
Remove the wheel. Reinstall a wheel nut, with the flat side toward the rotor,
to hold the rotor in place.
2. Loosen the parking brake cable at the equalizer. At the caliper, remove the
parking brake cable, damper and spring from the lever.
3. Hold the parking brake lever and re move the lock nut. Remove the lever,
seal and anti-friction washer.
4. Position a C-clamp ov er the caliper and force the piston into its bore.
Remove the C-clamp. Rein stall the lever, seal and nut to the caliper.
5. Loosen the brake tube nut and disc onnect the brake tube from the caliper.
Plug the tube to prevent t he loss of brake fluid.
At the right rear wheel, it may be necessary to remove the rear bolt from the
lower control arm to allow the lower caliper mounting bolt to be removed.
6. Remove the mounting bolts using a
3/8 in. Allen head socket. Remove the
caliper and inspect the mounting bolts for corrosion. If necessary, replace
the mounting bolts.
To install:
7. Place the caliper onto the rotor and install the m ounting bolts. Torque the
mounting bolts to 30-45 ft . lbs. (40.7-61 Nm).
8. Install a new anti-friction washer and lubricate the lever with silicone brake
lube. Install the lever on the actuator with the lever pointing down. Rotate the
lever toward the front of the car and hol d while installing the nut. Torque the
nut to 30-40 ft. lbs. (40.7-54.2 Nm), then rotate the lever back against the
stop on the caliper.
9. Install damper and spring. Connect the parking brake cable. Tighten the
cable at the equalizer until the lever starts to move off the stop on the
caliper, then loosen the adjustment unt il the lever moves back against the
stop.
10. Remove the nut holding the rotor in place and install the wheel. Lower the
car and fill the master cylin der with brake fluid.
1989-92 MODELS
1. Raise and safely support the vehicle.
2. Loosen the parking brake cable at the equalizer.
3. Remove the wheel and tire assembly. Inst all 2 wheel nuts to retain the rotor.
4. Remove the bolt, inlet fitting and was hers from the caliper housing. Plug the
holes in the caliper housing and inlet fitting.
5. Remove the caliper lever return spri ng only if it is defective. Discard the
spring if the coils are opened.
6. Disconnect the parking brake cable from the caliper lever and caliper
bracket.
7. Remove the 2 caliper guide pin holes.
8. Remove the caliper housing from the rotor and mounting bracket.
To install:
Page 287 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 287
DRIVE TRAIN
MANUAL TRANSMISSION
UNDERSTANDING THE MANUAL TRANSMISSION
Because of the way an internal combus tion engine breathes, it can produce
torque (or twisting force) only withi n a narrow speed range. Most overhead
valve pushrod engines must turn at about 2500 rpm to produce their peak
torque. Often by 4500 rpm, they are prod ucing so little torque that continued
increases in engine speed produce no power increases.
The torque peak on overhead camshaft engines is, generally, much higher, but
much narrower.
The manual transmission and clutch are employed to vary the relationship
between engine RPM and the speed of the w heels so that adequate power can
be produced under all circumst ances. The clutch allows engine torque to be
applied to the transmission input shaft gradually, due to mechanical slippage.
The vehicle can, consequently, be star ted smoothly from a full stop.
The transmission changes the ratio between the rotating speeds of the engine
and the wheels by the use of gears. 4-speed or 5-speed transmissions are most
common. The lower gears al low full engine power to be applied to the rear
wheels during acceleration at low speeds.
The clutch driveplate is a thin disc, the center of which is splined to the
transmission input shaft. Both sides of the disc are covered with a layer of
material which is similar to brake li ning and which is capable of allowing
slippage without roughness or excessive noise.
The clutch cover is bolted to the engine flywheel and incorporates a diaphragm
spring which provides the pressure to engage the clutch. The cover also houses
the pressure plate. When the clutch pe dal is released, the driven disc is
sandwiched between the pressu re plate and the smooth surface of the flywheel,
thus forcing the disc to turn at th e same speed as the engine crankshaft.
The transmission contains a mainshaft which passes all the way through the
transmission, from the clutch to the dr iveshaft. This shaft is separated at one
point, so that front and rear portions can turn at different speeds.
Power is transmitted by a countershaft in the lower gears and reverse. The
gears of the countershaft mesh with gear s on the mainshaft, allowing power to
be carried from one to the other. Countershaft gears are often integral with that
shaft, while several of the mainshaft gea rs can either rotate independently of
the shaft or be locked to it. Shifting from one gear to the next causes one of the
gears to be freed from rotating with the shaft and locks another to it. Gears are
locked and unlocked by internal dog clutc hes which slide between the center of
the gear and the shaft. The forward gears us ually employ synchronizers; friction
Page 294 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 294
25. Connect the negative battery cable at the battery.
CLUTCH
UNDERSTANDING THE CLUTCH
The purpose of the clutch is to disconnect and connect engine power at the
transmission. A vehicle at rest requires a lot of engine torque to get all that
weight moving. An internal combustion engine does not develop a high starting
torque (unlike steam engines) so it must be allowed to operate without any load
until it builds up enough torque to move the vehicle. To a point, torque
increases with engine rpm. The clutch a llows the engine to build up torque by
physically disconnecting t he engine from the transmission, relieving the engine
of any load or resistance.
The transfer of engine power to the tr ansmission (the load) must be smooth and
gradual; if it weren't, driv e line components would wear out or break quickly.
This gradual power transfer is made possi ble by gradually releasing the clutch
pedal. The clutch disc and pressure plat e are the connecting link between the
engine and transmission. When the clutch pedal is released, the disc and plate
contact each other (the clutch is engag ed) physically joining the engine and
transmission. When the pedal is pushed in, the disc and plate separate (the
clutch is disengaged) disconnecting the engine from the transmission.
Most clutch assemblies consists of t he flywheel, the clutch disc, the clutch
pressure plate, the throw out bearing and fork, the actuating linkage and the
pedal. The flywheel and clutch pressure plate (driving members) are connected
to the engine crankshaft and rotate with it. The clutch disc is located between
the flywheel and pressure plate, and is splined to the transmission shaft. A
driving member is one that is attached to the engine and transfers engine power
to a driven member (clutch disc) on t he transmission shaft. A driving member
(pressure plate) rotates (drives) a driv en member (clutch disc) on contact and,
in so doing, turns the transmission shaft.
There is a circular di aphragm spring within th e pressure plate cover
(transmission side). In a relaxed state (w hen the clutch pedal is fully released)
this spring is convex; that is, it is dished outward toward the transmission.
Pushing in the clutch peda l actuates the attached linkage. Connected to the
other end of this is the throw out fork, which hold the throw out bearing. When
the clutch pedal is depre ssed, the clutch linkage pushes the fork and bearing
forward to contact the diaphragm spring of the pressure plate. The outer edges
of the spring are secured to the pressure plate and are pivoted on rings so that
when the center of the spring is compre ssed by the throw out bearing, the outer
edges bow outward and, by so doing, pu ll the pressure plate in the same
direction - away from the clutch disc. This action se parates the disc from the
plate, disengaging the clutch and allowing the transmission to be shifted into
another gear. A coil type clutch return sp ring attached to the clutch pedal arm
permits full release of the pedal. Releasing the pedal pulls the throw out bearing
away from the diaphragm spring resulting in a reversal of spring position. As
bearing pressure is gradually released from the spring center, the outer edges
Page 304 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 304
Never release a depressed clutch pedal
with the bleeder screw open or air will
be drawn into the system.
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION
UNDERSTANDING AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSIONS
The automatic transmission allows eng ine torque and power to be transmitted
to the rear wheels within a narrow range of engine operating speeds. It will
allow the engine to turn fast enough to produce plenty of power and torque at
very low speeds, while keeping it at a s ensible rpm at high vehicle speeds (and
it does this job without driv er assistance). The transmission uses a light fluid as
the medium for the transmission of power. This fluid also works in the operation
of various hydraulic control circui ts and as a lubricant. Because the
transmission fluid performs all of thes e functions, trouble within the unit can
easily travel from one part to another. For this reason, and because of the
complexity and unusual oper ating principles of the transmission, a very sound
understanding of the basic principles of operation will simplify troubleshooting.
TORQUE CONVERTER
The torque converter replaces the convent ional clutch. It has three functions:
1. It allows the engine to idle with t he vehicle at a standstill, even with the
transmission in gear.
2. It allows the transmission to shi ft from range-to-range smoothly, without
requiring that the driver close the throttle during the shift.
3. It multiplies engine torque to an incr easing extent as vehicle speed drops
and throttle opening is increased. This has the effect of making the
transmission more responsive and redu ces the amount of shifting
required.
The torque converter is a metal case which is shaped like a sphere that
has been flattened on opposite sides. It is bolted to the rear end of the
engine's crankshaft. Generally, the ent ire metal case rotates at engine
speed and serves as the engine's flywheel.
The case contains three sets of bl ades. One set is attached directly to
the case. This set forms the torus or pump. Another set is directly
connected to the output shaft, and forms the turbine. The third set is
mounted on a hub which, in turn, is mounted on a stationary shaft
through a one-way clutch. This third set is known as the stator.
A pump, which is driven by the conv erter hub at engine speed, keeps the
torque converter full of transmission fluid at all times. Fluid flows
continuously through the unit to provide cooling.
Under low speed acceleration, the tor que converter functions as follows:
Page 318 of 875
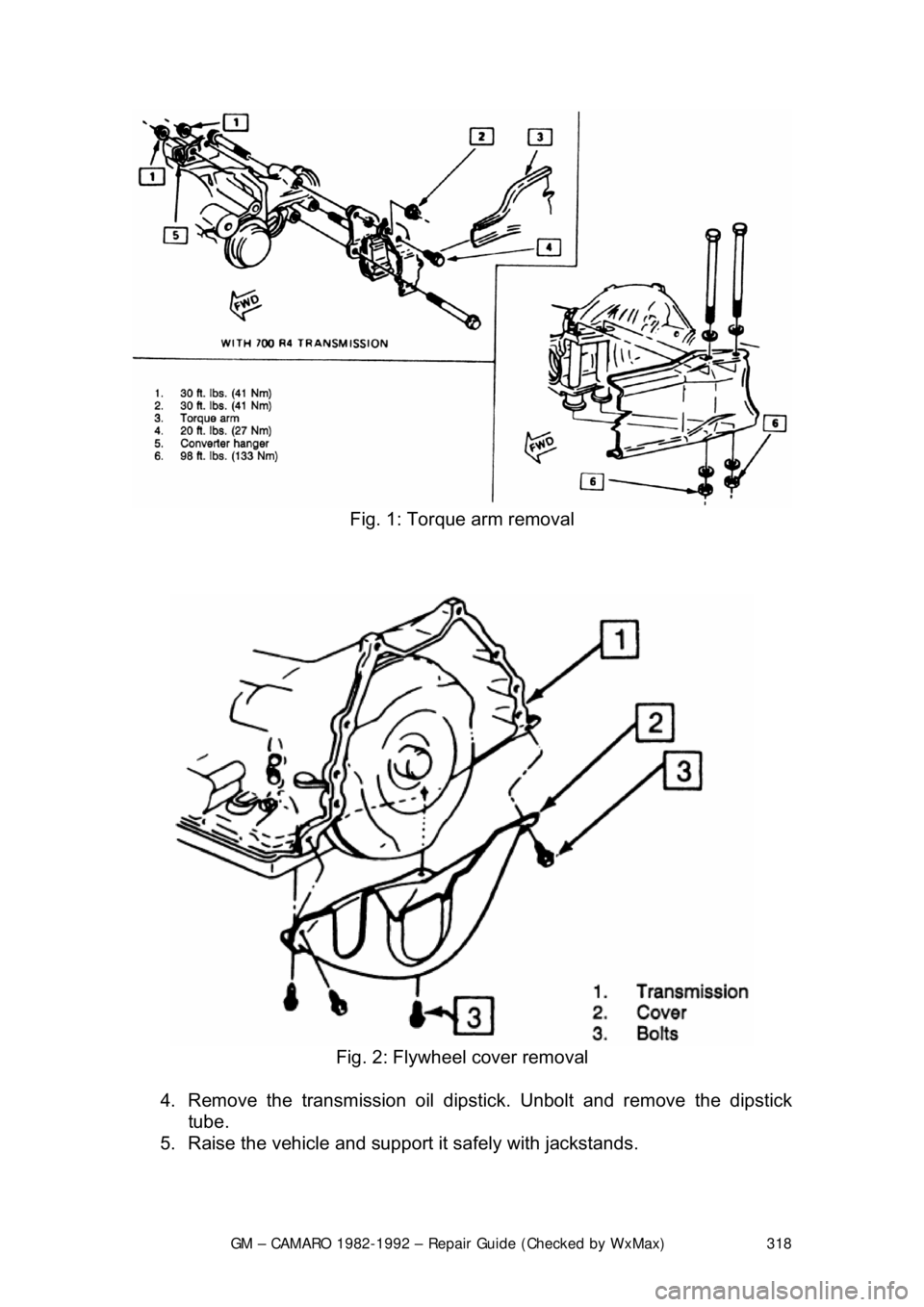
GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 318
Fig. 1: Torque arm removal
Fig. 2: Flywheel cover removal
4. Remove the transmission oil dipsti ck. Unbolt and remove the dipstick
tube.
5. Raise the vehicle and support it safely with jackstands.
Page 321 of 875
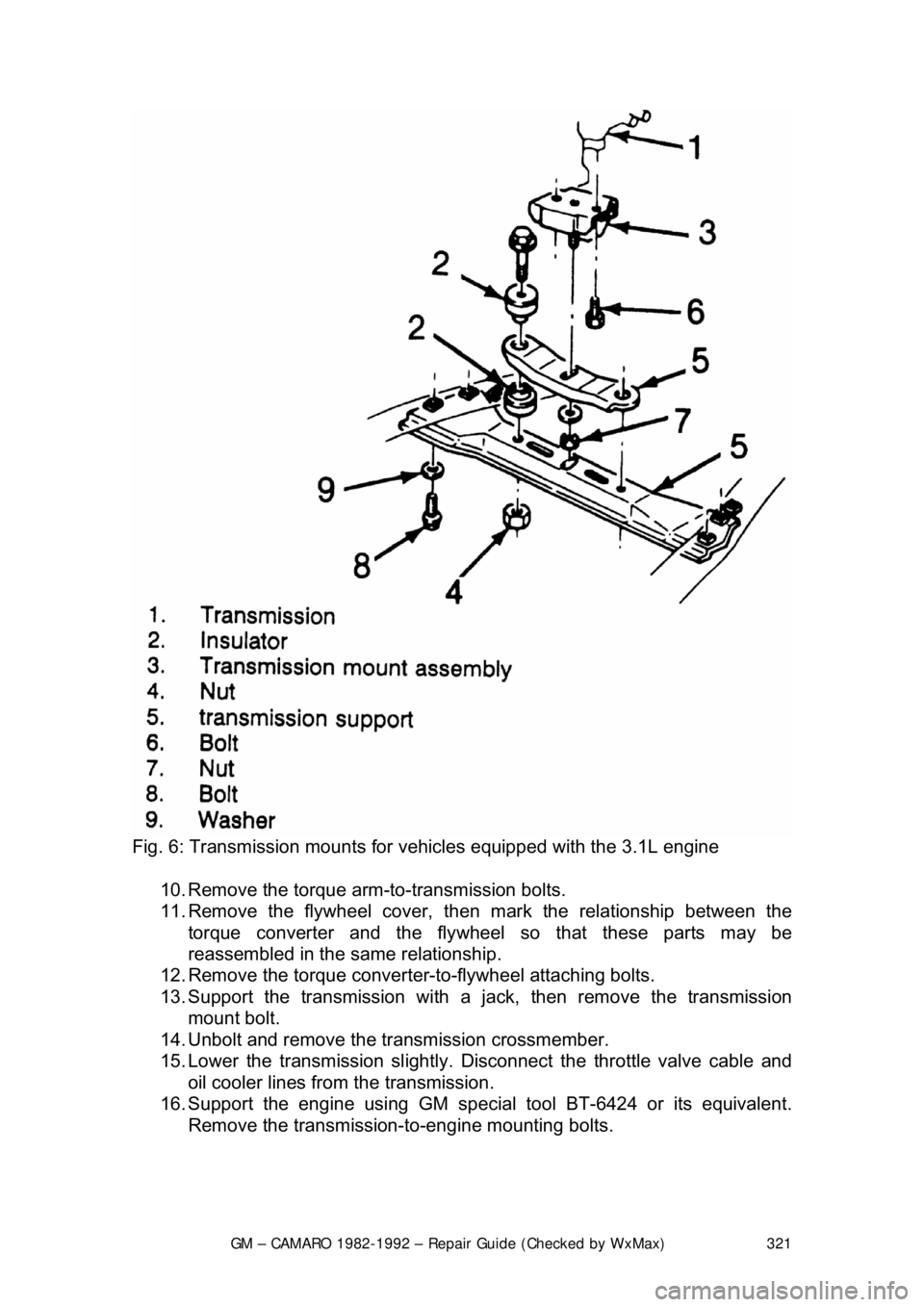
GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 321
Fig. 6: Transmission mounts for vehi cles equipped with the 3.1L engine
10. Remove the torque arm-to-transmission bolts.
11. Remove the flywheel cover, t hen mark the relationship between the
torque converter and the flywheel so that these parts may be
reassembled in the same relationship.
12. Remove the torque converter-t o-flywheel attaching bolts.
13. Support the transmission with a ja ck, then remove the transmission
mount bolt.
14. Unbolt and remove the transmission crossmember.
15. Lower the transmission slightly. Disco nnect the throttle valve cable and
oil cooler lines from the transmission.
16. Support the engine using GM specia l tool BT-6424 or its equivalent.
Remove the transmission- to-engine mounting bolts.