1982 CHEVROLET CAMARO automatic transmission
[x] Cancel search: automatic transmissionPage 290 of 875
GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 290
4. Remove the switch attaching bo
lt and remove the clutch switch.
5. Installation is the reverse of t he removal procedure. The switch will
automatically adjust when depres sed for the first time.
SPEED SENSOR
REMOVAL & INSTALLATION
5-SPEED TRANSMISSION 1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. Disconnect the electrical connector.
3. Remove the attaching bolt and remove the sensor.
4. Installation is the reverse of the removal procedure. The bolt torque is 89
inch lbs. (10 Nm).
SHIFT HANDLE
REMOVAL & INSTALLATION 1. Disconnect the negative battery cable.
2. Raise and safely support the vehicle.
3. Disconnect the shift rods from the control lever.
4. Lower the vehicle. Remove the shifter knob.
5. Remove the parking lever grip.
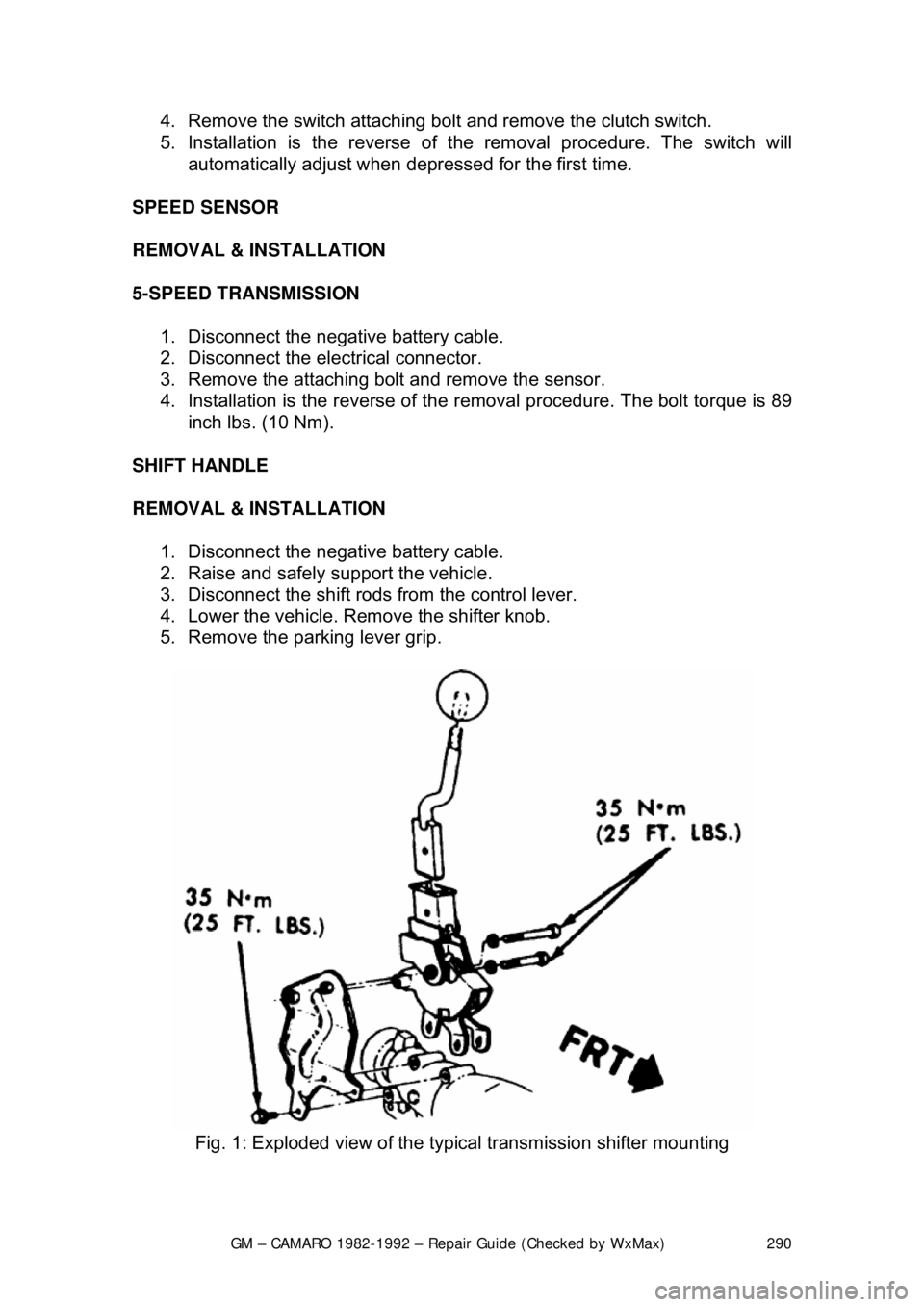
Fig. 1: Exploded view of the typi cal transmission shifter mounting
Page 304 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 304
Never release a depressed clutch pedal
with the bleeder screw open or air will
be drawn into the system.
AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION
UNDERSTANDING AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSIONS
The automatic transmission allows eng ine torque and power to be transmitted
to the rear wheels within a narrow range of engine operating speeds. It will
allow the engine to turn fast enough to produce plenty of power and torque at
very low speeds, while keeping it at a s ensible rpm at high vehicle speeds (and
it does this job without driv er assistance). The transmission uses a light fluid as
the medium for the transmission of power. This fluid also works in the operation
of various hydraulic control circui ts and as a lubricant. Because the
transmission fluid performs all of thes e functions, trouble within the unit can
easily travel from one part to another. For this reason, and because of the
complexity and unusual oper ating principles of the transmission, a very sound
understanding of the basic principles of operation will simplify troubleshooting.
TORQUE CONVERTER
The torque converter replaces the convent ional clutch. It has three functions:
1. It allows the engine to idle with t he vehicle at a standstill, even with the
transmission in gear.
2. It allows the transmission to shi ft from range-to-range smoothly, without
requiring that the driver close the throttle during the shift.
3. It multiplies engine torque to an incr easing extent as vehicle speed drops
and throttle opening is increased. This has the effect of making the
transmission more responsive and redu ces the amount of shifting
required.
The torque converter is a metal case which is shaped like a sphere that
has been flattened on opposite sides. It is bolted to the rear end of the
engine's crankshaft. Generally, the ent ire metal case rotates at engine
speed and serves as the engine's flywheel.
The case contains three sets of bl ades. One set is attached directly to
the case. This set forms the torus or pump. Another set is directly
connected to the output shaft, and forms the turbine. The third set is
mounted on a hub which, in turn, is mounted on a stationary shaft
through a one-way clutch. This third set is known as the stator.
A pump, which is driven by the conv erter hub at engine speed, keeps the
torque converter full of transmission fluid at all times. Fluid flows
continuously through the unit to provide cooling.
Under low speed acceleration, the tor que converter functions as follows:
Page 308 of 875
GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 308
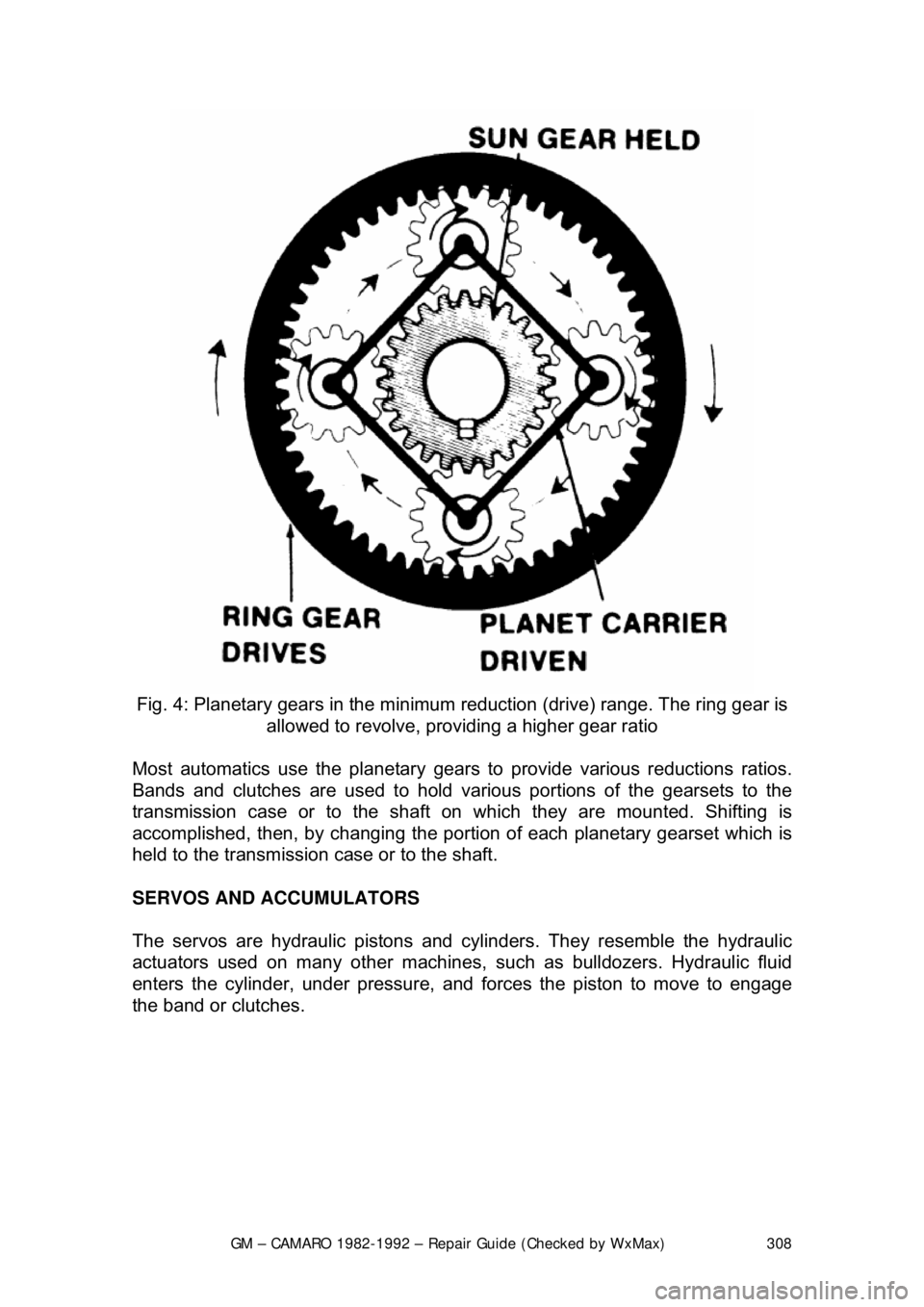
Fig. 4: Planetary gears in the minimum reduction (drive) range. The ring gear is
allowed to revolve, providing a higher gear ratio
Most automatics use the pl anetary gears to provide various reductions ratios.
Bands and clutches are used to hold va rious portions of the gearsets to the
transmission case or to the shaft on which they are mounted. Shifting is\
accomplished, then, by c hanging the portion of each planetary gearset which is
held to the transmission case or to the shaft.
SERVOS AND ACCUMULATORS
The servos are hydraulic pistons and cylinders. They resemble the hydrau\
lic
actuators used on many other machines, such as bulldozers. Hydraulic fluid
enters the cylinder, under pressure, and fo rces the piston to move to engage
the band or clutches.
Page 309 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 309
Fig. 5: Servos, operated by pressure, ar e used to apply or release the bands, to
either hold the ring gear or allow it to rotate
The accumulators are used to cushi on the engagement of the servos. The
transmission fluid must pass through the ac cumulator on the way to the servo.
The accumulator housing contains a thin piston which is sprung away from the
discharge passage of the accumulato r. When fluid passes through the
accumulator on the way to the servo, it must move the piston against spring
pressure, and this action smooths out the action of the servo.
HYDRAULIC CONTROL SYSTEM
The hydraulic pressure used to operat e the servos comes from the main
transmission oil pump. This fluid is channel ed to the various servos through the
shift valves. There is generally a manual shift valve which is operated by the
transmission selector lever and an automat ic shift valve for each automatic
upshift the transmission provides.
Many new transmissions are electroni cally controlled. On these models,
electrical solenoids are used to better control the hydraulic fluid. Usually, the
solenoids are regulated by an electronic control module.
There are two pressures which affect t he operation of these valves. One is the
governor pressure which is effected by vehicle speed. The other is the
modulator pressure which is effected by intake manifold vacuum or throttle
position. Governor pressure rises wit h an increase in vehicle speed, and
Page 364 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 364
5. Drain the radiator and remove t
he radiator hoses. Disconnect the heater
hoses and the transmission cooler lines.
6. Remove the upper half of the radi ator shroud, if equipped with a manual
transmission. Remove the radiator and fan shroud assembly, if equipped
with an automatic transmission.
7. Disconnect the throttle linkage, includi ng the cruise control detent cable.
8. Remove the air conditioning compressor and lay aside.
Do not disconnect the air conditioning lines.
9. Disconnect the power steering pump and drain the fluid into a suitable
container. Remove the vacuum brake booster line.
10. Remove the distributor cap and spark plug wires.
11. Disconnect the engine electrical connection at the bulkhead connection
and disconnect any necessary vacuum hoses.
12. Working inside the vehicle, re move the right-hand hush panel and
disconnect the ECM harness at the EC M. Raise and safely support the
vehicle. Remove the right fenderwell splash shield and feed the harness
through the fenderwell.
13. Disconnect the exhaust pipes at the exhaust manifolds and remove
exhaust system from the vehicle.
14. Remove the flywheel cover and remo ve the converter bolts, if equipped
with automatic transmission.
15. Disconnect the transmission an d starter wire connections.
16. Remove the bellhousing and t he motor mount through-bolts.
17. Disconnect the clutch fork return spring, if equipped with a manual
transmission. Lower the vehicle.
18. Relieve the fuel system pressu re. Disconnect the fuel lines.
19. Support the transmission with a suit able jack. Attach an engine lifting
device.
20. Remove the engine assembly.
To install: 21. Position the engine assembly in the vehicle.
22. Attach the motor mount to engine br ackets and lower the engine in place.
Remove the engine lifting device and the transmission jack.
23. Raise and support the vehicle safely.
24. Install the motor mount through-bolts and tighten the nuts to specification. Install t he bellhousing bolts and tight en to 35 ft. lbs. (47
Nm).
25. On vehicles with automatic transmissi on, install the converter to flywheel
attaching bolts to 46 ft. lbs. (63 Nm).
26. Install the flywheel splash shield and tighten to 89 inch lbs. (10 Nm).
Install the clutch return spring, if equipped with manual transmission.
27. Connect the starter wires and the fuel lines.
28. Install the exhaust system.
29. Lower the vehicle.
30. Install the power steering pump and the air conditioning compressor.
Page 366 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 366
8. Remove the air conditioning co
mpressor and lay aside. Remove the
power steering pump and lay aside.
Do not disconnect the air conditioning or power steering lines.
9. Remove the vacuum brake booster line.
10. Remove the distributor cap and spark plug wires.
11. Disconnect the necessary elec trical connections and hoses.
12. Raise and safely support the vehicle.
13. Disconnect the exhaust pipes at the exhaust manifolds.
14. Remove the flywheel cover and remove the converter bolts.
15. Disconnect the star ter wire connections.
16. Remove the bellhousing and t he motor mount through-bolts.
17. Lower the vehicle.
18. Relieve the fuel system pressu re. Disconnect the fuel lines.
19. Support the transmission with a suit able jack. Attach an engine lifting
device.
20. Remove the engine assembly.
To install: 21. Position the engine assembly in the vehicle.
22. Attach the motor mount to engine br ackets and lower the engine in place.
Remove the engine lifting device and the transmission jack.
23. Raise and support the vehicle safely.
24. Install the motor mount through-bolts and tighten the nuts to 50 ft. lbs. (68 Nm). Install the bellhousing bolts and tighten to 35 ft. lbs. (47 Nm).
25. On vehicles with automatic transmissi on, install the converter to flywheel
attaching bolts to 46 ft. lbs. (63 Nm).
26. Install the flywheel splash shield and tighten to 89 inch lbs. (10 Nm).
27. Connect the starter wires and the fuel lines.
28. Install the exhaust pipe on the exhaust manifold.
29. Lower the vehicle.
30. Install the power steering pump and the air conditioning compressor.
31. Connect the necessary wires and hoses.
32. Install the radiator, fan and fan sh roud. Connect the radiator and heater
hoses and the transmission cooler lines.
33. Connect the vacuum brake booster li ne, the throttle linkage and cruise
control cable. Install the distributor cap.
34. Fill the cooling system with the proper type and amount of coolant and
the crankcase with the proper type of oil to the correct level.
35. Install the water pump drive bel t, the air cleaner duct and the hood.
36. Connect the negative battery cable, st art the engine and check for leaks.
Page 368 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 368
23. Remove the AIR/converter bracket
and ground wires from the rear of the
cylinder head.
24. Attach a suitable lifting devic e and remove the engine assembly.
To install: 25. Position the engine assembly in the vehicle.
26. Attach the motor mount to engine brackets and lower the engine into
place.
27. Remove the engine lifting device and the transmission jack.
28. Raise and safely support the vehicle.
29. Install the motor mount through-bolts and tighten to 50 ft. lbs. (68 (Nm).
30. Install the bellhousing bolts and tighten to 35 ft. lbs. (47 Nm).
31. On vehicles with automatic transmissi on, install the converter to flywheel
bolts. Tighten the bolts to 46 ft. lbs. ( 63 Nm). Install the flywheel cover.
32. Connect the starter wires and the fuel lines.
33. Connect the exhaust pipe at the exhaust manifold.
34. Lower the vehicle.
35. Connect the necessary wires and hoses.
36. Install the power steering pump and air conditioning compressor in their
respective brackets.
37. Install the radiator, fan and fan sh roud, radiator hoses and heater hoses.
38. Connect the transmission cooler lines and cooling fan electrical
connectors.
39. Install the distributor.
40. Install the plenum ex tension, if equipped.
41. Fill the cooling system with the proper type and quantity of coolant and
the crankcase with the proper type of oil to the correct level.
42. Install the air cleaner and the hood.
43. Connect the negative battery cable, start the engine, check for leaks and
check timing.
Page 581 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 581
Fig. 1: Coolant temperature sensor. The in take air temperature sensor is similar
in appearance
IDLE AIR CONTROL (IAC) VALVE
OPERATION
Engine idle speeds are controlled by the ECM through the IAC valve mounted
on the throttle body. The ECM sends volt age pulses to the IAC motor windings
causing the IAC motor shaft and pintle to move IN or OUT a given distance
(number of steps) for each pulse (called counts). The movement of the pintle
controls the airflow around the throttle plat e, which in turn, controls engine idle
speed. IAC valve pintle position counts ca n be observed using a scan tool. Zero
counts correspond to a fully closed passage, while 140 counts or more
corresponds to full flow.
Idle speed can be categorized in 2 ways : actual (controlled) idle speed and
minimum idle speed. Contro lled idle speed is obtained by the ECM positioning
the IAC valve pintle. Resulting idle speed is determined by total air fl\
ow
(IAC/passage + PCV + throttle valve + ca librated vacuum leaks). Controlled idle
speed is specified at normal operating c onditions, which consists of engine
coolant at normal operating temper ature, air conditioning compressor OFF,
manual transmission in neutral or automatic transmission in D.
Minimum idle air speed is set at t he factory with a stop screw. This setting
allows a certain amount of air to bypas s the throttle valves regardless of IAC
valve pintle positioning. A co mbination of this air flow and IAC pintle positioning
allows the ECM to control engine idle speed. During normal engine idle
operation, the IAC valve pintle is positioned a calibrated number of steps
(counts) from the seat. No adjustment is required during routine maintenance.
Tampering with the minimum idle speed adjustment may result in premature
failure of the IAC valve or imprope rly controlled engine idle operation.