1982 CHEVROLET CAMARO tire pressure
[x] Cancel search: tire pressurePage 48 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 48
BRAKES
BASIC OPERATING PRINCIPLES
Hydraulic systems are used to actuate t he brakes of all modern automobiles.
The system transports the power required to force the frictional surfaces of the
braking system together from the pedal to the individual brake units at each
wheel. A hydraulic system is used for two reasons.
First, fluid under pressure can be carried to all parts of an automobile by small
pipes and flexible hoses without taking up a significant amount of room or
posing routing problems.
Second, a great mechanical advantage can be given to the brake pedal end of
the system, and the foot pressure requi red to actuate the brakes can be
reduced by making the surface area of t he master cylinder pistons smaller than
that of any of the pistons in t he wheel cylinders or calipers.
The master cylinder consists of a flui d reservoir along with a double cylinder
and piston assembly. Double type master cylinders are designed to separate
the front and rear braking systems hydraulic ally in case of a leak. The master
cylinder coverts mechanical motion from t he pedal into hydraulic pressure within
the lines. This pressure is translated back into mechanical motion at th\
e wheels
by either the wheel cylinder (drum brak es) or the caliper (disc brakes).
Steel lines carry the brake fluid to a po int on the vehicle's frame near each of
the vehicle's wheels. The fluid is then ca rried to the calipers and wheel cylinders
by flexible tubes in order to allow for suspension and steering movements.
In drum brake systems, each wheel cylinde r contains two pistons, one at either
end, which push outward in opposite direct ions and force the brake shoe into
contact with the drum.
In disc brake systems, the cylinders ar e part of the calipers. At least one
cylinder in each caliper is used to fo rce the brake pads against the disc.
All pistons employ some type of seal, us ually made of rubber, to minimize fluid
leakage. A rubber dust boot seals the outer end of the cylinder against dust and
dirt. The boot fits around the outer end of the piston on disc brake calipers, and
around the brake actuating rod on wheel cylinders.
The hydraulic system operates as follows : When at rest, the entire system, from
the piston(s) in the master cylinder to t hose in the wheel cylinders or calipers, is
full of brake fluid. Upon app lication of the brake pedal, fluid trapped in front of
the master cylinder piston(s) is forced through the lines to the wheel cylinders.
Here, it forces the pistons outward, in the case of drum brakes, and inward
toward the disc, in the case of disc brakes. The motion of the pistons is
opposed by return springs mounted outside the cylinders in drum brakes, and
by spring seals, in disc brakes.
Page 50 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 50
DISC BRAKES
Instead of the traditional ex
panding brakes that press out ward against a circular
drum, disc brake systems utilize a disc (rotor) with brake pads positioned on
either side of it. An easily-seen analog y is the hand brake arrangement on a
bicycle. The pads squeeze onto the rim of the bike wheel, slowing its motion.
Automobile disc brakes use the identical principle but apply the braking effort to
a separate disc instead of the wheel.
The disc (rotor) is a casting, usually eq uipped with cooling fins between the two
braking surfaces. This enables air to ci rculate between the braking surfaces
making them less sensitive to heat bui ldup and more resistant to fade. Dirt and
water do not drastically affect braking ac tion since contaminants are thrown off
by the centrifugal action of the rotor or scraped off the by the pads. Also, the
equal clamping action of the two brake pad s tends to ensure uniform, straight
line stops. Disc brakes are inherently se lf-adjusting. There are three general
types of disc brake:
1. A fixed caliper.
2. A floating caliper.
3. A sliding caliper.
The fixed caliper design uses two pistons mounted on either side of the rotor (in
each side of the caliper). The caliper is mounted rigidly and does not move.
The sliding and floating designs are quite similar. In fact, these two types are
often lumped together. In both designs, the pad on the inside of the rotor is
moved into contact with the rotor by hy draulic force. The caliper, which is not
held in a fixed position, moves slightly, bringing the outside pad into contact with
the rotor. There are various methods of attaching floating calipers. Some pivot
at the bottom or top, and some slide on mounting bolts. In any event, the end
result is the same.
DRUM BRAKES
Drum brakes employ two brake shoes mounted on a st ationary backing plate.
These shoes are positioned inside a circul ar drum which rotates with the wheel
assembly. The shoes are held in place by springs. This allows them to slide
toward the drums (when they are applied) while keeping the linings and drums
in alignment. The shoes are actuated by a wheel cylinder which is mounted at
the top of the backing plat e. When the brakes are app lied, hydraulic pressure
forces the wheel cylinder's actuating links outward. Since these links bear
directly against the top of the brake s hoes, the tops of the shoes are then forced
against the inner side of the drum. This action forces the bottoms of the two
shoes to contact the brake drum by rotati ng the entire assembly slightly (known
as servo action). When pressure within the wheel cylinder is relaxed, return
springs pull the shoes back away from the drum.
Most modern drum brakes are designed to self-adjust themselves during
application when the vehicle is moving in reverse. This motion causes both
Page 51 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 51
shoes to rotate very slightly with the
drum, rocking an adjusting lever, thereby
causing rotation of the adjusting scr ew. Some drum brake systems are
designed to self-adjust duri ng application whenever the br akes are applied. This
on-board adjustment system reduces the need for maintenance adjustments
and keeps both the brake function and pedal feel satisfactory.
POWER BOOSTERS
Virtually all modern vehicles use a va cuum assisted power brake system to
multiply the braking force and reduce pedal effort. Since vacuum is always
available when the en gine is operating, the system is simple and efficient. A
vacuum diaphragm is located on the front of the master cylinder and assists the
driver in applying the brakes, reducing both the effort and travel he must put into
moving the brake pedal.
The vacuum diaphragm housing is normally connected to the intake manifold by
a vacuum hose. A check valve is placed at the point where the hose enters the
diaphragm housing, so that during periods of low manifold vacuum brakes
assist will not be lost.
Depressing the brake pedal closes o ff the vacuum source and allows
atmospheric pressure to enter on one side of the diaphragm. This causes the
master cylinder pistons to move and app ly the brakes. When the brake pedal is
released, vacuum is applied to both si des of the diaphragm and springs return
the diaphragm and master cylinder pist ons to the released position.
If the vacuum supply fails, the brake pedal rod will contact the end of the master
cylinder actuator rod and the system will apply the br akes without any power
assistance. The driver will notice that much higher pedal effort is needed to stop
the car and that the pedal f eels harder than usual.
VACUUM LEAK TEST
1. Operate the engine at idle without t ouching the brake pedal for at least one
minute.
2. Turn off the engine and wait one minute.
3. Test for the presence of assist va cuum by depressing the brake pedal and
releasing it several times. If vac uum is present in the system, light
application will produce less and less pedal travel. If there is no vacuum, air
is leaking into the system.
SYSTEM OPERATION TEST
1. With the engine OFF, pump the brake p edal until the supply vacuum is
entirely gone.
2. Put light, steady pressu re on the brake pedal.
3. Start the engine and let it idle. If the system is operating correctly, the brake
pedal should fall toward the floor if t he constant pressure is maintained.
Page 73 of 875
GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 73
To install:
9. Install the new line or hose, starti
ng with the end farthest from the master
cylinder. Connect the other end, then confirm that both fittings are correctly
threaded and turn smoothly using finger pressure. Make sure the new line
will not rub against any ot her part. Brake lines must be at least 1/2 in.
(13mm) from the steering column and other moving parts. Any protective
shielding or insulators must be rein stalled in the original location.
WARNING - Make sure the hose is NO T kinked or touching any part of the
frame or suspension after installation. These conditions may cause the hose to
fail prematurely.
10. Using two wrenches as bef ore, tighten each fitting.
11. Install any retaining clips or brackets on the lines.
12. If removed, install the wheel and tire assemblies, then carefully lower the
vehicle to the ground.
13. Refill the brake master cylinder re servoir with clean, fresh brake fluid,
meeting DOT 3 specifications. Pr operly bleed the brake system.
14. Connect the negative battery cable.
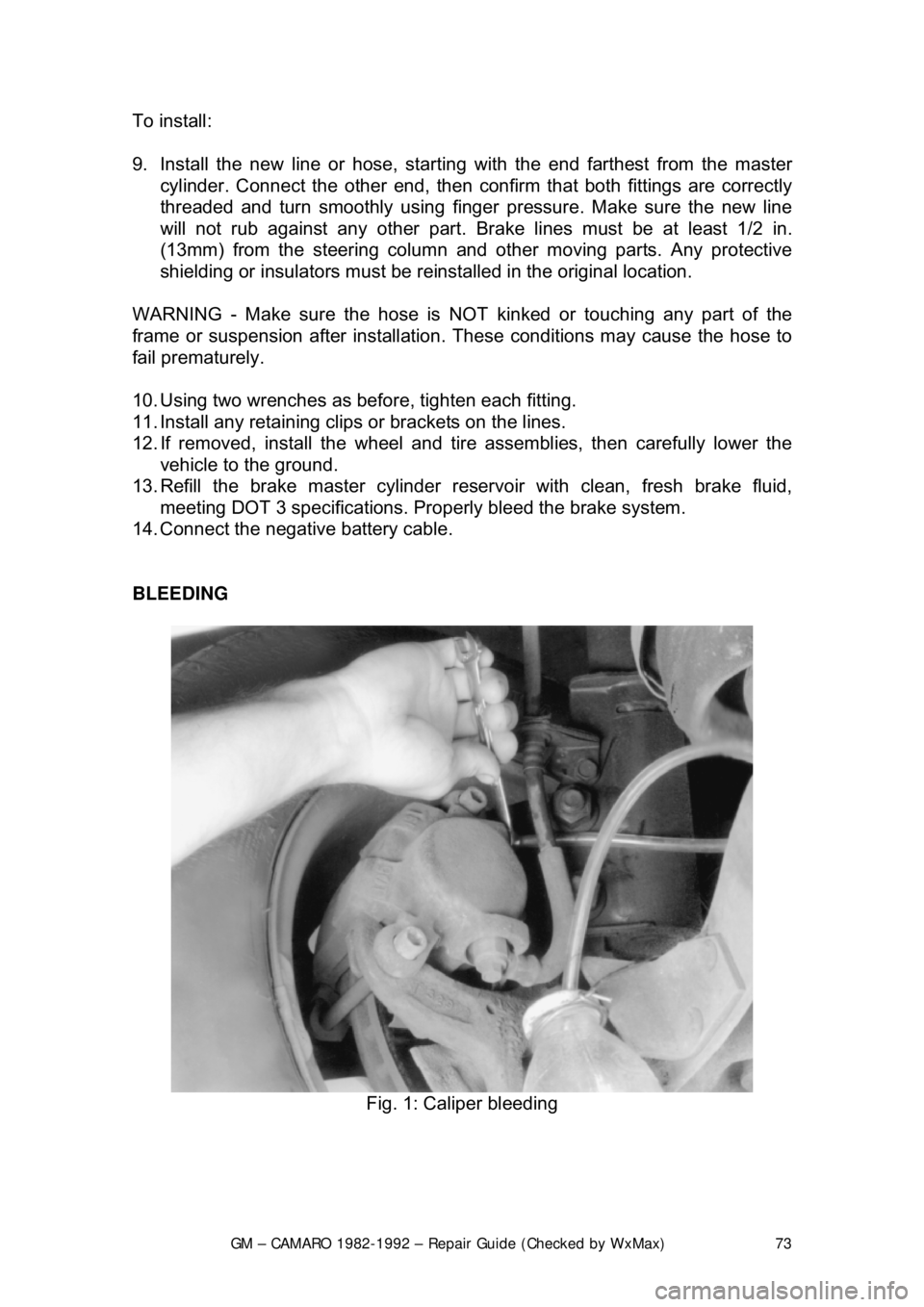
BLEEDING
Fig. 1: Caliper bleeding
Page 75 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 75
5. Have your assistant sl
owly depress the brake pedal. As this is done, open
the bleeder screw 3/4 of a turn and allow the flui d to run through the tube.
Then close the bleeder screw before the pedal reaches the end of its travel.
Have your assistant slo wly release the pedal. Rep eat this process until no
air bubbles appear in the expelled fluid.
6. Repeat the procedure on the other three br akes, checking the level of fluid in
the master cylinder reservoir often.
7. Upon completion, check the brak e pedal for sponginess and the brake
warning light for unbalanced pressure . If necessary, repeat the entire
bleeding procedure.
FRONT DISC BRAKES
CAUTION - Some brake pads contain asbest os, which has been determined to
be a cancer causing agent. Never clean the brake surfaces with compressed
air! Avoid inhaling any dust from any brake surface! When cleaning brake
surfaces, use a commercially available brake cleaning fluid.
BRAKE PADS
CAUTION - Some brake pads contain asbest os, which has been determined to
be a cancer causing agent. Never clean the brake surfaces with compressed
air! Avoid inhaling any dust from any brake surface! When cleaning brake
surfaces, use a commercially available brake cleaning fluid.
INSPECTION
The pad thickness should be inspected ever y time that the tires are removed for
rotation. The outer pad can be checked by looking in each end, which is the
point at which the highest rate of wear occurs. The inner pad can be checked by
looking down through the inspection hole in the top of the caliper. If the
thickness of the pad is worn to within 0.030 in. (0.8mm) of the rivet at either end
of the pad, all the pads should be replaced.
Always replace all pads on both front wheel s at the same time. Failure to do so
will result in uneven braking action and premature wear.
REMOVAL & INSTALLATION
Page 123 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 123
5. Pull the parking lever 4 clicks. T
he parking brake levers on both calipers
should be against the lever stops on the caliper housings. If the levers are
not against the stops, check for binding in the rear cables and/or loosen the
cables at the equalizer nut until both left and right levers are against their
stops.
6. Adjust the equalizer adjusting nut unt il the parking brake levers on both
calipers just begin to mo ve off their stops.
7. Back off the adjuster nut until the le vers move back, barely touching their
stops.
8. Operate the parking brak e lever several times to check adjustment. After
cable adjustment, the parking brake le ver should travel no more than 14
ratchet clicks. The rear wheels shoul d not turn forward when the parking
brake lever is applied 8-16 ratchet clicks.
9. Release the parking brake lever. Both rear whee ls must turn freely in both
directions. The parking brake levers on both calipers should be resting on
their stops.
10. Remove the wheel nuts retaining t he rotors. Install the wheel and tire
assemblies.
11. Lower the vehicle.
PARKING BRAKE FREE-TRAVEL
ADJUSTMENT
1989-92 MODELS
REAR DISC BRAKES
Disc brake pads must be new or parallel to within 0.006 in. (0.15mm). Parking
brake adjustment is not valid wit h heavily tapered pads and may cause
caliper/parking brake binding. Replace tapered brak e pads. Parking brake free-
travel should only be made if the caliper has been taken apart. This adjustment
will not correct a condition where the caliper levers will not return to their stops.
1. Have an assistant apply a light brake pedal load, enough to stop the rotor
from turning by hand. This takes up all clearances and ensures that
components are correctly aligned.
2. Apply light pressure to the caliper lever.
3. Measure the free-travel between t he caliper lever and the caliper housing.
The free-travel must be 0.0024-0.028 in. (0.6-0.7mm).
4. If the free-travel is incorrect, do the following: a. Remove the adjuster screw.
b. Clean the thread adhesive re sidue from the threads.
c. Coat the threads with adhesive.
d. Screw in the adjuster screw far enough to obtain 0.024-0.028 in. (0.6-
0.7mm) free-travel between the caliper lever and the caliper housing.
5. Have an assistant release the brak e pedal, then apply the brake pedal firmly
3 times. Recheck the free-travel and adjust as necessary.
Page 819 of 875

GM – CAMARO 1982-1992 – Repair Guide (Checked by WxMax) 819
INSPECTION
Inspect the tires for lacerations, puncture
marks, nails and other sharp objects.
Repair or replace as necessary. Also check the tires for treadwear and air
pressure as outlined in General Information & Maintenance of this repair guide.
Check the wheel assemblies for dents, crac ks, rust and metal fatigue. Repair or
replace as necessary.
WHEEL LUG STUDS
REMOVAL & INSTALLATION
WITH DISC BRAKES
1. Raise and support the appropriate end of the vehicle safely using
jackstands, then remove the wheel.
2. Remove the brake pads and caliper. Support the caliper aside using wire
or a coat hanger. For details, please re fer to Brakes of this repair guide.
3. Remove the outer w heel bearing and lift off the rotor. For details on
wheel bearing removal, installation and adjustment, please refer to
General Information & Maintenan ce of this repair guide.
4. Properly support the rotor using pre ss bars, then drive the stud out using
an arbor press.
If a press is not available, CAREFULLY drive the old stud out using a blunt drift.
MAKE SURE the rotor is properly and ev enly supported or it may be damaged.
Fig. 1: View of the rotor and stud assembly