1967 CHEVROLET CAMARO length
[x] Cancel search: lengthPage 324 of 659
AIR INJECTOR REACTOR SYSTEM 6T-4
Air injection Tube
Inspection (Fig. 5)
• There is no periodic service or inspection for the
air injection tubes, yet on In Line engines whenever
the cylinder head is removed or on V8 engines when-
ever the exhaust manifolds are removed, inspect the
air injection tubes for carbon build up and warped or
burnt tubes.
• Remove any carbon build up with a wire brush.
• Warped or burnt tubes must be replaced.
Replacement
• On In Line engines remove carbon from tubes and
using penetrating oil, work tubes out of cylinder
head.
• On V8 engines clamp exhaust manifold in a vise,
remove carbon from tubes and using penetrating oil,
work tubes out of manifold.
• Install new tubes in cylinder head or manifold.
Air Injection Pump
Inspection
Accelerate engine to approximately 1500 KPM and
observe air flow from hose.Osf). If air flow increases as
engine is accelerated, pump is operating satisfactorily.
If air flow does not increase or is not present, proceed
as follows:
• Check for proper drive belt tension.
• Check for a leaky pressure relief valve. Air maybe
heard leaking with the pump running.
NOTE:
The Air Injection Reactor System is
not completely noiseless. Under normal condi-
tions noise rises in pitch as engine speed in-
creases. To determine if excessive noise is the
fault of the Air Injection Reactor System, oper-
ate the engine with the pump drive belt removed.
IN LINE
INJECTION
si
AIR AAANIFOLD^
ASSEMBLY
AIR MANIFOLD
ASSEMBLY ^S
~jk
VALVE
V-8
ff
>yi
INJECTION
» TUBE
' ,•
Fig.
5—Air Injection Tube (Typical)
Fig.
6-HRemoving Pressure Relief Valve
If excessive noise does not exist with the belt
removed proceed as follows:
Check for proper installation of relief valve silencer
on L-6 and 283, 327, 350 cu. in. V-8 engines.
Check for a seized Air Injection Pump.
Check hoses, tubes, air manifolds and all connec-
tions for leaks and proper routing.
Cheqk carburetor air cleaner for proper installation.
Check air injection pump for proper mounting.
If none of the above conditions exist and the air in-
jection pump has excessive noise remove then repair
as outlined in the Overhaul Manual.
Replacement
Disconnect,
t&e
hoses at the pump.
Remove pump pulley as outlined.
Remove pump mounting bolts and remove pump.
Install pump with mounting bolts loose.
Install pump pulley as outlined.
Install and adjust belt as outlined.
Connect the hoses at the pump.
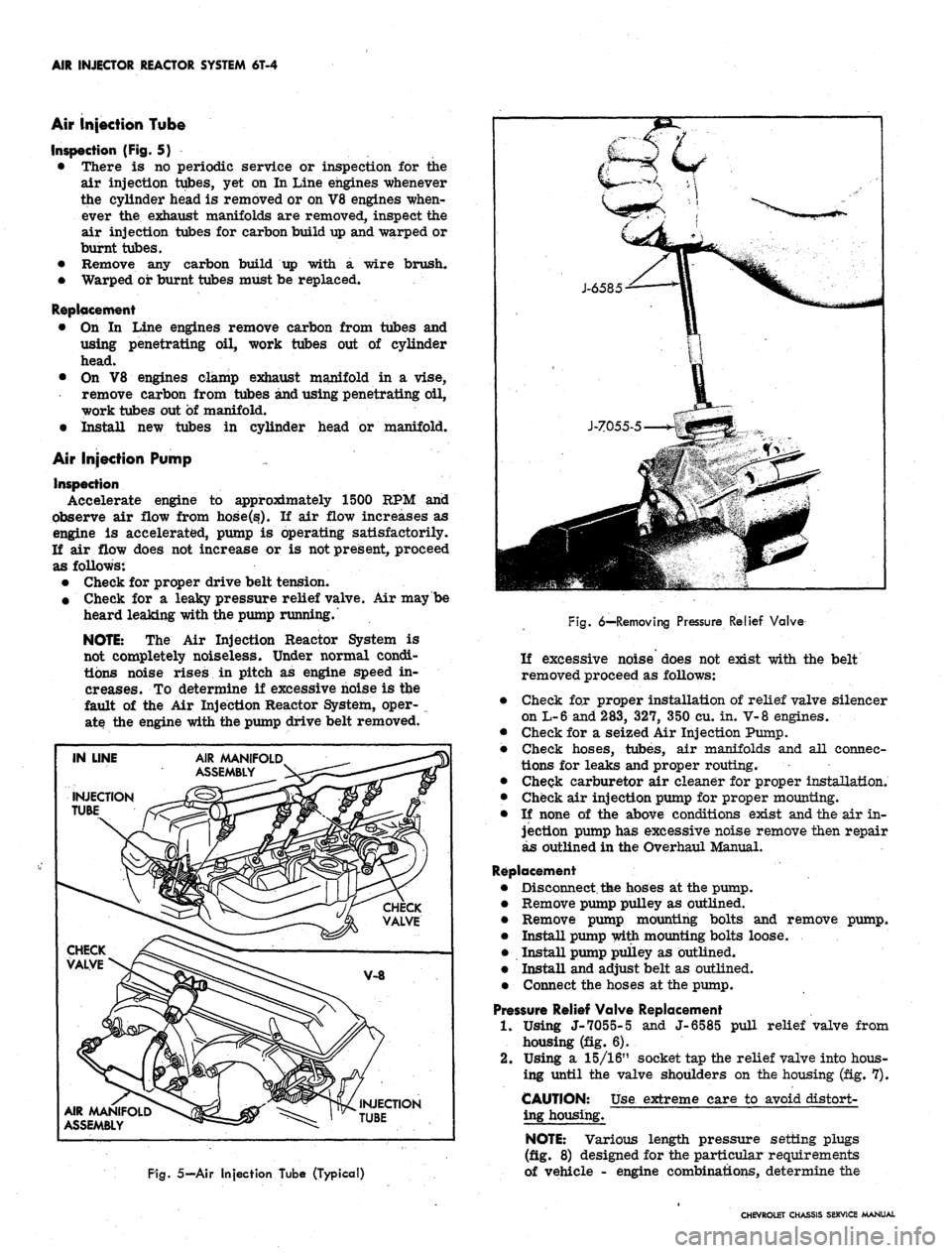
Pressure Relief Valve Replacement
1.
Using J-7055-5 and J-6585 pull relief valve from
housing (fig. 6).
2.
Using a 15/16" socket tap the relief valve into hous-
ing until the valve shoulders on the housing (fig. 7).
CAUTION: Use extreme care to avoid distort-
ing housing.
NOTE:
Various length pressure setting plugs
(fig. 8) designed for the particular requirements
of vehicle - engine combinations, determine the
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL
Page 326 of 659

SECTION 6Y
ENGINE ELECTRICAL
CONTENTS
OF
THIS SECTION
Page
System
6Y-19
6Y-32
6Y-34
BATTERY
INDEX
Page
General Description 6Y_i
Types of Batteries 6Y-1
Dry Charged Batteries 6Y-2
Activating Dry Charged Batteries 6Y-2
Wet Charged Batteries 6Y 2
Periodic Service 6Y-3
Common Causes of Failure 6Y-3
Delco Eye 6Y_3
Electrolyte Level
AY
3
Water Usage ] \ 6Y_3
Cleaning 6Y_4
Cables 6Y_4
Carrier and Holddown 6Y-4
Page
Safety Precautions 6Y-4
Charging Procedures . . gY_4
Slow Charging gY-4
Fast Charging . * 6Y-4
Emergency Boost Charging 6Y-4
Test Procedures QY-S
Visual Inspection 6Y-5
Instrument 6Y-5
Full Charge Hydrometer Test. 6Y-5
Specific Gravity Readings 6Y-5
Cell Comparison Test . 6Y-5
Installing Battery 6Y-5
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The battery (fig. lb) is made up of a number of separ-
ate elements, each located in an individual cell in a hard
rubber case. Each element consists of an assembly of
positive plates and negative plates containing dissimilar
active materials and kept apart by separators. Hie ele-
ments are immersed in an electrolyte composed of dilute
sulfuric acid. Plate straps located on the top of each ele-
ment connect all the positive plates and all the negative
plates into groups. The elements are connected in series
electrically by connectors that pass directly through the
case partitions between cells. The battery top is a one-
piece cover of hard rubber construction. Tfte cell con-
nectors, by-passing through the cell partitions, connect
the elements along the shortest practical path (fig. 2b).
With the length of the electrical circuit inside the
Battery reduced to a minimum, the internal voltage drop
is decreased resulting in improved performance, par-
ticularly during engine cranking at low temperatures.
The hard, smooth one-piece cover greatly reduces the
tendency for corrosion to form on the top of the Battery.
The cover is bonded to the case with sealing compound
that forms an air tight seal between the cover and case.
Protection for the Battery charging circuit (10 gage
wire) is provided by a pigtail lead which is a fusible Hnk
off the battery positive cable (14 gage wire). This lead is
an integral part of the Battery cable assembly and serv-
icing requires replacing the complete cable assembly.
TYPES
OF
BATTERIES
There are two types of Batteries—the "dry charge"
type and the "wet charge" type. The difference in types
depends on the method of manufacture.
ONE PIECE
CELL COVER
VENT PLUG
ELECTROLYTE LEVEL
INDICATOR
HOLD-DOWN SLOT
Fig.
lb—Battery
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL
Page 329 of 659

ENGINE-ELECTRICAL
6Y-4
CLEANING
The external condition of the Battery should be checked
periodically for damage or for the presence of dirt and
corrosion. The top of the Battery should be kept clean.
An accumulation of acid film and dirt may permit current
to flow between the terminals, which will slowly dis-
charge the Battery. For best results when cleaning the
top of Batteries, wash first with a diluted ammonia or a
soda solution to neutralize any acid present; then flush
with clean water. Care must be taken to keep vent plugs
tight, so that the neutralizing solution does not enter the
cells.
CABLES
To insure good electrical contact, the cables should be
clean and tight on the Energizer posts. If the posts or
cable terminals are corroded, the cables should be dis-
connected and the terminals and clamps cleaned sepa-
rately with a soda solution and a wire brush. After
cleaning and installing clamps, apply a thin coating of
petroleum jelly on the cable clamps to retard corrosion.
CARRIER
AND
HOLD-DOWN
The Battery carrier and hold-down should be clean and
free from corrosion before installing the Battery. The
carrier should be in a sound mechanical condition so that
it will support the Battery securely and keep it level.
To prevent the Battery from shaking in its carrier,
the hold-down bolts should be tight (60-80 in. lbs.). How-
ever, the bolts should not be tightened to the point where
the Battery case or cover will be placed under a severe
strain.
BATTERY SAFETY PRECAUTIONS
When Batteries are being charged, an explosive gas
mixture forms in each cell. Part of this gas escapes
through the holes in the vent plugs and may form an
explosive atmosphere around the Battery itself if ventila-
tion is poor. This explosive gas may remain in or around
the Battery for several hours after it has been charged.
Sparks or flames can ignite this gas causing an internal
explosion which may shatter the Battery.
The following precautions should be observed to pre-
vent an explosion:
1.
Do not smoke near Batteries being charged or which
have been very recently charged.
2.
Do not break live circuits at the terminals- of Batr
teries because a spark usually occurs at the point
where a live circuit is broken. Care must always be
taken when connecting or disconnecting booster leads
or cable clamps on fast chargers. Poor connections
are a common cause of electrical arcs which cause
BATTERY CHARGING PROCEDURES
There are three methods of recharging Batteries.
They differ basically in the length of time the Battery is
charged and the rate at which charging current is sup-
plied. One is the Slow Charge method, the second is the
Fast Charge method, and the third is the Emergency
Boost Charge method.
Before recharging a Battery by any method, the elec-
trolyte level must be checked and adjusted if necessary.
SLOW CHARGING
The Slow Charge method supplies the Battery with a
relatively low current flow for a relatively long period of
time. This is the only method that will bring the Battery
to a full state of charge.
The Slow Charge method consists of charging at
approximately a 4 ampere rate for 24 hours or more if
necessary to bring the Battery to full charge. A fully
charged condition is reached when the cells are gassing
freely and three corrected specific gravity readings
taken at hourly intervals show no increase.
FAST CHARGING
The Fast Charge method supplies current to the Bat-
tery at a 40 to 50 ampere rate for a 1 1/2 hour period of
time. If the electrolyte temperature reaches 125°F before
the 1 1/2 hour period is completed, the Battery must be
taken off charge temporarily, or the charging rate
reduced to avoid damage to the Battery.
Although a Battery cannot be brought to a fully charged
condition during Fast Charge, it can be substantially
recharged or "boosted". In order to bring the Battery to
a fully charged condition, the charging cycle must be
finished by the Slow Charge method.
EMERGENCY BOOST CHARGING
In cases where the Battery is not sufficiently charged
to crank the engine, an emergency boost charge may be
applied as a temporary expedient in order to crank the
engine. The Emergency Boost Charge method consists of
charging at a 40 to 50 ampere rate for a period of one-
half hour.
It should be particularly noted that the Emergency
Boost Charge will not necessarily restore the Battery to
a useful state of. charge for continued service. After an
emergency boost charge, failure to charge the Battery
further, either by a long uninterrupted driving period or
by the Fast Charge or Slow Charge method, may result
in failure to crank the engine the next time cranking is
attempted. A Battery should never be condemned on the
basis of failure to crank the engine after an emergency
boost charge. Although an emergency boost charge may
put enough energy into the Battery to crank the engine
once, further charging usually is necessary in order to
create a sufficient reserve to crank a second and third
time.
12
VOLT BATTERY SUGGESTED
CHARGING RATES
(100 Amp/hr or Less Capacity)
TYPE OF
CHARGE
Boost Charge for
Light Load Test
Slow Charge
Fast Charge
Quick Boost .
Dry Charge
Warm-up Boost
LENGTH
OF TIME
20 Minutes
24 Hours
1-1/2 Hours
30 Minutes
10 Minutes
CHARGING
RATE
50 Amps
4 Amps
40-50 Amps
40-50 Amps
15 Amps
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL
Page 334 of 659

ENGINE-ELECTRICAL 6Y-9
63 AMP 1
MODELS ONLY'
BATTERY FUSIBLE
LINK
HORN
FUSIBLE LINK'
TRANSISTOR
FUSIBLE LINK'
Fig.
4c— Circuitry - Voltage Regulator Assemblies (Corvette)
Engine compartment wiring harness incorporates sev-
eral fusible links. Each link is identified with its gage
size. A fusible link is a length of special wire (normally
four wire gages smaller than the circuit it is protecting)
used in wiring circuits that are not normally fused, such
as the ignition circuit. The same size wire with a hypalon
insulation must be used when replacing a fusible link.
The links are:
1.
The pigtail lead at the battery positive cable (except
Corvette) is a 14 gage, brown fusible link protecting
the 10 gage battery charging circuit. This wire is an
integral part of the battery cable assembly and serv-
icing requires replacing the complete battery cable
assembly. On Corvette models this link is installed
as a molded splice at the solenoid "Bat" terminal
and servicing requires splicing in a new link.
2.
A 16 gage black fusible link is located at the horn
4.
relay to protect all unfused wiring of 12 gage or
larger. It is installed as a molded splice and serv-
icing requires splicing in a new link.
The generator warning light and field circuitry (16
gage wire) is protected by a fusible link (20 gage
orange wire) used in the "battery feed to voltage
regulator #3 terminal" wire. The link is installed as
a molded splice in the generator and forward lamp
harness and is serviced by splicing in a new 20 gage
wire as required.
The ammeter circuit on all models is protected by
two orange, 20 gage wire fusible links installed as
molded splices in the circuit at the junction block or
the solenoid "Bat" terminal (Corvette only) and at
the horn relay. Each link is serviced by splicing in a
new 20 gage wire as required.
MAINTENANCE AND ADJUSTMENTS
At regular intervals, inspect the terminals for cor-
rosion an4 loose connections, and the wiring for frayed
insulation. Check mounting bolts for tightness. Check the
drive belt for alignment, proper tension and wear. Be-
cause of the higher inertia and load capacity of the rotor
used in A.C. generators, PROPER BELT TENSION is
more critical than on D.C. generators.
Since the Delcotron and its companion regulator are
designed for use on negative polarity systems only, the
following precautions must be observed. Failure to ob-
serve these precautions may result in serious damage to
the charging system.
1.
When installing a battery, always make absolutely
sure the ground polarity of the battery, generator and
regulator is the same.
2.
When connecting a booster battery, make certain to
connect the correct battery terminals together.
3.
When connecting a charger to the battery, connect the
correct charger leads to the battery
%
terminals.
4.
Never operate the generator on an uncontrolled open
TO SOLENOID
BAT ACC RES. WIRE
Fig.
5c—Typical Wiring Diagram Showing Lead Connections
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL
Page 360 of 659

SECTION 7
CLUTCH AND TRANSMISSIONS
CONTENTS OF THIS SECTION
Clutch
Three-Speed . . .
Overdrive
Three-Speed, (Warner T-16)
Four-Speed (Muncie) . . . .
Page
7-1
7-6
7-9
7-14
7-16
CLUTCH
Page
Four-Speed (Saginaw) 7-20
Powerglide 7-23
Turbo Hydra-Matic 7-36
Special Tools 7-43
INDEX
General Description
Maintenance and Adjustments
Linkage Inspection
Clutch Linkage Adjustment
Component Parts Replacement
Clutch Assembly ......
Removal from Vehicle .
Page
7-1
7-1
7-1
7-2
7-3
7-3
7-3
Installation in Vehicle
Clutch Pedal ..'....,
Clutch Cross Shaft . . .
Removal.......
Repairs
Installation .....
Page
7-4
7-4
7-4
7-4
7-4
7-4
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
A diaphragm spring-type clutch assembly is used with
manual transmissions.
The clutch assembly is enclosed in a 360° bell housing
which must be removed to gain access to the clutch.
V-8 engines (equipped with a 4 speed transmission)
use a bent-finger, centrifugal diaphragm type clutch as-
sembly. All its integral release fingers are bent back to
gain a centrifugal boost and to insure quick re engagement
at high engine speeds.
This type of clutch has the advantages of increasing
pressure plate load as the driven plate wears, and of low
pedal effort with high plate loads without requiring over-
center booster springs on the clutch linkage.
The pressure plate is a high tensile strength iron de-
signed for maximum speed conditions.
The clutch release bearing (fig. 4), used with the bent
finger diaphragm clutch, has an overall length of approxi-
mately
1-1/4".
The longer bearing, used with the straight
diaphragm, will cause inability to obtain free pedal travel,
especially as the clutch wears, resulting in slippage and
rapid wear.
DO
NOT INTERCHANGE!
The clutch is operated by conventional linkage consist-
ing of two groups, upper linkage and lower linkage.
The return spring pre-loads clutch linkage, removing
looseness due to wear. The clutch free pedal travel,
therefore, will increase with linkage wear and decrease
with driven disc wear, and free travel felt at pedal is
throwout bearing lash.
MAINTENANCE AND ADJUSTMENTS
LINKAGE INSPECTION
There are several things which affect good clutch op-
eration. Therefore, it is necessary, before performing
any major clutch operations, to make preliminary in-
spections to determine whether trouble is actually in the
clutch.
Check the clutch linkage to be sure the clutch releases
fully as follows:
1.
With engine running, hold the clutch pedal approxi-
mately 1/2" from floor mat and move shift lever be-
tween first and reverse several times. If this can be
done smoothly, the clutch is fully releasing. If shift
is not smooth, clutch is not fully releasing and ad-
justment is necessary.
2.
Check clutch pedal bushings for sticking or excessive
wear.
3.
Check fork for proper installation on ball stud. Lack
of lubrication on fork can cause fork to be pulled off
the ball.
4.
Check for bent, cracked or damaged cross shaft
levers or support bracket.
5.
Loose or damaged engine mounts may aUiow the en-
gine to shift its position causing a bind on clutch
linkage at the cross shaft. Check to be sure there is
Fig.
1 - Chevrolet Clutch Pedal Free Travel Adjustment
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL
Page 361 of 659

CLUTCH AND TRANSMISSIONS 7-2
Fig.
2 - Chevelle Clutch Pedal Free Travel Adjustment (V-8 Shown)
some clearance between cross shaft and both its
mounting brackets.
CLUTCH LINKAGE ADJUSTMENT
There is one linkage adjustment (clutch fork push rod
or pedal push rod) to compensate for all normal clutch
wear.
The clutch pedal should have
1-1/4"
free travel (meas-
ured at clutch pedal pad) before the throwout bearing en-
gages the clutch diaphragm spring levers. Lash is re-
quired to prevent clutch slippage which would occur if the
bearing was held against the fingers and to prevent the
bearing from running continually until failure.
Chevrolet Linkage Adjustment (Fig. 1}
With Nuts (A) & (B) loose on Rod (D)
&
before installa-
tion of Clutch Pedal Return Spring
(E),
apply approximately
5 lbs. load in direction of arrow (F) to eliminate clear-
ance between throwout bearing and clutch fingers. Move
Rod (D) in direction of arrow (G) until Clutch Pedal Arm
makes contact with Bumper Stop on instrument panel
brace. Run Nut (B) toward Swivel until dimension (X) is
9/32". Tighten Nut (A) to lock Swivel (C) against Nut (B).
Install Clutch Pedal Return Spring (E).
The foregoing procedure will provide a free pedal
travel of 1" to
1-1/2"
measured on a perpendicular from
the crown of the, pedal pad to the bare metal toe pan.
Chevelle Linkage Adjustment (Fig. 2)
1.
Disconnect spring between cross shaft lever and
clutch fork.
2.
Loosen push rod locknut about three turns.
3.
If there is no free travel, shorten the rod (by turning
at square wrench area) until it is free of clutch fork.
4.
Hold the clutch fork rearward to move throwout
lightly against clutch release fingers, then adjust rod
length until rod just touches ,its seat in the fork.
5.
Adjust locknut to obtain approximately 3/16" clear-
ance between nut and rod sleeve end.
6. Turn the rod with wrench, until the nut just comes in
contact with rod sleeve end, then hold the rod with
wrench and tighten locknut.
7.
Check free pedal travel at pedal (1" to
1-1/2"
is
proper clearance). Readjust if necessary.
Chevy II Linkage Adjustment (Fig. 3}
L-4 & L-6 Models
1.
Loosen locknut "A" and lengthen or shorten push rod
in swivel as required by turning with wrench on ma-
chined flat "B". (Shorten push rod to increase pedal
lash).
2.
Hold push rod at flat "B" and tighten locknut "A".
3.
Recheck pedal free travel.
NOTE: A measurement of approximately 3/16"
between push rod and its seat in fork will give
required pedal free travel.
V-8 Models
The eight cylinder linkage has a two-piece clutch fork
push rod (fig. 3). Adjust clutch pedal free travel by turn-
ing the adjusting rod portion of the push rod to obtain apr
proximately 3/16" clearance between clutch fork and end
of rod, ttien tighten locknut to 8-12 lbs. ft. and check free
travel at pedal. Pedal free travel on all models should
be 1" to
1-1/2".
Corvette Linkage Adjustment
Refer to fig. 1 and the following procedure:
1.
Disconnect pedal return spring.
2.
With Nuts (A) and (B) loose on Rod (D) apply push
hard load in direction of arrow (F) to eliminate
clearance between throwout bearing and clutch
fingers.
3.
Run Nut (B) towards Swivel (C) until dimension (X)
is 3/8" to 7/16".
4.
Tighten Nut (A) to lock swivel against Nut (B).
5.
Connect pedal return spring and check pedal free
travel for
1-1/4"
minimum to 2" maximum.
6. Check every 3,000 miles.
7.
Adjust free travel to 2" to 2-1/2" for heavy duty op-
eration. The return spring may be removed for
heavy duty conditions.
Camaro Linkage Adjustment
Refer to Figure 4 and the following procedure:
Apply a 10 lb. load in direction of Arrow (E) to hold
Clutch Pedal against Clutch Pedal Bumper.
Apply a 10 lb. load to Clutch Fork in direction of Arrow
(D) to eliminate clearance between throwout bearing and
clutch fingers.
Insert a .198 Spacer (F) between clutch fork and Ad-
justing Rod (A).
Rotate Adjusting Rod against Spacer until it has a 5 in.
lb.
torque.
Hold Adjusting Rod and tighten Nut (C) against Swivel
(B) or Rod (B).
Remove Spacer. Install return spring and extension to
clutch fork.
Pedal will have approximately 1" to
1-1/8"
free travel.
A clutch that has been slipping prior to free play ad-
justment may still slip right after the new adjustment due
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL
Page 376 of 659

CLUTCH AND TRANSMISSIONS 7-17
VIEW A
Fig.
1M - Four-Speed (Muncie) Transmission Gearshift Linkage (Chevrolet Shown)
5.
Repeat steps 3 and 4 for Hod (K) and (L).
6. Remove Locating Gauge and check shift to insure
proper operation.
GEAR SHIFT LEVER REVERSE
BLOCKER CABLE (Fig. 3M)
Replacement
In the event replacement is necessary use the following
procedure.
1.
Remove seat separator (console) assembly.
2.
Remove shift lever seal retainer and slide seal up
on lever.
3.
Remove shift lever knob, and the 2 lever to bracket
retaining nuts and remove the lever assembly.
4.
Replace blocker cable - thread new cable up through
lever and MT" handle and install cable retainer
through access slot. Adjust retainer to hold blocker
end .010/.020" above lever bracket surface, then lock
and cut off excess cable.
5.
Reverse Steps 1, 2 and 3 to install.
Figure 3M shows the adjustment and lubrication proce-
dure for the mechanism. This Figure applies to both
models of lever assemblies.
NOTE: If, for any reason, the cable assembly
is removed from the handle, it is difficult to in-
stall without rework. This is due to the fact that
the extra length of the cable is trimmed after
assembly and, therefore, it is almost impossible
to get the shortened cable to enter the cable hole
in the cylindrical retainer.
If new service cable assemblies are not available, the
original part can be re-used by butt soldering a 2.00 inch
piece of small wire to the cable end. Trim the solder
joint so that it will pass through the hole in the retainer.
After assembly, trim off the excess wire as shown in
Figure 3M.
Adjustment
1.
With set screw loose, assemble cable through hole
in cylindrical retainer above handle.
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL
Page 389 of 659

CLUTCH AND TRANSMISSIONS
7*30
V-8 Models-With Uni-Directional Linkage
1.
Remove air cleaner.
2.
Disconnect accelerator linkage at carburetor.
3.
Disconnect accelerator return and TV rod return
springs.
4.
With right hand, pull TV upper rod forward until
transmission is through detent. With left hand, open
carburetor to wide open throttle position. Carbure-
tor must reach wide open throttle position at the
same time the ball stud contacts end of slot in upper
TV rod.
5. Adjust swivel on end of upper TV rod to obtain set-
ting described in Step 4. Allowable tolerance is
approximately 1/32".
6. Connect and adjust accelerator linkage as described
in Section 6.
7. Check for throttle linkage freedom.
Neutral Safety Switch Adjustment
The adjustment at the neutral safety switch is de-
scribed in the Electrical Section 12.
Throttle Return Check Valve (Dashpot) Adjustment
The adjustment of the throttle return check valve is
described in Section 6M for each carburetor installation.
Fig.
12PG - Floor Mounted Control Lever and
Bracket Assembly (Chevrolet Shown)
COMPONENT PARTS REPLACEMENT
TRANSMISSION REPLACEMENT (EXC. CORVETTE)
Removal
1.
Raise car on hoist (preferably) or on stand jack and
remove oil pan drain plug to drain oil.
NOTE:
If desired, the oil may be drained after
transmission removal.
2.
Disconnect the oil cooler lines (external cooled
models), vacuum modulator line and the speedometer
drive cable fitting at the transmission. Tie lines
out of the way.
3.
Disconnect manual and TV control lever rods from
transmission.
4.
Disconnect propeller shaft from transmission.
5. Install suitable transmission lift equipment to jack
or other lifting device and attach on transmission.
6. Disconnect engine rear mount on transmission ex-
tension, then disconnect the transmission support
crossmember and slide rearward.
7. Remove converter underpan, scribe flywheel-con-
verter relationship for assembly, then remove the
flywheel-to-converter attaching bolts.
NOTE:
The "light" side of the converter is
denoted by a "blue" stripe painted across the
ends of the converter cover and housing. This
marking should be aligned as closely as possible
with the "white" stripe painted on the. engine
side of the flywheel outer rim (heavy side of
engine) to maintain balance.
8. Support engine at the oil pan rail with a jack or other
suitable brace capable of supporting the engine
weight when the transmission is removed.
9. Lower the rear of the transmission slightly so that
the upper transmission housing-to-engine attaching
bolts can be reached using a universal socket and a
long extension. Remove upper bolts.
CAUTION: Oh V-8 engines, care must be taken
not to lower rear of transmission too far as the
distributor housing may be forced against the
dash causing damage to the distributor. It is
best to have an assistant observe clearance of
all upper engine components while the trans-
mission rear end is being lowered.
10.
Remove remainder of transmission housing-to-
engine attaching bolts.
11.
Remove the transmission by moving it slightly to the
rear and downward, then remove from beneath the
car and transfer to a work bench.
NOTE:
Observe converter when moving the
transmission rearward. If it does not move
with the transmission, pry it free of flywheel
before proceeding.
CAUTION: Keep front of transmission upward
to prevent the converter from falling out. Install
converter Tool J-9549 (or a similar tool con-
structed as shown in Figure 13PG, or, in an
emergency, a length of strong wire may be used)
immediately after removal from the engine.
Installation
NOTE:
The "light" side, of the converter is
denoted by a "blue" stripe painted across the
ends of the converter cover and housing. This
marking should be aligned as closely as possible
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL