1967 CHEVROLET CAMARO turn signal
[x] Cancel search: turn signalPage 43 of 659

HEATER AND AIR CONDITIONING 1A-20
and its resistance is decreasing. In the HI FRONT
position, two thermistors (the master delay and high
blower delay thermistors) are warming. The air
door is in recirculation position until the engine
coolant reaches 75 degrees.
2.
The coolant reaches then 75 degrees and the thermal
vacuum valve opens applying vacuum to the air door
to admit outside air (unless the temperature dial is
set for cooling). Ram air will flow through the sys-
tem when the car is moving.
3.
Next, the master delay thermistor attains the tem-
perature at which it will pass sufficient current to
close the circuit through the master delay relay.
The relay circuit powers the blower motor at 9 volts.
4.
If the control is in the HI FRONT position, the high
blower delay thermistor will close the circuit
through the high blower relay which supplies full
available voltage to the blower motor. This function
occurs after the master delay thermistor has taken
effect because the high blower delay thermistor
uses the master delay type thermistor with a 10 ohm
1/4 watt resistor connected in
.
series. The nigh
blower delay thermistor must then warm to a higher
temperature than the master delay thermistor before
its resistance (plus that of the 10 ohm resistor)
drops enough to actuate the high blower relay.
5. If the controls are set for DE ICE, full outside air
and full voltage to the blower motor are effective
immediately regardless of temperatures or elapsed
times o
In accomplishing automatic control, the system follows
three steps to transform an electronic signal into me-
chanical energy through which the control is achieved.
Electronic Circuit
Two temperature sensors (Thermistors), and the duct
potentiometer connected in series, are located so as to
sense the temperature of the outside air, inside air and
system output air. The resistance of each sensor will
vary according to its temperature. The control head
temperature dial varies in resistance as it is adjusted by
the operator to suit his comfort requirements. The
resistance of the temperature dial control is applied
directly to the amplifier and is not in series with the
sensors and duct potentiometer. Thus temperature dif-
ferences in the sensor string plus the requirements fed
into the system by the operator cause changes in total
circuit resistance which allow a varying voltage flow
through the circuit.
Changing the Electronic Signal to Electrical Voltage
This minute voltage flow from the sensor string -
temperature dial circuit - is fed into the amplifier where
it is transformed into a usable amplifier output voltage,
the strength of which is determined by the strength of the
original amplifier input signal. This voltage is then
supplied to the transducer.
Changing the Electrical Voltage to a Vacuum Signal
Amplifier output voltage, varying according to tem-
perature requirements, is converted by the Transducer
into a modulator transducer output vacuum. This modu-
lated vacuum is applied to the Power Servo.
Changing the Vacuum Signal to Mechanical Energy
The Power Servo, controlled by the modulated Trans-
ducer output vacuum, operates the vacuum electrical and
mechanical components of the system as required to
provide automatic control of system operation.
Other major system components are mounted con-
ventionally in the engine compartment. Underhood com-
ponents and system airflow remain much the same as in
the Four-Season system except for the addition of the
automatic control provisions. The system operates on
100%
outside air, a mixture of outside and inside air, or
100%
recirculated air depending on the demands of the
system. The diaphragm operated .air selector door will
modulate outside air to the system during maximum air
conditioning requirements when the control unit is in
"Hi Front" position. Control of the blower is also com-
pletely automatic and dependent upon system demands.
Controls
The Comfortron controls the Chevrolet air conditioner
and heater in such a precise manner that the automobile
temperature remains relatively constant under all driving
conditions. By adjusting the thumb wheel on the Control
Head to any temperature desired between 65° and 85° F.
(See Figure 27) the automatic system will adjust the in-
car temperature even though the outside weather condi-
tions may vary considerably. The system will provide
maximum capacity for heating or cooling until the in-car
temperature reaches the pre-set Control Head Tempera-
ture. Where cooling is required, the system will start
immediately upon being turned "ON". During marginal
ambient temperatures the system will not always start
at the highest blower speeds of the control setting.
Therefore, occasionally the system can't be heard
starting*
Five over-riding functions are available so that special
conditions can be handled. Each Control Head function
will be discussed in detail below:
"Off" Position
In the "Off" position, the blower is turned off and the
outside air door is closed. No outside air should enter
the automobile.
"Lo Front" Position
The blower has five low to moderate speeds; Hi, M3,
M2,
M1 and Lo. The blower voltage will shift as directed
by the automatic controls. The "Lo Front" position
provides a quieter mode of automatic operation due to
reduction of blower noise.
"Hi Front" Position
The "Hi Front" position provides five high blower
speeds as called for by the automatic controls: The use
of the "Hi" blower speed results in a rapid cool down in
hot weather and rapid heating during cold weather. As
the in-car temperature approaches the temperature set-
ting on the Comfortron Control Head, the blower speed
will change, provided mild outside temperatures are
experienced. During very hot or cold weather, the blower
will reduce its speed only to the point where it is still
capable of maintaining the correct inrcar temperature.
"Rear" Position
The "Rear" position provides five high blower speeds.
The automatic controls select these speeds and blend the
discharge air to the proper temperature. By the use of
high blower speeds, increased airflow is obtained for
better rear seat passenger comfort.
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL
Page 322 of 659
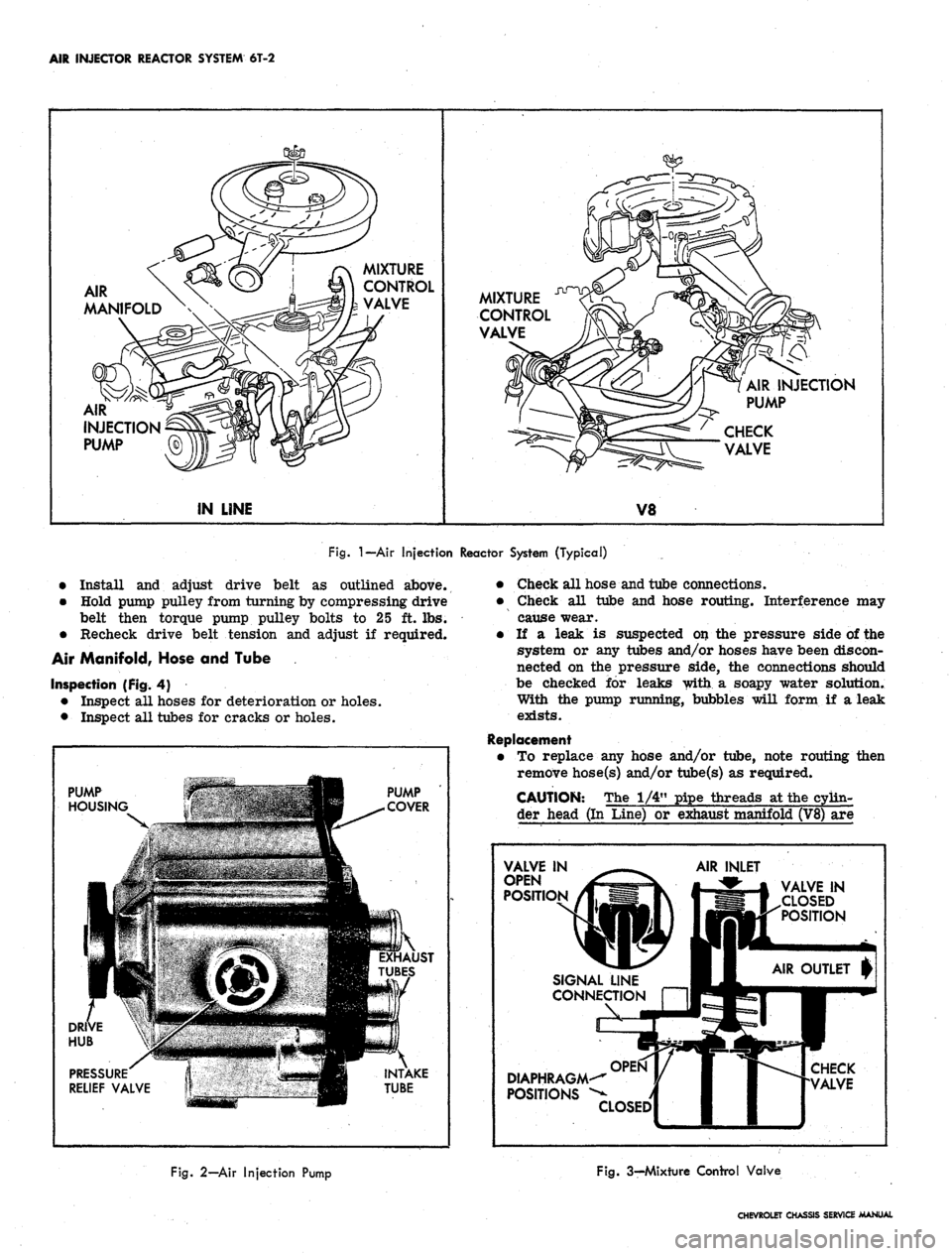
AIR INJECTOR REACTOR SYSTEM
6T-2
AIR
MANIFOLD
MIXTURE
CONTROL
VALVE
AIR
INJECTION
PUMP
IN LINE
MIXTURE
CONTROL
VALVE
AIR INJECTION
PUMP
CHECK
VALVE
V8
Fig.
I—Air
Injection Reactor System (Typical)
• Install
and
adjust drive belt
as
outlined above.
• Hold pump pulley from turning
by
compressing drive
belt then torque pump pulley bolts
to 25 ft. lbs.
• Recheck drive belt tension
and
adjust
if
required.
Air Manifold, Hose and Tube
Inspection (Fig. 4)
• Inspect
all
hoses
for
deterioration
or
holes.
• Inspect
all
tubes
for
cracks
or
holes.
PUMP
HOUSING
91
DRIVE V
HUB
PRESSURE
RELIEF VALVE
•H
PUMP
'
Mm ^
COVER
A.
J^HTEXHAUST
wBBE
TUBES
SB
^1 INTAKE
JH TUBE
• Check
all
hose and tube connections.
• Check
all
tube
and
hose routing. Interference
may
cause wear.
•
If a
leak
is
suspected
on the
pressure side
of the
system
or any
tubes and/or hoses have been discon-
nected
on the
pressure side,
the
connections should
be checked
for
leaks with
a
soapy water solution.
With
the
pump running, bubbles will form
if
aleak
exists.
Replacement
•
To
replace
any
hose and/or tube, note routing then
remove hose(s) and/or tube(s)
as
required.
CAUTION:
The 1/4"
pipe threads
at the
cylin-
der head
(In
Line)
or
exhaust manifold
(V8) are
VALVE
IN
OPEN
POSITION
INLET
VALVE
IN
CLOSED
POSITION
DIAPHRAGM
POSITIONS
SIGNAL
LINE
CONNECTION
ALVE
Fig.
2—Air Injection Pump
Fig.
3—Mixture Control Valve
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL
Page 395 of 659

CLUTCH AND TRANSMISSIONS 7-36
TURBO HYDRA-MATIC TRANSMISSION
INDEX
Page
General Description . . , . 7-36
Maintenance and Adjustments . 7-37
Transmission Fluid 7-37
Fluid Level Indicator 7-37
Shift Control Linkage Adjustment ........... 7-37
Neutral Safety Switch Adjustment 7-37
Draining and Refilling Transmission . . . 7-37
Pressure Regulator Valve 7-38
Control Valve Body . 7-39
Governor ..'.... 7-40
Modulator and Modulator Valve 7-40
Parking Linkage . . 7-40
Page
Rear Seal -. 7-40
Other Service Operations . . 7-40
Transmission Replacement 7-40
Turbo Hydra-Matic Diagnosis Procedure. ......... 7-41
Sequence . ; ; 7-41
Oil Level and Condition Check 7-41
Manual Linkage 7-41
Oil Leaks .' 7-41
Case Porosity - Repair ................ 7-42
Oil Pressure Check 7-42
Transmission Shift Points 7-42
Special Tools 7-43
GENERAL DESCRIPTION
The Turbo Hydra-Matic transmission is a fully auto-
matic unit consisting primarily of a 3-element hydraulic
torque converter and a compound planetary gear set.
Three multiple-disc clutches, one sprag unit, one roller
clutch and two bands provide the friction elements re-
quired to obtain the desired function of the compound
planetary gear set.
The torque converter couples the engine to the plane-
tary gears through oil and provides hydraulic torque
multiplication when required. The compound planetary
gear set produces three forward speeds and reverse.
The
3-
element torque converter consists of a pump or
driving member, a turbine or driven member, and a
stator assembly. The stator is mounted on a one-way
roller clutch which will allow the stator to turn clock-
wise but not counter-clockwise.
The torque converter housing is filled with oil and
is attached to the engine crankshaft by a flex plate and
always rotates at engine speed. The converter pump is
an integral part of the converter housing, therefore the
pump blades, rotating at engine speed, set the oil within
the converter into motion and direct it to the turbine,
causing the turbine to rotate.
As the oil passes through the turbine it is traveling in
such a direction that if it were not re-directed by the
stator it would hit the rear of the converter pump blades
and impede its pumping action. So at low turbine speeds,
the oil is re-directed by the stator to the converter pump
in such a manner that it actually assists the converter
pump to deliver power or multiply engine torque.
As turbine speed increases, the direction of the oil
leaving the turbine changes and flows against the rear
side of the stator vanes in a clockwise direction. Since
the stator is now impeding the smooth flow of oil, its
roller clutch releases and it revolves freely on its shaft.
Once the stator becomes inactive, there is no further
multiplication of engine torque within the converter. At
this point, the converter is merely acting as a fluid
coupling as both the converter pump and turbine are
being driven at approximately the same speed - or at a
one-to-one ratio.
A hydraulic system pressurized by a gear type pump
provides the working pressure required to operate the
friction elements and automatic controls.
External control connections to transmission are:
Manual Linkage
Engine Vacuum
12 Volt Electrical
Signal
To select the desired op-
erating range.
To operate a vacuum mod-
ulator unit.
To operate an electrical
detent solenoid.
A vacuum modulator is used to automatically sense
any change in the torque input to the transmission. The
vacuum, modulator transmits this signal to the pressure
regulator for line pressure control, to the 1-2 accumula-
tor valve, and to the shift valves so that all torque re-
quirements of the transmission are met and smooth
shifts are obtained at all throttle openings.
The detent solenoid is activated by an alectric switch
on the carburetor. When the throttle is fully opened, the
switch on the carburetor is closed, activating the detent
solenoid and. causing the transmission to downshift at
speeds below approximately 70 MPH.
The selector quadrant has six selector positions: P,R,
N,D,
L2,L1.
P.
*
- Park position positively locks the output shaft to
the transmission case by means of a locking pawl
to prevent the vehicle from rolling in either di-
rection. The engine may be started in Park
position.
R. - Reverse enables the vehicle to be operated in a
reverse direction.
N.
- Neutral position enables the engine to be started
and run without driving the vehicle.
D,
- Drive Range is used for all normal driving condi-
tions and maximum economy. Drive Range has
three gear ratios, from the starting ratio to
direct drive. Detent downshifts are available by
depressing the accelerator to the floor.
L2.
- L2 Range has the same starting ratio as Drive
Range, but prevents the transmission from shift-
ing above second speed to retain second speed
acceleration when extra performance is desired.
L2 Range can also be used for engine braking.
L2 Range can be selected at any vehicle speed,
and the transmission will shift to second gear and
remain in second until the vehicle speed or the
throttle are changed to obtain first gear operation
in the same manner as in D Range.
CHIVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL
Page 444 of 659

STEERING 9-4
8. Reassemble pitman arm to sector shaft, lining up
marks made during disassembly. Refer to torque
specifications at rear of manual for correct torque
value.
9. Install horn cap or ornament and connect steering
column harness at chassis connector.
NOTE:
Chevy.n models are equipped with a
shim at the frame to steering gear mounting
bolts.
Shims may be removed or installed as
required for proper steering gear alignment.
STEERING WHEEL ALIGNMENT AND
HIGH POINT CENTERING
1.
Set front wheels in straight ahead position. This can
be checked by driving vehicle a short distance on a
flat surface to determine steering wheel position at
which vehicle follows a straight path.
2.
With front wheels set straight ahead, check position
of mark on wormshaft designating steering gear high
point. This mark should be at the top side of the shaft
at 12 o'clock position and lined up with the mark in
the coupling lower clamp.
3.
If gear has been moved off high point when setting
wheels in straight ahead position, loosen adjusting
sleeve clamps on both left and right hand tie rods,
then turn both sleeves an equal number of turns in
the same direction to bring gear back on high point.
CAUTION: Turning the sleeves an unequal
number of turns or in differential directions will
disturb the toe-in setting of the wheels.
4.
Readjust toe-in as outlined in Section 3 (if necessary).
5. With wheels in a straight ahead position and the
steering gear on highpoint, check the steering wheel
alignment by measuring the distance from each hori-
zontal spoke to the horizontal centerline of the
steering wheel (fig. 5). If the horizontal spokes are
over 1-1/8 inches from the horizontal position the
wheel should be removed and centered. (See steering
wheel removal in this section.)
TOE-IN ADJUSTMENT
Adjust the steering linkage for proper toe-in setting as
outlined in Section 3.
CORVETTE STEERING RATIO (Fig. 6)
The Corvette steering ratio may be changed as follows:
CAUTION: Do not use the rearward hole in the
steering arm with power steering equipment or
interference may result.
1.
Remove tie rod ball stud nut at steering arm and
disconnect tie rod from steering arm.
2.
Move tie rod end to forward hole for 17.6:1 ratio
(fast ratio) or rear hole for 20.2:1 ratio (standard
ratio).
3.
Install tie rod stud nut and tighten securely. Repeat
operation on opposite steering arm.
COMPONENT REPLACEMENT AND REPAIRS
STEERING WHEEL
REGULAR PRODUCTION (Fig. 7)
Removal
1.
Disconnect steering column harness from chassis
wiring harness at connector (fig. 8).
2.
Pull out horn button cap or center ornament and
retainer.
3.
Remove three screws from the receiving cup.
4.
Remove the receiving cup, belleville spring, bushing,
and pivot ring.
5. Remove the steering wheel nut and washer.
6. Using Tool J-2927, install centering adapter on
steering shaft, thread puller anchor screws into
threaded holes provided in steering wheel. Turn
center bolt of tool clockwise to remove steering
wheel (fig. 9).
Installation
CAUTION: Direction signal control assembly
must be in "neutral position when assembling
steering wheel to prevent damage to cancelling
cam and control assembly.
1.
With directional cancelling cam and horn contact as-
sembly in place, set wheel onto steering shaft.
Fig. 7—-Regular Wheel and Horn Attachments
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL
Page 445 of 659

STEERING 9-5
Fig.
8—Steering Column Wiring Connector
Secure with washer and nut. Refer to torque speci-
fications at rear of manual for correct torque values.
Install belleville spring (with dish of spring up), pivot
ring, bushing and receiving cup with screws.
Install retainer and horn button cap or center
ornament.
Connect steering column harness to chassis wiring
connector.
Fig.
9—Removing Steering Wheel with J-2927
Fig.
10—Simulated Wood Steering Wheel and Attaching Parts
SIMULATED WOOD (Fig. 10)
Removal
1.
Disconnect steering column harness from chassis
wiring harness at connector.
2.
Remove horn cap assembly by pulling up.
3.
Remove contact assembly attaching screws and re-
move contact assembly.
NOTE:
If steering wheel only is to be replaced,
perform step 4. If directional signal cancelling
cam is to be replaced, omit step 4 and proceed
with steps 5 and 6.
4.
Remove remaining screws from steering wheel and
remove wheel from hub assembly.
5. Remove steering wheel nut and washer.
6. Using Tool J-2927, install centering adapter on
steering shaft, thread puller anchor screws into
threaded holes provided in hub assembly. Turn
center bolt of tool clockwise to remove hub
assembly.
Installation
CAUTION: Directional signal control assembly
must be in neutral position when assembling hub
assembly to prevent damage to cancelling cam
and control assembly.
1.
With directional cancelling cam and horn contact in
place, install hub assembly on steering shaft. Secure
with washer and nut. Refer to torque specifications
at rear of manual for correct torque value.
2.
Attach steering wheel to hub assembly using the six
attaching screws and tighten securely.
3.
Place horn contact on steering wheel and attach with
three screws. Tighten securely.
4.
Snap horn button in place.
5. Connect steering column harness to chassis wiring
connector.
CORVETTE TELESCOPING (Fig. 11)
Removal
1.
Disconnect steering column harness at wiring
connector.
2.
Pry off horn button cap.
3.
Remove three screws securing horn contact to spacer
and hub.
4.
Remove two screws securing lock screw to lock
knob,
and remove lock screw, lock knob, and spacer.
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL
Page 446 of 659

STEERING 9-6
Fig.
11
—Corvette Telescoping Wheel Option
5.
7.
NOTE:
If steering wheel only is to be replaced,
perform Step 5 below only. If directional signal
cancelling cam is to be replaced, omit Step 5
and proceed with Steps 6 and 7.
Remove six screws securing steering wheel to hub
and remove wheel.
Remove nut and washer from shaft and using steering
wheel puller Tool J-2927, remove steering wheel and
hub from vehicle.
Slide cancelling cam and spring off shaft.
Installation
NOTE:
Refer to torque specifications at rear of
manual for correct torque values.
1.
If necessary, slide cancelling cam and spring on end
of shaft.
2.
If hub was removed from steering wheel, attach hub
to steering wheel with screws removed during dis-
assembly.
3.
Place steering wheel and hub assembly in position
and secure to column with washer and nut.
4.
Position spacer on steering wheel.
5. Position lock knob on steering wheel.
6. Install lock screw through lock knob, turn into shaft,
and adjust to lock position.
7. Attach spacer to wheel with three screws.
8. Place lock knob in lock position and attach to lock
screw with two screws.
9. Remove three screws holding spacer. Attach horn
contact to spacer and steering wheel with three
screws.
10.
Install horn button cap.
11.
Connect steering column harness at chassis plug.
STEERING COUPLING (Fig. 12)
Removal
NOTE:
Chevy n models are equipped with a
clamp arrangement rather than the conventional
"rag joint" steering coupling. Refer to Steering
Gear - Chevy II, for service procedures.
1.
Remove nuts and washers securing steering coupling
to flanged end of steering column (fig. 12).
2.
Remove coupling clamp bolt (fig. 12) and slightly
spread coupling clamp.
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL
Page 450 of 659

STEERING 9-10
SECTOR SHAFT SEAL REPLACEMENT
A faulty seal may be replaced without removal of
steering gear from car by removing pitman arm as out-
lined under Maintenance and Adjustments--Steering Gear
Adjustments and proceed as follows:
1.
Loose lash adjuster lock nut and turn lash adjuster
screw several turns counterclockwise.
2.
Remove three cap screws holding side cover to gear
bushing.
3.
Pull side cover and sector shaft from gear housing
as a unit. Do not separate side cover from sector
shaft.
4.
Pull sector shaft seal from gear housing using
hooked tool or pliers.
5. Coat new seal with chassis grease and position in
sector shaft bore.
6. Place a socket or piece of pipe of suitable diameter
on top of seal and drive seal into bore by tapping
pipe or socket with soft hammer.
7. Install sector shaft side cover assembly, being care-
ful not to damage new seal with splines on end of
shaft; splines may be wrapped with a few turns of
tape to prevent this.
8. Install new side cover gasket and align side cover on
gear housing and install cap screw.
9. Perform steering gear adjustment and install pitman
arm as outlined under Maintenance and Adjustments.
STEERING COLUMN
All models are equipped with new energy absorbing
steering columns. The columns are of five basic designs
as follows:
1.
Syncromesh. The syncromesh column is used on
models with standard, column mounted, conventional
shift levers. The shift tube, within the outer mast
jacket, includes two lower shift levers for connection
to the transmission control linkage.
2.
Automatic and floor shift. This column is used on
models equipped with column mounted powerglide
shift levers, or models with floor shift. If the ve-
hicle has the column mounted powerglide shift con-
trol, the inner shift tube has a single lower shift
lever for connection to the transmission control
linkage. On floor shift models, no lower shift levers
are present on the shift tube.
3.
Tilt wheel option. The upper end and steering shaft
of this column is specially designed to accommodate
the optional tilt steering wheel.
4.
Standard Corvette Column. The standard Corvette
column is similar in design to the Automatic and
Floor Shift column used on other models, except
no shift tube is used. Other differences are pointed
out in the disassembly and assembly procedures for
Standard Corvette column.
5. Telescopic wheel option. The upper end and steering
shaft of this column is specially designed to ac-
commodate the optional telescoping steering wheel.
To perform service procedures on steering column
upper end components, it is not necessary to remove the
column from the vehicle. The steering wheel, horn com-
ponents, turn signal switch, upper housing with bearing,
shift control lever, hazard warning knob, and upper shift
bowl may all be removed with the column remaining in
the vehicle. When servicing the above components, omit
the removal procedure and proceed with the applicable
disassembly procedures. Because of the numerous dif-
ferences in steering column types, be sure to refer to the
set of instructions below which apply to the exact column
to be serviced:
CAUTION: The outer mast jacket, shift tube, _
steering shaft, and instrument panel column
mounting b
racket
are designed as energy ab-
sorbing units. Because of the design of these
components, it is absolutely necessary to handle
the column with care when performing any serv-
ice operation required. Avoid hammering, jar-
ring, dropping, or leaning on any portion of the
column.
Removal
1.
Disconnect steering column harness at connector.
Disconnect neutral safety switch and back-up lamp
switch connectors if so equipped.
Remove steering wheel as outlined in this section.
Remove nuts and washers securing flanged end of
column to steering gear. On Chevy H models, re-
move nut and clamp bolt securing lower end of steer-
ing column to steering gear.
Disconnect transmission control linkage, if so
equipped, from lower column shift tube, levers.
Chevrolet and Chevy II only: Remove screws at-
taching upper and lower mast jacket covers together.
On Chevrolet, remove screws attaching lower cover
to instrument panel (figs. 15 and 18). Remove lower
cover.
Chevelle only: Remove screws securing mast jacket
trim cover to instrument panel and remove cover
(fig. 15).
Corvette, only: Remove screws securing escutcheon
to instrument panel. Remove screws securing upper
and lower covers together and remove covers.
On Chevrolet and Chevelle columns with Powerglide
shift levers, loosen set screw at six o'clock position
at bottom of column and remove the transmission
shift indicator pointer (fig. 15).
9. Chevrolet only (fig. 19):
a. Remove screws securing cover trim to dash
panel and remove cover trim.
2.
3.
4.
5.
6.
7.
8.
Fig.
18—Mast Jacket Cover Attachments—Chevy II
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL
Page 452 of 659

STEERING 9-12
1.
Steering Wheel Nut
2i Screw
3. Retaining Ring
4.
Thrust Washer
5. Wave Washer
6. Turn Signal Switch
7. Upper Bearing and
Housing Assembly
8. Cover
Fig.
24—Syncromesh Steering Column—Exploded View
9. Spring
1.0. Lock Ring
11.
Thrust Washer
12.
Shift Lever Spring
13.
Shift Bowl
14.
Shroud
15.
Bearing
16.
Mast Jacket
17.
Flange Plate
18.
Wiring Protector
19.
Shift Tube Assembly
20.
Adapter
21.
Bolt
22.
Reinforcing Ring
23.
Steering Shaft
24.
Bearing
25.
Tolerance Ring Kit
26.
Flange
cover, and seal to dash panel and remove covers.
13.
Corvette only (Fig. 23)
a. Remove clamp bolt and washer from support as-
sembly on engine side of dash panel.
b.
Remove screws securing support assembly and
seal to engine side of dash panel.
14.
Support column and remove screws, nuts, and bolts
securing instrument panel mounting bracket to un-
derside of instrument panel. On Chevrolet, Chevelle,
Camaro, and Chevy II models, remove and retain
wedge shims. On Chevrolet models, remove
retainers.
15.
Move front seat back as far as possible to provide
maximum clearance, and carefully lift column up out
of position and remove from vehicle. If column is
equipped with lower shift levers, mechanic at engine
compartment can pilot levers through dash panel
opening as column is lifted.
Disassembly'—Syncromesh Column (Fig. 24)
1.
Unsnap and remove wiring protector (fig. 25).
CAUTION: Secure column in bench vise for
service one of two ways shown in Figure 26.
Clamping column in vise in any other manner
CHEVROLET CHASSIS SERVICE MANUAL