2022 TOYOTA COROLLA brakes
[x] Cancel search: brakesPage 204 of 678

2024-5. Using the driving support systems
*: If equipped
The system can detect the follow-
ing:
Vehicles
Bicyclists
Pedestrians
■Pre-collision warning
When the system determines that
the possibility of a frontal collision is
high, a buzzer will sound and a
warning mess age will be displayed
on the multi-information display to
urge the driver to take evasive
action.
■Pre-collision brake assist
When the system determines that
the possibility of a frontal collision is
high, the system applies greater
braking force in relation to how
strongly the brake pedal is
depressed.
■Pre-collision braking
If the system determines that the
possibility of a frontal collision is
extremely high, the brakes are
automatically applied to help avoid
the collision or reduce the impact of
the collision.
PCS (Pre-Collision Sys-
tem)*
The pre-collision system uses
a radar sensor and front cam-
era to detect objects ( P.205)
in front of the vehicle. When
the system determines that the
possibility of a frontal collision
with an object is high, a warn-
ing operates to urge the driver
to take evasive action and the
potential brake pressure is
increased to help the driver
avoid the collision. If the sys-
tem determines that the possi-
bility of a frontal collision with
an object is extremely high, the
brakes are automatically
applied to help avoid the colli-
sion or help reduce the impact
of the collision.
The pre-collision system can
be disabled/enabled and the
warning timing can be
changed. ( P.204)
Detectable objects
System functions
Page 210 of 678

2084-5. Using the driving support systems
• If a vehicle ahead has extremely high
ground clearance
• If a vehicle ahead is carrying a load
which protrudes past its rear bumper • If a vehicle ahead is irregularly
shaped, such as a tractor or side car
• If a vehicle ahead is a child sized bicy- cle, a bicycle that is carrying a large
load, a bicycle ridden by more than
one person, or a uniquely shaped bicycle (bicycle with a child seat, tan-
dem bicycle, etc.)
• If a pedestrian/or the riding height of a bicyclist ahead is shorter than approx-
imately 1 m (3.2 ft.) or taller than
approximately 2 m (6.5 ft.) • If a pedestrian/bicyclist is wearing
oversized clothing (a rain coat, long
skirt, etc.), making their silhouette obscure
• If a pedestrian is bending forward or
squatting or bicyclist is bending for- ward
• If a pedestrian/bicyclist is moving fast
• If a pedestrian is pushing a stroller, wheelchair, bicycle or other vehicle
• When driving in inclement weather
such as heavy rain, fog, snow or a
sandstorm • When driving through steam or smoke
• When the surrounding area is dim,
such as at dawn or dusk, or while at night or in a tunnel, making a detecta-
ble object appear to be nearly the
same color as its surroundings
• When driving in a place where the sur- rounding brightness changes sud-
denly, such as at the entrance or exit
of a tunnel • After the engine has started the vehi-
cle has not been driven for a certain
amount of time • While making a left/right turn and for a
few seconds after making a left/right
turn • While driving on a curve and for a few
seconds after driving on a curve
• If your vehicle is skidding • If the front of the vehicle is raised or
lowered
• If the wheels are misaligned
• If a wiper blade is blocking the front
camera • The vehicle is being driven at
extremely high speeds
• When driving on a hill • If the radar sensor or front camera is
misaligned
●In some situations such as the follow-
ing, sufficient braking force may not
be obtained, prev enting the system from performing properly:
• If the braking functions cannot operate
to their full extent, such as when the brake parts are extremely cold,
extremely hot, or wet
• If the vehicle is not properly main- tained (brakes or ti res are excessively
worn, improper tire inflation pressure,
etc.)
• When the vehicle is being driven on a gravel road or other slippery surface
■If VSC is disabled
●If VSC is disabled ( P.317), the pre-collision brake assist and pre-col-
lision braking functions are also disa-
Page 232 of 678
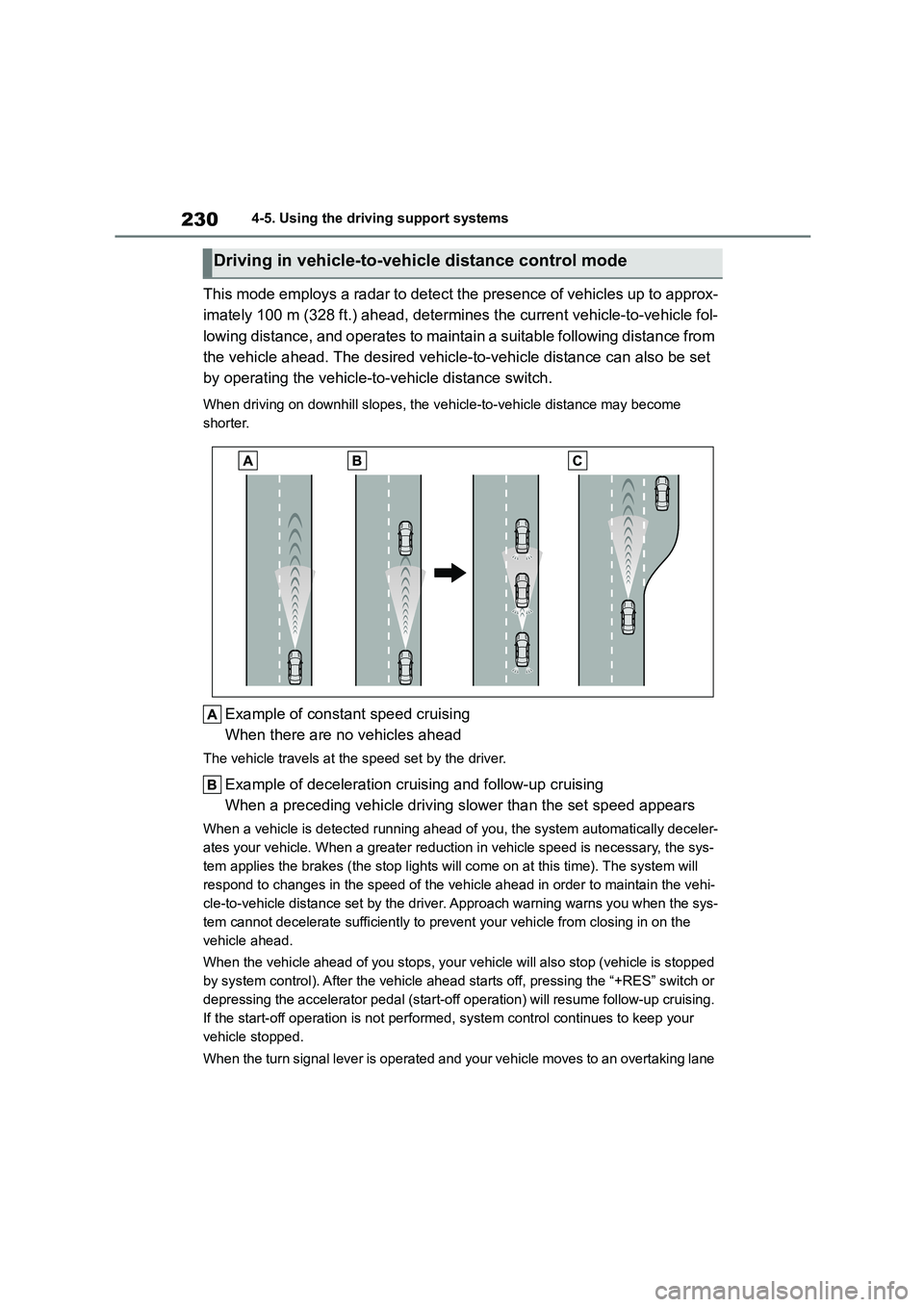
2304-5. Using the driving support systems
This mode employs a radar to detect the presence of vehicles up to approx-
imately 100 m (328 ft.) ahead, determines the current vehicle-to-vehicle fol-
lowing distance, and operates to maintain a suitable following distance from
the vehicle ahead. The desired vehicle-to-vehicle distance can also be set
by operating the vehicle-to -vehicle distance switch.
When driving on downhill slopes, the vehicle-to-vehicle distance may become
shorter.
Example of const ant speed cruising
When there are no vehicles ahead
The vehicle travels at the speed set by the driver.
Example of deceleration cruising and follow-up cruising
When a preceding vehicle driving slower than the set speed appears
When a vehicle is de tected running ahead of you, the system automatically deceler-
ates your vehicle. When a greater reduction in vehicle speed is necessary, the sys-
tem applies the brakes (the stop lights will come on at this time). The system will
respond to changes in the speed of the vehicle ahead in order to maintain the vehi-
cle-to-vehicle distance set by the driver. Approach warning warns you when the sys-
tem cannot decelerate sufficiently to prevent your vehicle from closing in on the
vehicle ahead.
When the vehicle ahead of you stops, your vehicle will also stop (vehicle is stopped
by system control). After the vehicle ahead starts off, pressing the “+RES” switch or
depressing the accelerator pedal (start-off operation) will resume follow-up cruising.
If the start-off operation is not performed, system control continues to keep your
vehicle stopped.
When the turn signal lever is operated and your vehicle moves to an overtaking lane
Driving in vehicle-to-vehicle distance control mode
Page 243 of 678
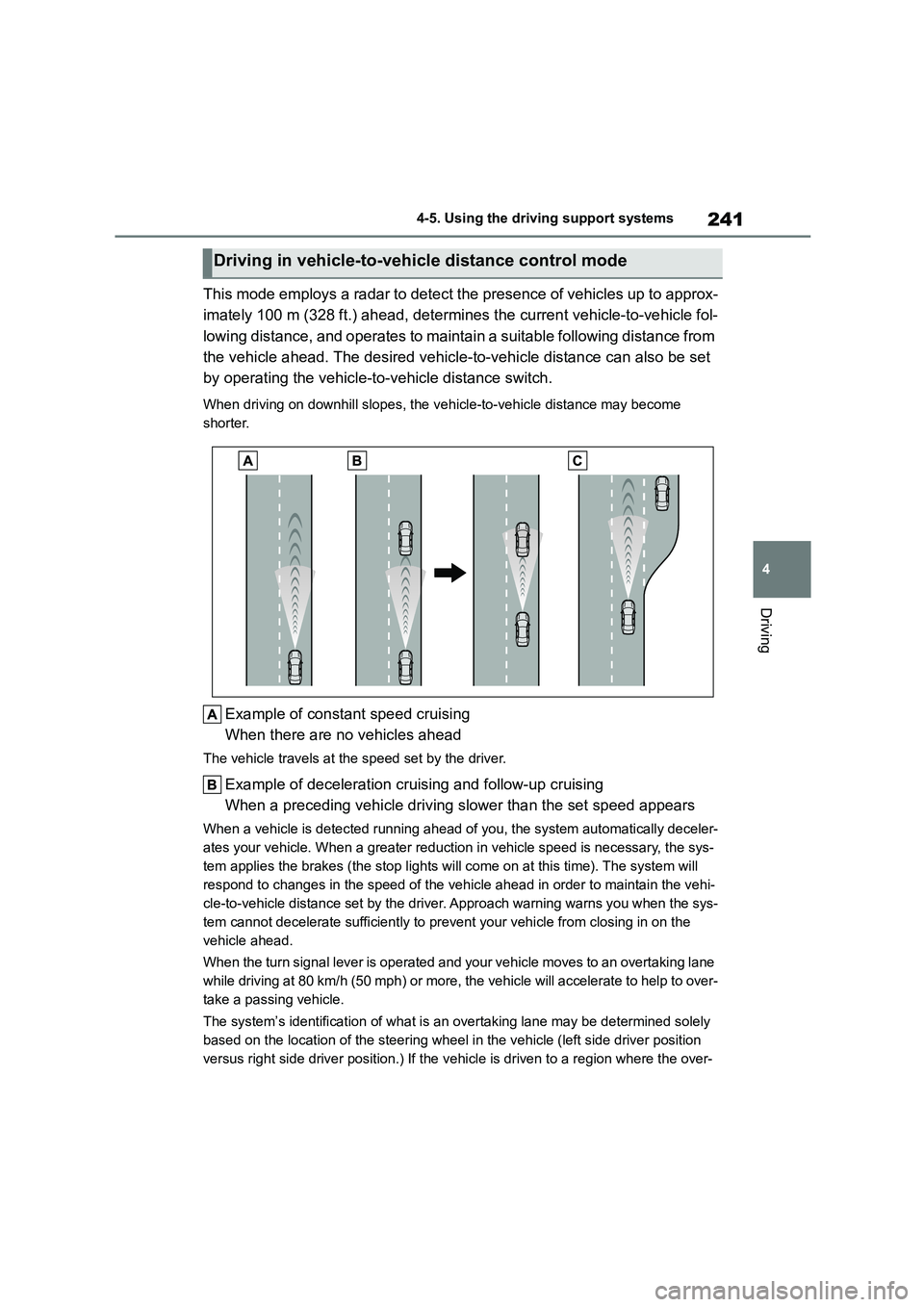
241
4
4-5. Using the driving support systems
Driving
This mode employs a radar to detect the presence of vehicles up to approx-
imately 100 m (328 ft.) ahead, determines the current vehicle-to-vehicle fol-
lowing distance, and operates to maintain a suitable following distance from
the vehicle ahead. The desired vehicle-to-vehicle distance can also be set
by operating the vehicle-to -vehicle distance switch.
When driving on downhill slopes, the vehicle-to-vehicle distance may become
shorter.
Example of const ant speed cruising
When there are no vehicles ahead
The vehicle travels at the speed set by the driver.
Example of deceleration cruising and follow-up cruising
When a preceding vehicle driving slower than the set speed appears
When a vehicle is de tected running ahead of you, the system automatically deceler-
ates your vehicle. When a greater reduction in vehicle speed is necessary, the sys-
tem applies the brakes (the stop lights will come on at this time). The system will
respond to changes in the speed of the vehicle ahead in order to maintain the vehi-
cle-to-vehicle distance set by the driver. Approach warning warns you when the sys-
tem cannot decelerate sufficiently to prevent your vehicle from closing in on the
vehicle ahead.
When the turn signal lever is operated and your vehicle moves to an overtaking lane
while driving at 80 km/h (50 mph) or more, the vehicle will accelerate to help to over-
take a passing vehicle.
The system’s identificat ion of what is an overtaking lane may be determined solely
based on the location of the steering wheel in the vehicle (left side driver position
versus right side driver position.) If the v ehicle is driven to a region where the over-
Driving in vehicle-to-vehicle distance control mode
Page 268 of 678

2664-5. Using the driving support systems
■If “Parking Assist Unavailable
Please Clean Parking Assist Sen- sor” is displayed on the multi-infor-
mation display
A sensor may be covered with ice, snow, dirt, etc. Remove the ice, snow,
dirt, etc., from the sensor to return the
system to normal.
Also, due to ice forming on a sensor at
low temperatures, a warning message
may be displayed or the sensor may not be able to detect an object. Once the ice
melts, the system will return to normal.
■Sensor detection information
The following situations may occur dur- ing use.
●The sensors may be able to only detect objects near the front and rear
bumpers.
●Depending on the shape of the object
and other factors, the detection dis-
tance may shorten, or detection may be impossible.
●If an object is extremely close to a sensor, it may not be detected.
●There will be a short delay between object detection and display. Even at
low speeds, there is a possibility that
the object will come within the sen- sor’s detection areas before the dis-
play is shown and the warning beep
sounds.
●It might be difficult to hear the buzzer
due to the volume of the audio system or air flow noise of the air conditioning
system.
●It may be difficult to hear the buzzer if
buzzers for other systems are sound-
ing.
■Objects which the system may not
be properly detected
The shape of the object may prevent the
sensor from detecting it. Pay particular
attention to the following objects:
●Wires, fences, ropes, etc.
●Cotton, snow and other materials that
absorb sound waves
●Sharply-angled objects
●Low objects
●Tall objects with upper sections pro- jecting outwards in the direction of
your vehicle
People may not be detected if they are wearing certain types of clothing.
■Situations in which the system may
not operate properly
Certain vehicle conditions and the sur- rounding environment may affect the
ability of a sensor to correctly detect
objects. Particular instances where this may occur are listed below.
●There is dirt, snow or ice on a sensor. (Cleaning the sensors will resolve this
problem.)
●A sensor is frozen. (Thawing the area
will resolve this problem.)
In especially cold weather, if a sensor is frozen the sensor display may be
displayed abnormally, or objects, such
as a wall, may not be detected.
●When a sensor or the area around a
sensor is extremely hot or cold.
●On an extremely bumpy road, on an
incline, on gravel, or on grass.
●When vehicle horns, vehicle detec-
tors, motorcycle engines, air brakes of large vehicles, the clearance sonar of
other vehicles or other devices which
produce ultrasonic waves are near the
vehicle
●A sensor is coated with a sheet of
spray or heavy rain.
●If objects draw too close to the sensor.
●When a pedestrian is wearing clothing
that does not reflect ultrasonic waves
Page 269 of 678

267
4
4-5. Using the driving support systems
Driving
(ex. skirts with gathers or frills).
●When objects that are not perpendicu-
lar to the ground, not perpendicular to
the vehicle traveling direction, une- ven, or waving are in the detection
range.
●Strong wind is blowing
●When driving in inclement weather such as fog, snow or a sandstorm
●When an object that cannot be detected is between the vehicle and a
detected object
●If an object such as a vehicle, motor-
cycle, bicycle or pedestrian cuts in
front of the vehicle or runs out from the side of the vehicle
●If the orientation of a sensor has been changed due to a collision or other
impact
●When equipment that may obstruct a
sensor is installed, such as a towing
eyelet, bumper protector (an addi- tional trim strip, et c.), bicycle carrier,
or snow plow
●If the front of the vehicle is raised or
lowered due to the carried load
●If the vehicle cannot be driven in a
stable manner, such as when the
vehicle has been in an accident or is malfunctioning
●When a tire chains, compact spare tire or an emergency tire puncture repair
kit is used
■Situations in which the system may
operate even if there is no possibil- ity of a collision
In some situations, such as the follow-
ing, the system may operate even
though there is no possibility of a colli- sion.
●When driving on a narrow road
●When driving toward a banner, flag,
low-hanging branch or boom barrier (such as those used at railroad cross-
ings, toll gates and parking lots)
●When there is a rut or hole in the sur-
face of the road
●When driving on a metal cover (grat-
ing), such as those used for drainage
ditches
●When driving up or down a steep
slope
●If a sensor is hit by a large amount of
water, such as when driving on a flooded road
●There is dirt, snow, water drops or ice on a sensor. (Cleaning the sensors
will resolve this problem.)
●A sensor is coated with a sheet of
spray or heavy rain
●When driving in inclement weather
such as fog, snow or a sandstorm
●When strong winds are blowing
●When vehicle horns, vehicle detec- tors, motorcycle engines, air brakes of
large vehicles, the clearance sonar of
other vehicles or other devices which
produce ultrasonic waves are near the vehicle
●If the front of the vehicle is raised or lowered due to the carried load
Page 278 of 678

2764-5. Using the driving support systems
●When a detected vehicle turns while
approaching the vehicle
●When there are spinning objects near
your vehicle such as the fan of an air conditioning unit
●When water is splashed or sprayed toward the rear bumper, such as from
a sprinkler
●Moving objects (flags, exhaust fumes,
large rain droplets or snowflakes, rain
water on the road surface, etc.)
●When the distance between your vehi-
cle and a guardrail, wall, etc., that enters the detection area is short
●Gratings and gutters
●When a sensor or the area around a
sensor is extremely hot or cold
●If the suspension has been modified
or tires of a size other than specified are installed
●If the front of the vehicle is raised or lowered due to the carried load
*: If equipped
■Parking Support Brake func-
tion (static objects) (if
equipped)
Ultrasonic sensors are used to
detect static objects, such as a wall,
in the detection area when driving
at a low speed or backing up.
( P. 2 8 3 )
■Parking Support Brake func-
tion (rear-crossing vehicles) (if
equipped)
Rear radar sensors are used to
detect approaching vehicles in the
PKSB (Parking Suppor t
Brake)*
The Parking Support Brake
system consists of the follow-
ing functions that operate
when driving at a low speed or
backing up, such as when
parking. When the system
determines that a collision with
a detected object is high, a
warning operates to urge the
driver to take evasive action. If
the system determines that the
possibility of a collision with a
detected object is extremely
high, the brakes are automati-
cally applied to help avoid the
collision or help reduce the
impact of the collision.
PKSB (Parking Support
Brake) system
Page 281 of 678
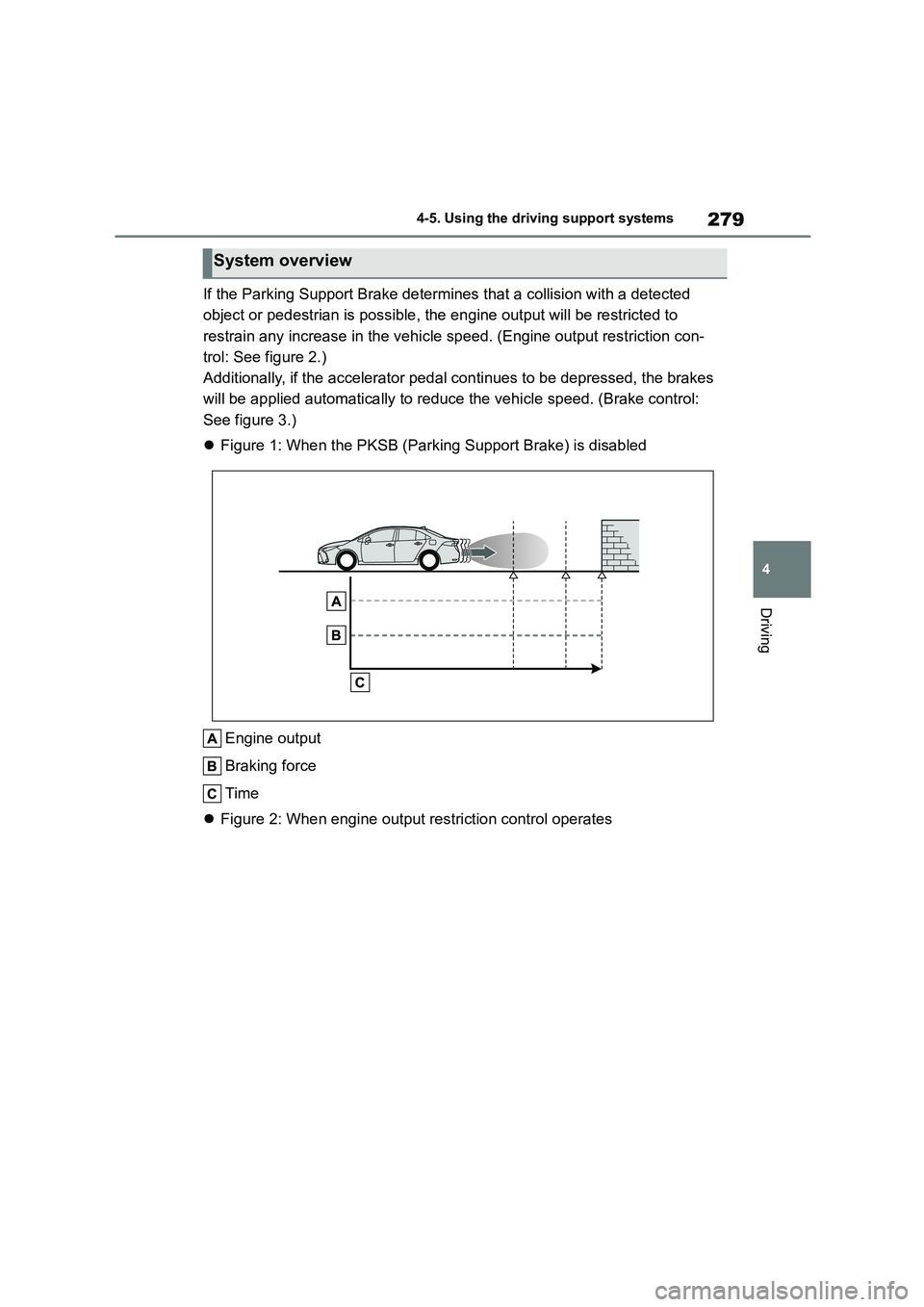
279
4
4-5. Using the driving support systems
Driving
If the Parking Supp ort Brake determines that a collision with a detected
object or pedestrian is possible, the engine output will be restricted to
restrain any increase in the vehicle sp eed. (Engine output restriction con-
trol: See figure 2.)
Additionally, if the accelerator pedal continues to be depressed, the brakes
will be applied automatica lly to reduce the vehicle speed. (Brake control:
See figure 3.)
Figure 1: When the PKSB (Parking Support Brake) is disabled
Engine output
Braking force
Time
Figure 2: When engine output restriction control operates
System overview