2010 JAGUAR XFR oil level
[x] Cancel search: oil levelPage 1276 of 3039
Published: 11-May-2011
Engine Ignition - V8 5.0L Petrol/V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol - Engine Ignition
Diagnosis and Testing
Principles of Operation
For a detailed description of the engine ignition system and operation, refer to the relevant Description and Operation section
of the workshop manual. REFER to: (303-07B Engine Ignition - V8 5.0L Petrol/V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol)
Engine Ignition (Description and Operation), Engine Ignition (Description and Operation), Engine Ignition (Description and Operation).
Inspection and Verification
CAUTION: Diagnosis by substitution from a donor vehicle is NOT acceptable. Substitution of control modules does not
guarantee confirmation of a fault and may also cause additional faults in the vehicle being checked and/or the donor vehicle.
NOTE: Check and rectify basic faults before beginning diagnostic routines involving pinpoint tests.
1. Verify the customer concern.
2. Visually inspect for obvious signs of mechanical and electrical damage.
Visual Inspection
Mechanical Electrical
Engine oil level
Cooling system coolant level
Fuel level
Fuel contamination/grade/quality
Exhaust gas recirculation (EGR) valves
Fuses
Wiring harness
Loose or corroded electrical connectors
Ignition coils
Sensor(s)
Engine Control Module (ECM)
Transmission Control Module (TCM)
3. If an obvious cause for an observed or reported concern is found, correct the cause (if possible) before proceeding to
the next step.
4. If the cause is not visually evident, verify the symptom and refer to the Symptom Chart, alternatively check for
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) and refer to the DTC Index.
Symptom Chart
Symptom Possible Causes Action Engine cranks, but does not
fire
Engine breather system
disconnected/restricted
Ignition system
Fuel system
Electronic engine control Ensure the engine breather system is free from restriction
and is correctly installed. Check for ignition system, fuel
system and electronic engine control DTCs and refer to the
relevant DTC Index Engine cranks and fires, but
will not start
Evaporative emissions purge
valve
Fuel pump
Spark plugs
HT short to ground (tracking)
check rubber boots for
cracks/damage
Ignition system Check for evaporative emissions, fuel system and ignition
system related DTCs and refer to the relevant DTC Index Difficult cold start
Engine coolant level/anti-
freeze content
Battery
Electronic engine controls
Exhaust Gas Recirculation
(EGR) valve stuck open
Fuel pump
Purge valve Check the engine coolant level and condition. Ensure the
battery is in a fully charged and serviceable condition.
Check for electronic engine controls, engine emissions, fuel
system and evaporative emissions system related DTCs
and refer to the relevant DTC Index
Page 1353 of 3039
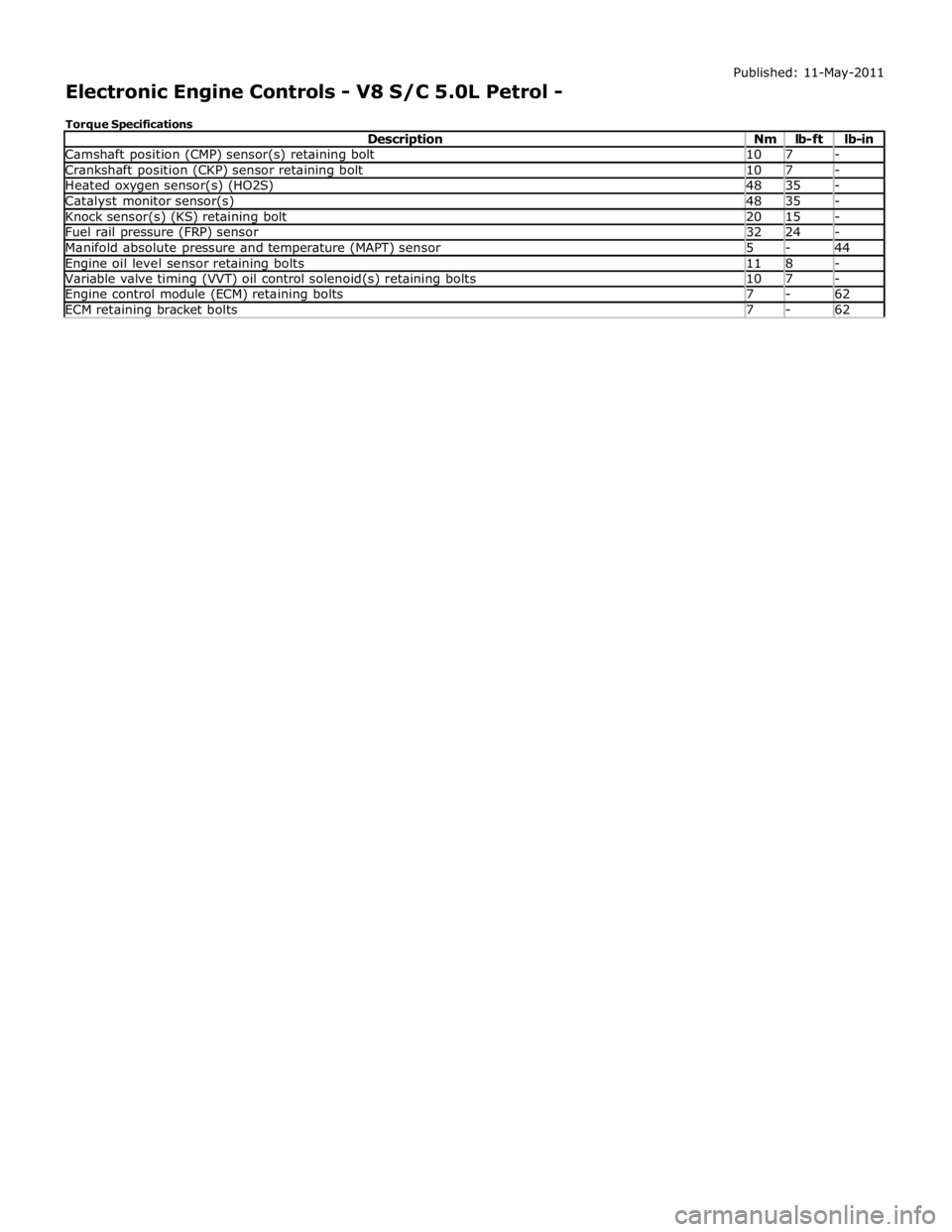
Camshaft position (CMP) sensor(s) retaining bolt 10 7 - Crankshaft position (CKP) sensor retaining bolt 10 7 - Heated oxygen sensor(s) (HO2S) 48 35 - Catalyst monitor sensor(s) 48 35 - Knock sensor(s) (KS) retaining bolt 20 15 - Fuel rail pressure (FRP) sensor 32 24 - Manifold absolute pressure and temperature (MAPT) sensor 5 - 44 Engine oil level sensor retaining bolts 11 8 - Variable valve timing (VVT) oil control solenoid(s) retaining bolts 10 7 - Engine control module (ECM) retaining bolts 7 - 62 ECM retaining bracket bolts 7 - 62
Page 1361 of 3039

DIAGNOSTICS
The ECM stores each fault as a DTC (diagnostic trouble code). The DTC and associated environmental and freeze frame data can be read using Jaguar approved diagnostic equipment, which can also read real time data from each sensor, the adaption
values currently being employed and the current fueling, ignition and idle speed settings.
ENGINE CONTROL MODULE Component Description
The ECM is installed in the front passenger side of the engine compartment, on a bracket attached to the engine bulkhead. The ECM has the capability of adapting its fuel and ignition control outputs in response to several sensor inputs. The ECM receives inputs from the following:
CKP sensor. CMP (camshaft position) sensors (4 off).
ECT (engine coolant temperature) sensor.
Knock sensors (4 off).
MAP (manifold absolute pressure) sensor.
MAFT sensors (2 off). MAPT (manifold absolute pressure and temperature) sensor.
Throttle position sensor.
Heated oxygen sensors (4 off).
APP sensor. Ambient air temperature sensor.
FRP (fuel rail pressure) sensor. For additional information, refer to 303-04G Fuel Charging and Controls.
Engine cooling fan. For additional information, refer to 303-03D Engine Cooling.
Stoplamp switch. For additional information, refer to 206-09 Anti-Lock Control - Stability Assist.
Speed control cancel/suspend switch. For additional information, refer to 310-03D Speed Control.
Oil level and temperature sensor. For additional information, refer to 303-01F Engine.
Fuel LP (low pressure) sensor. For additional information, refer to 310-01D Fuel Tank and Lines.
Fuel pump driver module. For additional information, refer to 310-01D Fuel Tank and Lines.
The ECM provides outputs to the following: Electronic throttle.
Main relay.
Heater elements of the heated oxygen sensors (4 off).
Fuel injectors (8 off). For additional information, refer to 303-04G Fuel Charging and Controls. www.JagDocs.com
Page 1369 of 3039
Published: 16-Sep-2013
Electronic Engine Controls - V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol - Electronic Engine Controls
Diagnosis and Testing
Principle of Operation
For a detailed description of electronic engine controls, refer to the relevant Description and Operation section of the workshop
manual. REFER to: (303-14D Electronic Engine Controls - V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol)
Electronic Engine Controls (Description and Operation), Electronic Engine Controls (Description and Operation), Electronic Engine Controls (Description and Operation).
Inspection and Verification
1. Verify the customer concern.
2. Visually inspect for obvious signs of damage and system integrity.
Visual Inspection
Mechanical Electrical
Engine oil level and condition
Cooling system coolant level
Fuel level
Fuel contamination/grade/quality
Throttle body
Front End Accessory Drive (FEAD) belt
Air cleaner condition
Fuses
Wiring harness
Electrical connector(s)
Sensor(s)
Engine Control Module
Transmission Control Module
3. If an obvious cause for an observed or reported concern is found, correct the cause (if possible) before proceeding to
the next step.
4. If the cause is not visually evident, verify the customer concern and refer to the Symptom Chart below, alternatively,
check for Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) and refer to the DTC Index.
Symptom Chart
Symptom Possible Cause Action Engine non-start Engine does not crank
Security system /Immobilizer
engaged
Engine in shut-down mode
ECM relay
Battery
Starting system
Engine seized
Check that the security system is disarmed
Read DTCs and refer to DTC Index in this
section for ECM relay tests
Ensure the battery is in fully charged and
serviceable condition
For starting system tests refer to the
relevant section of the workshop manual
For engine system tests refer to the relevant
section of the workshop manual Engine cranks, but does not fire
Engine breather system
disconnected/restricted
Ignition system
Fuel system
Electronic engine controls
Ensure the engine breather system is free
from restriction and is correctly installed
For ignition system tests refer to the
relevant section of the workshop manual
For fuel system tests refer to the relevant
section of the workshop manual
Read DTCs and refer to DTC Index in this
section for electronic engine control tests Engine cranks and fires, but will not
start
Evaporative emissions purge
valve
Fuel pump
Spark plugs
Ignition coil failure(s)
For purge valve tests refer to the relevant
section of the workshop manual
For fuel system tests refer to the relevant
section of the workshop manual
For ignition system tests refer to the
relevant section of the workshop manual Difficult to start Difficult cold start
Check engine coolant
level/anti-freeze content
Battery
Electronic engine controls
Exhaust gas recirculation
Check the engine coolant level and
condition. Refer to the relevant sections of
the workshop manual
Ensure the battery is in a fully charged and
serviceable condition. Refer to the battery
Page 1389 of 3039
Published: 11-May-2011
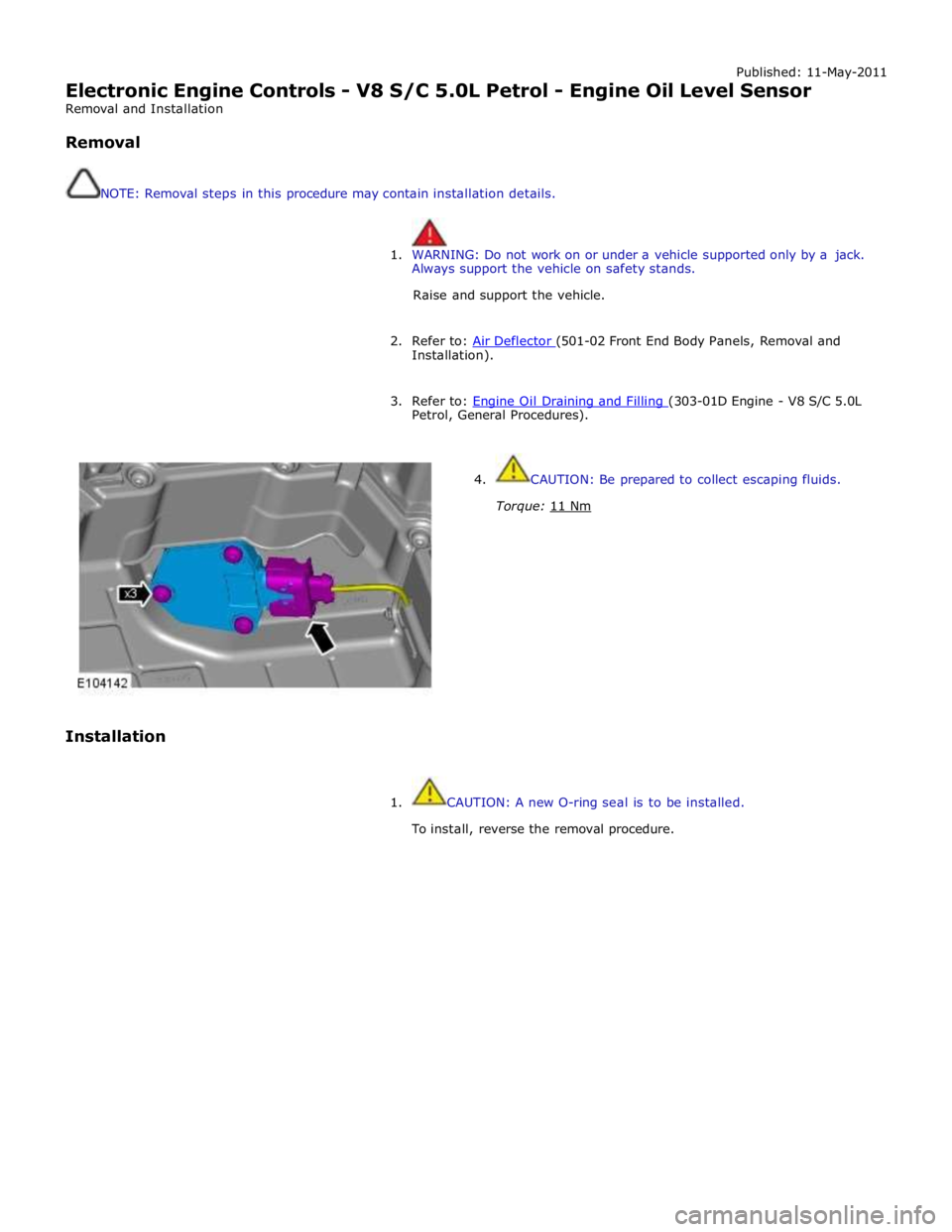
Electronic Engine Controls - V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol - Engine Oil Level Sensor
Removal and Installation
Removal
NOTE: Removal steps in this procedure may contain installation details.
1. WARNING: Do not work on or under a vehicle supported only by a jack.
Always support the vehicle on safety stands.
Raise and support the vehicle.
2. Refer to: Air Deflector (501-02 Front End Body Panels, Removal and Installation).
3. Refer to: Engine Oil Draining and Filling (303-01D Engine - V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol, General Procedures).
Installation
4. CAUTION: Be prepared to collect escaping fluids.
Torque: 11 Nm
1. CAUTION: A new O-ring seal is to be installed.
To install, reverse the removal procedure.
Page 1430 of 3039
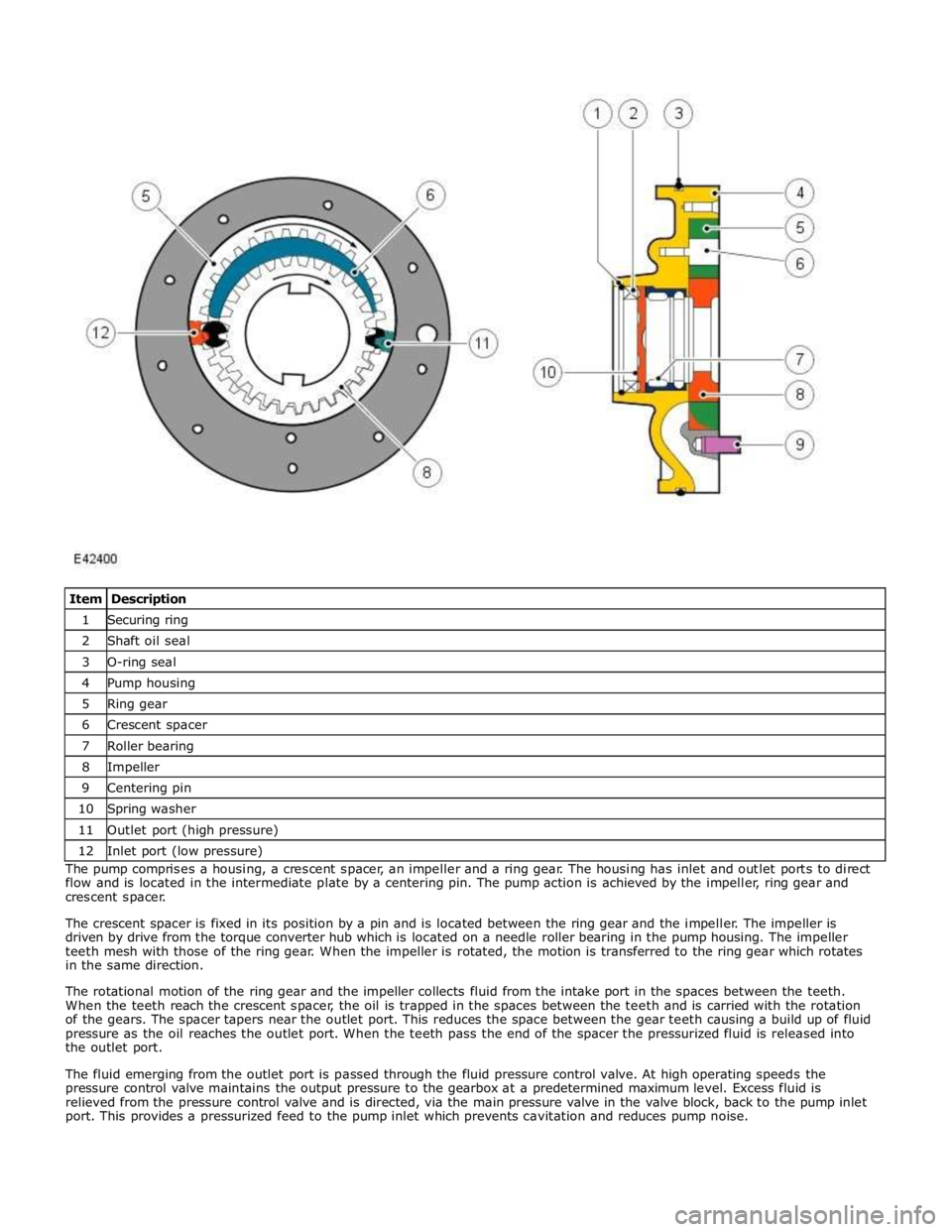
1 Securing ring 2 Shaft oil seal 3 O-ring seal 4 Pump housing 5 Ring gear 6 Crescent spacer 7 Roller bearing 8 Impeller 9 Centering pin 10 Spring washer 11 Outlet port (high pressure) 12 Inlet port (low pressure) The pump comprises a housing, a crescent spacer, an impeller and a ring gear. The housing has inlet and outlet ports to direct
flow and is located in the intermediate plate by a centering pin. The pump action is achieved by the impeller, ring gear and
crescent spacer.
The crescent spacer is fixed in its position by a pin and is located between the ring gear and the impeller. The impeller is
driven by drive from the torque converter hub which is located on a needle roller bearing in the pump housing. The impeller
teeth mesh with those of the ring gear. When the impeller is rotated, the motion is transferred to the ring gear which rotates
in the same direction.
The rotational motion of the ring gear and the impeller collects fluid from the intake port in the spaces between the teeth.
When the teeth reach the crescent spacer, the oil is trapped in the spaces between the teeth and is carried with the rotation
of the gears. The spacer tapers near the outlet port. This reduces the space between the gear teeth causing a build up of fluid
pressure as the oil reaches the outlet port. When the teeth pass the end of the spacer the pressurized fluid is released into
the outlet port.
The fluid emerging from the outlet port is passed through the fluid pressure control valve. At high operating speeds the
pressure control valve maintains the output pressure to the gearbox at a predetermined maximum level. Excess fluid is
relieved from the pressure control valve and is directed, via the main pressure valve in the valve block, back to the pump inlet
port. This provides a pressurized feed to the pump inlet which prevents cavitation and reduces pump noise.
Page 1435 of 3039

Published: 25-Aug-2011
Automatic Transmission/Transaxle - TDV6 3.0L Diesel /V8 5.0L Petrol/V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol - Diagnostics
Diagnosis and Testing
Principle of Operation
For a detailed description of the automatic transmission/transaxle, refer to the relevant Description and Operation section n
the workshop manual. REFER to: (307-01B Automatic Transmission/Transaxle - TDV6 3.0L Diesel /V8 5.0L Petrol/V8 S/C 5.0L
Petrol)
Transmission Description (Description and Operation), Transmission Description (Description and Operation), Transmission Description (Description and Operation).
Fluid Level and Condition Check
CAUTION: The vehicle should not be driven if the fluid level is low as internal failure can result.
NOTE: The transmission fluid temperature must not be allowed to exceed 50°C (122°F) whilst checking level. Should the
temperature rise above this figure, abort the check and allow the transmission fluid to cool to below 30°C (86°F).
This vehicle is not equipped with a fluid level indicator. An incorrect level may affect the transmission operation and could
result in transmission damage. To correctly check and add fluid to the transmission.
REFER to: Transmission Fluid Level Check (307-01B Automatic Transmission/Transaxle - TDV6 3.0L Diesel /V8 5.0L Petrol/V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol, General Procedures).
High Fluid Level
A fluid level that is too high may cause the fluid to become aerated due to the churning action of the rotating internal parts.
This will cause erratic control pressure, foaming, loss of fluid from the vent tube and possible transmission damage. If an
overfill condition is identified, with the engine at idle ensure the fluid temperature is within the specified range and allow the
excess fluid to drain until a small thread of fluid runs from the filler/level plug hole.
Low Fluid Level
A low fluid level could result in poor transmission engagement, slipping, or damage. This could also indicate a leak in one of
the transmission seals or gaskets.
REFER to: Transmission Fluid Level Check (307-01B Automatic Transmission/Transaxle - TDV6 3.0L Diesel /V8 5.0L Petrol/V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol, General Procedures).
Adding Fluid
CAUTION: The use of any other type of transmission fluid other than that specified can result in transmission damage.
If fluid needs to be added, add fluid in 0.50 liter increments through the fill hole Opening. Do not overfill the fluid. For fluid
type, refer to the General Specification chart in this section.
REFER to: Specifications (307-01B Automatic Transmission/Transaxle - TDV6 3.0L Diesel /V8 5.0L Petrol/V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol, Specifications).
Fluid Condition Check
1. Check the fluid level.
REFER to: Transmission Fluid Level Check (307-01B Automatic Transmission/Transaxle - TDV6 3.0L Diesel /V8 5.0L Petrol/V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol, General Procedures).
2. Observe the color and the odor of the fluid. The color under normal circumstances should be Honey.
3. Allow the fluid to drip onto a facial tissue and examine the stain.
4. If evidence of solid material is found, the transmission fluid pan should be removed for further inspection.
NOTE: In the event of a transmission unit replacement for internal failure, the oil cooler and pipes must also be replaced.
Inspection and Verification
1. Verify the customer concern.
2. Visually inspect for obvious signs of damage and system integrity.
Page 1440 of 3039
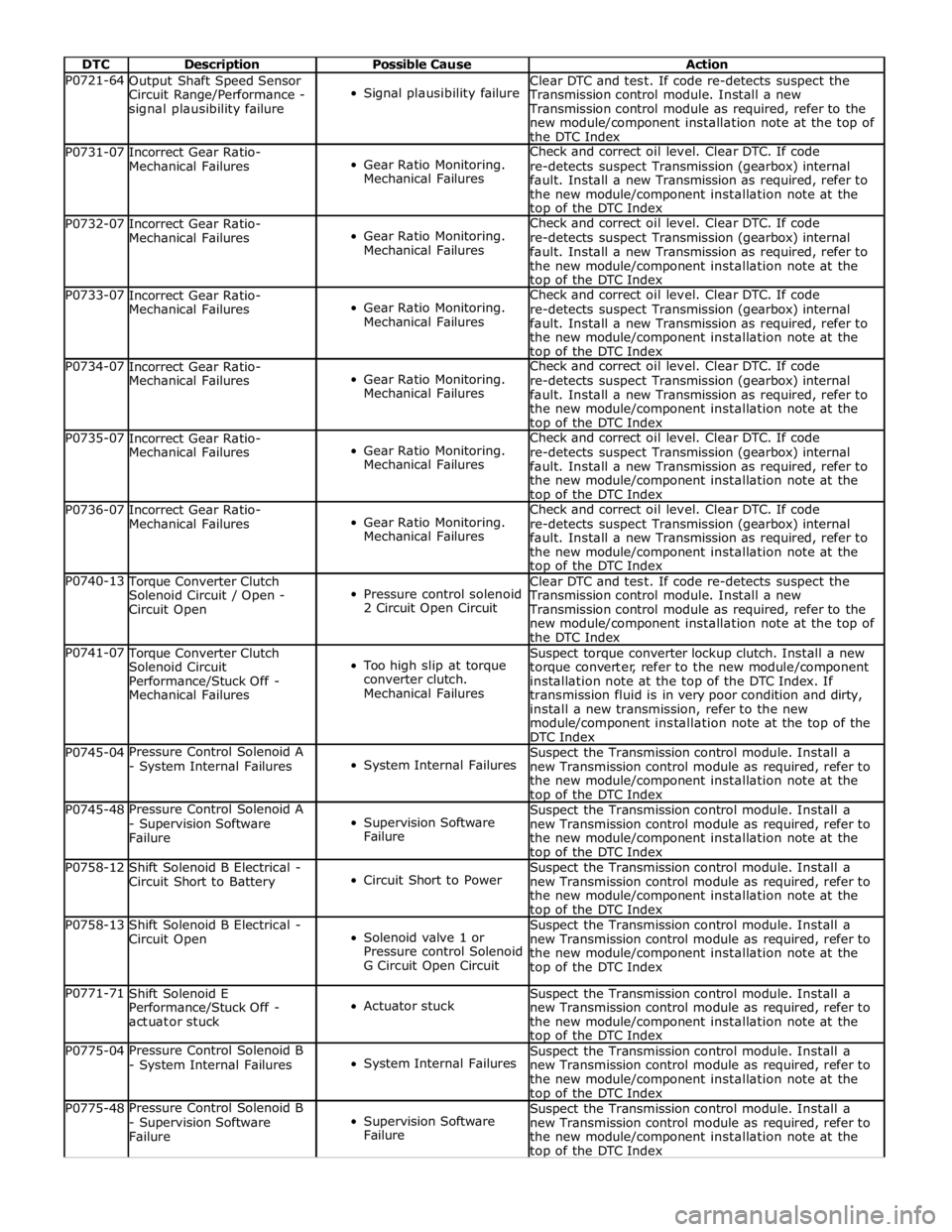
DTC Description Possible Cause Action P0721-64
Output Shaft Speed Sensor
Circuit Range/Performance -
signal plausibility failure
Signal plausibility failure Clear DTC and test. If code re-detects suspect the
Transmission control module. Install a new
Transmission control module as required, refer to the
new module/component installation note at the top of
the DTC Index P0731-07
Incorrect Gear Ratio-
Mechanical Failures
Gear Ratio Monitoring.
Mechanical Failures Check and correct oil level. Clear DTC. If code
re-detects suspect Transmission (gearbox) internal
fault. Install a new Transmission as required, refer to
the new module/component installation note at the top of the DTC Index P0732-07
Incorrect Gear Ratio-
Mechanical Failures
Gear Ratio Monitoring.
Mechanical Failures Check and correct oil level. Clear DTC. If code
re-detects suspect Transmission (gearbox) internal
fault. Install a new Transmission as required, refer to
the new module/component installation note at the top of the DTC Index P0733-07
Incorrect Gear Ratio-
Mechanical Failures
Gear Ratio Monitoring.
Mechanical Failures Check and correct oil level. Clear DTC. If code
re-detects suspect Transmission (gearbox) internal
fault. Install a new Transmission as required, refer to
the new module/component installation note at the top of the DTC Index P0734-07
Incorrect Gear Ratio-
Mechanical Failures
Gear Ratio Monitoring.
Mechanical Failures Check and correct oil level. Clear DTC. If code
re-detects suspect Transmission (gearbox) internal
fault. Install a new Transmission as required, refer to
the new module/component installation note at the top of the DTC Index P0735-07
Incorrect Gear Ratio-
Mechanical Failures
Gear Ratio Monitoring.
Mechanical Failures Check and correct oil level. Clear DTC. If code
re-detects suspect Transmission (gearbox) internal
fault. Install a new Transmission as required, refer to
the new module/component installation note at the top of the DTC Index P0736-07
Incorrect Gear Ratio-
Mechanical Failures
Gear Ratio Monitoring.
Mechanical Failures Check and correct oil level. Clear DTC. If code
re-detects suspect Transmission (gearbox) internal
fault. Install a new Transmission as required, refer to
the new module/component installation note at the top of the DTC Index P0740-13 Torque Converter Clutch
Solenoid Circuit / Open -
Circuit Open
Pressure control solenoid
2 Circuit Open Circuit Clear DTC and test. If code re-detects suspect the
Transmission control module. Install a new
Transmission control module as required, refer to the
new module/component installation note at the top of
the DTC Index P0741-07 Torque Converter Clutch
Solenoid Circuit
Performance/Stuck Off -
Mechanical Failures
Too high slip at torque
converter clutch.
Mechanical Failures Suspect torque converter lockup clutch. Install a new
torque converter, refer to the new module/component
installation note at the top of the DTC Index. If
transmission fluid is in very poor condition and dirty,
install a new transmission, refer to the new
module/component installation note at the top of the
DTC Index P0745-04 Pressure Control Solenoid A
- System Internal Failures
System Internal Failures Suspect the Transmission control module. Install a
new Transmission control module as required, refer to
the new module/component installation note at the top of the DTC Index P0745-48 Pressure Control Solenoid A
- Supervision Software
Failure
Supervision Software
Failure Suspect the Transmission control module. Install a
new Transmission control module as required, refer to
the new module/component installation note at the top of the DTC Index P0758-12
Shift Solenoid B Electrical -
Circuit Short to Battery
Circuit Short to Power Suspect the Transmission control module. Install a
new Transmission control module as required, refer to
the new module/component installation note at the top of the DTC Index P0758-13
Shift Solenoid B Electrical -
Circuit Open
Solenoid valve 1 or
Pressure control Solenoid
G Circuit Open Circuit Suspect the Transmission control module. Install a
new Transmission control module as required, refer to
the new module/component installation note at the
top of the DTC Index P0771-71
Shift Solenoid E
Performance/Stuck Off -
actuator stuck
Actuator stuck Suspect the Transmission control module. Install a
new Transmission control module as required, refer to
the new module/component installation note at the top of the DTC Index P0775-04 Pressure Control Solenoid B
- System Internal Failures
System Internal Failures Suspect the Transmission control module. Install a
new Transmission control module as required, refer to
the new module/component installation note at the top of the DTC Index P0775-48 Pressure Control Solenoid B
- Supervision Software
Failure
Supervision Software
Failure Suspect the Transmission control module. Install a
new Transmission control module as required, refer to
the new module/component installation note at the top of the DTC Index