2010 JAGUAR XFR wheel bolts
[x] Cancel search: wheel boltsPage 584 of 3039

Symptom Possible Cause Action Electrical circuit
For parking brake control and circuit tests.
REFER to: Parking Brake (206-05, Diagnosis and Testing). Slow or incomplete brake
pedal return
Brake pedal binding
Brake booster/master cylinder GO to Pinpoint Test K. Pinpoint Tests
PINPOINT TEST A : BRAKES NOISY TEST
CONDITIONS DETAILS/RESULTS/ACTIONS A1: INSPECT BRAKE PADS 1 Inspect the condition of the front and rear brake pads. Check for damage to any anti-squeal shims. Are the brake pads OK? Yes
GO to A2. No
Clean/install new front and rear brake pads as required. REFER to:
Brake Pads - Vehicles With: Standard Brakes (206-03A Front Disc Brake - V6 3.0L Petrol, Removal and Installation),
Brake Pads - Vehicles With: High Performance Brakes (206-03A Front Disc Brake - V6 3.0L Petrol, Removal and Installation),
Brake Pads (206-04A Rear Disc Brake - V6 3.0L Petrol, Removal and Installation), Brake Pads - Vehicles With: High Performance Brakes (206-04, Removal and Installation).
Re-test vehicle for brake noise. A2: INSPECT BRAKE DISCS 1 Inspect the brake discs for excessive corrosion, wear or disc thickness variation. Does excessive corrosion, wear or disc thickness variation exist? Yes
Install new front and rear brake discs and brake pads as required. REFER to:
Brake Pads - Vehicles With: Standard Brakes (206-03A Front Disc Brake - V6 3.0L Petrol, Removal and Installation),
Brake Pads - Vehicles With: High Performance Brakes (206-03A Front Disc Brake - V6 3.0L Petrol, Removal and Installation),
Brake Pads (206-04A Rear Disc Brake - V6 3.0L Petrol, Removal and Installation), Brake Pads - Vehicles With: High Performance Brakes (206-04, Removal and Installation),
Brake Disc - Vehicles With: Standard Brakes (206-03A Front Disc Brake - V6 3.0L Petrol, Removal and Installation),
Brake Disc - Vehicles With: High Performance Brakes (206-03A Front Disc Brake - V6 3.0L Petrol, Removal and Installation),
Brake Disc (206-04A Rear Disc Brake - V6 3.0L Petrol, Removal and Installation), Brake Disc - Vehicles With: High Performance Brakes (206-04, Removal and Installation).
Re-test vehicle for brake noise.
No
No action required, vehicle is OK.
PINPOINT TEST B : VIBRATION WHEN BRAKES ARE APPLIED TEST
CONDITIONS DETAILS/RESULTS/ACTIONS B1: ROAD TEST VEHICLE 1 Road test the vehicle between 40-80 km/h (25-50 mph) without applying brakes. Is the vibration present?
Yes
For noise vibration and harshness tests.
REFER to: Noise, Vibration and Harshness (NVH) (100-04 Noise, Vibration and Harshness, Diagnosis and Testing).
No
GO to B2. B2: CHECK FOR BRAKE VIBRATION 1 Road test the vehicle between 40-80 km/h (25-50 mph) with light and medium application on the brake pedal. Is a vibration present?
Yes
Check the brake caliper mounting bolts and wheel hub nuts and tighten to specification as required. Check
the balance of all road wheels and tires and repair as required. Check the brake discs for excessive wear,
runout, thickness variation or cracks. Install new brake discs and brake pads as required. GO to B3. No
No action required, vehicle is OK. B3: IS VIBRATION STILL PRESENT UNDER BRAKE APPLICATION? 1 Road test the vehicle between 40-80 km/h (25-50 mph) with light and medium application on the brake pedal.
Page 610 of 3039

BRAKE CALIPERS System Operation
When hydraulic pressure is supplied to the caliper, the pistons extend to force the inner pad against the brake disc. The caliper
reacts and slides along two guide pins to bring the outer pad into contact with the brake disc.
BRAKE PAD WEAR SENSORS
When a brake pad incorporating a brake pad wear sensor is approximately 75% worn, the sensor wire within the pad material
is worn through and the brake pad wear sensor goes open circuit. When the instrument cluster detects the open circuit, it
illuminates the amber LED (light emitting diode) in the brake warning indicator, displays an appropriate warning in the
message center and sounds a warning chime.
Refer to: Instrument Cluster (413-01 Instrument Cluster, Description and Operation).
NOTE: A new pad wear sensor lead must be fitted whenever the brake pads are changed, irrespective of the brake pad
warning sensor being triggered.
BRAKE CALIPERS Component Description
Each caliper is mounted within a fixed carrier that is secured to the front wheel knuckle with two bolts. The inboard brake pad
of the LH (left-hand) brake incorporates a wear sensor.
Each outboard brake pad is installed with a pressed steel anti-rattle spring. On SC (supercharger) vehicles, a badge with the
'R' symbol is formed on the anti-rattle spring.
BRAKE PAD WEAR SENSORS
The brake pad wear sensor is wired in series with a wear sensor on the RH (right-hand) rear brake and the instrument cluster.
If the thickness of one of the brake pads connected to a wear sensor decreases to a predetermined limit, the instrument
cluster illuminates the brake warning indicator.
Page 632 of 3039

BRAKE CALIPERS System Operation
When hydraulic pressure is supplied to the caliper, the pistons extend to force the inner pad against the brake disc. The caliper
reacts and slides along two guide pins to bring the outer pad into contact with the brake disc.
BRAKE PAD WEAR SENSORS
When a brake pad incorporating a brake pad wear sensor is approximately 75% worn, the sensor wire within the pad material
is worn through and the brake pad wear sensor goes open circuit. When the instrument cluster detects the open circuit, it
illuminates the amber LED (light emitting diode) in the brake warning indicator, displays an appropriate warning in the
message center and sounds a warning chime.
Refer to: Instrument Cluster (413-01 Instrument Cluster, Description and Operation).
NOTE: A new pad wear sensor lead must be fitted whenever the brake pads are changed, irrespective of the brake pad
warning sensor being triggered.
BRAKE CALIPERS Component Description
Each caliper is mounted within a fixed carrier that is secured to the rear wheel knuckle with two bolts. Each outboard brake pad
is installed with a wire anti-rattle spring.
The brake calipers on SC (supercharger) vehicles are painted and also include a logo badge, secured with two screws, which
must be removed in order to change the brake pads.
The inboard brake pad of the RH (right-hand) brake incorporates a wear sensor.
BRAKE PAD WEAR SENSORS
The brake pad wear sensor is wired in series with a wear sensor on the LH (left-hand) front brake and the instrument cluster. If
the thickness of one of the brake pads connected to a wear sensor decreases to a predetermined limit, the instrument cluster
illuminates the brake warning indicator.
Page 690 of 3039

Brake fluid Shell ESL Dot 4 Torque Specifications
Description Nm lb-ft lb-in Brake master cylinder primary pressure transducer 30 22 – Brake tubes to hydraulic control unit (HCU) 17 13 – Rear wheel speed sensor retaining bolt 6 – 53 Yaw rate sensor and accelerometer retaining nuts 7 – 62 Hydraulic control unit (HCU) retaining bolts 8 – 71 Steering wheel rotation sensor retaining screws 4 – 35 Steering column to lower shroud retaining screws 3 – 27 www.JagDocs.com
Page 719 of 3039

Symptom Possible Causes Action
Damaged fluid
cap/reservoir
Check and install a new fluid cap/reservoir as required
Loose or damaged
hoses and fittings
O-ring or Dowty seals
Tighten the hose connection or latch plate fixing to the
recommended torque.
REFER to: Specifications (211-00 Steering System - General Information, Specifications).
Check and install new components as required
Install new O-ring or Dowty seals as required
Fluid cooler
Check and install a new fluid cooler as required, refer to the new
module/component installation note at the top of the Symptom
Charts
Power steering pump
Check and install a new power steering pump as required, refer to
the new module/component installation note at the top of the
Symptom Charts Functional
Symptom Possible Causes Action
Steering wheel
misalignment
Steering not correctly centred
Check the steering alignment.
REFER to: Specifications (204-00 Suspension System - General
Information, Specifications).
Excessive free play at
steering wheel (refer to
the Steering Linkage
Inspection and Backlash
(Free play) Check in this
section)
Steering wheel loose
Check and tighten the steering
wheel retaining bolt as required.
REFER to: Specifications (211-00 Steering System - General
Information, Specifications).
Excess play in the steering linkage
Check and install new
components as required
Steering gear not correctly adjusted (causing
excessive backlash)
CAUTION: DO NOT attempt to
adjust the steering gear yoke. Failure to
follow this instruction will invalidate the
steering gear warranty
Check and install a new steering
gear as required, refer to the
new module/component
installation note at the top of
the Symptom Charts
Lower steering column universal joint pinch
bolts loose
Check and tighten the lower
steering column pinch bolts as
required.
REFER to: Specifications (211-00 Steering System - General
Information, Specifications).
Excessive wear in steering column universal
joints
Check and install a new steering
column or steering column lower
shaft as required, refer to the
new module/component
installation note at the top of
the Symptom Charts
Steering gear mounting bolts loose or
damaged
Check/tighten and install new
steering gear mounting bolts as
required.
REFER to: Specifications (211-00 Steering System - General
Information, Specifications). www.JagDocs.com
Page 722 of 3039

Noise
Symptom Possible Causes Action
Continuous noise
Low power steering fluid level
Check for leaks and rectify as required. For further
information refer to the symptom charts for
leakage in this section. Fill power steering fluid
reservoir to correct level
NOTE: Look for small air bubbles
visible in the fluid, air may also get
trapped in the hydraulic system
Air in hydraulic system
Bleed the power steering system.
REFER to: Power Steering System Bleeding (211-00 Steering System - General Information,
General Procedures).
Power steering pipe/hose in
contact with the vehicle body
Check and reposition, or install new IF
damaged/deformed, power steering pipe/hose
Power steering pipe/hose
restricted or twisted
Check and clear restriction to pipe/hose
Reposition power steering pipe/hose. Install new
pipe/hose IF permanently damaged/deformed
Power steering pump mounting
bolts loose
Tighten the power steering pump mounting bolts
to the correct torque.
REFER to: Specifications (211-00 Steering System - General Information, Specifications).
Noise gets worse
when system is
loaded
NOTE: Refer to the power
steering pressure check in this section
Low power steering fluid level
Aerated fluid
Low power steering pump
pressure
Check and fill power steering fluid reservoir to
correct level
Bleed the power steering system.
REFER to: Power Steering System Bleeding (211-00 Steering System - General Information,
General Procedures).
Check power steering pump pressure. If the pump
pressure is low, install a new power steering
pump
Front End Accessory
Drive (FEAD) belt
squeal
FEAD belt incorrectly tensioned
or glazed
Check FEAD belt tension
Check FEAD belt condition and install a new belt
as required
Chirp noise from the
steering pump when a
load is applied
Loose or worn FEAD belt
Check FEAD belt tension
Check FEAD belt condition and install a new belt
as required
Scrape/grind noise
from behind steering
wheel while steering
Steering column shroud foul
condition or clockspring
Correctly install the steering column shroud to
eliminate the foul condition
Install a new clockspring as required
Foreign objects
Remove foreign objects from between steering
column shroud and steering wheel/steering
column rotating components
Click
Clockspring or steering column
multifunction switch LH
Correctly install and install new components as
required
Loose universal joint pinch bolt
Install a new universal joint pinch bolt and
tighten to correct specification.
REFER to: Specifications (211-00 Steering System - General Information, Specifications).
Squeak
Steering column shroud joints
Apply Krytox spray to steering column shroud
joints
Clockspring
Install new clockspring as required
Page 745 of 3039
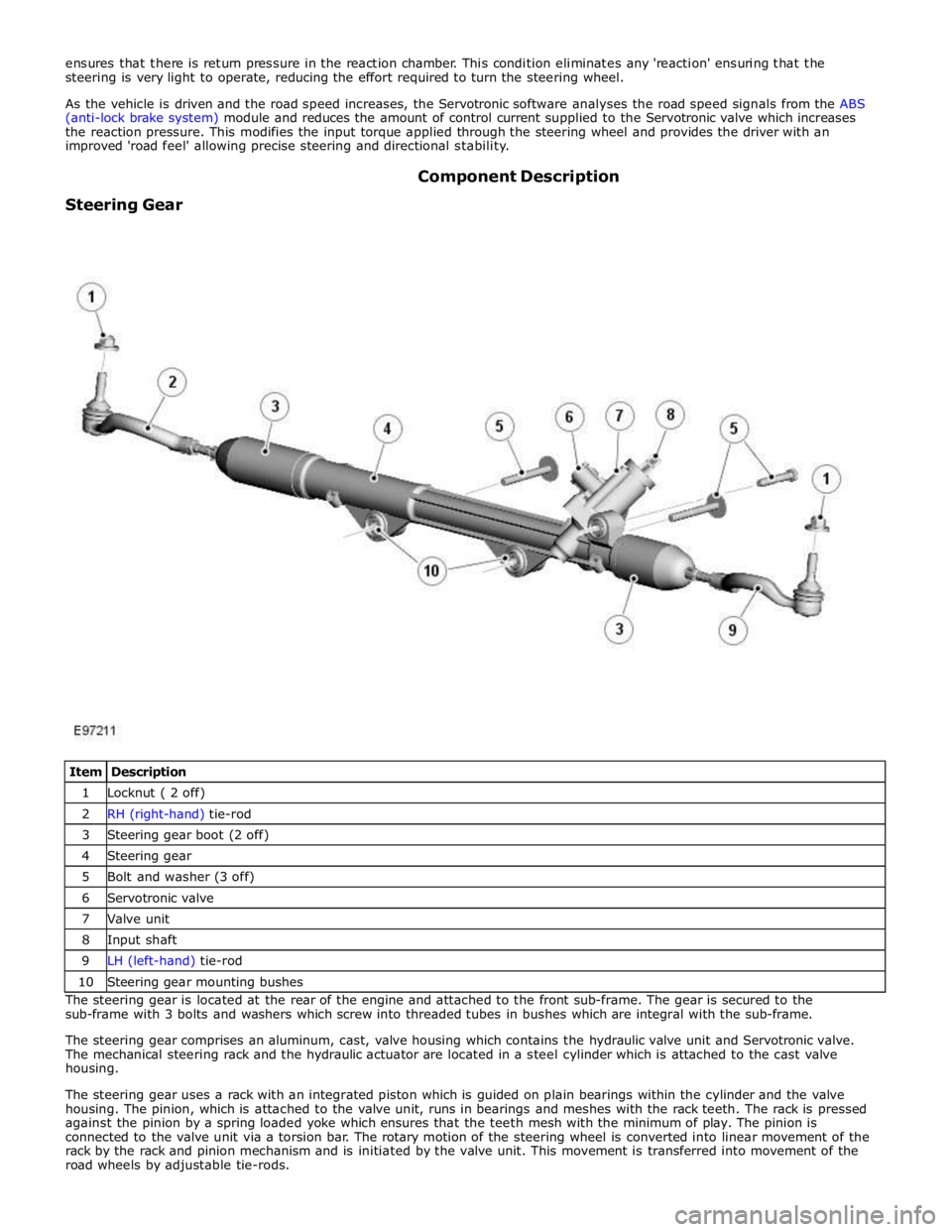
1 Locknut ( 2 off) 2 RH (right-hand) tie-rod 3 Steering gear boot (2 off) 4 Steering gear 5 Bolt and washer (3 off) 6 Servotronic valve 7 Valve unit 8 Input shaft 9 LH (left-hand) tie-rod 10 Steering gear mounting bushes The steering gear is located at the rear of the engine and attached to the front sub-frame. The gear is secured to the
sub-frame with 3 bolts and washers which screw into threaded tubes in bushes which are integral with the sub-frame.
The steering gear comprises an aluminum, cast, valve housing which contains the hydraulic valve unit and Servotronic valve.
The mechanical steering rack and the hydraulic actuator are located in a steel cylinder which is attached to the cast valve
housing.
The steering gear uses a rack with an integrated piston which is guided on plain bearings within the cylinder and the valve
housing. The pinion, which is attached to the valve unit, runs in bearings and meshes with the rack teeth. The rack is pressed
against the pinion by a spring loaded yoke which ensures that the teeth mesh with the minimum of play. The pinion is
connected to the valve unit via a torsion bar. The rotary motion of the steering wheel is converted into linear movement of the
rack by the rack and pinion mechanism and is initiated by the valve unit. This movement is transferred into movement of the
road wheels by adjustable tie-rods.
Page 775 of 3039

Steering wheel retaining bolt 60 44 - Steering column pinch bolt 35 26 - Steering column retaining nuts 30* 22 - Tilt solenoid retaining bolts 1 - 9 Telescopic solenoid retaining bolts 1 - 9 Telescopic housing retaining bolts 8 - 71 If you are re-using this fixing on a vehicle built prior to VIN N83337, then tighten to 25 Nm. If you are replacing a fixing, then
you must tighten to 30 Nm.