2010 JAGUAR XFR spark plugs
[x] Cancel search: spark plugsPage 50 of 3039
disconnected, a Radio Code Saver will allow sufficient current to pass to maintain the radio receiver/cassette player/mini disc
player and compact disc player memory, operate the clock and supply the door operated interior lights while isolating the
battery in the event of a short circuit.
Reconnecting the Battery
WARNING: If the battery has been on bench charge the cells may be giving off explosive hydrogen gas. Avoid creating
sparks, and if in doubt cover the vent plugs or covers with a damp cloth.
Always make sure that all electrical systems are switched OFF before reconnecting the battery to avoid causing sparks or
damage to sensitive electrical equipment.
Always reconnect the battery positive lead first and the negative last, ensuring that there is a good electrical contact and the
battery terminals are secure.
Restart the clock (where installed) and set it to the correct time.
Enter the radio receiver/cassette player/mini disc player and compact disc player keycodes and preset' frequencies, if known.
Following reconnection of the battery, the engine should be allowed to idle until it has reached normal operating temperature
as the stored idle and drive values contained within the ECM have been lost. Allow the vehicle to idle for a further three
minutes. Drive the vehicle at constant speeds of approximately 48 km/h (30 mph), 64 km/h (40 mph), 80 km/h (50 mph), 96
km/h (60 mph) and 112 km/h (70 mph) for three minutes each. This will allow the ECM to relearn idle and drive values, and
may cause driveability concerns if the procedure is not carried out.
Connecting a Slave Battery Using Jump Leads
WARNING: If the slave battery has recently been charged and is gassing, cover the vent plugs or covers with a damp
cloth to reduce the risk of explosion should arcing occur when connecting the jump leads.
CAUTIONS:
A discharged battery condition may have been caused by an electrical short circuit. If this condition exists there will be
an apparently live circuit on the vehicle even when all circuits are switched off. This can cause arcing when the jump leads are
connected.
Whilst it is not recommended that the vehicle is jump started, it is recognized that this may occasionally be the only
practical way to mobilize a vehicle. In such an instance the discharged battery must be recharged immediately after jump
starting to avoid permanent damage.
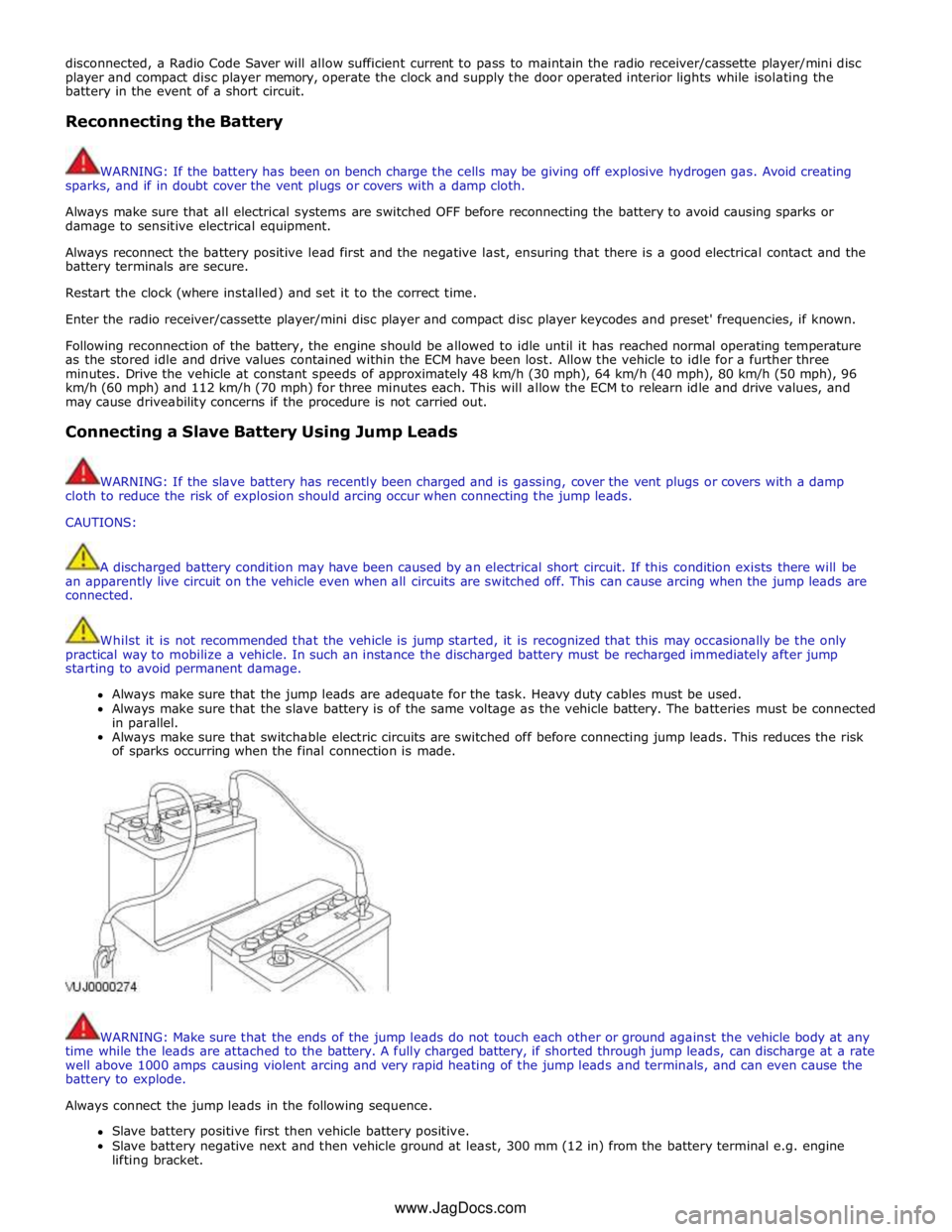
Always make sure that the jump leads are adequate for the task. Heavy duty cables must be used.
Always make sure that the slave battery is of the same voltage as the vehicle battery. The batteries must be connected
in parallel.
Always make sure that switchable electric circuits are switched off before connecting jump leads. This reduces the risk
of sparks occurring when the final connection is made.
WARNING: Make sure that the ends of the jump leads do not touch each other or ground against the vehicle body at any
time while the leads are attached to the battery. A fully charged battery, if shorted through jump leads, can discharge at a rate
well above 1000 amps causing violent arcing and very rapid heating of the jump leads and terminals, and can even cause the
battery to explode.
Always connect the jump leads in the following sequence.
Slave battery positive first then vehicle battery positive.
Slave battery negative next and then vehicle ground at least, 300 mm (12 in) from the battery terminal e.g. engine
lifting bracket. www.JagDocs.com
Page 811 of 3039
Engine System - General Information - Engine 5.0L
Diagnosis and Testing
Special Tool(s)
Oil pressure testing adaptor, 303-1451
Oil pressure testing gauge, 303-871 Principle of Operation Published: 11-May-2011
For a detailed description of the 5.0L engine, refer to the relevant Description and Operation sections in the workshop manual.
REFER to:
Engine (303-01C Engine - V8 5.0L Petrol, Description and Operation), Engine (303-01C Engine - V8 5.0L Petrol, Description and Operation), Engine (303-01C Engine - V8 5.0L Petrol, Description and Operation), Engine (303-01D Engine - V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol, Description and Operation), Engine (303-01D Engine - V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol, Description and Operation), Engine (303-01D Engine - V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol, Description and Operation).
Inspection and Verification
1. Verify the customer concern.
2. Visually inspect for obvious signs of damage and system integrity.
Visual Inspection
Mechanical Electrical Coolant leaks
Oil leaks
Leaks in the fuel system
Visibly damaged or worn parts
Loose or missing fixings Fuses
Loose or corroded electrical connectors
Harnesses
Sensors
3. If an obvious cause for an observed or reported concern is found, correct the cause (if possible) before proceeding to
the next step.
4. If the concern is not visually evident, verify the symptom and refer to the Symptom Chart, alternatively check for
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) and refer to the relevant DTC Index.
Symptom Chart
NOTES:
If an engine is suspect, and the vehicle remains under the Manufacturers warranty refer to the Warranty Policy and
Procedure manual (section B1.2), or determine if any prior approval programme is in operation, prior to the installation of a
new engine.
Due to the possibility of loose carbon, that has become trapped between the valve face and seat, effecting the pressure
readings, when carrying out a compression test and some cylinders are found to have low pressures, install the spark plugs,
road test the vehicle and re-test the suspect cylinders. If the correct pressures are restored, no further action is required. www.JagDocs.com
Page 813 of 3039

Component Tests
Engine Oil Leaks
NOTE: Before installing new gaskets or oil seals, make sure that the fault is clearly established.
If the oil leak cannot be identified clearly by a visual inspection, carry out an Ultraviolet test:
Fluorescent Oil Additive Method
1. Clean the engine with a suitable cleaning fluid (brake cleaner).
2. Drain the engine oil and refill with recommended oil, premixed with Diesel Engine Oil Dye or equivalent. Use a minimum
14.8 ml (0.5 ounce) to a maximum 29.6 ml (1 ounce) of fluorescent additive to all engines. If oil is not premixed,
fluorescent additive must first be added to the crankcase.
3. Run engine for 15 minutes. Stop the engine and inspect all seal and gasket areas for leaks using a 12 Volt Master UV
Diagnostic Inspection Kit or equivalent. A clear bright yellow or orange area will identify leak. For extremely small
leaks, several hours may be required for the leak to appear.
4. As necessary, pressurize the main oil gallery system to locate leaks due to incorrectly sealed, loose or cocked plugs. If
the flywheel bolts leak oil, look for sealer on the threads.
5. Repair all leaks as necessary.
Compression Test General Remarks
NOTES:
Removing fuses and disconnecting electrical components may cause the Engine Control Module (ECM) to log Diagnostic
Trouble Codes (DTCs). After the measurements have been carried out, DTCs should be cleared from memory by connecting to
the Manufacturer Approved Diagnostic System.
Only check the compression pressure with the valves set to the prescribed clearance (if this can be adjusted).
The compression pressure should be checked with the engine at normal operating temperature.
Check the Compression Pressure
WARNING: Move gear selector lever to 'P' position. Failure to follow this instruction may result in personal injury.
1. Remove the fuel pump relay.
2. Start the engine - the engine will start, run for a few seconds then stall.
3. Remove the spark plugs.
4. Install the compression tester.
5. Install an auxiliary starter switch in the starting circuit. With the ignition switch OFF, using the auxiliary starter switch,
crank the engine a minimum of five compression strokes and record the highest reading. Note the approximate number
of compression strokes required to obtain the highest reading.
6. Repeat the test on each cylinder, cranking the engine approximately the same number of compression strokes.
7. Install the removed components in reverse order, observing the specified tightening torques.
8. Clear all DTCs from the ECM.
Interpretation of the Results
NOTE: Due to the possibility of loose carbon that has become trapped between the valve face and seat effecting the
pressure readings, when carrying out a compression test and cylinders are found to have low pressures, install the spark plugs,
road test the vehicle and re-test the suspect cylinders. If the correct pressures are restored, no further action is required.
The indicated compression pressures are considered within specification if the lowest reading cylinder is within 75% of the
highest reading.
If the cylinder pressures are found to be low, carry out a leakdown test to determine the location of the fault (if any leakback
can be heard through the engine breather system suspect the piston rings, if any leakback can be heard through the inlet
system suspect the inlet valve or seat, if any leakback can be heard through the exhaust manifold suspect the exhaust valve
or seat. If the measurements for two cylinders next to each other are both too low then it is very likely that the cylinder head
gasket between them is burnt through. This can also be recognized by traces of engine oil in the coolant and/or coolant in the
Page 814 of 3039

engine oil).
Oil Consumption Test
The amount of oil an engine uses will vary with the way the vehicle is driven in addition to normal engine-to-engine variation.
This is especially true during the first 16,100 km (10,000 miles) when a new engine is being broken in or until certain internal
components become conditioned. Vehicles used in heavy-duty operation may use more oil. The following are examples of
heavy-duty operation:
Trailer towing applications
Severe loading applications
Sustained high speed operation
Engines need oil to lubricate the following internal components:
Cylinder block cylinder walls
Pistons and piston rings
Intake and exhaust valve stems
Intake and exhaust valve guides
All internal engine components
When the pistons move downward, a thin film of oil is left on the cylinder walls. As the vehicle is operated, some oil is also
drawn into the combustion chambers past the intake and exhaust valve stem seals and burned.
The following are examples of conditions that can affect oil consumption rates:
Engine size
Operator driving habits
Ambient temperatures
Quality and viscosity of oil
Engine is being run in an overfilled condition (check the oil level at least five minutes after a hot shutdown with the
vehicle parked on a level surface. The oil level should not be above the top of the cross-hatched area and the letter "F"
in FULL).
Operation under varying conditions can frequently be misleading. A vehicle that has been run for several thousand miles on
short trips or in below-freezing ambient temperatures may have consumed a "normal" amount of oil. However, when checking
the engine oil level, it may measure up to the full mark on the oil level indicator due to dilution (condensation and fuel) in the
engine crankcase. The vehicle then might be driven at high speeds on the highway where the condensation and fuel boil off.
The next time the engine oil is checked it may appear that a liter of oil was used in about 160 km (100 miles). Oil
consumption rate is about one liter per 2,400 km (1,500 miles).
Make sure the selected engine oil meets Jaguar specification and the recommended API performance category "SG" and SAE
viscosity grade as shown in the vehicle Owner's Guide. It is also important that the engine oil is changed at the intervals
specified for the typical operating conditions.
The following diagnostic procedure is used to determine the source of excessive oil consumption.
NOTE: Oil use is normally greater during the first 16,100 km (10,000 miles) of service. As mileage increases, oil use
decreases. High speed driving, towing, high ambient temperature and other factors may result in greater oil use.
1. Define excessive consumption, such as the number of miles driven per liter of oil used. Also determine customers
driving habits, such as sustained high speed operation, towing, extended idle and other considerations.
2. Verify that the engine has no external oil leaks as described under Engine Oil Leaks in this section.
3. Carry out an oil consumption test:
Run the engine to normal operating temperature. Switch engine OFF and allow oil to drain back for at least five
minutes .
With vehicle parked on level surface, check the engine oil level.
If required, add engine oil to set level exactly to the FULL mark.
Record the vehicle mileage.
Instruct the customer to return for a level check after driving the vehicle as usual for 1,610 km (1000 miles).
Check the oil level under the same conditions and at the same location as the initial check.
NOTE: If the oil consumption rate is unacceptable go to Step 4.
4. Check the Positive Crankcase Ventilation (PCV) system. Make sure the system is not plugged.
5. Check for plugged oil drain-back holes in the cylinder head and cylinder block.
6. If the condition still exists after carrying out the above tests go to step 9.
7. Carry out a cylinder compression test. Refer to the Compression Test procedure in this section. This can help determine
the source of oil consumption such as valves, piston rings or other areas.
8. Check valve guides for excessive guide clearance. Install new valve stem seals after verifying valve guide clearance.
9. Worn or damaged internal engine components can cause excessive oil consumption. Small deposits of oil on the tips of
the spark plugs can be a clue to internal oil consumption.
Page 816 of 3039

9. WEAK VALVE SPRINGS: When the needle oscillation becomes more violent as engine RPM is increased, weak valve
springs are indicated. The reading at idle could be relatively steady.
10. LATE VALVE TIMING: A steady but low reading could be caused by late valve timing.
11.
IGNITION TIMING RETARDED: Retarded ignition timing will produce a steady but somewhat low reading.
12.
INSUFFICIENT SPARK PLUG GAP: When spark plugs are gapped too close, a regular, small pulsation of the needle can
occur.
13. INTAKE LEAK: A low, steady reading can be caused by an intake manifold or throttle body gasket leak.
14.
BLOWN HEAD GASKET: A regular drop of fair magnitude can be caused by a blown head gasket or warped cylinder head
to cylinder block surface.
15.
RESTRICTED EXHAUST SYSTEM: When the engine is first started and is idled, the reading may be normal, but as the
engine RPM is increased, the back pressure caused by a clogged muffler, kinked tail pipe or other concerns will cause
the needle to slowly drop to 0 kPa (0 in-Hg). The needle then may slowly rise. Excessive exhaust clogging will cause
the needle to drop to a low point even if the engine is only idling.
When vacuum leaks are indicated, search out and correct the cause. Excess air leaking into the system will upset the fuel
mixture and cause concerns such as rough idle, missing on acceleration or burned valves. If the leak exists in an accessory
such as the power brake booster, the unit will not function correctly. Always repair vacuum leaks.
Engine Oil Pressure Check
NOTE: Prior to checking the engine oil pressure, a road test of 6 miles (10 kilometres), must be carried out. Do not
attempt to attain engine normal operating temperature by allowing the engine to idle.
1. Disconnect the battery ground cable. Refer to section 414-00 - Charging System - General Information of the workshop
manual
2. WARNINGS:
The spilling of hot engine oil is unavoidable during this procedure, care must be taken to prevent scalding.
Wear protective gloves.
Remove the engine oil filter element
REFER to: Oil Filter Element (303-01C Engine - V8 5.0L Petrol, Removal and Installation).
NOTE: Ensure the oil filter element is not contaminated during this procedure
3. Install the oil filter element into special tool (Oil filter adapter number 303-1451)
4. Install the special tool (Oil filter adapter number 303-1451) to the engine. Torque: 25 Nm
5. Install the special tool (Oil pressure testing gauge, 303-871) and tighten the union
6. Connect the battery ground cable
7. Refer to owner hand book, check and top-up the engine oil if required
8. Start and run the engine
9. Note the oil pressure readings with the engine running at idle and 3500 RPM
10.
Turn off the engine
11.
Disconnect the battery ground cable
12. Remove the special tools
1. Clean the components
13.
Install the engine oil filter element
REFER to: Oil Filter Element (303-01C Engine - V8 5.0L Petrol, Removal and Installation).
NOTE: Ensure the oil filter element is not contaminated during this procedure
14.
Connect the battery ground cable
15. Refer to owner hand book, check and top-up the engine oil if required
www.JagDocs.com
Page 844 of 3039
Engine - V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol -
Engine Data Published: 17-Jun-2014
Engine Description Engine Capacity Maximum Engine Torque (EEC) (SAE) Maximum Engine
Power (EEC) (SAE) Compression
Ratio
Bore
Stroke • 90° "Vee" • 8 Cylinder • 32 Valves 4.999 ccm
625 Nm at 2.500 - 5.500
RPM 375 kW at 6.000 - 6.500
RPM 9.5 ± 0.50 92.509 ±
0.009 mm 93 ± 0.1
mm Engine Firing Order
Standard Firing order ISO 1:2:7:3:4:5:6:8 DIN 1:5:4:2:6:3:7:8 Engine Valve Clearance (cold)
Intake Valve Exhaust Valve 0.20 ±0.02 0.25 ±0.02 Spark Plugs
Specification Spark Plug Gap ILKR6C-10 1 mm Lubricants, Fluids, Sealers and Adhesives
NOTE: When servicing or draining the engine oil, the 0w20 oil is compatible with 5w20. Any residue mix is acceptable.
Description Specification Engine Oil - Vehicles built up to March 2014 SAE 5W20 WSS-M2C925-A Engine Oil - Vehicles built from March 2014 SAE 0W20 STJLR.51.5122 Sealant WSE-M4G323-A6 Core plug and stub pipe retainer WSK-M2G349-A7 Jaguar Premium Cooling System Fluid WSS-M97B44-D Capacities
NOTE: For supercharged 5.0L engines.
Description Litres Engine oil, initial fill 8.9 Engine oil, service fill with oil filter change 7.25 Engine oil, service fill without oil filter change 6.75 Capacities
NOTE: For naturally aspirated 5.0L engines.
Description Litres Engine oil, initial fill 8.75 Engine oil, service fill with oil filter change 7.25 Engine oil, service fill without oil filter change 6.75 Cylinder Head and Valve Train
Item Specification Cylinder head maximum permitted warp (flatness specification) 0.2 mm (0.008 in) Valve guide inner diameter (mm) 5.51 ± 0.01 Intake valve effective length (mm) (tip to gauge line) 117.21 ± 0.1 Exhaust valve effective length (mm) (tip to gauge line) 94.39 ± 0.1 Valve stem to guide clearance intake diametrical (mm) 0.022 - 0.057 Valve stem to guide clearance exhaust diametrical (mm) 0.03 - 0.065 Valve head diameter intake (mm) 36 ± 0.1 Valve head diameter exhaust (mm) 30 ± 0.1 Intake valve face angle (degrees) 44.875 ± 0.125 Exhaust valve face angle (degrees) 44.875 ± 0.125 Valve stem diameter intake (mm) 5.4705 ± 0.0075 Valve stem diameter exhaust (mm) 5.4625 ± 0.0075 Valve spring free length (mm) - inlet 46.1 Valve spring free length (mm) - exhaust 46.1 Valve spring installed height (mm) - inlet 35.74 Valve spring installed height (mm) - exhaust 35.1 Camshaft lobe lift intake (mm) 10 Camshaft lobe lift exhaust (mm) 9.36 Camshaft journal to cylinder head bearing surface clearance diametrical (mm) 0.025 - 0.065 Camshaft journal diameter - all positions 26.965 ± 0.01 Bearing diameter - all positions 27.01 ± 0.01
Page 845 of 3039

Item Specification Camshaft journal maximum run out limit (mm) Camshaft journals to end journals 0.03 Camshaft journals to adjacent journals 0.015 Camshaft journal maximum out of round (mm) - all journals 0.005 Torque Specification
NOTE: A = Refer to procedure for correct torque sequence.
Description Nm lb-ft lb-in Engine cover mounting bolts 10 7 - Accessory drive belt tensioner retaining bolt 40 30 - Supercharger belt idler/tensioner bracket retaining bolts 25 18 - Secondary drive belt idler retaining bolts 40 30 - Power steering pump pulley retaining bolts 25 18 - Power steering pump retaining bolts 25 18 - Power steering pump bracket to engine retaining bolts 25 18 - Generator retaining bolts 48 35 - Starter motor retaining bolts 48 35 - Air conditioning compressor retaining bolts 25 18 - Engine mounting to engine mounting bracket retaining nuts 48 35 - Engine mounting to subframe retaining nuts 63 46 - Engine mounting bracket to engine retaining bolts 48 35 - Crankshaft damper pulley retaining LH threaded bolt 200 + 270° 148 + 180° - Flexplate retaining bolts 45 + 90° 33 + 90° - Exhaust manifold heat shield retaining bolts A - - Exhaust manifold retaining bolts A - - Engine wiring harness bracket retaining bolts 10 7 - Coolant outlet pipe 10 7 - Intercooler retaining bolts 25 18 - Intake manifold retaining bolts 25 18 - Oil Cooler retaining bolts 13 10 - Knock sensor (KS) retaining bolt 20 14 - Ignition coil retaining bolts 8 - 71 Spark plugs 20 15 - Fuel rail retaining bolts A - - High pressure fuel pipe retaining bolts A - - High pressure fuel pump retaining bolts 12 9 - Oil filter housing assembly retaining bolts 12 9 - Oil filter cap 28 21 - Lifting eye bolts 25 + 90° 18 + 90° - Manifold absolute pressure and temperature (MAPT) sensor sensor retaining bolts 5 - 44 Coolant pump retaining bolts 12 9 - Variable valve timing (VVT) oil control solenoid retaining bolts 10 7 - Camshaft position (CMP) sensor retaining bolts 10 7 - Camshaft cover retaining bolts 13 10 - Front upper timing cover retaining bolts 12 9 - Front lower timing cover retaining bolts A - - Engine rear cover retaining bolts A - - VVT to camshaft retaining bolts 32 24 - Camshaft bearing caps retaining bolts 11 8 - Primary timing chain fixed guide retaining bolts 12 9 - Primary timing chain tensioner retaining bolts 12 9 - Primary timing chain tensioner guide blade retaining bolts 25 18 - Auxiliary chain tensioner guide retaining bolts 21 15 - Auxiliary chain fixed guide retaining bolt 12 9 - Oil pump sprocket retaining bolt 21 15 - Cylinder head retaining bolts A - - Engine oil level (EOL) sensor retaining bolt 12 9 - Oil pan to oil sump body retaining bolts 12 9 - Oil sump body to engine retaining bolts 25 18 - Oil pan drain plug 23 17 - Oil transfer tube to Oil pan body retaining bolts 11 8 - Oil pump to engine block retaining bolts 25 18 - Pick-up pipe to oil pump retaining bolts 12 9 - Windage tray retaining bolts 25 18 - Piston cooling jet retaining bolts 12 9 - Engine block coolant draining plug 50 37 - Connecting Rod bolts Stage 1 10 7 - Stage 2 50 37 -
Page 1177 of 3039

Fuel Charging and Controls - V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol -
WARNINGS: Published: 11-May-2011
Do not smoke or carry lighted tobacco or open flame of any type when working on or near any fuel related components.
Highly flammable vapors are always present and may ignite. Failure to follow these instructions may result in personal injury.
Before any work is carried out on the fuel system, ground the vehicle to earth and maintain the ground connection until
the work is complete.
CAUTION: Before disconnecting or removing components, make sure the area around the joint faces and connections are
clean. Plug open connections to prevent contamination.
NOTE: Tighten the fuel rail high pressure fuel pump fuel line unions and fuel rail crossover pipe unions as it is instructed
in service manual.
Description Nm lb-ft lb-in Ignition coil-on-plugs retaining bolts 7 - 62 Spark plugs 20 15 - Fuel rail retaining bolt Stage 1 - 20 Stage 2 - 30 Stage 1 - 15 Stage 2 - 22 - Fuel rail crossover pipe unions 21 15 - Fuel rail crossover pipe retaining bolts 12 9 - Fuel pressure regulator 33 24 - Fuel rail high pressure fuel pump fuel line unions 21 15 - Fuel rail high pressure fuel pump fuel line M8 bolt 25 18 - Fuel rail high pressure fuel pump fuel line M6 bolt 11 8 - Fuel rail high pressure fuel pump fuel line M5 nut 6 - 53 Fuel rail high pressure fuel pump fuel line shield M10 bolt 29 21 - Fuel rail high-pressure fuel pump fuel line shield M6 bolt 11 8 - Fuel rail high pressure fuel pump torx bolts 12 9 - Throttle body retaining bolts 10 7 - Accessory drive belt idler pulley retaining bolts 25 18 - Steering gear retaining bolts 100 74 - Steering column lower universal joint assembly bolts 35 26 - Coolant expansion tank retaining bolt 10 7 - Engine compartment brace retaining bolts 45 33 - www.JagDocs.com