2010 JAGUAR XFR light
[x] Cancel search: lightPage 183 of 3039

Published: 12-May-2014
General Information - Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Index DTC: Headlamp
Control Module (HCM)
Description and Operation
Headlamp Leveling Control Module (HLCM)
CAUTION: Diagnosis by substitution from a donor vehicle is NOT acceptable. Substitution of control modules does not
guarantee confirmation of a fault, and may also cause additional faults in the vehicle being tested and/or the donor vehicle.
NOTES:
If a control module or a component is suspect and the vehicle remains under manufacturer warranty, refer to the Warranty
Policy and Procedures manual, or determine if any prior approval programme is in operation, prior to the installation of a new
module/component.
Generic scan tools may not read the codes listed, or may read only 5-digit codes. Match the 5 digits from the scan tool to
the first 5 digits of the 7-digit code listed to identify the fault (the last 2 digits give extra information read by the
manufacturer-approved diagnostic system).
When performing voltage or resistance tests, always use a digital multimeter accurate to three decimal places, and with
an up-to-date calibration certificate. When testing resistance always take the resistance of the digital multimeter leads into
account.
Check and rectify basic faults before beginning diagnostic routines involving pinpoint tests.
Inspect connectors for signs of water ingress, and pins for damage and/or corrosion.
If DTCs are recorded and, after performing the pinpoint tests, a fault is not present, an intermittent concern may be the
cause. Always check for loose connections and corroded terminals.
Check DDW for open campaigns. Refer to the corresponding bulletins and SSMs which may be valid for the specific
customer complaint and carry out the recommendations as required.
The table below lists all Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) that could be logged in the Headlamp Leveling Control Module
(HLCM). For additional diagnosis and testing information, refer to the relevant Diagnosis and Testing section in the workshop
manual.
For additional information, refer to: Headlamps (417-01 Exterior Lighting, Diagnosis and Testing).
DTC Description Possible Causes Action B1041-04
Leveling Control -
System internal
failures
Module internal
failure
Suspect Headlamp Leveling Module internal fault. Replace
as required, refer to the new module/component
installation note at the top of the DTC Index B1041-54
Leveling Control -
Missing calibration
NOTE: This DTC will
normally be logged when a
new module has been
installed.
Leveling sensor
calibration routine
not carried out
NOTE: Sensor calibration routine must be carried out with the
vehicle unladen.
Calibrate the Headlamp Leveling Sensors using the
manufacturer approved diagnostic system, carry the out
routine 'Headlamp Control Module System Calibration' from
the 'Module programming and configuration - Setup and
Configuration - Lighting' B10AE-11
Headlamp Leveling
Motor - Circuit short
to ground
Headlamp Leveling
Motor Control Circuit -
short to ground
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check Headlamp
Leveling Motor Control Circuit for short to ground B10AE-12
Headlamp Leveling
Motor - Circuit short
to battery
Headlamp Leveling
Motor Control Circuit -
short to power
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check Headlamp
Leveling Motor Control Circuit for short to power
Page 185 of 3039

DTC Description Possible Causes Action U0300-00
Internal Control
Module Software
Incompatibility - No
sub type
information
Car Configuration File
(CCF) information
incompatible to
Headlamp Leveling
Module
Check/amend the Car Configuration File (CCF) using the
manufacturer approved diagnostic system. Confirm the
latest Strategy and Calibration software is installed in the
Headlamp Leveling Module, using the manufacturer
approved diagnostic system update the Headlamp Leveling
Module software as required. If DTC returns suspect an
internal fault with the Headlamp Leveling Module Replace
as required, refer to the new module/component
installation note at the top of the DTC Index U0415-00
Invalid Data
Received From
Anti-Lock Brake
System (ABS)
Control Module - No
sub type
information
NOTE: Steering angle
sensor not calibrated
Invalid data received
from ABS module
NOTE: The steering wheel center (straight ahead) position is
recalculated each ignition cycle
Clear the DTC then cycle the ignition state to off then on.
Carry out a short road test to calibrate the Steering Wheel
Angle Sensor. If DTC returns, check the Anti-lock Brake
System Module for related DTCs and refer to relevant DTC
Index U2100-00
Initial Configuration
Not Complete - No
sub type
information
Car Configuration File
(CCF) information not
received completely
NOTE: The Car Configuration File (CCF) parameters required
are (Vehicle type)(Headlamp type)(Gearbox type) and (Dayrunning
light)
Check/amend Car Configuration File (CCF) as required using
the manufacturer approved diagnostic system. Using the
manufacturer approved diagnostic system, clear the stored
DTC then cycle the Ignition State to off, wait 30 seconds.
Return the Ignition state to on and check for stored DTCs,
if the DTC returns check other modules for related stored
DTCs. If no other modules have related DTCs confirm the
security and condition of the Headlamp Leveling Module
circuit connections. If no other DTCs are stored and the
circuit is correct suspect an internal fault with the
Headlamp Leveling Module Replace as required, refer to the
new module/component installation note at the top of the
DTC Index U2101-00
Control Module
Configuration
Incompatible - No
sub type
information
Car Configuration File
(CCF) information
incompatible to
Headlamp Leveling
Module
NOTE: The Car Configuration File (CCF) parameters required
are (Vehicle type)(Headlamp type)(Gearbox type) and (Dayrunning
light)
Check/amend Car Configuration File (CCF) as required using
the manufacturer approved diagnostic system U3002-81
Vehicle
Identification
Number - Invalid
serial data received
The stored Vehicle
Identification Number
is not the same as
the Central Broadcast
Vehicle Identification
Number
The Headlamp
Leveling Module has
previously been
installed to another
vehicle
Check the correct Headlamp Leveling Module is installed to
vehicle specification. Refit original or replace the module as
required. Refer to the new module/component installation
note at the top of the DTC Index U3003-16
Battery Voltage -
Circuit voltage
below threshold
The power supply to
the Module has been
below 9 Volts for
more than 1000
milliseconds
Suspect Battery or Charging fault. Check the battery
condition and state of charge. Check the vehicle charging
system. Refer to the relevant workshop manual section.
Clear the DTC, cycle ignition state to off then on, if DTC
returns refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check
power and ground circuit to the Headlamp Leveling Module U3003-17
Battery Voltage -
Circuit voltage
above threshold
The power supply to
the Module has been
above 16 Volts for
more than 1000
milliseconds
Suspect Charging fault. Check the battery condition and
state of charge. Check the vehicle charging system. Refer
to the relevant workshop manual section
Page 191 of 3039
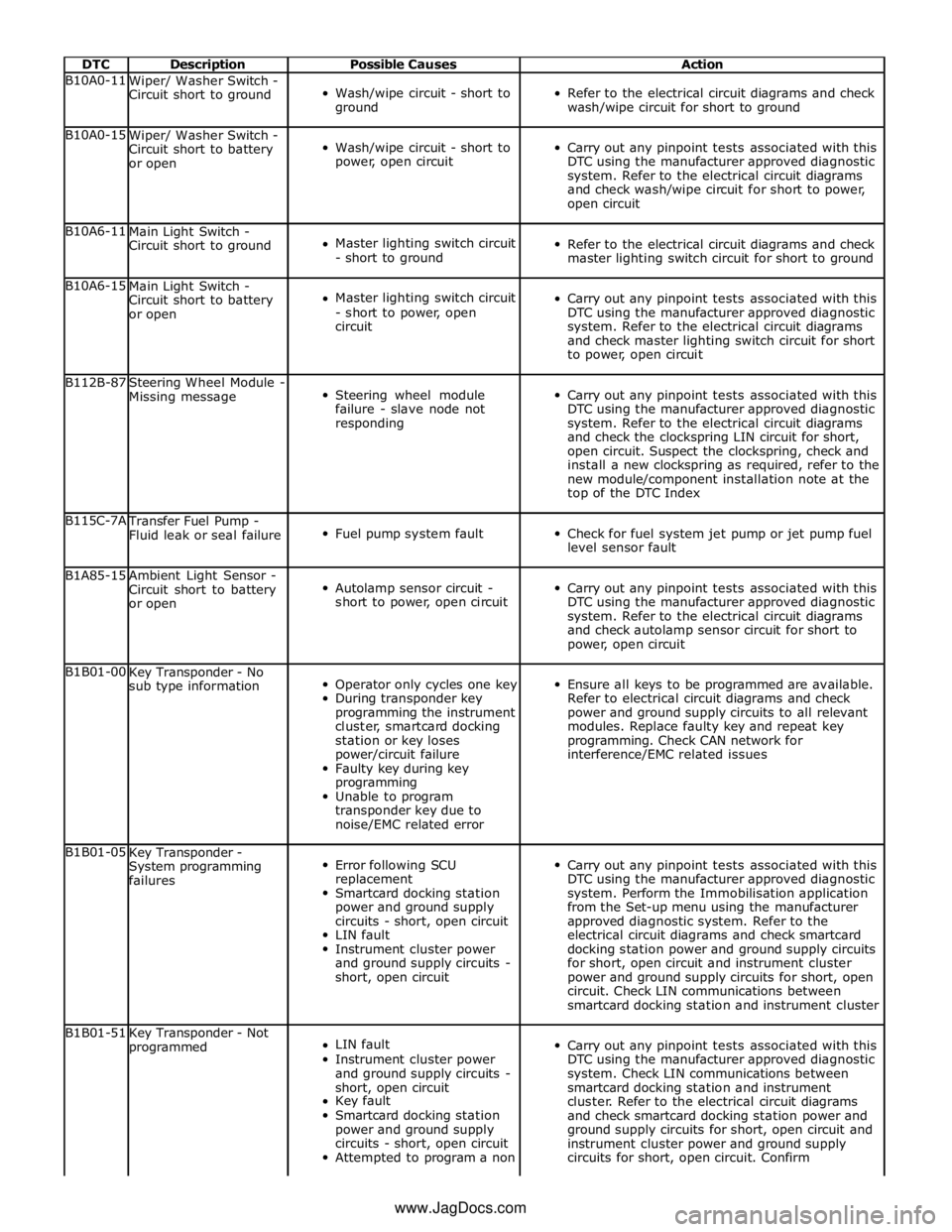
DTC Description Possible Causes Action B10A0-11
Wiper/ Washer Switch -
Circuit short to ground
Wash/wipe circuit - short to
ground
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check
wash/wipe circuit for short to ground B10A0-15
Wiper/ Washer Switch -
Circuit short to battery
or open
Wash/wipe circuit - short to
power, open circuit
Carry out any pinpoint tests associated with this
DTC using the manufacturer approved diagnostic
system. Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams
and check wash/wipe circuit for short to power,
open circuit B10A6-11
Main Light Switch -
Circuit short to ground
Master lighting switch circuit
- short to ground
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check
master lighting switch circuit for short to ground B10A6-15
Main Light Switch -
Circuit short to battery
or open
Master lighting switch circuit
- short to power, open
circuit
Carry out any pinpoint tests associated with this
DTC using the manufacturer approved diagnostic
system. Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams
and check master lighting switch circuit for short
to power, open circuit B112B-87
Steering Wheel Module -
Missing message
Steering wheel module
failure - slave node not
responding
Carry out any pinpoint tests associated with this
DTC using the manufacturer approved diagnostic
system. Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams
and check the clockspring LIN circuit for short,
open circuit. Suspect the clockspring, check and
install a new clockspring as required, refer to the
new module/component installation note at the
top of the DTC Index B115C-7A Transfer Fuel Pump -
Fluid leak or seal failure
Fuel pump system fault
Check for fuel system jet pump or jet pump fuel
level sensor fault B1A85-15
Ambient Light Sensor -
Circuit short to battery
or open
Autolamp sensor circuit -
short to power, open circuit
Carry out any pinpoint tests associated with this
DTC using the manufacturer approved diagnostic
system. Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams
and check autolamp sensor circuit for short to
power, open circuit B1B01-00
Key Transponder - No
sub type information
Operator only cycles one key
During transponder key
programming the instrument
cluster, smartcard docking
station or key loses
power/circuit failure
Faulty key during key
programming
Unable to program
transponder key due to
noise/EMC related error
Ensure all keys to be programmed are available.
Refer to electrical circuit diagrams and check
power and ground supply circuits to all relevant
modules. Replace faulty key and repeat key
programming. Check CAN network for
interference/EMC related issues B1B01-05
Key Transponder -
System programming
failures
Error following SCU
replacement
Smartcard docking station
power and ground supply
circuits - short, open circuit
LIN fault
Instrument cluster power
and ground supply circuits -
short, open circuit
Carry out any pinpoint tests associated with this
DTC using the manufacturer approved diagnostic
system. Perform the Immobilisation application
from the Set-up menu using the manufacturer
approved diagnostic system. Refer to the
electrical circuit diagrams and check smartcard
docking station power and ground supply circuits
for short, open circuit and instrument cluster
power and ground supply circuits for short, open
circuit. Check LIN communications between
smartcard docking station and instrument cluster B1B01-51
Key Transponder - Not
programmed
LIN fault
Instrument cluster power
and ground supply circuits -
short, open circuit
Key fault
Smartcard docking station
power and ground supply
circuits - short, open circuit
Attempted to program a non
Carry out any pinpoint tests associated with this
DTC using the manufacturer approved diagnostic
system. Check LIN communications between
smartcard docking station and instrument
cluster. Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams
and check smartcard docking station power and
ground supply circuits for short, open circuit and
instrument cluster power and ground supply
circuits for short, open circuit. Confirm www.JagDocs.com
Page 252 of 3039
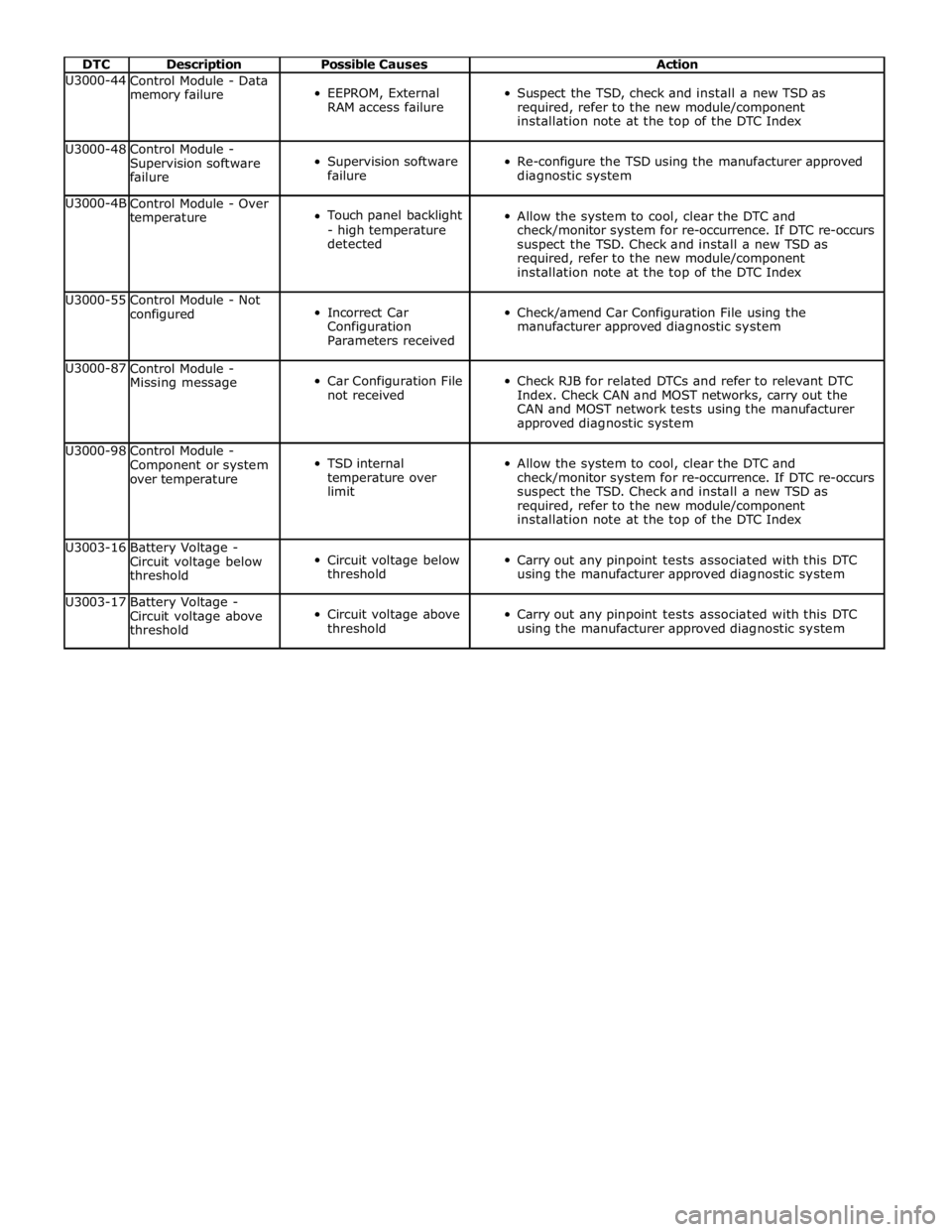
DTC Description Possible Causes Action U3000-44
Control Module - Data
memory failure
EEPROM, External
RAM access failure
Suspect the TSD, check and install a new TSD as
required, refer to the new module/component
installation note at the top of the DTC Index U3000-48
Control Module -
Supervision software
failure
Supervision software
failure
Re-configure the TSD using the manufacturer approved
diagnostic system U3000-4B
Control Module - Over
temperature
Touch panel backlight
- high temperature
detected
Allow the system to cool, clear the DTC and
check/monitor system for re-occurrence. If DTC re-occurs
suspect the TSD. Check and install a new TSD as
required, refer to the new module/component
installation note at the top of the DTC Index U3000-55
Control Module - Not
configured
Incorrect Car
Configuration
Parameters received
Check/amend Car Configuration File using the
manufacturer approved diagnostic system U3000-87
Control Module -
Missing message
Car Configuration File
not received
Check RJB for related DTCs and refer to relevant DTC
Index. Check CAN and MOST networks, carry out the
CAN and MOST network tests using the manufacturer
approved diagnostic system U3000-98
Control Module -
Component or system
over temperature
TSD internal
temperature over
limit
Allow the system to cool, clear the DTC and
check/monitor system for re-occurrence. If DTC re-occurs
suspect the TSD. Check and install a new TSD as
required, refer to the new module/component
installation note at the top of the DTC Index U3003-16
Battery Voltage -
Circuit voltage below
threshold
Circuit voltage below
threshold
Carry out any pinpoint tests associated with this DTC
using the manufacturer approved diagnostic system U3003-17
Battery Voltage -
Circuit voltage above
threshold
Circuit voltage above
threshold
Carry out any pinpoint tests associated with this DTC
using the manufacturer approved diagnostic system
Page 300 of 3039

Noise Conditions
Gear noise is typically a howling or whining due to gear damage or incorrect bearing preload. It can occur at various
speeds and driving conditions, or it can be continuous
Chuckle is a particular rattling noise that sounds like a stick against the spokes of a spinning bicycle wheel. It occurs
while decelerating from approximately 64 km/h (40 miles/h) and can usually be heard all the way to a stop. The
frequency varies with vehicle speed
Knock is very similar to chuckle, though it may be louder and occurs on acceleration or deceleration. The tear down will
disclose what has to be corrected
Check and rule out tires, exhaust and trim items before disassembling the transmission to diagnose and correct gear noise.
The noises described under Road Test usually have specific causes that can be diagnosed by observation as the unit is
disassembled. The initial clues are the type of noise heard on the road test and the driving conditions.
Vibration Conditions
wear. NOTE: New Constant Velocity (CV) joints should not be installed unless disassembly and inspection revealed unusual
Clicking, popping or grinding noises may be caused by the following:
Cut or damaged CV joint boots resulting in inadequate or contaminated lubricant in the outboard or inboard CV joint
bearing housings
Loose CV joint boot clamps
Another component contacting the rear drive half shaft
Worn, damaged or incorrectly installed wheel bearing, suspension or brake component
Vibration at highway speeds may be caused by the following:
Out-of-balance front or rear wheels
Out-of-round tires
Driveline imbalance
Driveline run-out (alignment)
NOTE: Rear drive half shafts are not balanced and are not likely to contribute to rotational vibration disturbance.
Shudder or vibration during acceleration (including from rest) may be caused by the following:
Driveline alignment
Excessively worn or damaged outboard or inboard CV joint bearing housing
Excessively high CV joint operating angles caused by incorrect ride height. Check ride height, verify correct spring rate
and check items under Inoperative Conditions
Excessively worn driveshaft components
Leakage Conditions
1. Inspect the CV joint boots for evidence of cracks, tears or splits.
2. Inspect the underbody for any indication of grease splatter in the vicinity of the rear drive half shaft, outboard and
inboard CV joint boot locations, which is an indication of CV joint boot or CV joint boot clamp damage.
3. Inspect the inboard CV joint bearing housing seal for leakage.
Inoperative Conditions
If a CV joint or rear drive half shaft pull-out occurs, check the following:
suspension components for correct location, damage or wear
bushings for wear
subframe for damage
bent or worn components
- Stabilizer bar link
- Left-hand rear suspension lower arm and bushing
- Right-hand rear suspension lower arm and bushing
- Rear wheel hub and rear drive half shaft
Road Test
A gear-driven unit will produce a certain amount of noise. Some noise is acceptable and may be audible at certain speeds or
under various driving conditions as on a newly paved blacktop road. The slight noise is in no way detrimental and must be
considered normal.
The road test and customer interview (if available) provide information needed to identify the condition and give direction to
the correct starting point for diagnosis.
1. Make notes throughout the diagnosis routine. Make sure to write down even the smallest piece of information, because
Page 301 of 3039

it may turn out to be the most important.
2. Do not touch anything until a road test and a thorough visual inspection of the vehicle have been carried out. Leave the
tire pressures and vehicle load just where they were when the condition was first observed. Adjusting tire pressures,
vehicle load or making other adjustments may reduce the conditions intensity to a point where it cannot be identified
clearly. It may also inject something new into the system, preventing correct diagnosis.
3. Make a visual inspection as part of the preliminary diagnosis routine, writing down anything that does not look right.
Note tire pressures, but do not adjust them yet. Note leaking fluids, loose nuts and bolts, or bright spots where
components may be rubbing against each other. Check the luggage compartment for unusual loads.
4. Road test the vehicle and define the condition by reproducing it several times during the road test.
5. Carry out the Road Test Quick Checks as soon as the condition is reproduced. This will identify the correct diagnostic
procedure. Carry out the Road Test Quick Checks more than once to verify they are providing a valid result. Remember,
the Road Test Quick Checks may not tell where the concern is, but they will tell where it is not.
Road Test Quick Checks
1. 24-80 km/h (15-50 miles/h): With light acceleration, a moaning noise is heard and possibly a vibration is felt in the
front floor pan. It is usually worse at a particular engine speed and at a particular throttle setting during acceleration at
that speed. It may also produce a moaning sound, depending on what component is causing it. Refer to Tip-In Moan in
the Symptom Chart.
2. Acceleration/deceleration: With slow acceleration and deceleration, a shake is sometimes noticed in the steering
wheel/column, seats, front floor pan, front door trim panel or front end sheet metal. It is a low frequency vibration
(around 9-15 cycles per second). It may or may not be increased by applying brakes lightly. Refer to Idle Boom/Shake
/Vibration in the Symptom Chart.
3. High speed: A vibration is felt in the front floor pan or seats with no visible shake, but with an accompanying sound or
rumble, buzz, hum, drone or booming noise. Coast with the clutch pedal depressed or shift control selector lever in
neutral and engine idling. If vibration is still evident, it may be related to wheels, tires, front brake discs, wheel hubs
or front wheel bearings. Refer to High Speed Shake in the Symptom Chart.
4. Engine rpm sensitive: A vibration is felt whenever the engine reaches a particular rpm. It will disappear in neutral
coasts. The vibration can be duplicated by operating the engine at the problem rpm while the vehicle is stationary. It
can be caused by any component, from the accessory drive belt to the torque converter which turns at engine speed
when the vehicle is stopped. Refer to High Speed Shake in the Symptom Chart.
5. Noise/vibration while turning: Clicking, popping, or grinding noises may be due to a worn, damaged, or incorrectly
installed front wheel bearing, rear drive half shaft or CV joint.
6. Noise/vibration that is road speed relative: This noise/vibration can be diagnosed independent of engine speed or gear
selected (engine speed varies but torque and road speed remain constant). The cause may be a rear drive
axle/differential whine.
Road Conditions
An experienced technician will always establish a route that will be used for all NVH diagnosis road tests. The road selected
should be reasonably smooth, level and free of undulations (unless a particular condition needs to be identified). A smooth
asphalt road that allows driving over a range of speeds is best. Gravel or bumpy roads are unsuitable because of the additional
road noise produced. Once the route is established and consistently used, the road noise variable is eliminated from the test
results.
NOTE: Some concerns may be apparent only on smooth asphalt roads.
If a customer complains of a noise or vibration on a particular road and only on a particular road, the source of the concern
may be the road surface. If possible, try to test the vehicle on the same type of road.
Vehicle Preparation
Carry out a thorough visual inspection of the vehicle before carrying out the road test. Note anything which is unusual. Do not
repair or adjust any condition until the road test is carried out, unless the vehicle is inoperative or the condition could pose a
hazard to the technician.
After verifying the condition has been corrected, make sure all components removed have been installed.
Lift Test
After a road test, it is sometimes useful to do a similar test on a lift.
When carrying out the high-speed shake diagnosis or engine accessory vibration diagnosis on a lift, observe the following
precautions:
WARNING: If only one drive wheel is allowed to rotate, speed must be limited to 55 km/h (35 miles/h) indicated on the
speedometer since actual wheel speed will be twice that indicated on the speedometer. Speed exceeding 55 km/h (35 miles/h)
or allowing the drive wheel to hang unsupported could result in tire disintegration, differential failure, constant velocity joint
Page 304 of 3039

Tire beads correctly seated Are the tires OK? Yes
GO to D2. No
Inspect the wheels. For additional information, refer to Section 204-00. D2: INSPECT WHEEL BEARINGS 1 Inspect the wheel bearings. For additional information, refer to Section 204-00. Are the wheel bearings OK? Yes
GO to D3. No
Repair as necessary. Repeat the Road Test as outlined. D3: INSPECT THE CONSTANT VELOCITY (CV) JOINT BOOTS 1 Inspect the CV joint boots. Spin the rear tire by hand
Inspect for evidence of cracks, tears, splits or splattered grease Are the CV joint boots OK? Yes
GO to D4. No
Repair as necessary. Repeat the Road Test as outlined. D4: INSPECT WHEEL AND TIRE RUNOUT 1 Inspect the wheel and tire runout. Carry out the Wheel and Tire Check procedure.
REFER to: Lifting (100-02 Jacking and Lifting, Description and Operation). Is the wheel and tire runout OK? Yes
Balance the wheels and tires. Refer to the wheel balance equipment manufacturers instructions.
No
Repair as necessary.
REFER to: Lifting (100-02 Jacking and Lifting, Description and Operation). Repeat the Road Test as outlined.
PINPOINT TEST E : NON-AXLE NOISE TEST
CONDITIONS DETAILS/RESULTS/ACTIONS E1: INSPECT VEHICLE TRIM 1 Check the grille and trim mouldings to see if they are the source of the noise. Are the vehicle trim components causing the noise? Yes
Install new trim or repair as necessary. For additional information, refer to Section 501-08.
No
GO to E2. E2: CHECK THE A/C SYSTEM FOR NOISE 1 Check the A/C system components for noise by turning the A/C system on and off. Is the A/C system causing the noise? Yes
Diagnose the A/C system.
REFER to: Lifting (100-02 Jacking and Lifting, Description and Operation). No
GO to E3. E3: CHECK NON-FACTORY ACCESSORIES 1 Inspect any accessories for being the source of the noise. Example: grounding body-to-frame, antennas, visors, bug deflectors and fog lights? Are the accessories the cause of the noise? Yes
Adjust, repair or install new accessories or fasteners as required.
No
Verify the customer concern.
Page 332 of 3039

Upper Control Arm
The forged-aluminum upper control arm is a wishbone design and connects to the vehicle body through two plain bushes, and
links to the swan neck wheel knuckle by an integral ball joint. The upper control arm is inclined to provide anti-dive
characteristics under heavy braking, while also controlling geometry for vehicle straight-line stability.
Lower Control Arm
The forged aluminum lower control arms are of the wishbone design; the arms separate to allow for optimum bush tuning:
The rear lateral control arm is fitted with a bush at its inner end which locates between brackets on the subframe. The
arm is secured with an eccentric bolt which provides the adjustment of the suspension camber geometry. The outer end
of the control arm has a tapered hole which locates on a ball joint fitted to the wheel knuckle. An integral clevis bracket
on the forward face of the lateral control arm allows for the attachment of the forward control arm. A bush is fitted
below the clevis bracket to provide for the attachment of the stabilizer bar link. A cross-axis joint is fitted to a
cross-hole in the control arm to provide the location for the clevis attachment of the spring and damper assembly.
The forward control arm is fitted with a fluid-block rubber bush at its inner end which locates between brackets on the
subframe. The arm is secured with an eccentric bolt which provides adjustment of the castor and camber geometry. The
outer end of the control arm is fitted with a cross-axis joint and locates in the integral clevis bracket on the lateral
control arm.
Wheel Knuckle
The cast aluminum wheel knuckle is a swan neck design and attaches to the upper control arm and lower lateral control arm.
The lower lateral control arm locates on a non serviceable ball-joint integral with the wheel knuckle. The lower boss on the
rear of the knuckle provides for the attachment of the steering gear tie-rod ball joint.
The wheel knuckle also provides the mounting locations for the:
wheel hub and bearing assembly
the wheel speed sensor (integral to the wheel hub and bearing assembly)
brake caliper and disc shield.
Stabilizer Bar
The stabilizer bar is attached to the front of the subframe with bushes and mounting brackets. The pressed steel mounting
brackets locate over the bushes and are attached to the cross member with bolts screwed into threaded locations in the
subframe. The stabilizer bar has crimped, 'anti-shuffle' collars pressed in position on the inside edges of the bushes. The
collars prevent sideways movement of the stabilizer bar.
The stabilizer bar is manufactured from 32mm diameter tubular steel on supercharged models and 31mm diameter tubular
steel on diesel and normally aspirated models and has been designed to provide particular characteristics in maintaining roll
rates, specifically in primary ride comfort.
Each end of the stabilizer bar curves rearwards to attach to a ball joint on a stabilizer link. Each stabilizer link is secured to a
bush in the lower lateral arm with a bolt and locknut. The links allow the stabilizer bar to move with the wheel travel providing
maximum effectiveness.
The only difference between the front stabilizer bars, in addition to the diameter, is in the shape to accommodate engine
variant:
a slightly curved bar, between bush centers, for V6 diesel (31 mm dia) and V8 gasoline supercharged (32 mm dia),
a straight bar, between bush centers, for V6 and V8 normally aspirated gasoline engines (31 mm dia).
Spring and Damper Assembly
The spring and damper assemblies are located between the lower lateral arm and the front suspension housing in the inner
wing. Dependant on vehicle model there are three types of coil spring and damper available:
a standard oil passive damper (All models except supercharged),
an adaptive damper, also known as Computer Active Technology Suspension (CATS) on 4.2L supercharged vehicles up to
2010MY, For additional information refer to Vehicle Dynamic Suspension 4.2L.
a continuously variable adaptive damper, also known as Adaptive Dynamics System on 5.0L supercharged vehicles from
2010MY. For additional information refer to Vehicle Dynamic Suspension 5.0L.
The dampers are a monotube design with a spring seat secured by a circlip onto the damper tube. The damper's lower
spherical joint is an integral part of the lateral lower control-arm, and the damper takes the form of a clevis-end, which
straddles the spherical joint.
The damper piston is connected to a damper rod which is sealed at its exit point from the damper body. The threaded outer
end of the damper rod locates through a hole in the top mount. A self locking nut secures the top mount to the damper rod.
The damper rod on the adaptive damper has an electrical connector on the outer end of the damper rod.
Supercharged 4.2L vehicles up to 2010MY: The adaptive damper functions by restricting the flow of hydraulic fluid through
internal galleries in the damper's piston. The adaptive damper has a solenoid operated valve, which when switched allows a
greater flow of hydraulic fluid through the damper's piston. This provides a softer damping characteristic from the damper. The
adaptive damper defaults to a firmer setting when not activated. The solenoid is computer controlled and can switch between
soft and hard damping settings depending on road wheel inputs and vehicle speed.
Supercharged 5.0L vehicles from 2010MY: The variable damper functions by adjustment of a solenoid operated variable orifice,
which opens up an alternative path for oil flow within the damper. When de-energized the bypass is closed and all the oil flows