2010 JAGUAR XFR fuel
[x] Cancel search: fuelPage 1622 of 3039
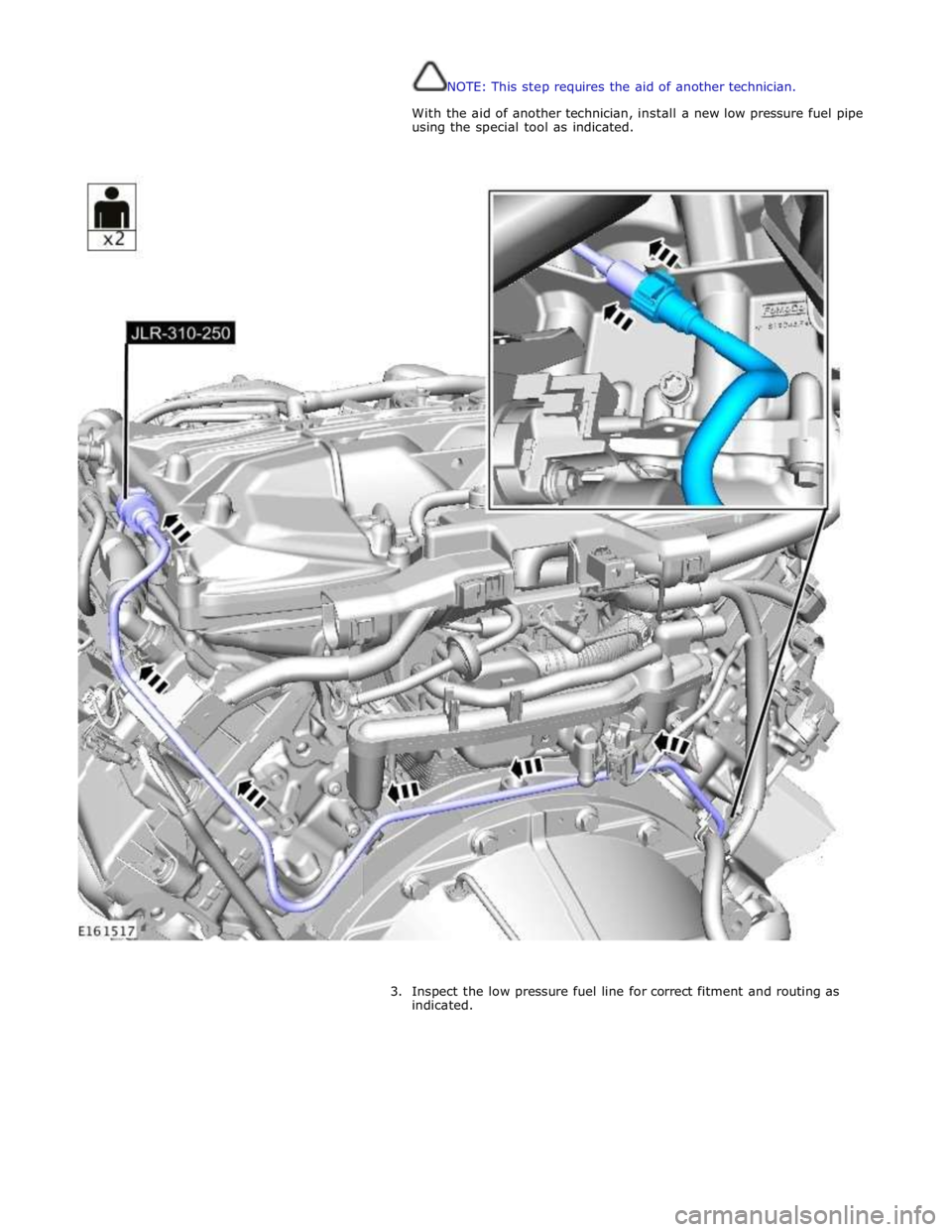
NOTE: This step requires the aid of another technician.
With the aid of another technician, install a new low pressure fuel pipe
using the special tool as indicated.
3. Inspect the low pressure fuel line for correct fitment and routing as
indicated.
Page 1633 of 3039

DTC Description Possible Cause Action ECM fault
P210500 Throttle Actuator
Control System -
Forced Engine
Shutdown
Throttle MIL
request due to fuel
cut Carry out any pinpoint tests associated with this DTC using the
manufacturer approved diagnostic system P211800 Throttle Actuator
Control Motor Current
Range/Performance
Throttle motor
control circuit -
short to ground,
power, high
resistance Carry out any pinpoint tests associated with this DTC using the
manufacturer approved diagnostic system. Refer to the electrical
circuit diagrams and check throttle motor control circuit for short to
ground, power, high resistance P211900 Throttle Actuator
Control Throttle Body
Range/Performance
Throttle spring
faulty Carry out any pinpoint tests associated with this DTC using the
manufacturer approved diagnostic system. Suspect throttle body
faulty. Check and install a new throttle body as required, refer to
the new module/component installation note at top of DTC Index P212200 Throttle/Pedal
Position Sensor/Switch
D Circuit Low
APP sensor circuit 2
- low input Carry out any pinpoint tests associated with this DTC using the
manufacturer approved diagnostic system. Refer to the electrical
circuit diagrams and check APP sensor circuit 2 for short to ground, open circuit P212216 Throttle/Pedal
Position Sensor/Switch
D Circuit Low Input
Accelerator pedal
position (APP)
sensor circuit 1 -
short to ground,
power
Accelerator pedal
position (APP)
sensor failure Carry out any pinpoint tests associated with this DTC using the
manufacturer approved diagnostic system. Refer to electrical circuit
diagrams and check accelerator pedal position (APP) sensor circuit 1
for short to ground, power. Set ignition status to 'ON' engine 'OFF'
check and record 'Pedal value sensor 1' datalogger signal. With
pedal in idle position, value of signal should be approximately 0%,
if not suspect the pedal position sensor, check and install a new
sensor as required P212300 Throttle/Pedal
Position Sensor/Switch
D Circuit High
APP sensor circuit 2
- high input Carry out any pinpoint tests associated with this DTC using the
manufacturer approved diagnostic system. Refer to the electrical
circuit diagrams and check APP sensor circuit 2 for short to power P212317 Throttle/Pedal
Position Sensor/Switch
D Circuit High Input
Accelerator pedal
position (APP)
sensor circuit 1 -
short to power
Accelerator pedal
position (APP)
sensor failure Carry out any pinpoint tests associated with this DTC using the
manufacturer approved diagnostic system. Refer to electrical circuit
diagrams and check accelerator pedal position (APP) sensor circuit 1
for short to ground, power. Set ignition status to 'ON' engine 'OFF'
check and record 'Pedal value sensor 1' datalogger signal. With
pedal in fully depressed position, value of signal should be
approximately 99%, if not suspect the pedal position sensor, check
and install a new sensor as required P212716 Throttle/Pedal
Position Sensor/Switch
E Circuit Low Input
Accelerator pedal
position (APP)
sensor circuit 2 -
short to ground,
high resistance
Accelerator pedal
position (APP)
sensor failure Carry out any pinpoint tests associated with this DTC using the
manufacturer approved diagnostic system. Refer to electrical circuit
diagrams and check accelerator pedal position (APP) sensor circuit 2
for short to ground, power. Set ignition status to 'ON' engine 'OFF'
check and record 'Pedal value sensor 2' datalogger signal. With
pedal in idle position, value of signal should be approximately 0%,
if not suspect the pedal position sensor, check and install a new
sensor as required P212817 Throttle/Pedal
Position Sensor/Switch
E Circuit High Input
Accelerator pedal
position (APP)
sensor circuit 2 -
short to power
Accelerator pedal
position (APP)
sensor failure Carry out any pinpoint tests associated with this DTC using the
manufacturer approved diagnostic system. Refer to electrical circuit
diagrams and check accelerator pedal position (APP) sensor circuit 2
for short to ground, power. Set ignition status to 'ON' engine 'OFF'
check and record 'Pedal value sensor 2' datalogger signal. With
pedal in fully depressed position, value of signal should be
approximately 99%, if not suspect the pedal position sensor, check
and install a new sensor as required P213528 Throttle/Pedal
Position Sensor/Switch
A/B Voltage
Correlation
APP sensor circuit 1
and 2 range
performance -
sub-processor Carry out any pinpoint tests associated with this DTC using the
manufacturer approved diagnostic system. Refer to the electrical
circuit diagrams and check APP sensor circuits 1 and 2 for short to
ground, power and high resistance. Clear the DTCs and retest. If
the code remains, replace the APP sensor P213529 Throttle/Pedal
Position Sensor/Switch
A/B Voltage
Correlation
APP sensor -
excessive difference
between
raw values of circuit
1 and 2 -
sub-processor Carry out any pinpoint tests associated with this DTC using the
manufacturer approved diagnostic system. Refer to the electrical
circuit diagrams and check APP sensor circuits 1 and 2 for short,
open circuit
Page 1639 of 3039

Published: 11-May-2011
Speed Control - V8 5.0L Petrol/V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol - Speed Control - Overview
Description and Operation
OVERVIEW
Speed Control
The speed control system is integrated with the engine management system and uses fueling intervention to automatically
maintain a set vehicle speed. Once engaged, the system can also be used to accelerate the vehicle without using the
accelerator pedal.
The speed control system comprises the following components:
On/Off/Suspend switch
'+' and '-' (set/accelerate and decelerate) steering wheel switches
Resume switch
Clock spring
Speed control warning indicator.
Adaptive Speed Control
The adaptive speed control system uses a forward looking radar sensor to scan the road ahead, looking for objects that are
moving at a different rate to itself. When a target is identified the adaptive speed control system will monitor the time gap
between it and the target vehicle. When that gap falls below a set driver selected level the adaptive speed control system will
intervene slowing the vehicle by backing off the throttle and/ or applying the brakes, until the correct gap is attained.
The adaptive speed control system comprises the following components:
Adaptive speed control sensor
Adaptive speed control module
Steering wheel control switches
ECM (engine control module)
Electric throttle actuator
ABS (anti-lock brake system) module and pump
Adaptive speed control warning indicator (in the instrument cluster).
Page 1641 of 3039

6 Clockspring 7 APP (accelerator pedal position) sensor 8 Electric throttle actuator 9 Brake lamp/brake test switch 10 Adaptive speed control radar sensor 11 Diagnostic socket 12 Instrument cluster 13 TCM (transmission control module) 14 Adaptive speed control module
SPEED CONTROL System Operation
The speed control system uses inputs from the brake lamp/brake test switch, the APP sensor, the ECM and the ABS module.
Speed control is operated by the driver using only the steering wheel switches. When speed control is active, the ECM regulates the PWM (pulse width modulation) signals to the fuel injectors to adjust the fuel supply as required to maintain the
set speed.
During speed control operation, the ECM controls vehicle speed by adjusting fuel injection duration and timing. When the accelerator pedal is pressed with speed control active, the ECM outputs a calculated throttle angle signal in place of the actual throttle angle signals produced by the APP sensor. The calculated throttle angle is derived from fuel demand.
The minimum set speed for speed control is 18 mph (30 (km/h). Speed control is automatically suspended if the following
conditions apply:
Vehicle speed falls below 18 mph (30 km/h)
The brake pedal is pressed
The cancel button is pressed
Neutral, park or reverse gear is selected
The difference between actual speed and the set speed is too great
If the engine speed becomes near to the red line (maximum engine speed)
If the accelerator pedal is used to accelerate beyond the set speed for too long.
ADAPTIVE SPEED CONTROL
The adaptive speed control system comprises the following components:
Adaptive speed control sensor
Adaptive speed control module
Steering wheel control switches
ECM
Electric throttle actuator
ABS module and pump Adaptive speed control warning indicator.
The adaptive speed control system uses a forward looking radar sensor to scan the road ahead, looking for objects that are
moving at a different rate to itself. When a target is identified the adaptive speed control system will monitor the time gap
between it and the target vehicle. When that gap falls below a set driver selected level the adaptive speed control system will
intervene slowing the vehicle by backing off the throttle and/ or applying the brakes, until the correct gap is attained. The
driver can chose between four gap settings, 1, 1.4, 1.8 and 2.2 seconds.
The system will detect but not react to the following:
Vehicles in the oncoming lane
Stationary vehicles
Pedestrians
Vehicles not in the same lane.
Adaptive speed control is active when the vehicle is moving. Adaptive Speed Control only functions when a set speed is
entered in normal speed control mode. The adaptive speed control system only intervenes with the set speed when it detects
a target vehicle, and then only if the minimum time gap is breached.
It is important to note that the system is intended for use in limited driving situations, does not remove control and
responsibility from the driver, and at all times can be quickly overridden. The adaptive speed control system is not a collision
warning system and will not react to stationary objects. The system does not operate below a minimum speed of
approximately 30 km/h (20 mph) since it is unsuitable for use in cities or congested traffic. The system is best suited to main
roads/ highways with gradual bends.
The ECM, throttle body and throttle control are unchanged from those used for non adaptive speed control variants.
The adaptive speed control system is based on the use of a front mounted radar sensor. The sensor transmits a 1.5° wide
beam forward of the vehicle and detects the returning signals reflected off other vehicles and objects ahead.
The 1.5° wide radar beam is mechanically scanned at a rate of 10 sweeps/second across a total arc of 15° centered on the
Page 1645 of 3039

Item Description 1 Forward alert switch The forward alert system utilizes the adaptive speed control system components. Forward alert is turned on and off
independently of adaptive speed control, via a switch mounted in the lower outboard knee bolster switchpack. Forward alert
will notify the driver by means of a chime, a warning indicator in the instrument cluster and an indication in the message
center, when a target vehicle comes into range. The system will NOT use throttle or brake intervention to slow the vehicle.
The forward alert switch is connected to the instrument cluster in a resistive ladder with the luggage compartment opening
switch and the fuel filler flap switch. The instrument cluster sends the forward alert information to the Adaptive speed control
module on the CAN bus.
WARNING: The system is intended as a driver aid and should be used as such. The system is NOT a collision warning or
avoidance device.
The system sensitivity can be adjusted in the same manner as the adaptive speed control, via the steering wheel mounted
switches. Each adjustment is accompanied by a message in the message center. FORWARD ALERT SWITCHES
Page 1664 of 3039

Published: 11-Jul-2014
Climate Control System - General Information - Climate Control System
Diagnosis and Testing
Principles of Operation
For a detailed description of the Climate Control System, refer to the relevant Description and Operation sections in the
Workshop Manual. REFER to:
Air Distribution and Filtering (412-01 Climate Control, Description and Operation), Air Distribution and Filtering (412-01 Climate Control, Description and Operation), Air Distribution and Filtering (412-01 Climate Control, Description and Operation), Heating and Ventilation (412-01 Climate Control, Description and Operation), Heating and Ventilation (412-01 Climate Control, Description and Operation), Heating and Ventilation (412-01 Climate Control, Description and Operation), Air Conditioning (412-01 Climate Control, Description and Operation), Air Conditioning (412-01 Climate Control, Description and Operation), Air Conditioning (412-01 Climate Control, Description and Operation), Control Components (412-01 Climate Control, Description and Operation), Control Components (412-01 Climate Control, Description and Operation), Control Components (412-01 Climate Control, Description and Operation), Electric Booster Heater (412-02 Auxiliary Climate Control, Description and Operation), Electric Booster Heater (412-02 Auxiliary Climate Control, Description and Operation), Electric Booster Heater (412-02 Auxiliary Climate Control, Description and Operation).
Inspection and Verification
WARNING: Servicing must be carried out by personnel familiar with both vehicle system and the charging and testing
equipment. All operations must be carried out in a well ventilated area away from open flame and heat sources.
CAUTION: Diagnosis by substitution from a donor vehicle is NOT acceptable. Substitution of control modules does not
guarantee confirmation of a fault, and may also cause additional faults in the vehicle being tested and/or the donor vehicle.
NOTE: Check and rectify basic faults before beginning diagnostic routines involving pinpoint tests.
1. Verify the customer concern
2. Visually inspect for obvious signs of damage and system integrity
Visual Inspection
Mechanical Electrical
Coolant level
Hose(s)
Coolant pump
Control flap(s)
Duct(s)
Vent(s)
Cabin air filter
Drive belt
Air conditioning compressor
Thermostatic expansion valve
Evaporator
Receiver drier
Air conditioning condenser
Refrigerant pipes Auxiliary
drive belt
Fuel fired booster heater
Fuel fired booster heater fuel pump
Fuel fired booster heater fuel pipes
Fuse(s)
Wiring harness
Electrical connectors
Blower
Air conditioning compressor
Electric cooling fan
Automatic Temperature Control Module (ATCM)
Refrigerant pressure sensor
3. If an obvious cause for an observed or reported concern is found, correct the cause (if possible) before proceeding to
the next step
4. If the cause is not visually evident, verify the symptom and refer to the Symptom Chart, alternatively check for
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) and refer to the DTC Index
5. Check DDW for open campaigns. Refer to the corresponding bulletins and SSMs which may be valid for the specific
customer complaint and carry out the recommendations as required
Page 1674 of 3039

Published: 11-May-2011
Climate Control System - General Information - Electronic Leak Detection
General Procedures
1. WARNING: Good ventilation is necessary in the area where A/C leak
testing is to be carried out. If the surrounding air is contaminated with
refrigerant gas, the leak detector will indicate this gas all the time.
Odors from other chemicals such as antifreeze, diesel fuel, disc brake
cleaner, or other cleaning solvents can cause the same problem. A fan,
even in a well ventilated area, is very helpful in removing small traces of
contamination from the air that might affect the leak detector. Failure to
follow this instruction may result in personal injury.
Attach an R-134a manifold gauge set or use a UL-approved
recovery/recycling device such as an R-134a A/C refrigerant center (which
meets SAE Standard J 1991). For additional information, refer to the
manufacturers equipment instructions.
Both gauges should indicate 413-551 kPa (60-80 psi) at 24°C
(75°F) with the engine off.
If little or no pressure is indicated, carry out the air conditioning
(A/C) system recovery, evacuation and charging procedure.
For additional information, refer to Air Conditioning (AC) System Recovery, Evacuation and Charging in this section.
2. Use an R134-a Automatic calibration halogen leak detector to leak test
the refrigerant system. For additional information, refer to the
manufacturers equipment instructions.
3. If a leak is found, carry out the air conditioning (A/C) system recovery
procedure.
For additional information, refer to Air Conditioning (AC) System Recovery, Evacuation and Charging in this section.
Page 1782 of 3039

Acts as an interface for the passive anti-theft system.
Refer to: Anti-Theft - Active (419-01A Anti-Theft - Active, Description and Operation).
Two analogue gauges are located in the instrument cluster; the speedometer and the tachometer. The speedometer is located
on the LH (left-hand) side of the instrument cluster. The tachometer is located on the RH (right-hand) side of the instrument
cluster
and displays engine speeds up to 7000 Revolutions Per Minute (RPM) for the supercharged engine, 8000 RPM for the naturally
aspirated engines and 6000 RPM for diesel variants.
The message center is a LCD located in a central position in the cluster. The message center displays system status information including fuel quantity remaining. www.JagDocs.com