2010 JAGUAR XFR warning
[x] Cancel search: warningPage 703 of 3039

Published: 09-Jul-2014
Anti-Lock Control - Stability Assist - Anti-Lock Control - Stability Assist
Diagnosis and Testing
Principle of Operation
For a detailed description of the Anti-Lock Control - Stability Assist system, refer to the relevant Description and Operation
sections in the workshop manual. REFER to: (206-09 Anti-Lock Control - Stability Assist)
Anti-Lock Control - Stability Assist (Description and Operation), Anti-Lock Control - Stability Assist (Description and Operation), Anti-Lock Control - Stability Assist (Description and Operation).
Inspection and Verification
CAUTION: Diagnosis by substitution from a donor vehicle is NOT acceptable. Substitution of control modules does not
guarantee confirmation of a fault, and may also cause additional faults in the vehicle being tested and/or the donor vehicle.
1. Verify the customer concern.
2. Confirm if the Anti-Lock Brake System (ABS) warning light was illuminated, or still is.
NOTE: An intermittent fault may allow the warning light to go off. This does not necessarily mean the fault is not
present. Some warnings will appear to clear when the ignition is cycled. This is often because the warning has flagged as a
result of one of the vehicle's on-board diagnostic routines having run to detect the fault. If the same routine is not run when
the ignition status is set to ON, the warning will not re-flag until the routine does run.
3. Visually inspect for obvious signs of damage and system integrity.
Visual Inspection
Mechanical Electrical
Brake fluid level
Vacuum system
Wheel speed sensor installation
Wheel speed sensor air gap
Magnetic pulse wheel(s) (damaged/contaminated)
Steering angle sensor
Yaw rate sensor and accelerometer cluster installation
Incorrect wheel or tire size
Warning light operation
Fuses
Wheel speed sensors
Connectors/Pins
Harnesses
Steering wheel rotation sensor
Yaw rate sensor and accelerometer cluster
Booster pressure sensor
Hydraulic Control Unit (HCU)
4. If an obvious cause for an observed or reported concern is found, correct the cause (if possible) before proceeding to
the next step.
5. If the cause is not visually evident check for Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) and refer to the DTC Index.
DTC Index
For a list of Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) that could be logged on this vehicle, please refer to Section 100-00.
REFER to: Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Index - DTC: Anti-Lock Braking System (ABS) (100-00 General Information, Description and Operation).
Page 705 of 3039

Anti-Lock Control - Stability Assist - Front Wheel Speed Sensor
Removal and Installation
Removal Published: 11-May-2011
1. WARNING: Make sure to support the vehicle with axle stands.
Raise and support the vehicle.
2. Refer to: Fender Splash Shield (501-02 Front End Body Panels, Removal and Installation).
3. NOTE: LH illustration shown, RH is similar.
4. NOTE: LH illustration shown, RH is similar.
Page 708 of 3039

Published: 11-May-2011
Anti-Lock Control - Stability Assist - Hydraulic Control Unit (HCU)
Removal and Installation
Removal
All vehicles
1. Disconnect the battery ground cable.
For additional information, refer to: Battery Disconnect and Connect (414-01 Battery, Mounting and Cables, General Procedures).
Left-hand drive vehicles
2. Remove the secondary bulkhead RH panel.
For additional information, refer to: Secondary Bulkhead Panel RH - 3.0L NA V6 - AJ27 (501-02 Front End Body Panels, Removal and Installation).
Right-hand drive vehicles
3. Remove the secondary bulkhead LH panel.
For additional information, refer to: Secondary Bulkhead Panel LH - 3.0L NA V6 - AJ27 (501-02 Front End Body Panels, Removal and Installation).
All vehicles
4. WARNING: Do not work on or under a vehicle supported only by a
jack. Always support the vehicle on safety stands.
Raise and support the vehicle.
5. Connect brake bleed pipes and bottles to the left-hand front and the
left-hand rear brake caliper bleed nipples and loosen the brake caliper
bleed nipples.
6. NOTE: To prevent the loss of brake fluid, using the special tool
apply the brake pedal and set to 40mm ( 1.6 in ) below the rest
position.
Using the special tool, press and hold the brake pedal.
7. Remove the bleed pipes and bottles.
Tighten the left-hand front brake caliper bleed nipple. 1. For vehicles with supercharger: Tighten to 14Nm.
2. For vehicles without supercharger: Tighten to 8 Nm.
Tighten the left-hand rear brake caliper bleed nipple.
1. All vehicles: Tighten to 14 Nm.
Disconnect and remove the brake bleed pipes and bottles.
Install the bleed nipple dust caps. Brake pedal hold down tool
JDS9013 Special Tool(s)
Page 712 of 3039

Anti-Lock Control - Stability Assist - Rear Wheel Speed Sensor
Removal and Installation Published: 11-May-2011
NOTES: Removal
Removal steps in this procedure may contain installation details.
The ignition must be switched off.
Some variation in the illustrations may occur, but the essential information is always correct.
1. WARNING: Do not work on or under a vehicle supported only by a jack.
Always support the vehicle on safety stands.
Raise and support the vehicle.
2. Disconnect the wheel speed sensor electrical connector.
Page 718 of 3039

Steering System - General Information - Steering System
Diagnosis and Testing
Principle of Operation Published: 11-May-2011
For a detailed description of the steering system operation, refer to the relevant Description and Operation sections of the
workshop manual. REFER to:
Power Steering (211-02 Power Steering, Description and Operation), Power Steering (211-02 Power Steering, Description and Operation), Power Steering (211-02 Power Steering, Description and Operation), Steering Linkage (211-03 Steering Linkage, Description and Operation), Steering Linkage (211-03 Steering Linkage, Description and Operation), Steering Linkage (211-03 Steering Linkage, Description and Operation), Steering Column (211-04 Steering Column, Description and Operation), Steering Column (211-04 Steering Column, Description and Operation), Steering Column (211-04 Steering Column, Description and Operation), Steering Column Switches (211-05 Steering Column Switches, Description and Operation), Steering Column Switches (211-05 Steering Column Switches, Description and Operation), Steering Column Switches (211-05 Steering Column Switches, Description and Operation).
Inspection and Verification
1. Verify the customer concern.
2. Visually inspect for obvious signs of damage and system integrity.
Visual Inspection
Mechanical Electrical
Tire condition/pressure
Fluid level
Leaks
Security, condition and correct installation of suspension components
Security, condition and correct installation of steering system components
Fuses
Harnesses for damage/corrosion
Electrical connector(s)
Damaged/corroded pins
CAUTION: If a steering gear assembly is returned under warranty with leaking output shaft seals, but there is also
damage to the steering gear boot/boots the steering gear warranty will be invalid. This is due to the steering gear output
shaft seals being damaged due to foreign materials entering the steering gear boot and damaging the steering gear output
shaft seals thereafter.
3. If an obvious cause for an observed or reported concern is found, correct the cause (if possible) before proceeding to
the next step.
4. If the concern is not visually evident, verify the symptom and refer to the symptom chart.
Symptom Charts
WARNING: It is not possible to CHECK the torque of a patchlock bolt, if the torque is suspected to be low, the bolt must
be REMOVED/DISCARDED and a new bolt MUST be INSTALLED and torque to the correct value.
NOTE: If the module or a component is suspect and the vehicle remains under manufacturer warranty, refer to the
Warranty Policy and Procedures manual (section B1.2), or determine if any prior approval programme is in operation, prior to
the installation of a new module/component.
Fluid Leakage
NOTE: Confirm the location of the fluid leak. CLEAN the area of the leak, inspect the area and confirm the exact position.
Ensure the fluid is not from another system on the vehicle.
Symptom Possible Causes Action
Power steering
fluid leakage
Overfilled system
Correct the fluid level as required
Steering gear
Check and install new steering gear as required, refer to the new
module/component installation note at the top of the Symptom
Charts
Page 731 of 3039
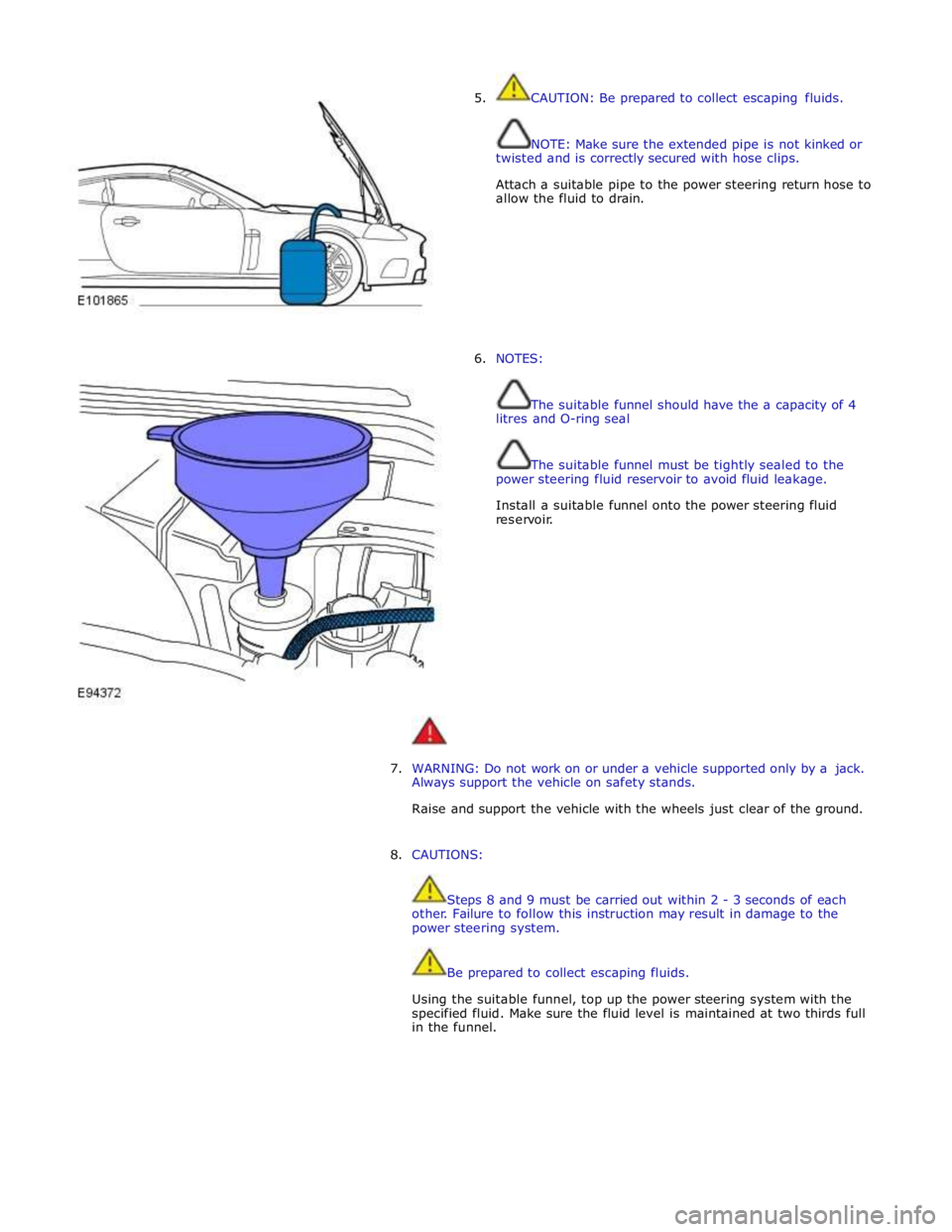
5. CAUTION: Be prepared to collect escaping fluids.
NOTE: Make sure the extended pipe is not kinked or
twisted and is correctly secured with hose clips.
Attach a suitable pipe to the power steering return hose to
allow the fluid to drain.
6. NOTES:
The suitable funnel should have the a capacity of 4
litres and O-ring seal
The suitable funnel must be tightly sealed to the
power steering fluid reservoir to avoid fluid leakage.
Install a suitable funnel onto the power steering fluid
reservoir.
7. WARNING: Do not work on or under a vehicle supported only by a jack.
Always support the vehicle on safety stands.
Raise and support the vehicle with the wheels just clear of the ground.
8. CAUTIONS:
Steps 8 and 9 must be carried out within 2 - 3 seconds of each
other. Failure to follow this instruction may result in damage to the
power steering system.
Be prepared to collect escaping fluids.
Using the suitable funnel, top up the power steering system with the
specified fluid. Make sure the fluid level is maintained at two thirds full
in the funnel.
Page 734 of 3039
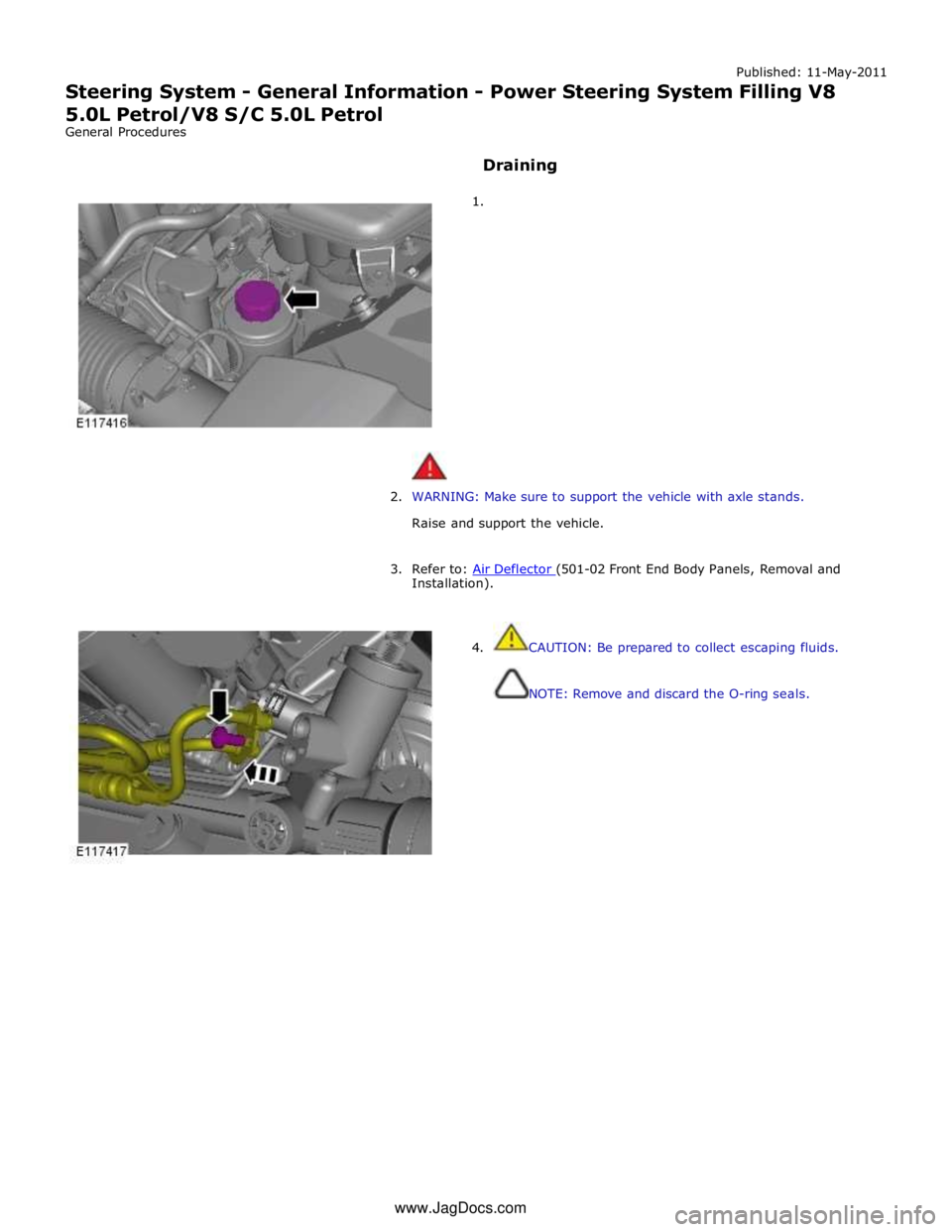
Published: 11-May-2011
Steering System - General Information - Power Steering System Filling V8 5.0L Petrol/V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol
General Procedures
Draining
1.
2. WARNING: Make sure to support the vehicle with axle stands.
Raise and support the vehicle.
3. Refer to: Air Deflector (501-02 Front End Body Panels, Removal and Installation).
4. CAUTION: Be prepared to collect escaping fluids.
NOTE: Remove and discard the O-ring seals. www.JagDocs.com
Page 744 of 3039

1 Return fluid control groove 2 Radial groove 3 Feed fluid control groove 4 Radial groove 5 Axial groove 6 Feed fluid control edge 7 Feed fluid radial groove 8 Return fluid control edge 9 Return fluid chamber 10 Cut-off valve 11 Radial groove 12 Servotronic transducer valve 13 Feed fluid radial groove 14 Radial groove 15 Orifice 16 Balls 17 Compression spring 18 Torsion bar 19 Power steering fluid reservoir 20 Valve rotor 21 Reaction piston 22 Reaction chamber 23 Centering piece 24 Pressure relief/flow limiting valve 25 Power steering pump 26 Inner tie-rod 27 Pinion 28 Valve sleeve 29 Steering gear rack 30 Steering gear housing 31 Power assist cylinder - right 32 Piston 33 Power assist cylinder - left When the steering wheel is turned to the right, the steering rack and piston moves to the left in the piston bore. The valve
rotor is rotated to the right (clockwise) and pressurized fluid is directed over the further opened feed fluid control edges and to
the associated axial grooves, the radial groove and via an external pipe to the left power assist cylinder chamber. The pressure
applied to the piston from the left power assist cylinder chamber provides the hydraulic assistance.
An adaptable pressure build-up is achieved by the partially or fully closed feed fluid control edges restricting or preventing a
connection between the fluid pressure inlet and the other axial grooves connected to the radial groove.
Simultaneously, the fluid pressure outlet to the pressurized axial grooves are restricted or partially restricted by the closing
return fluid control edges. The fluid displaced by the piston from the right power assist cylinder chamber, flows through an
external pipe to the radial grooves. From there the fluid passes to the associated axial grooves and on to the return fluid
control grooves, via the further opened return fluid control edges.
The return flow of fluid to the reservoir passes via interconnecting bores which lead to the return fluid chamber. When the
steering wheel is turned to the left the operating sequence is as above but the pressure is applied to the opposite side of the
piston.
Servotronic Operation
The Servotronic software contains a number of steering maps which are selected via the car configuration file depending on the
vehicle mode and tire fitment.
If a failure of the Servotronic valve or software occurs, the system will suspend Servotronic assistance and only normal power
steering wheel be available. Fault codes relating to the fault are stored, but no warning lamps are illuminated and the driver
may be aware of the steering being 'heavier' than usual.
When the vehicle is manoeuvred into and out of a parking space (or other similar manoeuvre), the Servotronic software uses
road speed data from the ABS module to determine the vehicle speed, which in this case will be slow or stationary. The
Servotronic software analyses the signals and outputs an appropriate control current to the Servotronic transducer valve. The
Servotronic valve closes and prevents fluid flowing from the feed fluid radial groove to the reaction chamber. An orifice also