2010 JAGUAR XFR seats
[x] Cancel search: seatsPage 26 of 3039

SpecificationRemoval and InstallationRadiator Grille
Luggage Compartment Lid Moulding
Front Fender Moulding
Rocker Panel Moulding501-09: Rear View MirrorsSpecificationDescription and OperationComponent Location
Overview
System Operation and Component DescriptionDiagnosis and TestingRear View MirrorsRemoval and InstallationExterior Mirror
Exterior Mirror Cover
Exterior Mirror Glass
Exterior Mirror Motor
Interior Rear View Mirror501-10: SeatingSpecificationDescription and OperationComponent Location
Overview
System Operation and Component Description
Seat Cover InspectionDiagnosis and TestingSeats
Heater Mats
Seats - Vehicles With: Climate Controlled SeatsGeneral ProceduresSeat SmoothingRemoval and InstallationFront Seat (76.70.01)
Front Seat Backrest (76.70.06)
Front Seat Backrest Cover (76.70.15)
Front Seat Bolster
Front Seat Bolster Pump
Front Seat Cushion Cover
Front Seat Track Motor
Lumbar Assembly501-08: Exterior Trim and Ornamentation
Page 55 of 3039
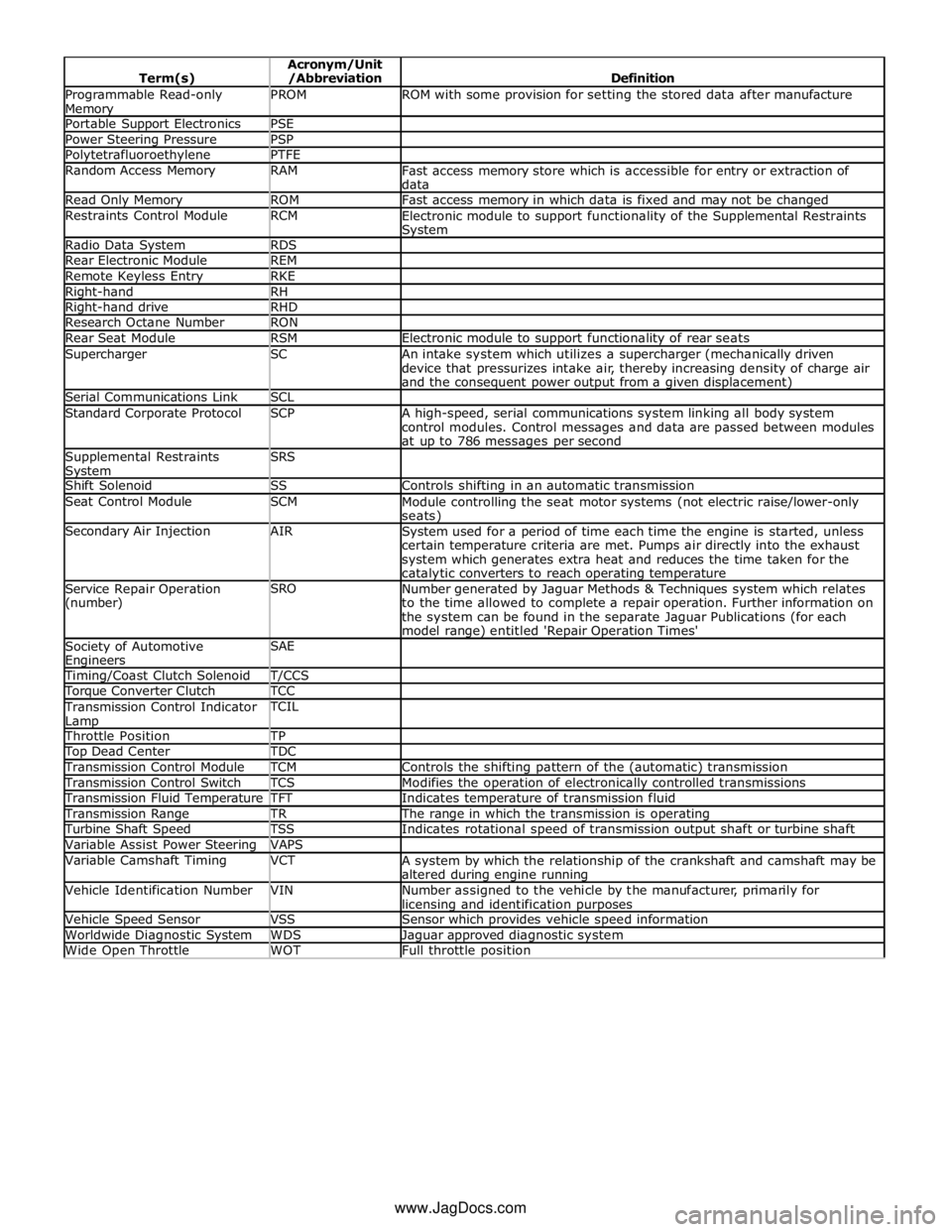
Programmable Read-only Memory PROM ROM with some provision for setting the stored data after manufacture Portable Support Electronics PSE Power Steering Pressure PSP Polytetrafluoroethylene PTFE Random Access Memory RAM
Fast access memory store which is accessible for entry or extraction of
data Read Only Memory ROM Fast access memory in which data is fixed and may not be changed Restraints Control Module RCM
Electronic module to support functionality of the Supplemental Restraints System Radio Data System RDS Rear Electronic Module REM Remote Keyless Entry RKE Right-hand RH Right-hand drive RHD Research Octane Number RON Rear Seat Module RSM Electronic module to support functionality of rear seats Supercharger SC
An intake system which utilizes a supercharger (mechanically driven
device that pressurizes intake air, thereby increasing density of charge air
and the consequent power output from a given displacement) Serial Communications Link SCL Standard Corporate Protocol SCP
A high-speed, serial communications system linking all body system
control modules. Control messages and data are passed between modules
at up to 786 messages per second Supplemental Restraints System SRS
Shift Solenoid SS Controls shifting in an automatic transmission Seat Control Module SCM
Module controlling the seat motor systems (not electric raise/lower-only seats) Secondary Air Injection AIR
System used for a period of time each time the engine is started, unless
certain temperature criteria are met. Pumps air directly into the exhaust
system which generates extra heat and reduces the time taken for the catalytic converters to reach operating temperature Service Repair Operation
(number) SRO
Number generated by Jaguar Methods & Techniques system which relates
to the time allowed to complete a repair operation. Further information on
the system can be found in the separate Jaguar Publications (for each
model range) entitled 'Repair Operation Times' Society of Automotive Engineers SAE
Timing/Coast Clutch Solenoid T/CCS Torque Converter Clutch TCC Transmission Control Indicator
Lamp TCIL
Throttle Position TP Top Dead Center TDC Transmission Control Module TCM Controls the shifting pattern of the (automatic) transmission Transmission Control Switch TCS Modifies the operation of electronically controlled transmissions Transmission Fluid Temperature TFT Indicates temperature of transmission fluid Transmission Range TR The range in which the transmission is operating Turbine Shaft Speed TSS Indicates rotational speed of transmission output shaft or turbine shaft Variable Assist Power Steering VAPS Variable Camshaft Timing VCT
A system by which the relationship of the crankshaft and camshaft may be
altered during engine running Vehicle Identification Number VIN
Number assigned to the vehicle by the manufacturer, primarily for licensing and identification purposes Vehicle Speed Sensor VSS Sensor which provides vehicle speed information Worldwide Diagnostic System WDS Jaguar approved diagnostic system Wide Open Throttle WOT Full throttle position www.JagDocs.com
Page 66 of 3039

4. Components or assemblies displaying this symbol give warning that the component contains a corrosive substance. See
Acids and Alkalis in this subsection.
5. Vehicles displaying the caution circle with a deleted lighted match symbol, caution against the use of naked lights or
flames within the immediate vicinity due to the presence of highly flammable or explosive liquids or vapors. See Fire in
this subsection.
6. All vehicles with the passenger air bag installed from the factory have a warning sticker attached to the instrument
panel, prohibiting the use of rear facing child seats in the front seating position. Failure to follow this instruction may
result in personal injury.
White Spirit
See Solvents.
Safety Precautions
WARNINGS:
Working on the fuel system results in fuel and fuel vapor being present in the atmosphere. Fuel vapor is extremely
flammable, hence great care must be taken whilst working on the fuel system. Adhere strictly to the following precautions:
Do not smoke in the work area
Display 'no smoking' signs around the area
Disconnect the battery before working on the fuel system
Do not connect/disconnect electrical circuits, use electrical equipment or other tools or engage in working practices
which in any way may result in the production of sparks
Ensure that a CO² fire extinguisher is close at hand
Ensure that dry sand is available to soak up any fuel spillage
Empty fuel using suitable fire proof equipment into an authorized explosion proof container
Page 73 of 3039

Supplementary Restraint System (SRS) Precautions
WARNING: Do not install rear facing child seats in the front passenger seat.
The SRS contains components which are potentially hazardous to service personnel if not handled correctly. The following
guidelines and precautions are intended to alert personnel to potential sources of danger and emphasise the importance of
ensuring the integrity of the SRS components installed to the vehicle.
WARNING: The following precautions MUST be adhered to when working on the SRS system:
The correct procedures must always be used when working on SRS components.
Persons working on the SRS system must be fully trained and have been issued with the safety guidelines.
The airbag modules contain extremely flammable and hazardous compounds. Contact with water, acids or heavy
metals may produce harmful or explosive results. Do not dismantle, incinerate or bring into contact with electricity
before the unit has been deployed.
Always replace a seat belt assembly that has withstood the strain of a severe vehicle impact or if the webbing
shows signs of fraying.
Always disconnect the vehicle battery before carrying out any electric welding on a vehicle installed with an SRS
system.
CAUTION: Do not expose airbag modules or seat belt pre-tensioners to temperatures exceeding 85° C (185° F).
It should be noted that these precautions are not restricted to operations performed when servicing the SRS system. The same
care should be exercised when working on ancillary systems and components located in the vicinity of SRS components; these
include but are not limited to:
Steering wheel airbag, rotary coupler.
Passenger front airbag.
Head airbag modules - front and rear.
Seat belt pre-tensioners.
SRS harnesses, link leads and connectors.
Side (thorax) air bags.
Making the system safe
Before working on or in the vicinity of SRS components, make sure the system is rendered safe by performing the following
operations:
Remove the ignition key.
Disconnect battery, earth lead first.
Wait 2 minutes for the SRS power circuit to discharge before commencing work.
NOTE: The SRS uses energy reserve capacitors to keep the system active in the event of electrical supply failure under
crash conditions. It is necessary to allow the capacitors sufficient time to discharge (2 minutes) in order to avoid the risk of
accidental deployment.
Installation
In order to make sure system integrity, it is essential that the SRS system is regularly checked and maintained so that it is
ready for effective operation in the event of a collision. Carefully inspect SRS components before installation. Do not install a
part that shows signs of being dropped or improperly handled, such as dents, cracks or deformation.
WARNING: The integrity of the SRS systems is critical for safety reasons. Make sure the following precautions are always
adhered to:
Do not install accessories or other objects to trim panels which cover ITS airbags.
Never install used SRS components from another vehicle or attempt to repair an SRS component.
When repairing an SRS system, only use genuine new parts.
Never apply electrical power to an SRS component unless instructed to do so as part of an approved test
procedure.
Special fixings are necessary for installing an airbag module – do not use other fixings and make sure that all
fixings are tightened to the correct torque.
Always use new fixings when replacing an SRS component.
CAUTIONS:
Take care not to trap airbag modules when installing interior trim components.
Make sure SRS components are not contaminated by oil or grease.
NOTES:
Following seat belt pre-tensioner deployment, the seat belts can still be used as conventional seat belts but will need to
Page 152 of 3039

Published: 12-May-2014
General Information - Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Index DTC:
Driver/Passenger Seat Module (DSM/PSM)
Description and Operation
Driver/Passenger Seat Module (DSM/PSM)
CAUTION: Diagnosis by substitution from a donor vehicle is NOT acceptable. Substitution of control modules does not
guarantee confirmation of a fault, and may also cause additional faults in the vehicle being tested and/or the donor vehicle.
NOTES:
If a control module or a component is suspect and the vehicle remains under manufacturer warranty, refer to the Warranty
Policy and Procedures manual, or determine if any prior approval programme is in operation, prior to the installation of a new
module/component.
Generic scan tools may not read the codes listed, or may read only 5-digit codes. Match the 5 digits from the scan tool to
the first 5 digits of the 7-digit code listed to identify the fault (the last 2 digits give extra information read by the
manufacturer-approved diagnostic system).
When performing voltage or resistance tests, always use a digital multimeter accurate to three decimal places, and with
an up-to-date calibration certificate. When testing resistance always take the resistance of the digital multimeter leads into
account.
Check and rectify basic faults before beginning diagnostic routines involving pinpoint tests.
Inspect connectors for signs of water ingress, and pins for damage and/or corrosion.
If DTCs are recorded and, after performing the pinpoint tests, a fault is not present, an intermittent concern may be the
cause. Always check for loose connections and corroded terminals.
Check DDW for open campaigns. Refer to the corresponding bulletins and SSMs which may be valid for the specific
customer complaint and carry out the recommendations as required.
The table below lists all Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) that could be logged in the Driver/Passenger Seat Module
(DSM/PSM). For additional diagnosis and testing information, refer to the relevant Diagnosis and Testing section in the
workshop manual.
For additional information, refer to: Seats (501-10 Seating, Diagnosis and Testing).
DTC Description Possible Causes Action B105F-11
Seat Cushion Extension
Motor Output - Circuit short
to ground
Driver seat cushion extension
motor circuit - short to ground
Carry out any pinpoint tests associated
with this DTC using the manufacturer
approved diagnostic system. Refer to the
electrical circuit diagrams and check driver
seat cushion extension motor circuit for
short to ground B105F-15
Seat Cushion Extension
Motor Output - Circuit short
to battery or open
Driver seat cushion extension
motor circuit - short to power,
open circuit
Carry out any pinpoint tests associated
with this DTC using the manufacturer
approved diagnostic system. Refer to the
electrical circuit diagrams and check driver
seat cushion extension motor circuit for
short to power, open circuit B1060-11
Seat Headrest Motor
Output - Circuit short to
ground
Driver seat headrest motor
circuit - short to ground
Carry out any pinpoint tests associated
with this DTC using the manufacturer
approved diagnostic system. Refer to the
electrical circuit diagrams and check driver
seat headrest motor circuit for short to
ground
Page 175 of 3039

Published: 17-Apr-2014
General Information - Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Index DTC: Front Seat Climate Control Module (DCSM)
Description and Operation
Front Seat Climate Control Module (DCSM)
CAUTION: Diagnosis by substitution from a donor vehicle is NOT acceptable. Substitution of control modules does not
guarantee confirmation of a fault, and may also cause additional faults in the vehicle being tested and/or the donor vehicle
NOTES:
If the control module or a component is suspect and the vehicle remains under manufacturer warranty, refer to the
warranty policy and procedures manual, or determine if any prior approval programme is in operation, prior to the installation
of a new module/component
Generic scan tools may not read the codes listed, or may read only 5-digit codes. Match the 5 digits from the scan tool to
the first 5 digits of the 7-digit code listed to identify the fault (the last 2 digits give extra information read by the
manufacturer-approved diagnostic system)
When performing voltage or resistance tests, always use a digital multimeter accurate to three decimal places and with a
current calibration certificate. When testing resistance, always take the resistance of the digital multimeter leads into account
Check and rectify basic faults before beginning diagnostic routines involving pinpoint tests
Inspect connectors for signs of water ingress, and pins for damage and/or corrosion
If diagnostic trouble codes are recorded and, after performing the pinpoint tests, a fault is not present, an intermittent
concern may be the cause. Always check for loose connections and corroded terminals
Where an 'on demand self-test' is referred to, this can be accessed via the 'diagnostic trouble code monitor' tab on the
manufacturers approved diagnostic system
The table below lists all diagnostic trouble codes (DTCs) that could be logged in the seat climate control module, for additional
diagnosis and testing information refer to the relevant diagnosis and testing section.
For additional information, refer to: Seats (501-10 Seating, Diagnosis and Testing).
DTC Description Possible Causes Action B10B9-13
Blower Control - Circuit
open
Connectors disconnected or
connector pin damage
Seat blower left circuit -
Open circuit
Blower motor assembly -
Short circuit to ground
Front seat climate control
module failure
Check for any disconnected connectors or damaged
connector pins
Carry out on demand self test using manufacturer
approved diagnostic system to confirm the fault is
present
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check
the front seat climate control module - Circuit
reference LH_FANS_RTN, Circuit reference
LH_FANS_PWR - For open circuit. Repair circuit as
required, clear DTC and retest
Carry out on demand self test using manufacturer
approved diagnostic system to confirm
rectification. Alternatively, carry out any pinpoint
tests associated with this DTC using the
manufacturer approved diagnostic system B10B9-4B
Blower Control - Over
temperature
Mechanical restriction in
blower motor assembly
Seat blower left circuit -
Short circuit to ground
Blower motor assembly -
Short circuit to ground
Front seat climate control
module failure
Check for mechanical restriction or debris in seat
blower
Carry out on demand self test using manufacturer
approved diagnostic system to confirm the fault is
present
Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and check
the front seat climate control module - Circuit
reference LH_FANS_RTN, Circuit reference
LH_FANS_PWR - For short circuit to ground. Repair
circuit as required, clear DTC and retest
Page 301 of 3039

it may turn out to be the most important.
2. Do not touch anything until a road test and a thorough visual inspection of the vehicle have been carried out. Leave the
tire pressures and vehicle load just where they were when the condition was first observed. Adjusting tire pressures,
vehicle load or making other adjustments may reduce the conditions intensity to a point where it cannot be identified
clearly. It may also inject something new into the system, preventing correct diagnosis.
3. Make a visual inspection as part of the preliminary diagnosis routine, writing down anything that does not look right.
Note tire pressures, but do not adjust them yet. Note leaking fluids, loose nuts and bolts, or bright spots where
components may be rubbing against each other. Check the luggage compartment for unusual loads.
4. Road test the vehicle and define the condition by reproducing it several times during the road test.
5. Carry out the Road Test Quick Checks as soon as the condition is reproduced. This will identify the correct diagnostic
procedure. Carry out the Road Test Quick Checks more than once to verify they are providing a valid result. Remember,
the Road Test Quick Checks may not tell where the concern is, but they will tell where it is not.
Road Test Quick Checks
1. 24-80 km/h (15-50 miles/h): With light acceleration, a moaning noise is heard and possibly a vibration is felt in the
front floor pan. It is usually worse at a particular engine speed and at a particular throttle setting during acceleration at
that speed. It may also produce a moaning sound, depending on what component is causing it. Refer to Tip-In Moan in
the Symptom Chart.
2. Acceleration/deceleration: With slow acceleration and deceleration, a shake is sometimes noticed in the steering
wheel/column, seats, front floor pan, front door trim panel or front end sheet metal. It is a low frequency vibration
(around 9-15 cycles per second). It may or may not be increased by applying brakes lightly. Refer to Idle Boom/Shake
/Vibration in the Symptom Chart.
3. High speed: A vibration is felt in the front floor pan or seats with no visible shake, but with an accompanying sound or
rumble, buzz, hum, drone or booming noise. Coast with the clutch pedal depressed or shift control selector lever in
neutral and engine idling. If vibration is still evident, it may be related to wheels, tires, front brake discs, wheel hubs
or front wheel bearings. Refer to High Speed Shake in the Symptom Chart.
4. Engine rpm sensitive: A vibration is felt whenever the engine reaches a particular rpm. It will disappear in neutral
coasts. The vibration can be duplicated by operating the engine at the problem rpm while the vehicle is stationary. It
can be caused by any component, from the accessory drive belt to the torque converter which turns at engine speed
when the vehicle is stopped. Refer to High Speed Shake in the Symptom Chart.
5. Noise/vibration while turning: Clicking, popping, or grinding noises may be due to a worn, damaged, or incorrectly
installed front wheel bearing, rear drive half shaft or CV joint.
6. Noise/vibration that is road speed relative: This noise/vibration can be diagnosed independent of engine speed or gear
selected (engine speed varies but torque and road speed remain constant). The cause may be a rear drive
axle/differential whine.
Road Conditions
An experienced technician will always establish a route that will be used for all NVH diagnosis road tests. The road selected
should be reasonably smooth, level and free of undulations (unless a particular condition needs to be identified). A smooth
asphalt road that allows driving over a range of speeds is best. Gravel or bumpy roads are unsuitable because of the additional
road noise produced. Once the route is established and consistently used, the road noise variable is eliminated from the test
results.
NOTE: Some concerns may be apparent only on smooth asphalt roads.
If a customer complains of a noise or vibration on a particular road and only on a particular road, the source of the concern
may be the road surface. If possible, try to test the vehicle on the same type of road.
Vehicle Preparation
Carry out a thorough visual inspection of the vehicle before carrying out the road test. Note anything which is unusual. Do not
repair or adjust any condition until the road test is carried out, unless the vehicle is inoperative or the condition could pose a
hazard to the technician.
After verifying the condition has been corrected, make sure all components removed have been installed.
Lift Test
After a road test, it is sometimes useful to do a similar test on a lift.
When carrying out the high-speed shake diagnosis or engine accessory vibration diagnosis on a lift, observe the following
precautions:
WARNING: If only one drive wheel is allowed to rotate, speed must be limited to 55 km/h (35 miles/h) indicated on the
speedometer since actual wheel speed will be twice that indicated on the speedometer. Speed exceeding 55 km/h (35 miles/h)
or allowing the drive wheel to hang unsupported could result in tire disintegration, differential failure, constant velocity joint
Page 782 of 3039
16 Ball (12 off) 17 Distance keeper 18 Crash tube The column comprises a cast magnesium mounting bracket which provides the attachment to the cross-beam. Attached to the
mounting bracket is a rake lever which is attached to the mounting bracket at the lower end with two pivot bearings. The
bearings allow the rake lever to rotate upwards or downward to adjust the column rake.
The rake lever also provides for the attachment of the rake housing which can slide within the lever to provide the reach
adjustment. Within the rake housing is the axial housing which is supported on each side with 6 ball bearings which allow the
rake housing to move forward or backwards. The bearings on each side are arranged in groups of 3 bearings and are separated
by a distance keeper which allows the housing to supported on bearings along its length. Within the axial housing is a tube
which is supported at the upper end of the column on the upper bearing. The tube has a central splined hole which provides for
the fitment of the splined shaft. The splined shaft can slide within the tube on the splines when the column reach is adjusted
or the column collapses in a crash condition. The splined shaft also passes rotary motion from the steering wheel through the
length of the column to the outer clamping yoke which is supported on the lower bearing.
The electric steering column lock is attached to the top of the rake lever. A lock bolt within the steering column lock engages in
one of 8 slots in the locking sleeve located at the lower end of the column preventing rotation of the steering wheel. The
locking sleeve is retained by a tolerance ring which in turn is located on the outer diameter of the tube yoke. The tolerance
ring allows a specified amount of torque to be applied to the splined shaft before it slips, preventing damage to the column
lock due to excessive force being applied to the steering wheel when the lock is engaged. The tolerance ring is designed to
slip on the splined shaft when the applied torque exceeds the fitted slip load of 200 Nm minimum. Repeated rotation of the
lock collar will reduce its slipping torque to 100 Nm minimum. The lock is controlled by the CJB.
A steering angle sensor is located at the upper end of the steering column and is attached to the crash adaptor. The sensor
measures steering rotation via a toothed wheel located on the splined tube at the upper end of the column. The sensor
receives a power supply from the CJB and supplies 2 signals (A and B) relating to the steering rotation to the ABS (anti-lock brake system) module. The module transmits this data on the high speed CAN bus for use by other vehicle systems. Refer to: Anti-Lock Control - Stability Assist (206-09 Anti-Lock Control - Stability Assist, Description and Operation).
The steering column is adjustable electrically, for reach and rake. The adjustment mechanism comprises an electric adjustment
motor, a lead screw, a rake solenoid, a reach solenoid, a reach clutch and a rake clutch. The column adjustment is controlled
manually using a joystick switch located on the LH (left-hand) side of the column lower cowl. The joystick can be moved
forward and backward to adjust the column reach in and out and moved up and down to adjust the rake. The switch selection
energizes the adjustment motor in the applicable direction and also engages the applicable solenoid and clutch.
When the joystick switch is rotated to the 'auto' position, the steering column will adjust to the uppermost rake position when
the ignition is switched off. It will re-adjust to the position corresponding to the memory position for the remote handset when
the ignition is switched on.
The memory function of the electric column is linked to and controlled by the driver's seat module. The module provides for the
storage of three separate memory positions which are stored against 3 individual remote handsets.
Refer to: Seats (501-10 Seating, Description and Operation).
The steering wheel locates on a splined shaft in the upper column assembly and is secured with a bolt. The steering wheel
houses the driver's airbag and switches for the audio system, gear change and speed control. A clockspring is used to connect
the steering wheel electrical components to the vehicle harness.
Two plastic shrouds are fitted to the upper column assembly. The lower shroud is fitted with an energy absorbing foam pad to
minimize leg injury in the event of an accident.
www.JagDocs.com