2010 JAGUAR XFR ESP
[x] Cancel search: ESPPage 1349 of 3039

Published: 03-Jun-2014
Evaporative Emissions - V8 5.0L Petrol/V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol - Evaporative
Emissions
Diagnosis and Testing
Principles of Operation
For a detailed description of the Evaporative Emissions system, refer to the relevant Description and Operation section in the
workshop manual.
Inspection and Verification
CAUTION: Diagnosis by substitution from a donor vehicle is NOT acceptable. Substitution of control modules does not
guarantee confirmation of a fault, and may also cause additional faults in the vehicle being tested and/or the donor vehicle.
NOTES:
If a control module or a component is suspect and the vehicle remains under manufacturer warranty, refer to the Warranty
Policy and Procedures manual, or determine if any prior approval programme is in operation, prior to the installation of a new
module/component.
When performing voltage or resistance tests, always use a digital multimeter accurate to three decimal places, and with
an up-to-date calibration certificate. When testing resistance always take the resistance of the digital multimeter leads into
account.
Check and rectify basic faults before beginning diagnostic routines involving pinpoint tests.
1. Verify the customer concern
2. Visually inspect for obvious signs of damage and system integrity
Visual Inspection
Mechanical Electrical
Fuel filler cap and seal
Fuel filler neck
Fuel pipes
Fuel tank
Evaporative emissions canister
Purge valve
Fuses
Wiring harnesses and connectors
Engine Control Module (ECM)
Purge valve
3. If an obvious cause for an observed or reported concern is found, correct the cause (if possible) before proceeding to
the next step
4. If the cause is not visually evident, verify the symptom and refer to the Symptom Chart, alternatively check for
Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) and refer to the DTC Index
5. Check DDW for open campaigns. Refer to the corresponding bulletins and SSMs which may be valid for the specific
customer complaint and carry out the recommendations as required
Symptom Chart
Symptom Possible Causes Action Difficulty in filling
fuel tank
Restriction in the vapour line between the fuel tank and the
carbon canister outlet/atmospheric port
Check for
restrictions/damage Fuel smell
System leak
Purge valve inoperative
Check for leaks
Check the purge valve
operation DTC Index
For a list of Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs) that could be logged on this vehicle, please refer to Section 100-00.
Page 1361 of 3039

DIAGNOSTICS
The ECM stores each fault as a DTC (diagnostic trouble code). The DTC and associated environmental and freeze frame data can be read using Jaguar approved diagnostic equipment, which can also read real time data from each sensor, the adaption
values currently being employed and the current fueling, ignition and idle speed settings.
ENGINE CONTROL MODULE Component Description
The ECM is installed in the front passenger side of the engine compartment, on a bracket attached to the engine bulkhead. The ECM has the capability of adapting its fuel and ignition control outputs in response to several sensor inputs. The ECM receives inputs from the following:
CKP sensor. CMP (camshaft position) sensors (4 off).
ECT (engine coolant temperature) sensor.
Knock sensors (4 off).
MAP (manifold absolute pressure) sensor.
MAFT sensors (2 off). MAPT (manifold absolute pressure and temperature) sensor.
Throttle position sensor.
Heated oxygen sensors (4 off).
APP sensor. Ambient air temperature sensor.
FRP (fuel rail pressure) sensor. For additional information, refer to 303-04G Fuel Charging and Controls.
Engine cooling fan. For additional information, refer to 303-03D Engine Cooling.
Stoplamp switch. For additional information, refer to 206-09 Anti-Lock Control - Stability Assist.
Speed control cancel/suspend switch. For additional information, refer to 310-03D Speed Control.
Oil level and temperature sensor. For additional information, refer to 303-01F Engine.
Fuel LP (low pressure) sensor. For additional information, refer to 310-01D Fuel Tank and Lines.
Fuel pump driver module. For additional information, refer to 310-01D Fuel Tank and Lines.
The ECM provides outputs to the following: Electronic throttle.
Main relay.
Heater elements of the heated oxygen sensors (4 off).
Fuel injectors (8 off). For additional information, refer to 303-04G Fuel Charging and Controls. www.JagDocs.com
Page 1364 of 3039
MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE SENSOR
The MAP sensor allows the ECM to calculate the load on the engine, which is used in the calculation of fuel injection time.
The MAP sensor is installed in the air inlet of the SC (supercharger). The sensor is secured with a single screw and sealed with an O-ring. A three pin electrical connector provides the interface with the engine harness.
If the MAP sensor fails, the ECM adopts a default value of 1 bar (14.5 lbf/in.2
). With a failed MAP sensor, the engine will suffer from poor starting, rough running and poor driveability.
MASS AIR FLOW AND TEMPERATURE SENSORS
The MAFT sensors allow the ECM to measure the mass and the temperature of the air flow into the engine. The mass air flow is measured with a hot film element in the sensor. The temperature of the air flow is measured with a NTC thermistor in the sensor. The mass air flow is used to determine the fuel quantity to be injected in order to maintain the stoichiometric air/fuel
mixture required for correct operation of the engine and the catalytic converters.
There are two MAFT sensors installed, one in each air cleaner outlet duct. Each MAFT sensor is secured with two screws and sealed with an O-ring. On each MAFT sensor, a five pin electrical connector provides the interface with the engine harness.
If the hot film element signal fails the ECM invokes a software backup strategy to calculate the mass air flow from other inputs. Closed loop fuel control, closed loop idle speed control and evaporative emissions control are discontinued. The engine
will suffer from poor starting, poor throttle response and, if the failure occurs while driving, the engine speed may dip before
recovering.
If the NTC thermistor signal fails the ECM adopts a default value of 25 °C (77 °F) for the intake air temperature.
Page 1365 of 3039
MANIFOLD ABSOLUTE PRESSURE AND TEMPERATURE SENSOR
The MAPT sensor allows the ECM to calculate the air charge density immediately before it enters the cylinders. This is used to adjust the ignition timing relative to the boost pressure, and to monitor the performance of the charge air coolers.
The MAPT sensor is installed in the rear of the LH intake manifold. The sensor is secured with a single screw and sealed with an O-ring. A four pin electrical connector provides the interface with the engine harness.
THROTTLE POSITION SENSORS
The TP (throttle position) sensors allow the ECM to determine the position and angular rate of change of the throttle blade. There are two TP sensors located in the electronic throttle. See below for details of the electronic throttle. If aTP sensor fails, the ECM:
Adopts a limp home mode where engine speed is limited to a maximum of approximately 2000 rev/min
Discontinues evaporative emissions control
Discontinues closed loop control of engine idle speed.
With a failed TP sensor, the engine will suffer from poor running and throttle response.
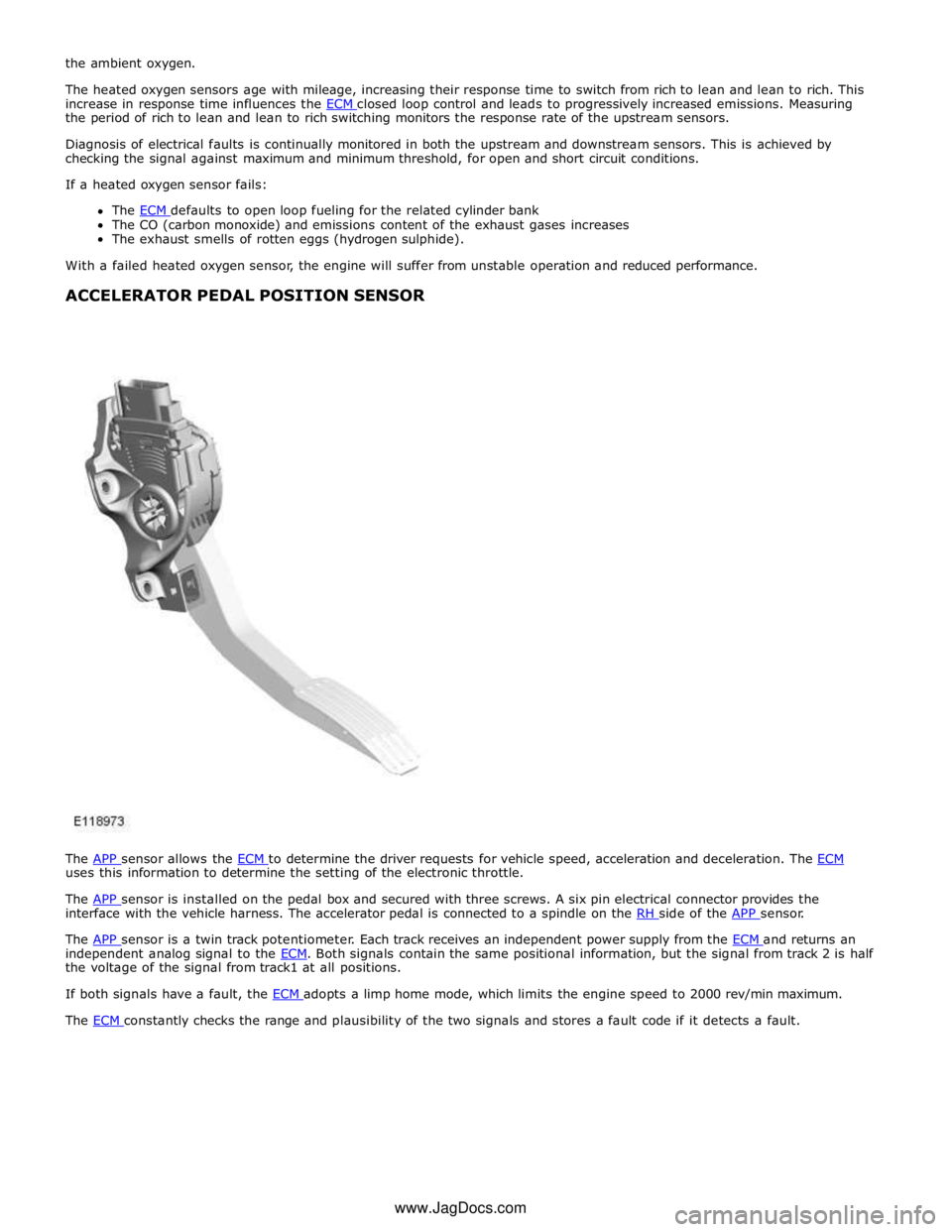
HEATED OXYGEN SENSORS
Item Description A Upstream heated oxygen sensor B Downstream heated oxygen sensor The heated oxygen sensors allow the ECM to measure the oxygen content of the exhaust gases, for closed loop control of the fuel:air mixture and for catalytic converter monitoring.
An upstream heated oxygen sensor is installed in the outlet of each exhaust manifold, which enables independent control of
the fuel:air mixture for each cylinder bank. A downstream heated oxygen sensor is installed in each catalytic converter, which
enables the performance of the catalytic converters to be monitored.
Oxygen sensors need to operate at high temperatures in order to function correctly. To achieve the high temperatures required,
the sensors are fitted with heater elements that are controlled by a PWM (pulse width modulation) signal from the ECM. The heater elements are operated immediately after each engine start and during low load conditions when the temperature of the
exhaust gases is insufficient to maintain the required sensor temperature. The PWM duty cycle is carefully controlled to prevent thermal shock to cold sensors. A non-functioning heater delays the sensor’s readiness for closed loop control and
increases emissions.
The upstream heated oxygen sensors produce a constant voltage, with a variable current that is proportional to the lambda
ratio. The downstream heated oxygen sensors produce an output voltage dependant on the ratio of the exhaust gas oxygen to
Page 1366 of 3039
the period of rich to lean and lean to rich switching monitors the response rate of the upstream sensors.
Diagnosis of electrical faults is continually monitored in both the upstream and downstream sensors. This is achieved by
checking the signal against maximum and minimum threshold, for open and short circuit conditions.
If a heated oxygen sensor fails:
The ECM defaults to open loop fueling for the related cylinder bank The CO (carbon monoxide) and emissions content of the exhaust gases increases
The exhaust smells of rotten eggs (hydrogen sulphide).
With a failed heated oxygen sensor, the engine will suffer from unstable operation and reduced performance.
ACCELERATOR PEDAL POSITION SENSOR
The APP sensor allows the ECM to determine the driver requests for vehicle speed, acceleration and deceleration. The ECM uses this information to determine the setting of the electronic throttle.
The APP sensor is installed on the pedal box and secured with three screws. A six pin electrical connector provides the interface with the vehicle harness. The accelerator pedal is connected to a spindle on the RH side of the APP sensor.
The APP sensor is a twin track potentiometer. Each track receives an independent power supply from the ECM and returns an independent analog signal to the ECM. Both signals contain the same positional information, but the signal from track 2 is half the voltage of the signal from track1 at all positions.
If both signals have a fault, the ECM adopts a limp home mode, which limits the engine speed to 2000 rev/min maximum. The ECM constantly checks the range and plausibility of the two signals and stores a fault code if it detects a fault. www.JagDocs.com
Page 1372 of 3039

Symptom Possible Cause Action No throttle response
Electronic engine controls
Read DTCs and refer to DTC Index in this
section for electronic engine control tests Speed control inhibited or disabled
Default mode enabled
Speed control, brake switch
Electronic engine controls
CAN fault
Check message center for default message,
read DTCs and refer to DTC Index
Refer to the relevant section of the
workshop manual for speed control, and
brake switch tests.
Read DTCs and refer to DTC Index in this
section for electronic engine control tests
Refer to the relevant section of the
workshop manual and the electrical wiring
diagrams to perform CAN network tests. Poor throttle response
Breather system
disconnected/restricted
Electronic engine controls
Transmission malfunction
Traction control event
Air leakage
Ensure engine breather system is free from
restriction and is correctly installed
Read DTCs and refer to DTC Index in this
section for electronic engine control tests
Refer to the workshop manual or
transmission troubleshooting guide for
transmission system tests.
Check for leakage in air intake system Engine defaults, warning light and
messages. Refer to the owner
handbook
Electronic engine controls
Read DTCs and refer to DTC Index in this
section for electronic engine control tests DTC Index
WARNING: Fuel injector voltage will reach 65Volts during operation and have a high current requirement.
CAUTION: When probing connectors to take measurements in the course of the pinpoint tests, use the adaptor kit, part
number 3548-1358-00.
NOTES:
If the module/component is suspect and the vehicle remains under the Manufacturers warranty, refer to the Warranty
Policy and Procedure manual (section B1.2), or determine if any prior approval programme is in operation, prior to the
installation of a new module/component.
Generic scan tools may not read the codes listed, or may read only five digit codes. Match the five digits from the scan
tool to the first five digits of the seven digit code listed to identify the fault (the last two digits give additional information
read by the manufacturer-approved diagnostic system).
When performing electrical voltage or resistance tests, always use a digital multimeter (DMM) accurate to three decimal
places, and with an up-to-date calibration certificate. When testing resistance, always take the resistance of the DMM leads
into account.
Check and rectify basic faults before beginning diagnostic routines involving pinpoint tests.
If DTCs are recorded and, after performing the pinpoint tests, a fault is not present, an intermittent concern may be the
cause. Always check for loose connections and corroded terminals.
DTC Description Possible Causes Action B10A2-31 Crash Input - No signal
Loss of communication between
Restraints Control Module (RCM)
and Engine Control Module
(ECM) Refer to the electrical circuit diagrams and
check Restraints Control Module (RCM) Pulse
Width Modulated (PWM) SRS signal line circuit,
hard wired connection between Engine Control
Module (ECM) and Restraints Control Module
(RCM) for short to ground, short to power, open
circuit. Repair circuit as required, clear DTC and
retest system to confirm repair.
Page 1442 of 3039
DTC Description Possible Cause Action P0829-07
5-6 Shift - Mechanical
Failures
Gear Ratio Monitoring.
Mechanical Failures Check and correct oil level. Clear DTC. If code
re-detects suspect Transmission internal fault. Install
a new Transmission as required, refer to the new
module/component installation note at the top of the
DTC Index P0829-77
6-5 Shift - Commanded
Position Not Reachable
Gear Ratio Monitoring.
Mechanical Failures Check and correct oil level. Clear DTC. If code
re-detects suspect Transmission internal fault. Install
a new Transmission as required, refer to the new
module/component installation note at the top of the
DTC Index P084F-01
Park / Neutral Switch Input
Circuit - General Electrical
Failure
Wrong voltage level
detected on Park/No Park
signal Check for correct output at Transmission control
module park signal pin (check in all positions) 12 volts
in Park, 0 volts in all other positions. If fault
identified, suspect the Transmission control module.
Install a new Transmission control module as required,
refer to the new module/component installation note
at the top of the DTC Index. If no fault identified,
check Park signal circuit to Transmission Shift Module
for short, open circuit. P0850-01
Park / Neutral Switch Input
Circuit - General Electrical
Failure
General electrical failure Suspect the Transmission control module. Install a
new Transmission control module as required, refer to
the new module/component installation note at the top of the DTC Index P0850-02
Park / Neutral Switch Input
Circuit - General signal
failure
General signal failure Check park lock mechanism. If park lock operation is
correct, suspect the transmission control module.
Check and install a new transmission control module
as required. Refer to the warranty policy and
procedures manual, or determine if any prior approval
programme is in operation, prior to the installation of
a new module/component P0850-29
Park / Neutral Switch Input
Circuit - signal invalid
Signal invalid Check park lock mechanism. If park lock operation is
correct, suspect the transmission control module.
Check and install a new transmission control module
as required. Refer to the warranty policy and
procedures manual, or determine if any prior approval
programme is in operation, prior to the installation of
a new module/component P850-1C
Park / Neutral Switch Input
Circuit - circuit voltage out
of range
Circuit voltage out of
range Check park lock mechanism, if park lock operation
correct suspect the Transmission control module.
Install a new Transmission control module as required,
refer to the new module/component installation note
at the top of the DTC Index P0919-93
Gear Shift Position Control
Error - no operation
No shifting despite driver
request Suspect the Transmission control module. Install a
new Transmission control module as required, refer to
the new module/component installation note at the top of the DTC Index P0919-94
Gear Shift Position Control
Error - unexpected operation
Shifting without driver
request Suspect the Transmission control module. Install a
new Transmission control module as required, refer to
the new module/component installation note at the top of the DTC Index P0938-29
Hydraulic Oil Temperature
Sensor Range/Performance -
signal invalid
Transmission fluid
temperature compared
with module temperature
fault Clear DTC. Carry out cold start road test, continue
driving vehicle until normal operating temperature is
achieved. Read DTCs, if DTC returns, suspect the
Transmission control module. Install a new
Transmission control module as required, refer to the
new module/component installation note at the top of
the DTC Index P0963-12
Pressure Control Solenoid A
Control Circuit High - Circuit
Short to Battery
Pressure control solenoid
1 Circuit Short to Power Suspect the Transmission control module. Install a
new Transmission control module as required, refer to
the new module/component installation note at the top of the DTC Index P0964-13
Pressure Control Solenoid B
Control Circuit / Open -
Circuit Open
Pressure Control Solenoid
B Control Circuit Open Suspect the Transmission control module. Install a
new Transmission control module as required, refer to
the new module/component installation note at the top of the DTC Index P0964-14
Pressure Control Solenoid B
Control Circuit / Open -
Circuit Short to Ground or
Open
Pressure Control Solenoid
B Control Circuit Short to
Ground or Open Suspect the Transmission control module. Install a
new Transmission control module as required, refer to
the new module/component installation note at the
top of the DTC Index P0966-11
Pressure Control Solenoid B
Control Circuit Low - Circuit
Short to Ground
Pressure control solenoid
2 Circuit Short to Ground Suspect the Transmission control module. Install a
new Transmission control module as required, refer to
the new module/component installation note at the top of the DTC Index www.JagDocs.com
Page 1546 of 3039

Published: 11-May-2011
Exhaust System - V8 5.0L Petrol/V8 S/C 5.0L Petrol - Exhaust System - Overview
Description and Operation
OVERVIEW
5.0L V8 NATURALLY ASPIRATED AND SUPERCHARGER - FROM 2010MY
The exhaust system fitted to models with the 5.0L V8 engines are fabricated from stainless steel. 5 separate assemblies make
up the complete system.
The front section comprises 2 separate assemblies (LH (left-hand) and RH (right-hand)) incorporating a catalytic converter for
each bank of cylinders. The rear section comprises 3 separate sections; a center section and two rear sections. The center
section assembly incorporates a rear silencer which is connected to a center resonator silencer. On supercharger models, the
center resonator is a one piece assembly with two inlet pipes from the center silencer and two outlet pipes to the rear
silencers. On naturally aspirated models, each outlet pipe from the center silencer connects into an individual center resonator.
The system is attached to the underside of the body with mounting rubbers which are located on steel hanger bars that are
welded to the system. The mounting rubbers locate on corresponding hangers which are welded or bolted to the underside of
the vehicle body.