2010 CHEVROLET EQUINOX tires
[x] Cancel search: tiresPage 290 of 394

9-22 Vehicle Care
Some driving conditions or climates
can cause a brake squeal when the
brakes are first applied or lightly
applied. This does not mean
something is wrong with the brakes.
Properly torqued wheel nuts are
necessary to help prevent brake
pulsation. When tires are rotated,
inspect brake pads for wear and
evenly tighten wheel nuts in the
proper sequence to torque
specifications inCapacities and
Specifications on page 11‑2.
Brake linings should always be
replaced as complete axle sets.
Brake Pedal Travel
See your dealer if the brake pedal
does not return to normal height,
or if there is a rapid increase in
pedal travel. This could be a sign
that brake service might be
required.
Brake Adjustment
Every time the brakes are applied,
with or without the vehicle moving,
the brakes adjust for wear.
Replacing Brake System Parts
The braking system on a vehicle is
complex. Its many parts have to be
of top quality and work well together
if the vehicle is to have really good
braking. The vehicle was designed
and tested with top-quality brake
parts. When parts of the braking
system are replaced, be sure to get
new, approved replacement parts.
If this is not done, the brakes might
not work properly. For example,
installing disc brake pads that are
wrong for the vehicle, can change
the balance between the front and
rear brakes —for the worse. The
braking performance expected can
change in many other ways if the
wrong replacement brake parts are
installed.
Brake Fluid
The brake master cylinder reservoir
is filled with DOT 3 brake fluid as
indicated on the reservoir cap. See
Engine Compartment Overview
on
page 9‑6for the location of the
reservoir.
There are only two reasons why the
brake fluid level in the reservoir
might go down:
.The brake fluid level goes down
because of normal brake lining
wear. When new linings are
installed, the fluid level goes
back up.
Page 295 of 394
Vehicle Care 9-27
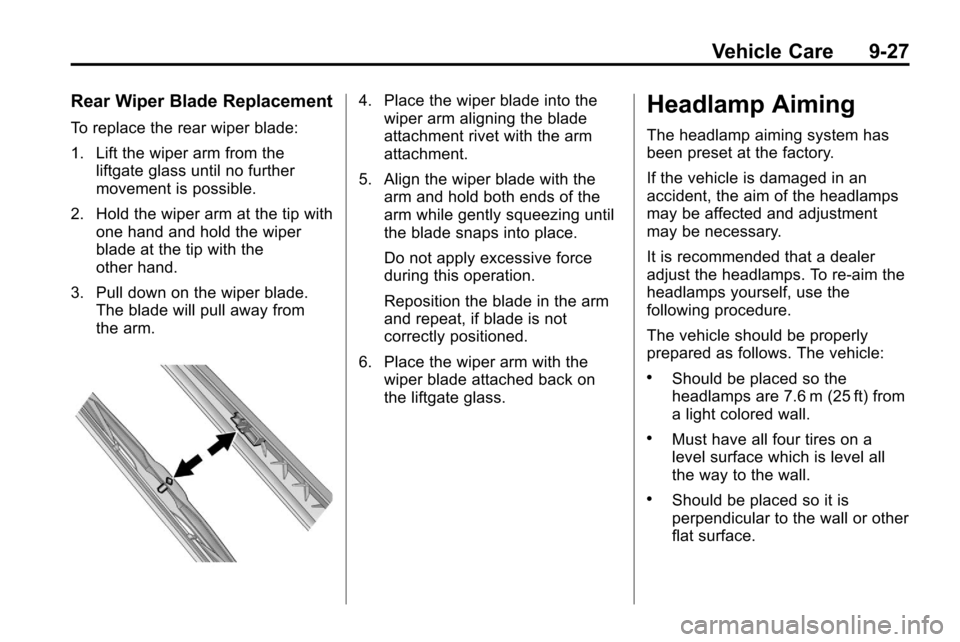
Rear Wiper Blade Replacement
To replace the rear wiper blade:
1. Lift the wiper arm from theliftgate glass until no further
movement is possible.
2. Hold the wiper arm at the tip with one hand and hold the wiper
blade at the tip with the
other hand.
3. Pull down on the wiper blade. The blade will pull away from
the arm.
4. Place the wiper blade into thewiper arm aligning the blade
attachment rivet with the arm
attachment.
5. Align the wiper blade with the arm and hold both ends of the
arm while gently squeezing until
the blade snaps into place.
Do not apply excessive force
during this operation.
Reposition the blade in the arm
and repeat, if blade is not
correctly positioned.
6. Place the wiper arm with the wiper blade attached back on
the liftgate glass.Headlamp Aiming
The headlamp aiming system has
been preset at the factory.
If the vehicle is damaged in an
accident, the aim of the headlamps
may be affected and adjustment
may be necessary.
It is recommended that a dealer
adjust the headlamps. To re-aim the
headlamps yourself, use the
following procedure.
The vehicle should be properly
prepared as follows. The vehicle:
.Should be placed so the
headlamps are 7.6 m (25 ft) from
a light colored wall.
.Must have all four tires on a
level surface which is level all
the way to the wall.
.Should be placed so it is
perpendicular to the wall or other
flat surface.
Page 296 of 394
9-28 Vehicle Care
.Should not have any snow, ice,
or mud on it.
.Should be fully assembled and
all other work stopped while
headlamp aiming is being
performed.
.Should be normally loaded with
a full tank of fuel and one person
or 75 kg (160 lbs) sitting on the
driver's seat.
.Tires should be properly inflated.
Headlamp aiming is done with the
vehicle's low-beam headlamps. The
high-beam headlamps will be
correctly aimed if the low-beam
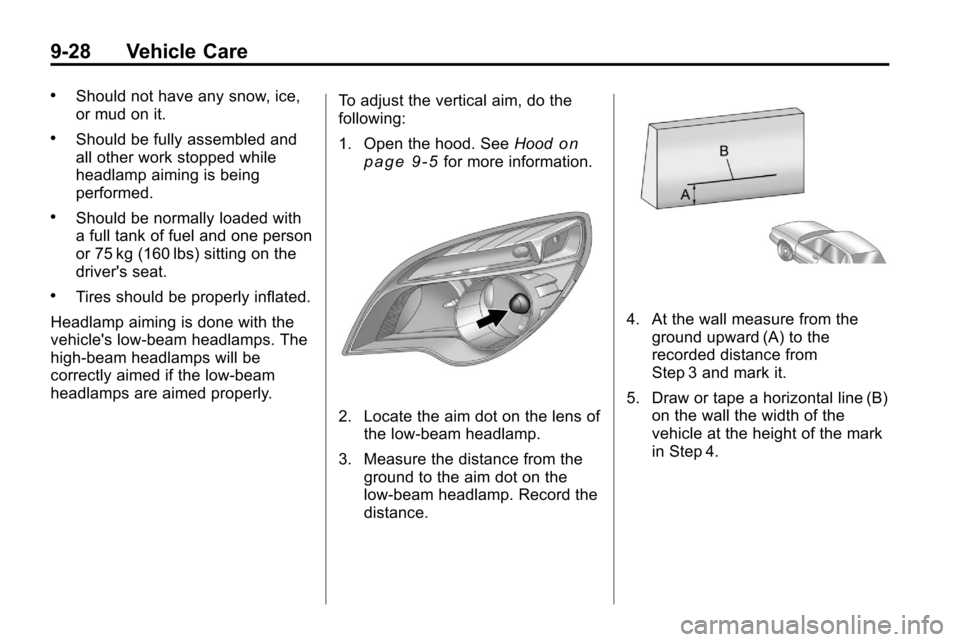
headlamps are aimed properly. To adjust the vertical aim, do the
following:
1. Open the hood. See
Hood
on
page 9‑5for more information.
2. Locate the aim dot on the lens of the low‐beam headlamp.
3. Measure the distance from the ground to the aim dot on the
low‐beam headlamp. Record the
distance.
4. At the wall measure from the
ground upward (A) to the
recorded distance from
Step 3 and mark it.
5. Draw or tape a horizontal line (B) on the wall the width of the
vehicle at the height of the mark
in Step 4.
Page 308 of 394

9-40 Vehicle Care
Wheels and Tires
Tires
Your new vehicle comes with
high-quality tires made by a
leading tire manufacturer. If you
ever have questions about your
tire warranty and where to
obtain service, see your vehicle
Warranty booklet for details. For
additional information refer to
the tire manufacturer.
{WARNING
Poorly maintained and improperly
used tires are dangerous.
.Overloading your tires can
cause overheating as a result
of too much flexing. You
could have an air-out and a
serious accident. SeeVehicle
Load Limits on page 8‑24.
(Continued)
WARNING (Continued)
.Underinflated tires pose the
same danger as overloaded
tires. The resulting accident
could cause serious injury.
Check all tires frequently to
maintain the recommended
pressure. Tire pressure
should be checked when your
tires are cold. See Tire
Pressure on page 9‑46.
.Overinflated tires are more
likely to be cut, punctured
or broken by a sudden
impact —such as when you
hit a pothole. Keep tires at
the recommended pressure.
.Worn, old tires can cause
accidents. If your tread is
badly worn, or if your tires
have been damaged,
replace them.
Tire Sidewall Labeling
Useful information about a tire is
molded into its sidewall. The
examples below show a typical
passenger vehicle tire and a
compact spare tire sidewall.
Passenger (P‐Metric) Tire Example
(A) Tire Size:The tire size is a
combination of letters and
numbers used to define a
particular tire's width, height,
aspect ratio, construction type,
Page 309 of 394

Vehicle Care 9-41
and service description. See the
“Tire Size”illustration later in this
section for more detail.
(B) TPC Spec (Tire
Performance Criteria
Specification)
:Original
equipment tires designed to
GM's specific tire performance
criteria have a TPC specification
code molded onto the sidewall.
GM's TPC specifications meet or
exceed all federal safety
guidelines.
(C) DOT (Department of
Transportation)
:The
Department of Transportation
(DOT) code indicates that the
tire is in compliance with the
U.S. Department of
Transportation Motor Vehicle
Safety Standards.
(D) Tire Identification Number
(TIN)
:The letters and numbers
following the DOT (Department
of Transportation) code is the Tire Identification Number (TIN).
The TIN shows the
manufacturer and plant code,
tire size, and date the tire was
manufactured. The TIN is
molded onto both sides of the
tire, although only one side may
have the date of manufacture.
(E) Tire Ply Material
:The type
of cord and number of plies in
the sidewall and under the tread.
(F) Uniform Tire Quality
Grading (UTQG)
:Tire
manufacturers are required to
grade tires based on three
performance factors: treadwear,
traction, and temperature
resistance. For more information
see Uniform Tire Quality
Grading
on page 9‑56.
(G) Maximum Cold Inflation
Load Limit
:Maximum load that
can be carried and the
maximum pressure needed to
support that load.
Compact Spare Tire Example
(A) Tire Ply Material:The type
of cord and number of plies in
the sidewall and under the tread.
(B) Temporary Use Only
:The
compact spare tire or temporary
use tire has a tread life of
approximately 5 000 km
(3,000 miles) and should not be
driven at speeds over 105 km/h
(65 mph). The compact spare
tire is for emergency use when a
regular road tire has lost air and
gone flat. If your vehicle has a
Page 310 of 394
9-42 Vehicle Care
compact spare tire, see
Compact Spare Tire
on
page 9‑68
and If a Tire Goes Flat
on page 9‑59.
(C) Tire Identification Number
(TIN)
:The letters and numbers
following the DOT (Department
of Transportation) code is the
Tire Identification Number (TIN).
The TIN shows the
manufacturer and plant code,
tire size, and date the tire was
manufactured. The TIN is
molded onto both sides of the
tire, although only one side may
have the date of manufacture.
(D) Maximum Cold Inflation
Load Limit
:Maximum load that
can be carried and the
maximum pressure needed to
support that load. (E) Tire Inflation
:The
temporary use tire or compact
spare tire should be inflated to
420 kPa (60 psi). For more
information on tire pressure and
inflation see Tire Pressure
on
page 9‑46
.
(F) Tire Size
:A combination of
letters and numbers define a
tire's width, height, aspect ratio,
construction type, and service
description. The letter T as the
first character in the tire size
means the tire is for temporary
use only.
(G) TPC Spec (Tire
Performance Criteria
Specification)
:Original
equipment tires designed to
GM's specific tire performance
criteria have a TPC specification
code molded onto the sidewall.
GM's TPC specifications meet or
exceed all federal safety
guidelines.
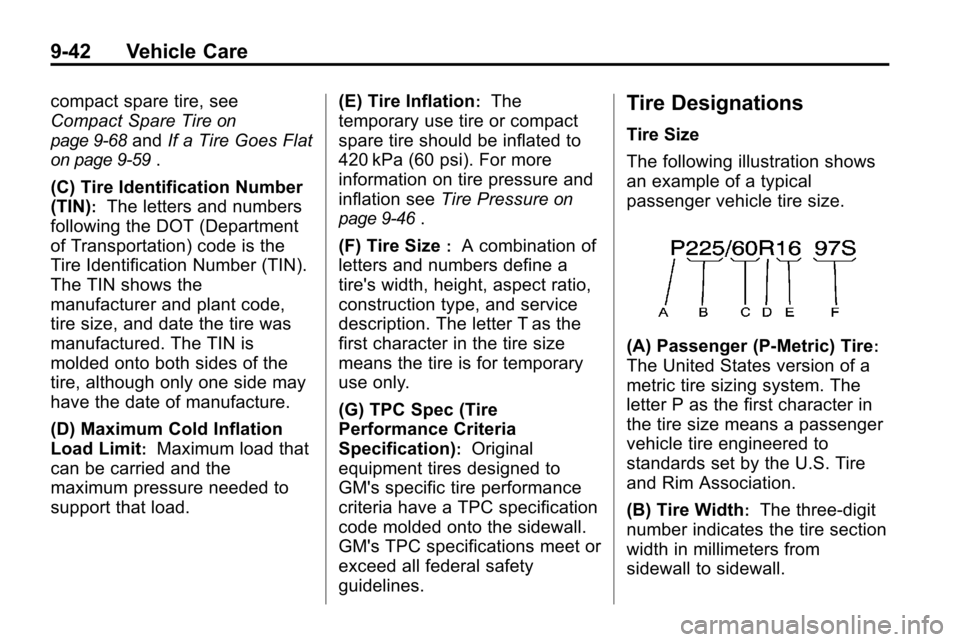
Tire Designations
Tire Size
The following illustration shows
an example of a typical
passenger vehicle tire size.
(A) Passenger (P‐Metric) Tire:
The United States version of a
metric tire sizing system. The
letter P as the first character in
the tire size means a passenger
vehicle tire engineered to
standards set by the U.S. Tire
and Rim Association.
(B) Tire Width
:The three‐digit
number indicates the tire section
width in millimeters from
sidewall to sidewall.
Page 313 of 394

Vehicle Care 9-45
Outward Facing Sidewall:The
side of an asymmetrical tire that
has a particular side that faces
outward when mounted on a
vehicle. The side of the tire that
contains a whitewall, bears
white lettering, or bears
manufacturer, brand, and/or
model name molding that is
higher or deeper than the same
moldings on the other sidewall
of the tire.
Passenger (P-Metric) Tire
:A
tire used on passenger cars and
some light duty trucks and
multipurpose vehicles.
Recommended Inflation
Pressure
:Vehicle
manufacturer's recommended
tire inflation pressure as shown
on the tire placard. See Tire
Pressure
on page 9‑46and
Vehicle Load Limits
on
page 8‑24
. Radial Ply Tire
:A pneumatic
tire in which the ply cords that
extend to the beads are laid at
90 degrees to the centerline of
the tread.
Rim
:A metal support for a tire
and upon which the tire beads
are seated.
Sidewall
:The portion of a tire
between the tread and the bead.
Speed Rating
:An
alphanumeric code assigned to
a tire indicating the maximum
speed at which a tire can
operate.
Traction
:The friction between
the tire and the road surface.
The amount of grip provided.
Tread
:The portion of a tire that
comes into contact with
the road. Treadwear Indicators
:Narrow
bands, sometimes called wear
bars, that show across the tread
of a tire when only 1.6 mm
(1/16 inch) of tread remains.
See When It Is Time for New
Tires
on page 9‑53.
UTQGS (Uniform Tire Quality
Grading Standards)
:A tire
information system that provides
consumers with ratings for a
tire's traction, temperature,
and treadwear. Ratings are
determined by tire
manufacturers using
government testing procedures.
The ratings are molded into the
sidewall of the tire. See Uniform
Tire Quality Grading
on
page 9‑56
.
Page 314 of 394

9-46 Vehicle Care
Vehicle Capacity Weight:The
number of designated seating
positions multiplied by 68 kg
(150 lbs) plus the rated cargo
load. See Vehicle Load Limits
on
page 8‑24
.
Vehicle Maximum Load on the
Tire
:Load on an individual tire
due to curb weight, accessory
weight, occupant weight, and
cargo weight.
Vehicle Placard
:A label
permanently attached to a
vehicle showing the vehicle's
capacity weight and the original
equipment tire size and
recommended inflation pressure.
See “Tire and Loading
Information Label” underVehicle
Load Limits
on page 8‑24.
Tire Pressure
Tires need the correct amount of
air pressure to operate
effectively.
Notice:Do not let anyone tell
you that under‐inflation or
over‐inflation is all right. It is
not. If your tires do not have
enough air (under‐inflation),
you can get the following:
.Too much flexing
.Too much heat
.Tire overloading
.Premature or
irregular wear
.Poor handling
.Reduced fuel economy If your tires have too much air
(over‐inflation), you can get
the following:
.Unusual wear
.Poor handling
.Rough ride
.Needless damage from
road hazards
A vehicle specific Tire and
Loading Information label is
attached to your vehicle. This
label shows your vehicle's
original equipment tires and the
correct inflation pressures for
your tires when they are cold.
The recommended cold tire
inflation pressure, shown on the
label, is the minimum amount of
air pressure needed to support
your vehicle's maximum load
carrying capacity.