2009 SUBARU TRIBECA oil viscosity
[x] Cancel search: oil viscosityPage 265 of 2453

EI-23
Front Bumper
EXTERIOR/INTERIOR TRIM
C: REPAIR
1. COATING METHOD FOR PP BUMPER
Process
No.Process name Job contents
1Bumper installation
Place the bumper on a paint worktable as
required. Use the paint worktable conforming
to inner shape of bumper if possible.
(1) Bumper
(2) Set bumper section
2MaskingMask specified part (black base) with masking tape. Use masking tape for PP (example,
Nichiban No. 533, etc. ).
3Degreasing/cleaningClean all parts to be painted with white gasoline, normal alcohol, etc. to remove dirt, oil, fat, etc.
4Primer paint Apply primer to all parts to be painted, using spray gun. Use primer (clear).
5Drying
Dry at normal temperature [10 — 15 min. at 20°C (68°F)].
In half-dried condition, PP primer paint is dissolved by solvent, e.g. thinner, etc.
Therefore, if dust or dirt must be removed, use ordinary alcohol etc.
6Top coat paint (I)
Non-colored Metallic paint
Use section (block) paint for top coat.
•Paint to be used (for each color):
Solid paint
Hardener PB
Thinner T-301
•Mixture ratio:
Main agent vs. hardener = 4:1
• Viscosity: 10 — 13 sec./20°C (68°F)
•Film thickness: 35 — 45 µ
•Spraying pressure: 245 — 343 kPa
(2.5 — 3.5 kg/cm2, 36 — 50 psi)
Use section (block) paint for top coat.
•Paint to be used (for each color):
Metallic paint
Hardener PB
Thinner T-306
•Mixture ratio:
Main agent vs. hardener = 10:1
•Viscosity: 10 — 13 sec./20°C (68°F)
•Film thickness: 15 — 20 µ
•Spraying pressure: 245 — 343 kPa
(2.5 — 3.5 kg/cm2, 36 — 50 psi)
7Drying Not required.
Dry at normal temperature [at least 10 min. at
20°C (68°F)].
In half-dried condition, avoid dust, dirt.
8Top coat paint (II)Not required.
Apply a clear coat to parts with top coat paint
(I), three times at 5 — 7 minutes intervals.
•Paint to be used:
Metallic paint
Hardener PB
Thinner T-301
•Mixture ratio:
Clear coat vs. hardener = 6:1
•Viscosity: 14 — 16 sec./20°C (68°F)
•Film thickness: 25 — 30 µ
•Spraying pressure: 245 — 343 kPa
(2.5 — 3.5 kg/cm2, 36 — 50 psi)
9Drying
60°C (140°F), 60 min. or 80°C (176°F), 30 min.
If higher than 80°C (176°F), PP may become be deformed. Keep maximum temperature below
80°C (176°F).
10 Inspection Check paint.
11 Removal of masking Remove the masking tape applied in procedure 2.
EI-00234(2)
(1)
Page 786 of 2453

DI-2
General Description
DIFFERENTIALS
1. General Description
A: SPECIFICATION
1. REAR DIFFERENTIAL
When replacing a rear differential assembly, select the correct one according to the following table.
NOTE:
•Using a different rear differential assembly will cause the drive train and tires to drag or emit abnormal
noise.
•For option code, refer to “ID” section.
2. IDENTIFICATION
Identification label positions are shown in the fol-
lowing figures. For details concerning identification,
refer to the “ID” section.
3. REAR DIFFERENTIAL GEAR OIL
Recommended gear oil:
GL–5 (75W–90)
NOTE:
Each oil manufacturer has its base oil and addi-
tives. Thus, do not mix two or more brands.
4. SERVICE DATA
Rear differential type VA2-type
Identification XX
LSD type—
Ty p e o f g e a r H y p o i d g e a r
Gear ratio (Number of gear teeth) 3.583 (43/12)
Oil capacity 0.82 (0.8 US qt, 0.7 lmp qt)
Rear differential gear oil GL-5
(1) Identification
ID-00114
(1)
(1) Item
(2) Rear differential gear oil
(3) API classification
(4) SAE viscosity No. and applicable temperature
MT-00001
(1)
(4)GL-5(3)
(2)
( C)( F)-30 -26 -15 15
9085W80W75W -90
25 30 -5 0-22-1523328659775
Drive pinion bearing preload Measure with spring measurement. (Mea-
sured from the companion flange bolt)
N (kgf, lb)
12.7 — 32.2 (1.3 — 3.28, 2.9 — 7.24)
Measure with torque wrench
N·m (kgf–m, ft–lb)0.48 — 1.22 (0.045 — 0.124, 0.32 — 0.9)
Hypoid driven gear to drive pinion backlash mm (in) 0.10 — 0.15 (0.0039 — 0.0059)
Page 1851 of 2453
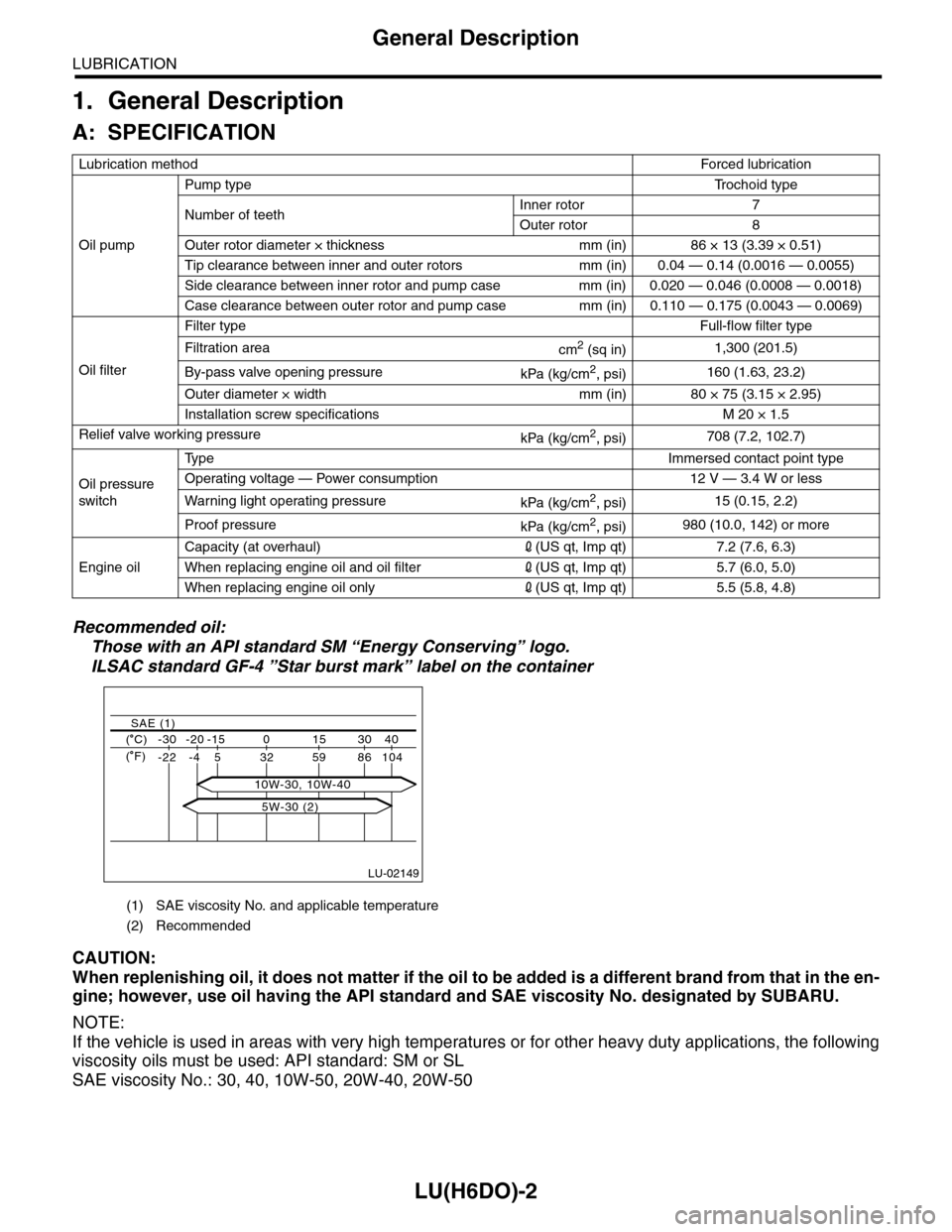
LU(H6DO)-2
General Description
LUBRICATION
1. General Description
A: SPECIFICATION
Recommended oil:
Those with an API standard SM “Energy Conserving” logo.
ILSAC standard GF-4 ”Star burst mark” label on the container
CAUTION:
When replenishing oil, it does not matter if the oil to be added is a different brand from that in the en-
gine; however, use oil having the API standard and SAE viscosity No. designated by SUBARU.
NOTE:
If the vehicle is used in areas with very high temperatures or for other heavy duty applications, the following
viscosity oils must be used: API standard: SM or SL
SAE viscosity No.: 30, 40, 10W-50, 20W-40, 20W-50
Lubrication methodForced lubr ication
Oil pump
Pump typeTr o c h o i d t y p e
Number of teethInner rotor 7
Outer rotor 8
Outer rotor diameter × thickness mm (in) 86 × 13 (3.39 × 0.51)
Tip clearance between inner and outer rotors mm (in) 0.04 — 0.14 (0.0016 — 0.0055)
Side clearance between inner rotor and pump case mm (in) 0.020 — 0.046 (0.0008 — 0.0018)
Case clearance between outer rotor and pump case mm (in) 0.110 — 0.175 (0.0043 — 0.0069)
Oil filter
Filter typeFull-flow filter type
Filtration areacm2 (sq in)1,300 (201.5)
By-pass valve opening pressurekPa (kg/cm2, psi)160 (1.63, 23.2)
Outer diameter × width mm (in) 80 × 75 (3.15 × 2.95)
Installation screw specifications M 20 × 1.5
Relief valve working pressurekPa (kg/cm2, psi)708 (7.2, 102.7)
Oil pressure
switch
Ty p eImmersed contact point type
Operating voltage — Power consumption 12 V — 3.4 W or less
Wa r ni n g l ig h t o p era t i ng pr e ss ur ekPa (kg/cm2, psi)15 (0.15, 2.2)
Proof pressurekPa (kg/cm2, psi)980 (10.0, 142) or more
Engine oil
Capacity (at overhaul)2(US qt, Imp qt) 7.2 (7.6, 6.3)
When replacing engine oil and oil filter2(US qt, Imp qt) 5.7 (6.0, 5.0)
When replacing engine oil only2(US qt, Imp qt) 5.5 (5.8, 4.8)
(1) SAE viscosity No. and applicable temperature
(2) Recommended
LU-02149
( C) -30 -20 -15 0 15 30 40
-22 -4 5 32 59 86 104
SAE (1)
( F)
5W-30 (2)
10W-30, 10W-40
Page 1856 of 2453

LU(H6DO)-7
Engine Oil
LUBRICATION
3. Engine Oil
A: INSPECTION
1) Park the vehicle on a level surface.
2) Remove the oil level gauge and wipe it clean.
3) Reinsert the level gauge all the way. Be sure that
the level gauge is correctly inserted and properly
orientated.
4) Remove it again and check the reading. If the
engine oil level is below “L” line, add oil to bring the
level up to “F” line.
5) After turning off the engine, wait a few minutes
for the oil to return to the oil pan before checking
the level.
NOTE:
To prevent overfilling of engine oil, do not add oil
above “F” line when the engine is cold.
B: REPLACEMENT
1) Open the engine oil filler cap for quick draining of
engine oil.
2) Lift-up the vehicle.
3) Drain engine oil by loosening the engine oil drain
plug.
NOTE:
Prepare the container for draining of engine oil.
4) Tighten the engine oil drain plug after draining
engine oil.
NOTE:
Use a new drain plug gasket.
Tightening torque:
44 N·m (4.5 kgf-m, 33 ft-lb)
5) Using engine oil of proper quality and viscosity,
fill engine oil through the oil filler duct to the upper
level on level gauge. Make sure that the vehicle is
parked on a level surface when checking oil level.
Recommended oil:
Refer to “SPECIFICATION” for the recom-
mended oil.
Engine oil capacity
Refer to “SPECIFICATION” for the engine oil
capacity.
6) Close the engine oil filler cap.
7) Start the engine and warm it up for a time.
8) After the engine stops, recheck the oil level. If
necessary, add engine oil up to the upper level on
level gauge.
(A) Oil level gauge
(B) Engine oil filler cap
(C) Upper level
(D) Lower level
PM-00279
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
PM-00280
(A) Oil level gauge
(B) Engine oil filler cap
(C) Upper level
(D) Lower level
PM-00279
(A)
(B)
(C)
(D)
Page 1949 of 2453
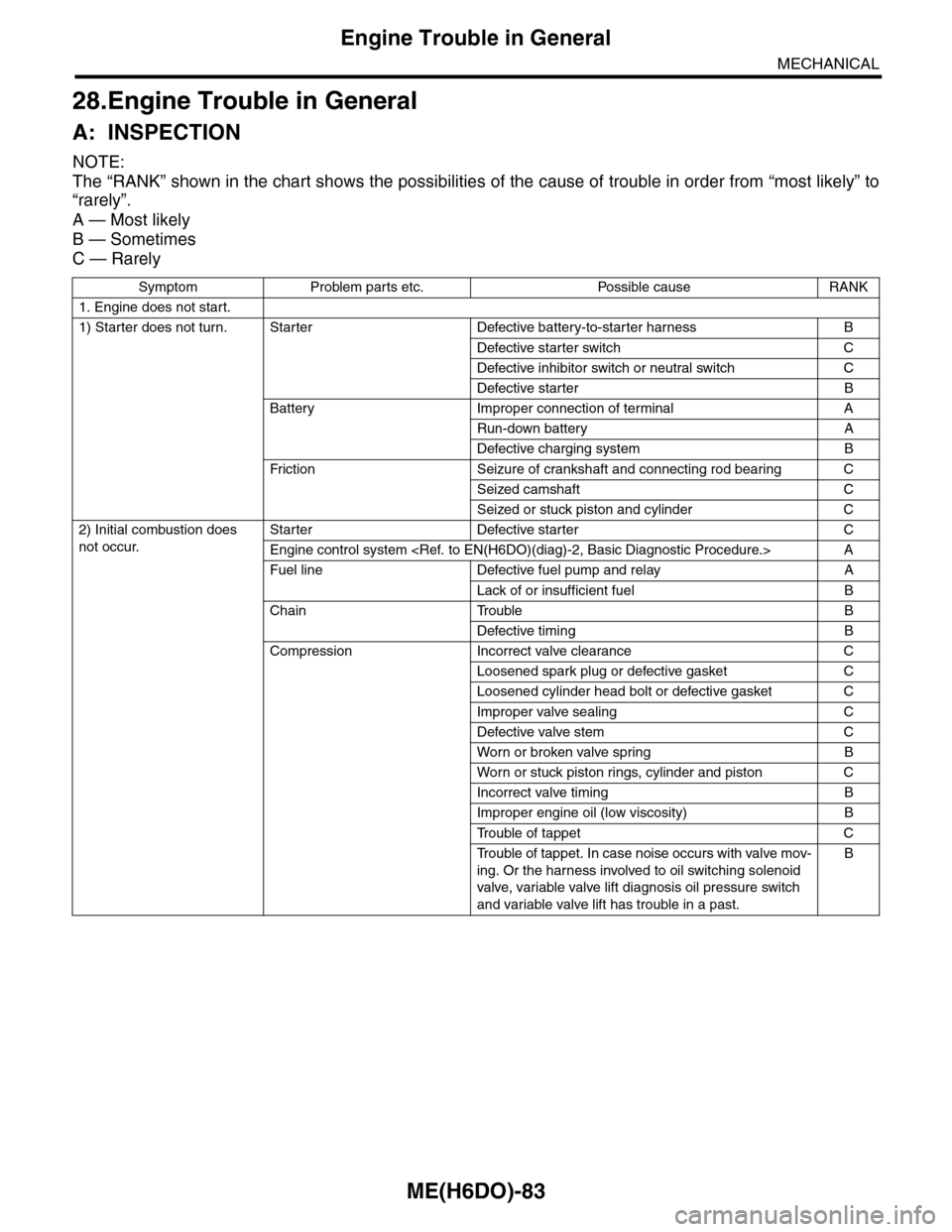
ME(H6DO)-83
Engine Trouble in General
MECHANICAL
28.Engine Trouble in General
A: INSPECTION
NOTE:
The “RANK” shown in the chart shows the possibilities of the cause of trouble in order from “most likely” to
“rarely”.
A — Most likely
B — Sometimes
C — Rarely
Symptom Problem parts etc. Possible cause RANK
1. Engine does not start.
1) Starter does not turn. Starter Defective battery-to-starter harness B
Defective starter switch C
Defective inhibitor switch or neutral switch C
Defective starter B
Battery Improper connection of terminal A
Run-down battery A
Defective charging system B
Fr iction Seizure of crankshaft and connecting rod bear ing C
Seized camshaft C
Seized or stuck piston and cylinder C
2) Initial combustion does
not occur.
Starter Defective starter C
Engine control system
Fuel line Defective fuel pump and relay A
Lack of or insufficient fuel B
Chain Trouble B
Defective timing B
Compression Incorrect valve clearance C
Loosened spark plug or defective gasket C
Loosened cylinder head bolt or defective gasket C
Improper valve sealing C
Defective valve stem C
Wor n or broken valve spr ing B
Wor n or stuck piston r ings, cylinder and piston C
Incorrect valve timing B
Improper engine oil (low viscosity) B
Tr o u b l e o f t a p p e t C
Tr o u b l e o f t a p p e t . I n c a s e n o i s e o c c u r s w i t h v a l v e m o v -
ing. Or the harness involved to oil switching solenoid
valve, variable valve lift diagnosis oil pressure switch
and variable valve lift has trouble in a past.
B
Page 1950 of 2453
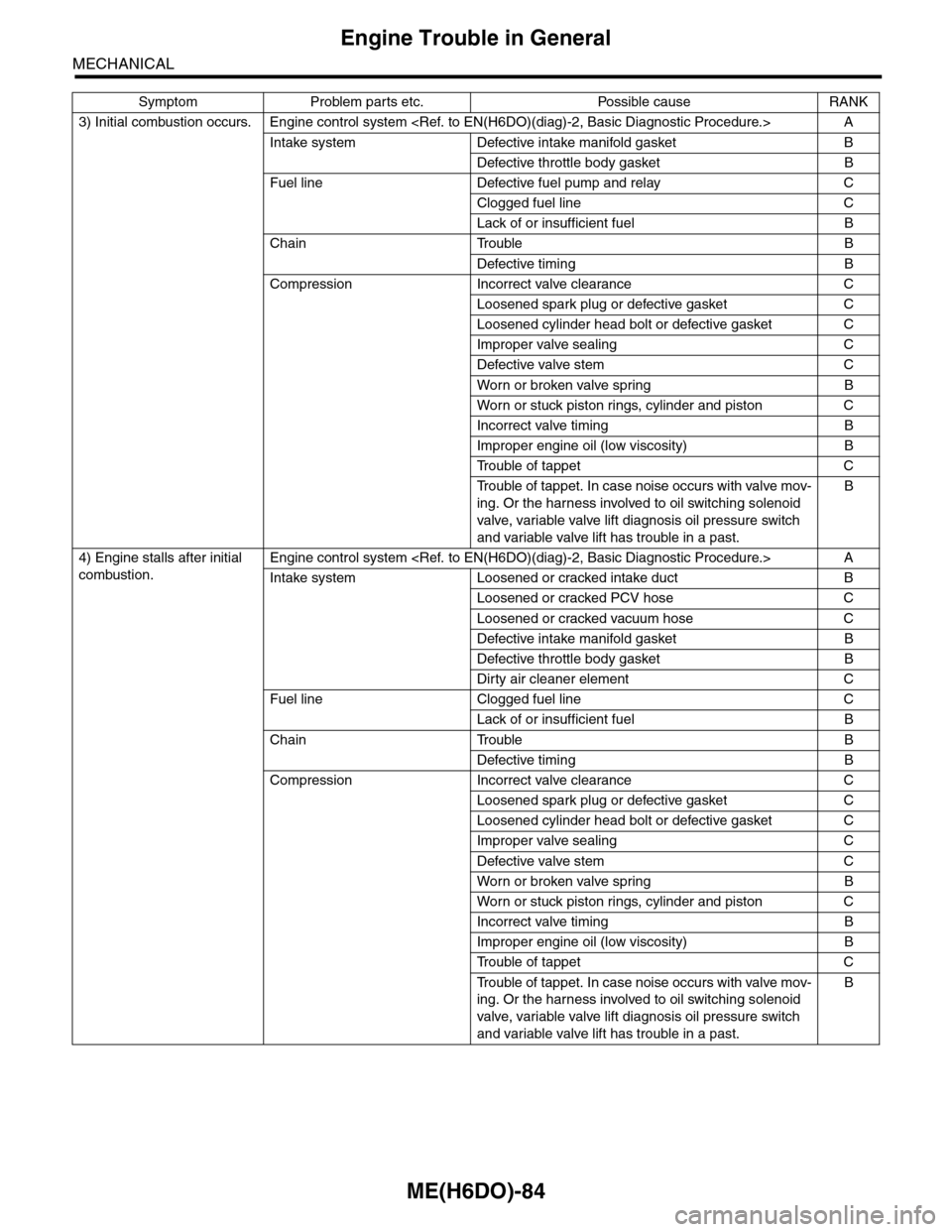
ME(H6DO)-84
Engine Trouble in General
MECHANICAL
3) Initial combustion occurs. Engine control system
Intake system Defective intake manifold gasket B
Defective throttle body gasket B
Fuel line Defective fuel pump and relay C
Clogged fuel line C
Lack of or insufficient fuel B
Chain Trouble B
Defective timing B
Compression Incorrect valve clearance C
Loosened spark plug or defective gasket C
Loosened cylinder head bolt or defective gasket C
Improper valve sealing C
Defective valve stem C
Wor n or broken valve spr ing B
Wor n or stuck piston r ings, cylinder and piston C
Incorrect valve timing B
Improper engine oil (low viscosity) B
Tr o u b l e o f t a p p e t C
Tr o u b l e o f t a p p e t . I n c a s e n o i s e o c c u r s w i t h v a l v e m o v -
ing. Or the harness involved to oil switching solenoid
valve, variable valve lift diagnosis oil pressure switch
and variable valve lift has trouble in a past.
B
4) Engine stalls after initial
combustion.
Engine control system
Intake system Loosened or cracked intake duct B
Loosened or cracked PCV hose C
Loosened or cracked vacuum hose C
Defective intake manifold gasket B
Defective throttle body gasket B
Dirty air cleaner element C
Fuel line Clogged fuel line C
Lack of or insufficient fuel B
Chain Trouble B
Defective timing B
Compression Incorrect valve clearance C
Loosened spark plug or defective gasket C
Loosened cylinder head bolt or defective gasket C
Improper valve sealing C
Defective valve stem C
Wor n or broken valve spr ing B
Wor n or stuck piston r ings, cylinder and piston C
Incorrect valve timing B
Improper engine oil (low viscosity) B
Tr o u b l e o f t a p p e t C
Tr o u b l e o f t a p p e t . I n c a s e n o i s e o c c u r s w i t h v a l v e m o v -
ing. Or the harness involved to oil switching solenoid
valve, variable valve lift diagnosis oil pressure switch
and variable valve lift has trouble in a past.
B
Symptom Problem parts etc. Possible cause RANK
Page 1951 of 2453
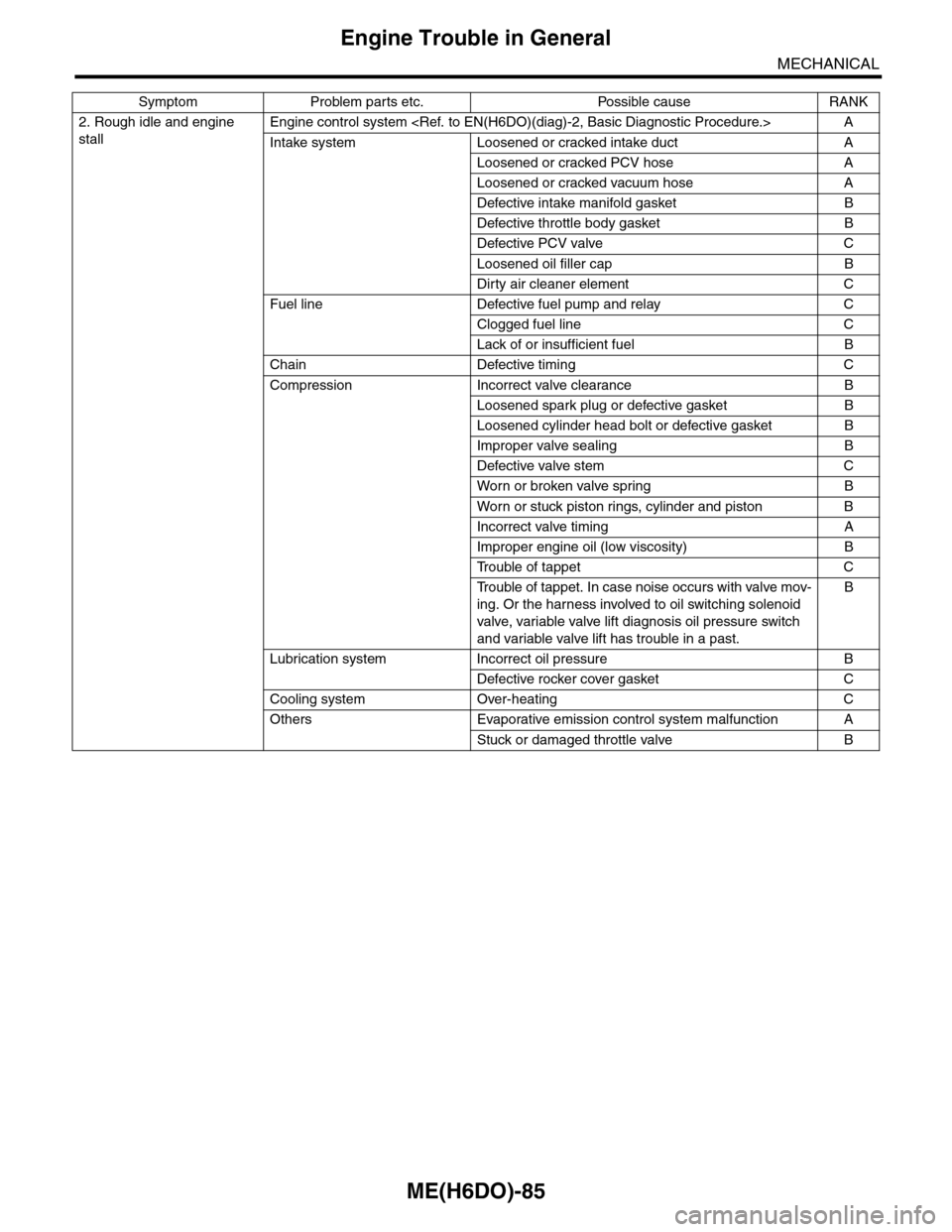
ME(H6DO)-85
Engine Trouble in General
MECHANICAL
2. Rough idle and engine
stall
Engine control system
Intake system Loosened or cracked intake duct A
Loosened or cracked PCV hose A
Loosened or cracked vacuum hose A
Defective intake manifold gasket B
Defective throttle body gasket B
Defective PCV valve C
Loosened oil filler cap B
Dirty air cleaner element C
Fuel line Defective fuel pump and relay C
Clogged fuel line C
Lack of or insufficient fuel B
Chain Defective timing C
Compression Incorrect valve clearance B
Loosened spark plug or defective gasket B
Loosened cylinder head bolt or defective gasket B
Improper valve sealing B
Defective valve stem C
Wor n or broken valve spr ing B
Wor n or stuck piston r ings, cylinder and piston B
Incorrect valve timing A
Improper engine oil (low viscosity) B
Tr o u b l e o f t a p p e t C
Tr o u b l e o f t a p p e t . I n c a s e n o i s e o c c u r s w i t h v a l v e m o v -
ing. Or the harness involved to oil switching solenoid
valve, variable valve lift diagnosis oil pressure switch
and variable valve lift has trouble in a past.
B
Lubrication system Incorrect oil pressure B
Defective rocker cover gasket C
Cooling system Over-heating C
Others Evaporative emission control system malfunction A
Stuck or damaged throttle valve B
Symptom Problem parts etc. Possible cause RANK
Page 1952 of 2453
ME(H6DO)-86
Engine Trouble in General
MECHANICAL
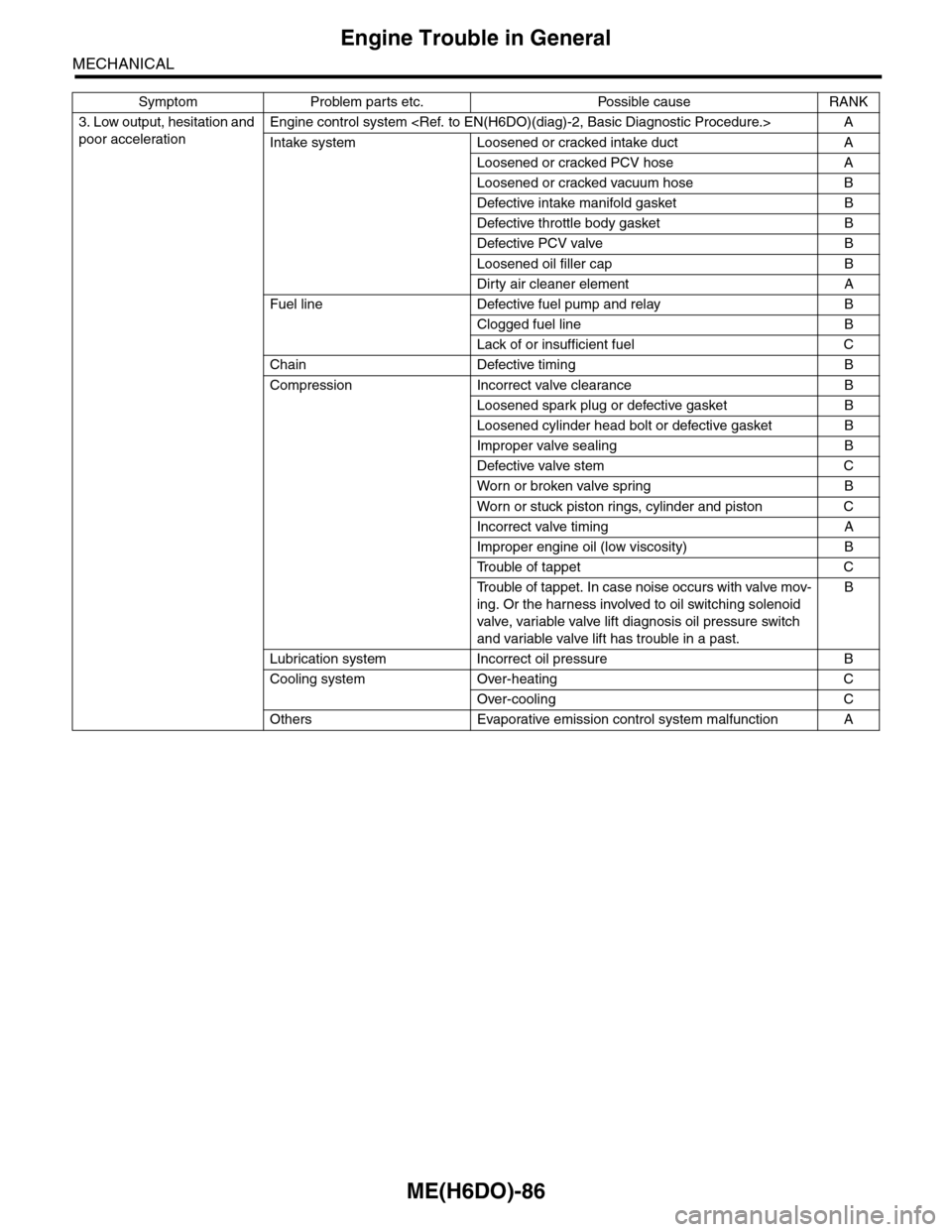
3. Low output, hesitation and
poor acceleration
Engine control system
Intake system Loosened or cracked intake duct A
Loosened or cracked PCV hose A
Loosened or cracked vacuum hose B
Defective intake manifold gasket B
Defective throttle body gasket B
Defective PCV valve B
Loosened oil filler cap B
Dirty air cleaner element A
Fuel line Defective fuel pump and relay B
Clogged fuel line B
Lack of or insufficient fuel C
Chain Defective timing B
Compression Incorrect valve clearance B
Loosened spark plug or defective gasket B
Loosened cylinder head bolt or defective gasket B
Improper valve sealing B
Defective valve stem C
Wor n or broken valve spr ing B
Wor n or stuck piston r ings, cylinder and piston C
Incorrect valve timing A
Improper engine oil (low viscosity) B
Tr o u b l e o f t a p p e t C
Tr o u b l e o f t a p p e t . I n c a s e n o i s e o c c u r s w i t h v a l v e m o v -
ing. Or the harness involved to oil switching solenoid
valve, variable valve lift diagnosis oil pressure switch
and variable valve lift has trouble in a past.
B
Lubrication system Incorrect oil pressure B
Cooling system Over-heating C
Over-cooling C
Others Evaporative emission control system malfunction A
Symptom Problem parts etc. Possible cause RANK