2007 ISUZU KB P190 Harness
[x] Cancel search: HarnessPage 3713 of 6020
Powertrain Interface Module – V6 Page 6E1–52
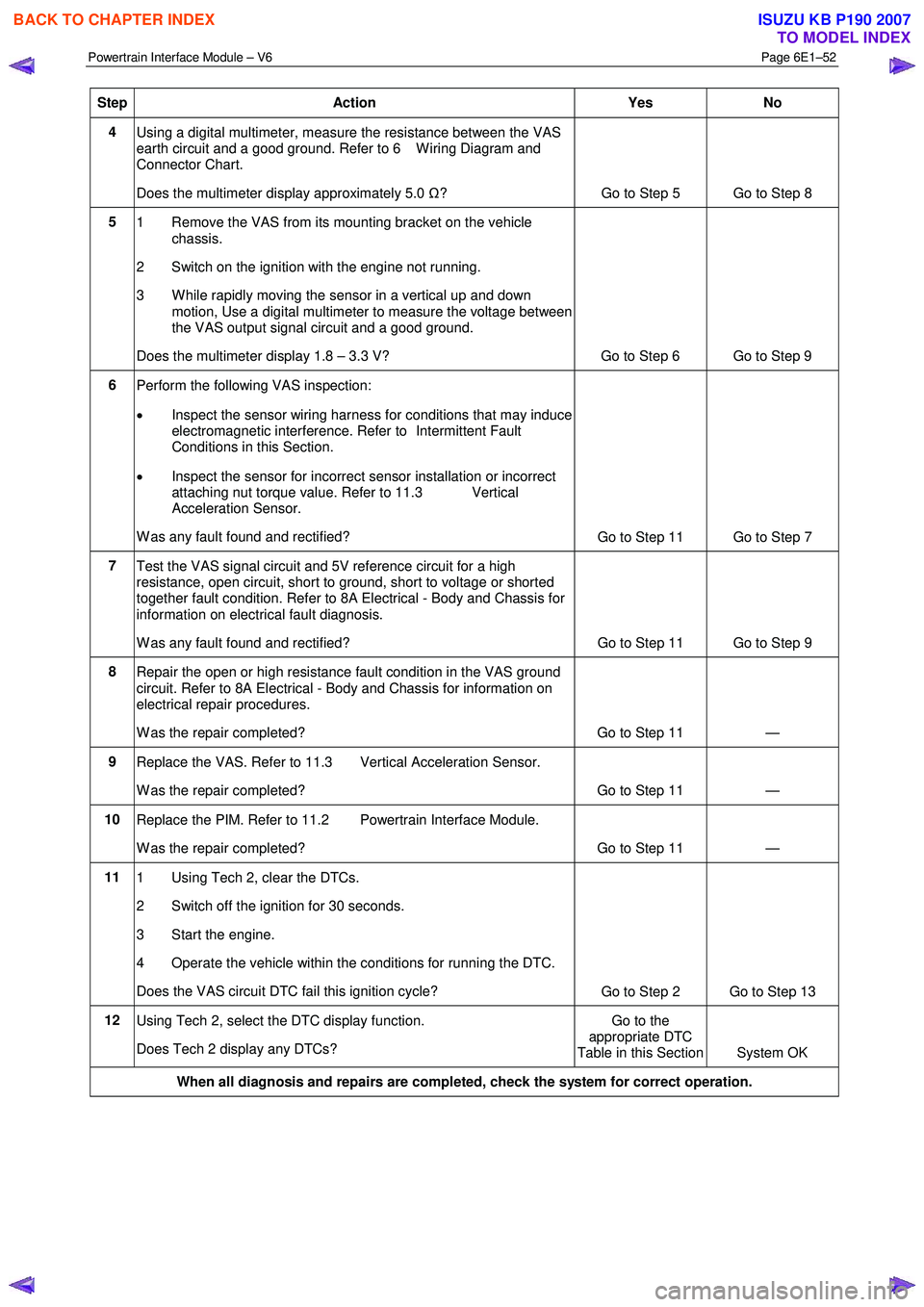
Step Action Yes No
4
Using a digital multimeter, measure the resistance between the VAS
earth circuit and a good ground. Refer to 6 W iring Diagram and
Connector Chart.
Does the multimeter display approximately 5.0 Ω?
Go to Step 5 Go to Step 8
5
1 Remove the VAS from its mounting bracket on the vehicle
chassis.
2 Switch on the ignition with the engine not running.
3 W hile rapidly moving the sensor in a vertical up and down motion, Use a digital multimeter to measure the voltage between
the VAS output signal circuit and a good ground.
Does the multimeter display 1.8 – 3.3 V? Go to Step 6 Go to Step 9
6 Perform the following VAS inspection:
• Inspect the sensor wiring harness for conditions that may induce
electromagnetic interference. Refer to Intermittent Fault
Conditions in this Section.
• Inspect the sensor for incorrect sensor installation or incorrect
attaching nut torque value. Refer to 11.3 Vertical
Acceleration Sensor.
W as any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 11 Go to Step 7
7
Test the VAS signal circuit and 5V reference circuit for a high
resistance, open circuit, short to ground, short to voltage or shorted
together fault condition. Refer to 8A Electrical - Body and Chassis for
information on electrical fault diagnosis.
W as any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 11 Go to Step 9
8
Repair the open or high resistance fault condition in the VAS ground
circuit. Refer to 8A Electrical - Body and Chassis for information on
electrical repair procedures.
W as the repair completed? Go to Step 11 —
9 Replace the VAS. Refer to 11.3 Vertical Acceleration Sensor.
W as the repair completed? Go to Step 11 —
10 Replace the PIM. Refer to 11.2 Powertrain Interface Module.
W as the repair completed? Go to Step 11 —
11 1 Using Tech 2, clear the DTCs.
2 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
3 Start the engine.
4 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
Does the VAS circuit DTC fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 2 Go to Step 13
12
Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does Tech 2 display any DTCs? Go to the
appropriate DTC
Table in this Section System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3715 of 6020
Powertrain Interface Module – V6 Page 6E1–54
• For an intermittent fault condition, refer to Intermittent Fault Conditions in this Section.
• The VSS in conjunction with the 40X reluctor wheel generates an AC signal voltage. The amplitude and frequency
of the signal generated is proportional to the vehicle speed. The PIM uses this signal from the VSS signal circuit to
determine the vehicle speed.
• Since fault condition in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this diagnostic
procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component. Refer to 8A Electrical -
Body and Chassis for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
• To assist diagnosis, refer to 6 W iring Diagram and Connector Chart in this Section, for the system wiring diagram
and connector charts.
Test Description
The following numbers refer to the step numbers in the diagnostic table:
3 The PIM supplies 2.5 V to signal circuit of the VSS circuit to reduce the Electro Magnetic interference (EMI). If the voltage is not within range, this indicates there is an PIM fault or a PIM circuit fault condition.
4 The PIM supplies 2.5 V to low reference circuit of the VSS circuit to reduce the Electro Magnetic interference (EMI). If the voltage is not within range, this indicates there is a PIM fault or a PIM circuit fault condition.
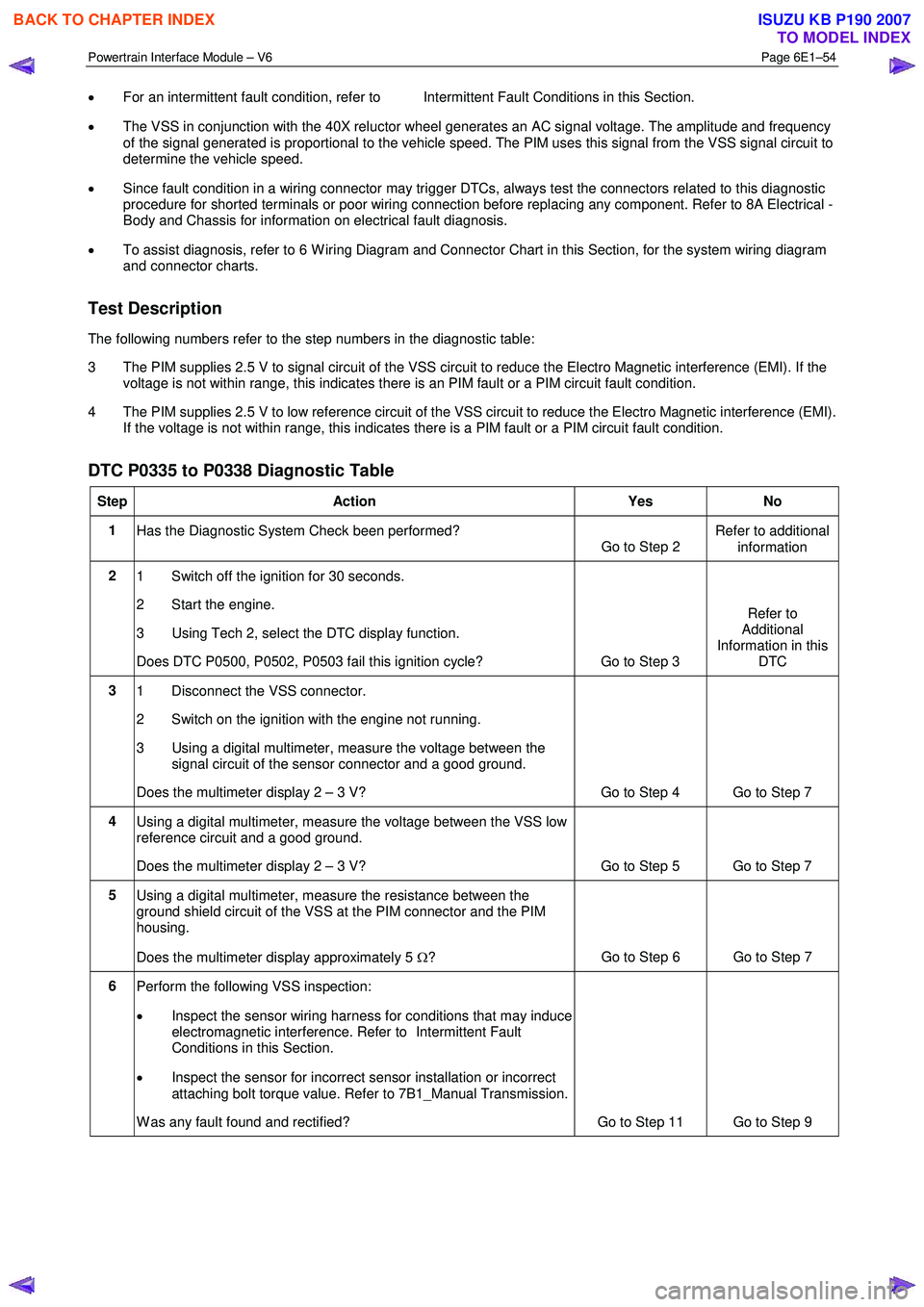
DTC P0335 to P0338 Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1
Has the Diagnostic System Check been performed?
Go to Step 2 Refer to additional
information
2 1 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
2 Start the engine.
3 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does DTC P0500, P0502, P0503 fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 3 Refer to
Additional
Information in this DTC
3 1 Disconnect the VSS connector.
2 Switch on the ignition with the engine not running.
3 Using a digital multimeter, measure the voltage between the signal circuit of the sensor connector and a good ground.
Does the multimeter display 2 – 3 V? Go to Step 4 Go to Step 7
4 Using a digital multimeter, measure the voltage between the VSS low
reference circuit and a good ground.
Does the multimeter display 2 – 3 V? Go to Step 5 Go to Step 7
5 Using a digital multimeter, measure the resistance between the
ground shield circuit of the VSS at the PIM connector and the PIM
housing.
Does the multimeter display approximately 5 Ω? Go to Step 6 Go to Step 7
6
Perform the following VSS inspection:
• Inspect the sensor wiring harness for conditions that may induce
electromagnetic interference. Refer to Intermittent Fault
Conditions in this Section.
• Inspect the sensor for incorrect sensor installation or incorrect
attaching bolt torque value. Refer to 7B1_Manual Transmission.
W as any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 11 Go to Step 9
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3723 of 6020

Powertrain Interface Module – V6 Page 6E1–62
10 Diagnostics For Non DTC Faults
10.1 PRND32L Display Diagnostics
Circuit Description
The powertrain interface module (PIM) receives transmission gear status via the GM Lan serial data bus from the
transmission control module (TCM) it is then sent to the instrument cluster by the PIM via a series of hard wired
connections to illuminate the appropriate gear position indicator within the instrument cluster. Some of these components
do not set a DTC, in the event of a component failure. The following diagnostic procedures are devised to assist in these
cases.
Additional Information
• Refer to 7.2 Diagnostic System Check to monitor DTC’s.
• Refer to 8A Electrical Body and Chassis for the following information:
• Automatic transmission Neutral Start and Back-up Lamp Switch and wiring,
• TCM wiring diagram.
• Refer to 6 W iring Diagram and Connector Chart for the following information:
• PIM connector illustration and terminal assignment, and
• PIM wiring diagram.
• For intermittent faults, refer to Intermittent Fault Conditions.
• Check for an intermittent fault in the wiring harness or connectors, if a fault cannot be found the system is
serviceable.
Since fault conditions in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this diagnostic
procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component. Refer to 8A Electrical - Body
and Chassis for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
Test Description
The following numbers refer to the step numbers in the diagnostic table:
1 This step tests for DTC’s in the overall system.
2 This step manually tests the PRND32L display.
4 This step uses Tech 2 to drive each indicator on.
7 This step tests for shorts to voltage.
8 This step tests neutral start and back-up lamp switch and automatic transmission.
12 This step tests the instrument cluster circuits.
15 This step manually tests the PRND32L display.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3724 of 6020
Powertrain Interface Module – V6 Page 6E1–63
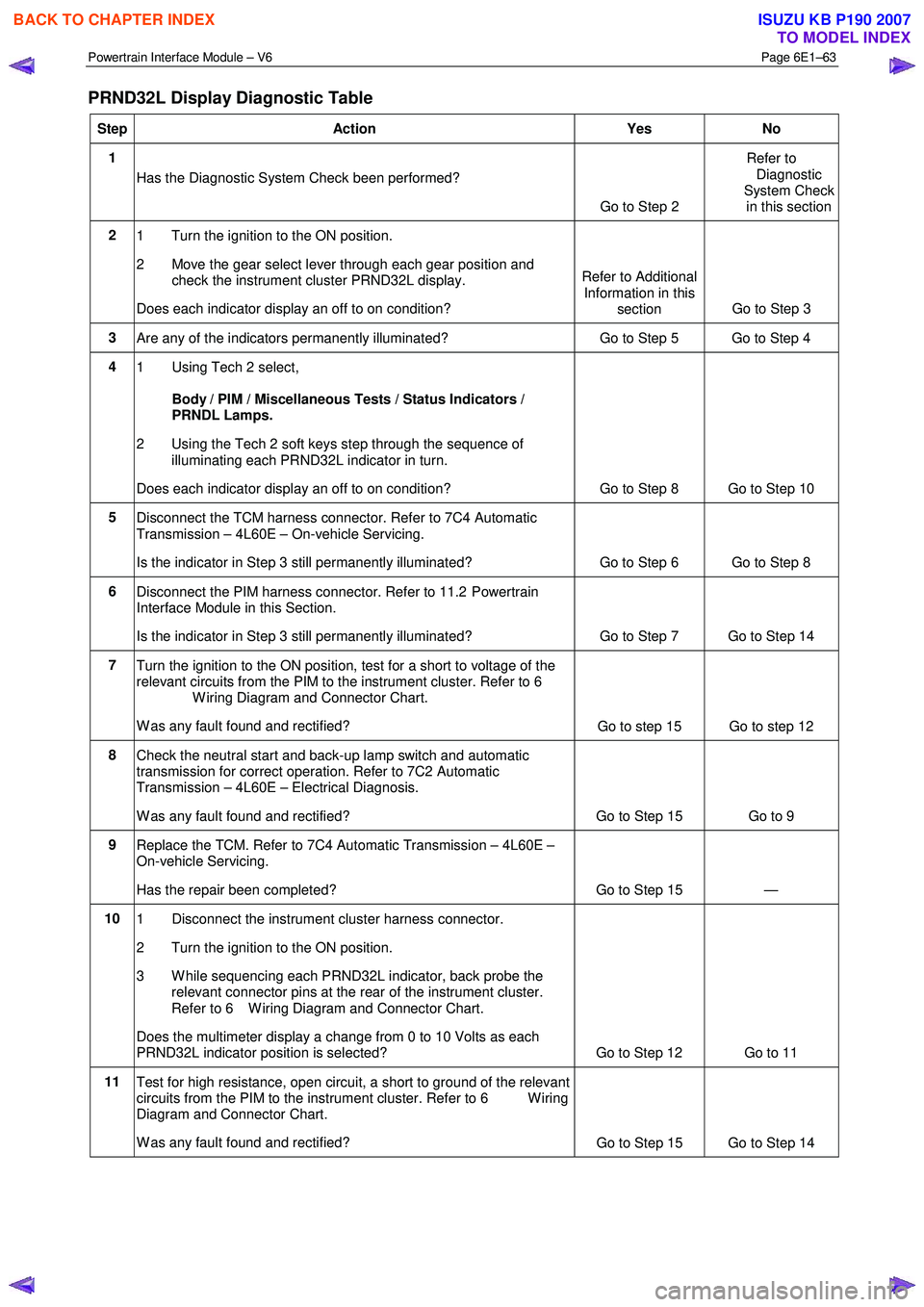
PRND32L Display Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1
Has the Diagnostic System Check been performed?
Go to Step 2 Refer to
Diagnostic
System Check in this section
2 1 Turn the ignition to the ON position.
2 Move the gear select lever through each gear position and check the instrument cluster PRND32L display.
Does each indicator display an off to on condition? Refer to Additional
Information in this section Go to Step 3
3
Are any of the indicators permanently illuminated? Go to Step 5 Go to Step 4
4 1 Using Tech 2 select,
Body / PIM / Miscellaneous Tests / Status Indicators /
PRNDL Lamps.
2 Using the Tech 2 soft keys step through the sequence of illuminating each PRND32L indicator in turn.
Does each indicator display an off to on condition? Go to Step 8 Go to Step 10
5
Disconnect the TCM harness connector. Refer to 7C4 Automatic
Transmission – 4L60E – On-vehicle Servicing.
Is the indicator in Step 3 still permanently illuminated? Go to Step 6 Go to Step 8
6 Disconnect the PIM harness connector. Refer to 11.2 Powertrain
Interface Module in this Section.
Is the indicator in Step 3 still permanently illuminated? Go to Step 7 Go to Step 14
7
Turn the ignition to the ON position, test for a short to voltage of the
relevant circuits from the PIM to the instrument cluster. Refer to 6
W iring Diagram and Connector Chart.
W as any fault found and rectified? Go to step 15 Go to step 12
8
Check the neutral start and back-up lamp switch and automatic
transmission for correct operation. Refer to 7C2 Automatic
Transmission – 4L60E – Electrical Diagnosis.
W as any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 15 Go to 9
9 Replace the TCM. Refer to 7C4 Automatic Transmission – 4L60E –
On-vehicle Servicing.
Has the repair been completed? Go to Step 15 —
10 1 Disconnect the instrument cluster harness connector.
2 Turn the ignition to the ON position.
3 W hile sequencing each PRND32L indicator, back probe the relevant connector pins at the rear of the instrument cluster.
Refer to 6 W iring Diagram and Connector Chart.
Does the multimeter display a change from 0 to 10 Volts as each
PRND32L indicator position is selected? Go to Step 12 Go to 11
11 Test for high resistance, open circuit, a short to ground of the relevant
circuits from the PIM to the instrument cluster. Refer to 6 W iring
Diagram and Connector Chart.
W as any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 15 Go to Step 14
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3725 of 6020
Powertrain Interface Module – V6 Page 6E1–64
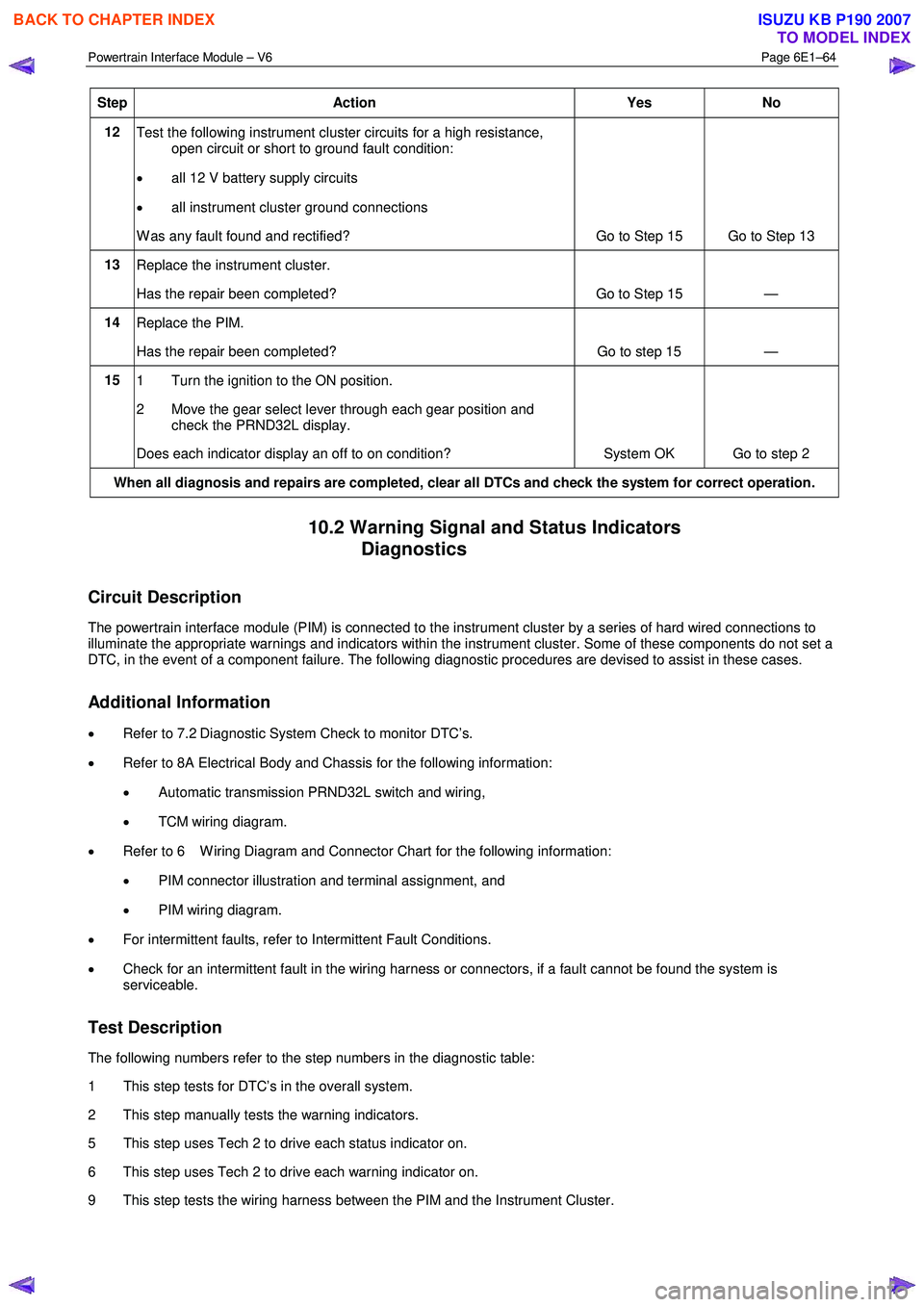
Step Action Yes No
12
Test the following instrument cluster circuits for a high resistance,
open circuit or short to ground fault condition:
• all 12 V battery supply circuits
• all instrument cluster ground connections
W as any fault found and rectified? Go to Step 15 Go to Step 13
13 Replace the instrument cluster.
Has the repair been completed? Go to Step 15 —
14 Replace the PIM.
Has the repair been completed? Go to step 15 —
15 1 Turn the ignition to the ON position.
2 Move the gear select lever through each gear position and check the PRND32L display.
Does each indicator display an off to on condition? System OK Go to step 2
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, clear all DTCs and check the system for correct operation.
10.2 Warning Signal and Status Indicators Diagnostics
Circuit Description
The powertrain interface module (PIM) is connected to the instrument cluster by a series of hard wired connections to
illuminate the appropriate warnings and indicators within the instrument cluster. Some of these components do not set a
DTC, in the event of a component failure. The following diagnostic procedures are devised to assist in these cases.
Additional Information
• Refer to 7.2 Diagnostic System Check to monitor DTC’s.
• Refer to 8A Electrical Body and Chassis for the following information:
• Automatic transmission PRND32L switch and wiring,
• TCM wiring diagram.
• Refer to 6 W iring Diagram and Connector Chart for the following information:
• PIM connector illustration and terminal assignment, and
• PIM wiring diagram.
• For intermittent faults, refer to Intermittent Fault Conditions.
• Check for an intermittent fault in the wiring harness or connectors, if a fault cannot be found the system is
serviceable.
Test Description
The following numbers refer to the step numbers in the diagnostic table:
1 This step tests for DTC’s in the overall system.
2 This step manually tests the warning indicators.
5 This step uses Tech 2 to drive each status indicator on.
6 This step uses Tech 2 to drive each warning indicator on.
9 This step tests the wiring harness between the PIM and the Instrument Cluster.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3726 of 6020
Powertrain Interface Module – V6 Page 6E1–65
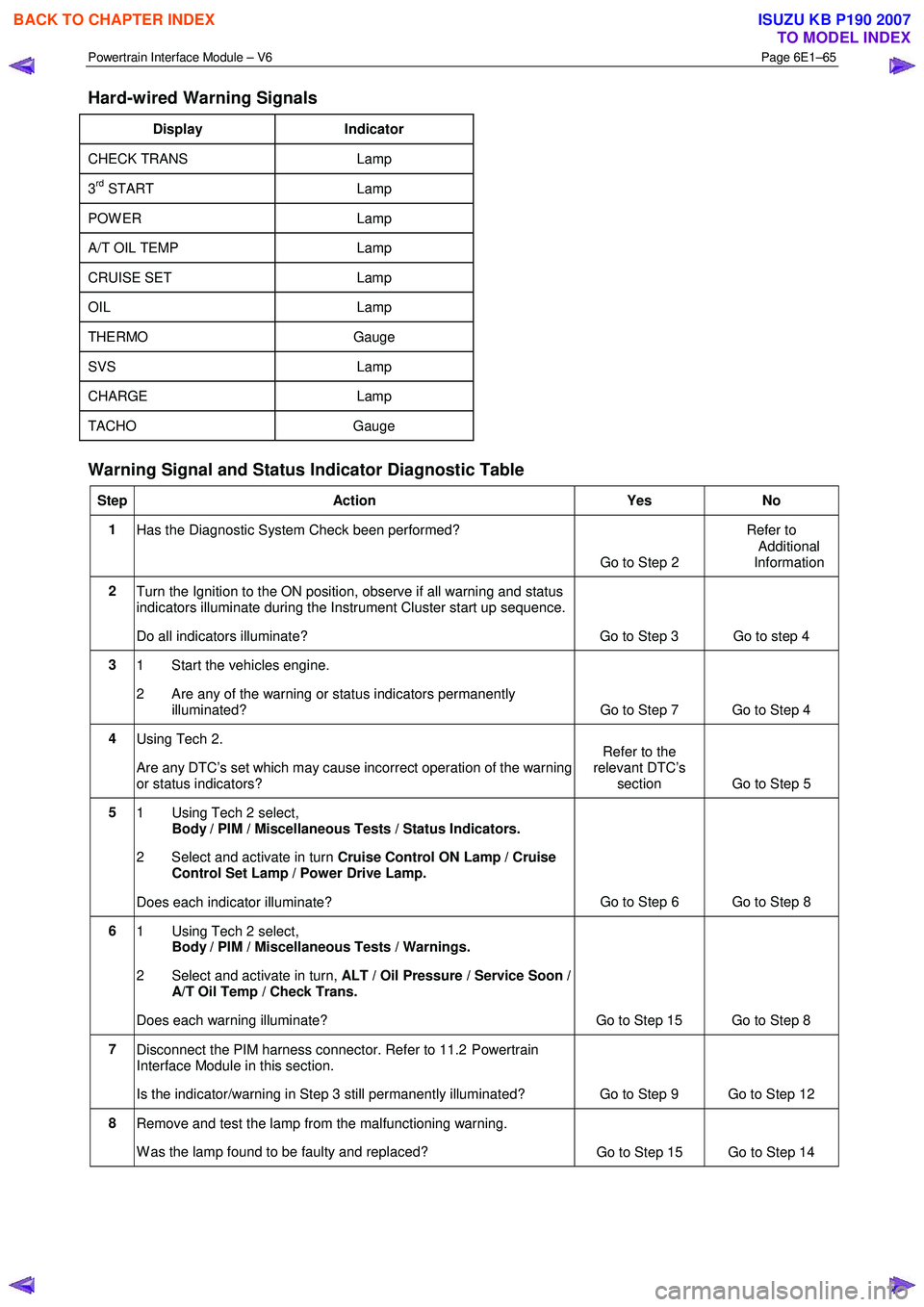
Hard-wired Warning Signals
Display Indicator
CHECK TRANS Lamp
3rd START Lamp
POW ER Lamp
A/T OIL TEMP Lamp
CRUISE SET Lamp
OIL Lamp
THERMO Gauge
SVS Lamp
CHARGE Lamp
TACHO Gauge
Warning Signal and Status Indicator Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1
Has the Diagnostic System Check been performed?
Go to Step 2 Refer to
Additional
Information
2 Turn the Ignition to the ON position, observe if all warning and status
indicators illuminate during the Instrument Cluster start up sequence.
Do all indicators illuminate? Go to Step 3 Go to step 4
3 1 Start the vehicles engine.
2 Are any of the warning or status indicators permanently illuminated? Go to Step 7 Go to Step 4
4 Using Tech 2.
Are any DTC’s set which may cause incorrect operation of the warning
or status indicators? Refer to the
relevant DTC’s section Go to Step 5
5
1 Using Tech 2 select,
Body / PIM / Miscellaneous Tests / Status Indicators.
2 Select and activate in turn Cruise Control ON Lamp / Cruise
Control Set Lamp / Power Drive Lamp.
Does each indicator illuminate? Go to Step 6 Go to Step 8
6
1 Using Tech 2 select,
Body / PIM / Miscellaneous Tests / Warnings.
2 Select and activate in turn, ALT / Oil Pressure / Service Soon /
A/T Oil Temp / Check Trans.
Does each warning illuminate? Go to Step 15 Go to Step 8
7 Disconnect the PIM harness connector. Refer to 11.2 Powertrain
Interface Module in this section.
Is the indicator/warning in Step 3 still permanently illuminated? Go to Step 9 Go to Step 12
8 Remove and test the lamp from the malfunctioning warning.
W as the lamp found to be faulty and replaced? Go to Step 15 Go to Step 14
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3728 of 6020
Powertrain Interface Module – V6 Page 6E1–67
10.3 Tachometer Diagnostics
Circuit Description
The powertrain interface module (PIM) receives the tachomer signal from the engine control module (ECM), it is then
sent to the instrument cluster by the PIM via a hard wired connection to drive the tachometer which displays the engine
RPM. Some of these components do not set a DTC, in the event of a component failure. The following diagnostic
procedures are devised to assist in these cases.
Additional Information
• Refer to 7.2 Diagnostic System Check to monitor DTC’s.
• Refer to 8A Electrical Body and Chassis for the following information:
• ECM wiring diagram.
• Refer to 6 W iring Diagram and Connector Chart for the following information:
• PIM connector illustration and terminal assignment, and
• PIM wiring diagram.
• For intermittent faults, refer to Intermittent Fault Conditions.
• Check for an intermittent fault in the wiring harness or connectors, if a fault cannot be found the system is
serviceable.
Since fault conditions in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this diagnostic
procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component. Refer to 8A Electrical - Body
and Chassis for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
Test Description
The following numbers refer to the step numbers in the diagnostic table:
1 This step tests for DTC’s in the overall system.
2 This step uses the instrument cluster self test to check the function of the tachometer.
3 This step uses Tech 2 to drive the tachometer.
6 This step tests for tachometer drive frequency.
10 This step tests the in-vehicle function of the tachometer.
Tachometer Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1
Has the Diagnostic System Check been performed?
Go to Step 2 Refer to
Additional
Information
2 Test the function of the tachometer using the instrument cluster self
diagnostic test procedure, refer to 8A Electrical Body and Chassis.
Does the tachometer display 3000 RPM? Go to Step 3 Go to Step 7
3 1 Using Tech 2 select,
Body / PIM / Miscellaneous Tests / Gauge Control Tests /
Tachometer.
2 Using the Tech 2 soft keys step the tacho through different RPM ranges.
Does the tachometer respond to the Tech 2 commands? Go to Step 5 Go to Step 4
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3730 of 6020

Powertrain Interface Module – V6 Page 6E1–69
10.4 Temperature Gauge Diagnostics
Circuit Description
The powertrain interface module (PIM) receives engine temperature status via the GM Lan serial data bus from the
engine control module (ECM) it is then sent to the instrument cluster by the PIM via a hard wired connection to drive the
temperature gauge to the appropriate position. Some of these components do not set a DTC, in the event of a
component failure. The following diagnostic procedures are devised to assist in these cases.
Additional Information
• Refer to 7.2 Diagnostic System Check to monitor DTC’s.
• Refer to 8A Electrical Body and Chassis for the following information:
• ECM wiring diagram.
• Refer to 6 W iring Diagram and Connector Chart for the following information:
• PIM connector illustration and terminal assignment, and
• PIM wiring diagram.
• For intermittent faults, refer to Intermittent Fault Conditions.
• Check for an intermittent fault in the wiring harness or connectors, if a fault cannot be found the system is
serviceable.
Since fault conditions in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this diagnostic
procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component. Refer to 8A Electrical - Body
and Chassis for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
Test Description
The following numbers refer to the step numbers in the diagnostic table:
1 This step tests for DTC’s in the overall system.
2 This step uses the instrument cluster self test to check the function of the temperature gauge.
3 This step uses Tech 2 to drive the temperature gauge.
6 This step tests for set DTC’s in the ECM.
11 This step tests the in-vehicle function of the temperature gauge.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007