2007 ISUZU KB P190 Harness
[x] Cancel search: HarnessPage 3732 of 6020

Powertrain Interface Module – V6 Page 6E1–71
11 Service Operations
11.1 Safety and Precautionary Measures
The following safety and precautionary
measures must be followed when servicing
and diagnosing the powertrain interface
module (PIM) System. Otherwise, personal
injury and / or improper braking system
operation may occur:
• W hen using electric welding equipment, disconnect the wiring harness connector from the PIM.
• Never disconnect or reconnect the PIM wiring harness connector when the ignition is switched ON.
• Do not touch the PIM connector pins or soldered components on the PIM circuit board to prevent possible
Electrostatic Discharge damage.
• To avoid wiring connector terminal damage, always use suitable wiring harness test leads (such as those in Tool
No, J35616) when performing tests on the PIM wiring connector.
• The PIM is extremely sensitive to Electro Magnetic Interference (EMI). Ensure the PIM wiring harness is routed
correctly and securely fitted to mounting clips when performing service procedures.
• Due to the sensitive nature of the PIM circuitry, specific wiring repair procedures have been developed. These
procedures and instructions are detailed in 8A Electrical - Body and Chassis and are the only recommended and
approved wiring repair methods.
• Ensure that all wiring harness connectors are seated correctly.
• Never disconnect the battery from the vehicle electrical system while the engine is running.
• Always disconnect the battery from the vehicle electrical system before charging.
• Do not use a fast charger for starting the vehicle.
• Ensure the battery cable terminals are secure.
• Before installing a new PIM, ensure the correct type is fitted. Always refer to the latest spare parts information.
11.2 Powertrain Interface Module
Do not touch the powertrain interface module
pins as Electrostatic Discharge (ESD) damage
may result. For further information on ESD,
refer to 1.2 Warning Caution and Notes.
When replacing the PIM, the PIM must be
reset prior to removal. Failure to perform this
procedure will result in the inability to:
• Test the PIM for warranty purposes.
• Install the PIM into other vehicles.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3733 of 6020

Powertrain Interface Module – V6 Page 6E1–72
Remove
1 If replacing the PIM, reset the PIM prior to PIM removal. Refer to PIM Reset in this Section.
2 Turn the ignition switch off.
3 Remove Fuse EB-4, refer to 8A Electrical-Body and Chassis.
4 Remove the right-hand front body hinge pillar trim assembly, refer to 10 Cab.
5 Disconnect the wiring harness connector (1) from the powertrain interface module (PIM) (2).
6 Remove the bolt (3) attaching the PIM to the hinge pillar inner panel.
Figure 6E1 – 16
Reinstall
Reinstallation of the PIM is the reverse of the removal procedure, noting the following:
1 Tighten the attaching bolt to the correct torque specification.
PIM attaching bolt
torque specification ...................................8.0 – 12.0 Nm
2 If the PIM has been replaced, perform the following procedures: • PIM service programming, refer to 12.4 Immobiliser Link to ECM / PIM.
• PIM Configuration, refer to 12.3 PIM Configuration.
• Diagnostic system check, refer to 7.2 Diagnostic System Check.
3 Road test the vehicle and check for correct vehicle operation.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3755 of 6020
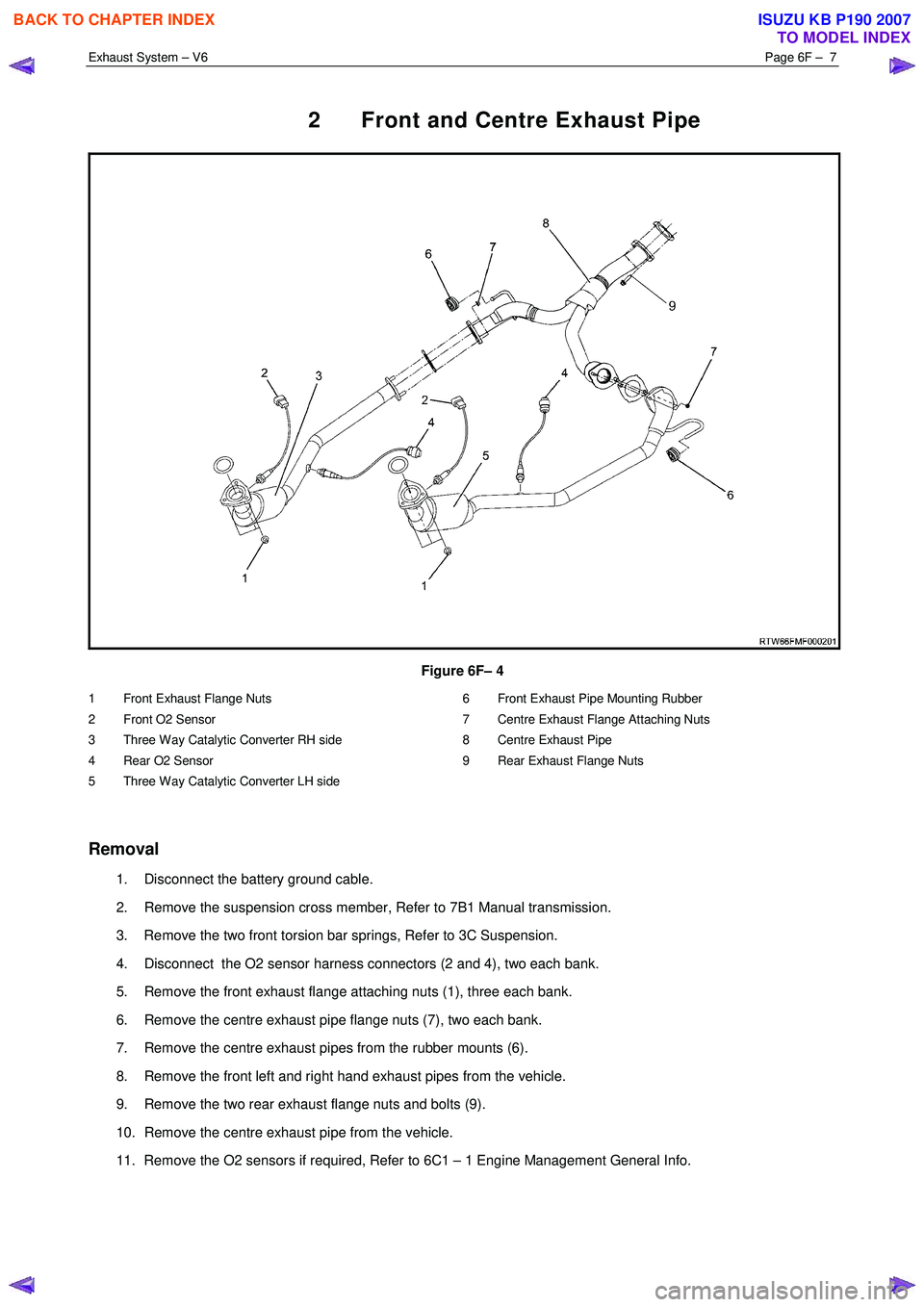
Exhaust System – V6 Page 6F – 7
2 Front and Centre Exhaust Pipe
Figure 6F– 4
1 Front Exhaust Flange Nuts
2 Front O2 Sensor
3 Three Way Catalytic Converter RH side
4 Rear O2 Sensor
5 Three Way Catalytic Converter LH side 6 Front Exhaust Pipe Mounting Rubber
7 Centre Exhaust Flange Attaching Nuts
8 Centre Exhaust Pipe
9 Rear Exhaust Flange Nuts
Removal
1. Disconnect the battery ground cable.
2. Remove the suspension cross member, Refer to 7B1 Manual transmission.
3. Remove the two front torsion bar springs, Refer to 3C Suspension.
4. Disconnect the O2 sensor harness connectors (2 and 4), two each bank.
5. Remove the front exhaust flange attaching nuts (1), three each bank.
6. Remove the centre exhaust pipe flange nuts (7), two each bank.
7. Remove the centre exhaust pipes from the rubber mounts (6).
8. Remove the front left and right hand exhaust pipes from the vehicle.
9. Remove the two rear exhaust flange nuts and bolts (9).
10. Remove the centre exhaust pipe from the vehicle.
11. Remove the O2 sensors if required, Refer to 6C1 – 1 Engine Management General Info.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3756 of 6020

Exhaust System – V6 Page 6F – 8
NOTE:
• Support the exhaust system at all times.
• Clean the threads of the attaching bolts, nuts,
studs and flanges with a suitable cleaning
solvent.
• Apply a high temperature anti-seize
compound to the manifold front pipe flange
joint studs, then align the flange over the
studs.
Reinstallation
1. Install any removed O2 sensors, Refer to 6C1 – 1 Engine Management General Info.
2. Position the centre exhaust pipe into location under the vehicle.
3. Install the two rear exhaust flange nuts and bolts (9).
4. Position the front exhaust pipes into location under the vehicle.
5. Install the centre exhaust pipes into the rubber mounts (6).
6. Install the exhaust flange fixing nuts (1), three each bank.
7. Install the rear exhaust pipe flange nuts (7), two each bank.
8. Reconnect the O2 sensor harness connectors (4), two each bank.
9. Install the two front torsion bar springs, Refer to 3C Suspension.
10. Install the suspension cross member, Refer to 7B1 Manual transmission.
11. Reconnect the battery ground cable.
O2 Sensor
tightening torque.....................................................50 Nm
Front Exhaust Flange Nuts
tightening torque.......................................40.0 – 60.0 Nm
Centre Exhaust Flange Nuts
tightening torque.....................................................43 Nm
Rear Exhaust Flange Nuts
tightening torque.....................................................43 Nm
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3785 of 6020
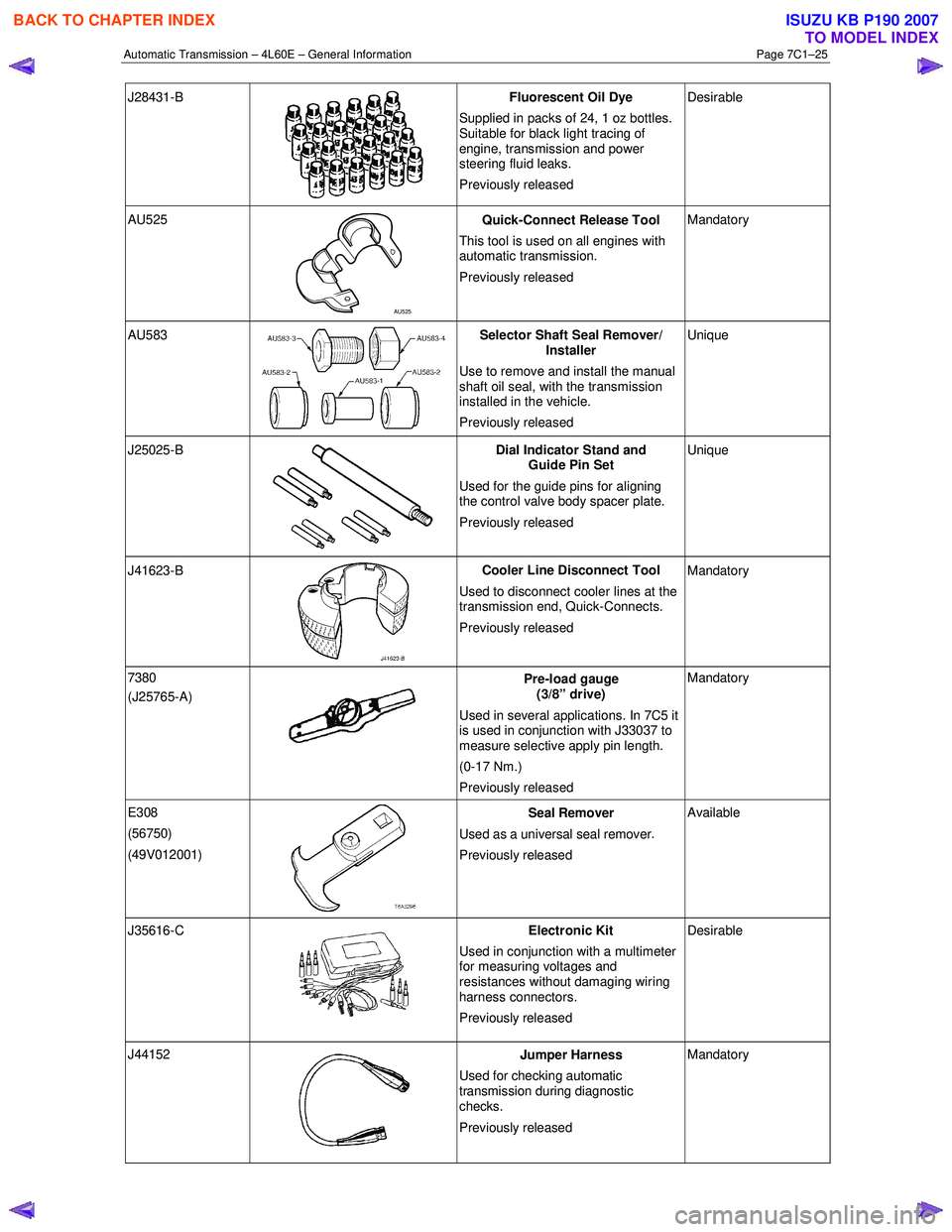
Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – General Information Page 7C1–25
J28431-B
Fluorescent Oil Dye
Supplied in packs of 24, 1 oz bottles.
Suitable for black light tracing of
engine, transmission and power
steering fluid leaks.
Previously released Desirable
AU525
AU525 Quick-Connect Release Tool
This tool is used on all engines with
automatic transmission.
Previously released Mandatory
AU583 Selector Shaft Seal Remover/
Installer
Use to remove and install the manual
shaft oil seal, with the transmission
installed in the vehicle.
Previously released Unique
J25025-B
Dial Indicator Stand and
Guide Pin Set
Used for the guide pins for aligning
the control valve body spacer plate.
Previously released Unique
J41623-B
Cooler Line Disconnect Tool
Used to disconnect cooler lines at the
transmission end, Quick-Connects.
Previously released Mandatory
7380
(J25765-A)
Pre-load gauge
(3/8” drive)
Used in several applications. In 7C5 it
is used in conjunction with J33037 to
measure selective apply pin length.
(0-17 Nm.)
Previously released Mandatory
E308
(56750)
(49V012001)
Seal Remover
Used as a universal seal remover .
Previously released Available
J35616-C
Electronic Kit
Used in conjunction with a multimeter
for measuring voltages and
resistances without damaging wiring
harness connectors.
Previously released Desirable
J44152
Jumper Harness
Used for checking automatic
transmission during diagnostic
checks.
Previously released Mandatory
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3796 of 6020

Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – Electrical Diagnosis Page 7C2–10
Limp Home Mode Description
If a major electrical system failure occurs which could affect vehicle safety or damage the transmission during normal
operation, the TCM enters a limp home mode. In the limp home mode, the transmission operates in the following
manner:
• The pressure control solenoid is off and the line pressure is at maximum to minimise clutch slippage.
• The TCC solenoid is off, therefore the torque converter clutch is disabled.
• The two shift solenoids are turned off. The transmission will operate in fourth gear if the vehicle has successfully
completed a 1-2 upshift in the current ignition cycle. If the vehicle has not completed a 1-2 upshift in the current
ignition cycle, the transmission will operate in third gear. If the transmission is operating in fourth gear, third gear
may be obtained if the engine is stopped briefly and re-started.
In limp home mode, the gear selector lever is ineffective at selecting forward gear ranges. In third or fourth gear, heat
builds up in the transmission quickly, particularly in stop and go traffic. Excessive heat build-up may cause transmission
failure if the vehicle is driven for extended distances in limp home mode.
1.3 Transmission Indicators and Messages
For information pertaining to the instrument cluster and the transmission information it displays, refer to the RA Rodeo
Owner Handbook.
1.4 Electronic Component Description
For all other electrical components not covered in this section, refer to General Motors Powertrain Group Electronically
Controlled Automatic Transmission Technician's Guide.
Transmission Control Module (TCM)
The Transmission Control Module (TCM) is located under the instrument panel, next to the brake pedal assembly and
connects directly to the transmission wiring harness. A single 49-way connector is used to make the connection between
the vehicle wiring harness and the TCM.
To access the connector for diagnosis:
1 Ensure the ignition switch is in the OFF position.
2 Disconnect the connector (1) from the transmission control module (TCM) (2) as follows, refer to Figure 7C2 – 2: a remove the securing pin (3),
b press the locking tab and swing the lever (4) to free the connector,
c remove the connector.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3813 of 6020

Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – Electrical Diagnosis Page 7C2–27
4 Diagnostics
4.1 Introduction
The transmission diagnostic procedure is organised in a logical structure that begins with the diagnostic system check
and as such must always be used as the starting point. The diagnostic system check directs the technician to the logical
steps necessary to diagnose a transmission driveability fault condition.
4.2 Basic Knowledge Required
A lack of basic understanding regarding
electronics, electrical wiring circuits and use
of electrical circuit testing tools when
performing any diagnostic procedure, could
result in incorrect diagnostic results or
damage to system components.
Understanding of the following is required to perform any of the diagnostic procedures detailed in this Service
Information:
• Basic electronics,
• Electrical wiring circuits,
• Electrical circuits testing, and
• Correct use of basic system diagnostic tools.
4.3 Diagnostic Precautions
When tests are required on connector
terminals, use the adapters in connector
adaptor kit J35616-C to prevent damage to
terminals.
The following precautions must be observed when performing all diagnostic procedures. Otherwise, incorrect diagnostic
results or damage to system components will occur:
1 Disconnection of the battery affects certain vehicle electronic systems.
2 Disconnect the battery negative lead when performing the following procedures:
• Disconnecting the electronic control module wiring harness connector/s or
• Charging the battery.
3 Disconnect the battery terminal ground lead and the electronic control module wiring harness connector before attempting any electric arc welding on the vehicle.
4 Do not start the engine if the battery terminal is not properly secured to the battery.
5 Do not disconnect or reconnect any of the following while the ignition is switched on or when the engine is running:
• Any electronic control module or system component electrical wiring connector, or
• Battery terminal leads.
6 Ensure that the correct procedure for disconnecting and connecting system electrical wiring harness connectors is always followed. For information on the correct procedure for disconnecting and connecting specific wiring
connectors, refer to 8A Electrical-Body and Chassis.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3814 of 6020

Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – Electrical Diagnosis Page 7C2–28
7 Ensure that all wiring harness connectors are fitted correctly and secure.
8 W hen steam or pressure cleaning vehicle components, such as engines, transmissions, etc., do not direct the cleaning nozzle at any system electrical wiring harness connectors or components.
9 Do not clear any DTCs unless instructed.
10 The fault must be present when using the Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Diagnostic Tables. Otherwise, misdiagnosis or replacement of good parts may occur.
11 Do not touch any electronic control module connector pins or soldered components on the circuit board. This is required to avoid the possibility of electrostatic discharge damage.
12 Use only the test equipment specified in the diagnostic tables, as other test equipment may give incorrect results or damage good components.
13 Electronic control modules are designed to withstand normal current draws associated with vehicle operation. However, the following fault conditions or incorrect test procedure may overload internal control module circuits and
irreparably damage the control module:
• A short to voltage fault condition in any of the control module low reference circuits may cause internal and/or
sensor damage. Therefore, any short to voltage fault condition in the control module low reference circuits
must be rectified before replacing a faulty component.
• A short to ground fault condition in any of the control module 5 volts reference circuits may cause internal
control module and/or sensor damage. Therefore, any short to ground fault condition in the control module 5
volt reference circuits must be rectified before replacing a faulty component.
• W hen using a test light to test an electrical circuit, do not use any of the control module low reference circuits
or 5 volts reference circuits as a reference point. Otherwise, excessive current draw from the test light may
damage the control module.
14 Disregard DTCs that set while performing the following diagnostic Steps:
• Using the Tech 2 output control function, or
• Disconnecting a control module system sensor connector then switching the ignition ON.
15 After completing the required diagnostics and service operations, road test the vehicle to ensure correct system operation.
4.4 Preliminary Checks
The Preliminary Checks is a set of visual and physical checks or inspections that may quickly identify a control module
system fault condition:
1 Refer to relevant Service Techlines for information regarding the fault condition.
2 Ensure that the battery is fully charged.
3 Inspect the battery connections for corrosion or a loose terminal.
4 Ensure that all relevant control module system related fuses are serviceable.
5 Inspect for incorrect aftermarket theft deterrent devices, lights or mobile phone installation.
6 Ensure that there is no speaker magnet positioned too close to any electronic module that contains relays.
7 Inspect the system wiring harness for proper connections, pinches or cuts.
8 Ensure that all control module related electrical wiring connectors are fitted correctly.
9 Inspect the control module ground connections for corrosion, loose terminal or incorrect position.
10 Ensure that the resistance between the control module housing and the battery ground cable is less than 0.5 ohms.
11 Check that the control module and its mounting bracket is secure.
12 Check all control module related components for correct installation.
13 Check the control module and related wiring harness routing to ensure that no rubbing or cutting of the wiring harness by sharp body components can occur.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007