2007 ISUZU KB P190 air condition
[x] Cancel search: air conditionPage 2823 of 6020

Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–46
Page 6A1–46
2.16 Cylinder Leakage Test
A leakage test may be performed to measure cylinder/combustion chamber leakage. High cylinder leakage may indicate
one or more of the following:
• worn or burnt valves,
• broken valve springs,
• stuck valve lifters,
• incorrect valve lash/adjustment,
• damaged piston,
• worn piston rings,
• worn or scored cylinder bore,
• damaged cylinder head gasket,
• cracked or damaged cylinder head, or
• cracked or damaged engine block.
1 Disconnect the battery ground negative cable.
2 Remove the spark plugs from all cylinders, refer to Section 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 – Service Operations.
3 Rotate the crankshaft to place the piston in the cyli nder being tested at top dead centre (TDC) of the compression
stroke.
4 Install a commercially available cylinder head leak down tester into the spark plug hole.
NOTE
If required, hold the crankshaft balancer bolt to
prevent the engine from rotating.
5 Apply shop air pressure to the cylinder head leak dow n tester and adjust according to the manufacturers
instructions.
6 Record the cylinder leakage value. Cylinder leakage t hat exceeds 25 percent is considered excessive and may
require component service. In excessive leakage situations, inspect for the following conditions:
• air leakage sounds at the throttle body or air inlet duct that may indicate a worn or burnt intake valve or a
broken valve spring,
• air leakage sounds at the exhaust system tailpipe that may indicate a worn or burnt exhaust valve or a broken
valve spring,
• air leakage sounds from the crankcase, oil level indicator tube, or oil fill tube that may indicate worn piston
rings, a damaged piston, a worn or scored cylinder bore, a damaged engine block or a damaged cylinder
head, or
• air bubbles in the cooling system may indicate a damaged cylinder head or a damaged cylinder head gasket.
7 Perform the leakage test on the rema ining cylinders and record the values.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2828 of 6020
Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–51
Page 6A1–51
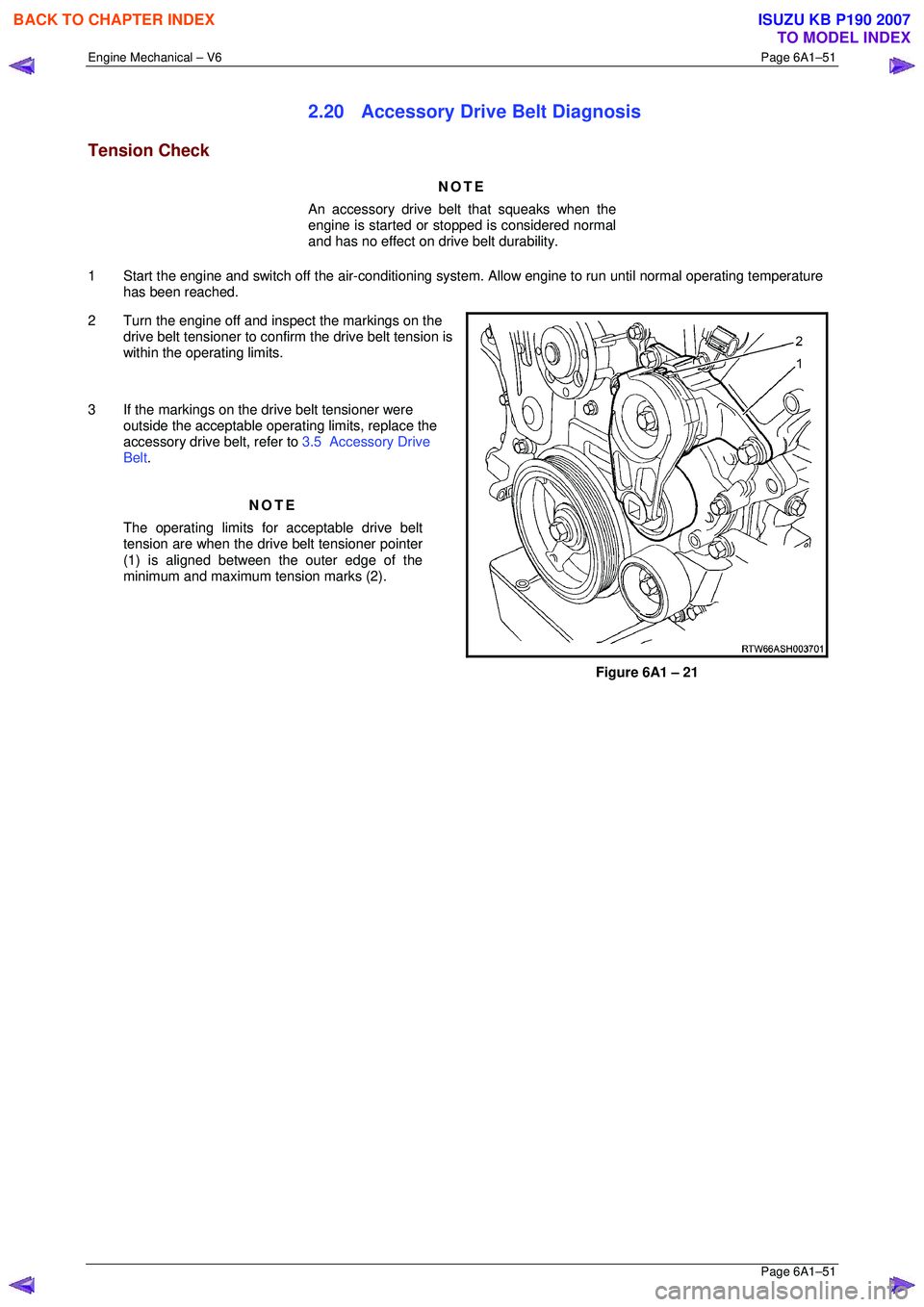
2.20 Accessory Drive Belt Diagnosis
Tension Check
NOTE
An accessory drive belt that squeaks when the
engine is started or st opped is considered normal
and has no effect on drive belt durability.
1 Start the engine and switch off the air-conditioning system . Allow engine to run until normal operating temperature
has been reached.
2 Turn the engine off and inspect the markings on the drive belt tensioner to confi rm the drive belt tension is
within the operating limits.
3 If the markings on the drive belt tensioner were outside the acceptable operat ing limits, replace the
accessory drive belt, refer to 3.5 Accessory Drive
Belt .
NOTE
The operating limits for acceptable drive belt
tension are when the driv e belt tensioner pointer
(1) is aligned between the outer edge of the
minimum and maximum tension marks (2).
Figure 6A1 – 21
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2830 of 6020

Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–53
Page 6A1–53
Drive Belt Chirp
Definition
Accessory drive belt chirping can be defined as a high-pitched noise that is heard once per revolution of the drive belt or
a pulley.
NOTE
Chirping during start-up in cold damp conditions
that abates once the engine reaches operating
temperature is considered normal.
Diagnostic Aids
The symptom may be intermittent due to moisture on the driv e belts or pulleys. It may be necessary to spray a small
amount of water on the drive belt to dup licate and confirm a customers concern. If spraying water onto the drive belt
system duplicates the symptom, cleaning the belt pulleys may be the solution.
A loose or incorrectly installed body component, suspension component or other item may be the cause of the noise.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to steps in the diagnostic table.
2 The noise may not be engine related. This step is to confirm the engine is making t he noise. If the engine is not
making the noise, do not proceed further with this diagnostic procedure.
3 The noise may be an internal engine noise. Removing the drive belt and operating the engine briefly will confirm
whether or not the noise is related to the drive belt.
CAUTION
When running the engine with the accessory
drive belt removed, the coolant pump will not
be operating and the engine may overheat if
left unsupervised even for a short period.
NOTE
There may also be a number of DTCs set when
running the engine with the accessory drive belt
removed.
4 Inspect all drive pump pulleys for pilling. NOTE
Pilling is the small balls (p ills) or strings of rubber
in the belt grooves caused by the accumulation of
rubber dust.
6 Misalignment of the accessory drive system pulleys ma y be caused by incorrect mounting of an accessory drive
component (A/C compressor, generator etc.) or pulley. Misa lignment may also be caused by incorrect installation of
a pulley during a previous repair. Test for a misaligned pulley using a straight edge in the pulley grooves across
two or three pulleys. If a misaligned pulley is found, refer to the relevant component service information for the
correct installation and removal procedures.
10 Inspecting the fasteners can elim inate the possibility that an incorrect fastener has been installed.
12 Inspecting the pulleys for being bent should include inspec ting for a dent or other damage that would prevent the
drive belt from not seating correctly in all of the pulley grooves or on the smooth surface when the back end of the
belt is used as the driving surface.
14 Replacing the drive belt when it is not damaged and there is no excessive p illing will only be a temporary repair.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2832 of 6020

Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–55
Page 6A1–55
Drive Belt Squeal
Definition
Accessory drive belt squealing can be defined as a loud screeching noise caused by a slipping drive belt. Belt squeal is
unusual in multi-rib belts. Drive belt squeal generally occurs when a heavy load is applied to the drive belt, such as an
air-conditioning compressor engagement, snapping the throttle, se ized pulley or a faulty accessory drive component.
Diagnostic Aids
If the noise is intermittent, confirm the accessory drive components by varying t heir loads, making sure they are operated
to their maximum capacity. An overcharged A/C system, restrictions in the power steering pressure circuit or a faulty
generator or coolant pump are likely c auses of accessory drive belt squeal.
A loose or incorrectly installed body component, suspension component or other item may be the cause of the noise.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to steps in the diagnostic table.
2 The noise may not be engine related. This step is to confirm the engine is making t he noise. If the engine is not
making the noise, do not proceed further with this diagnostic procedure.
3 The noise may be an internal engine noise. Removing the drive belt and operating the engine briefly will confirm
whether or not the noise is related to the drive belt.
CAUTION
When running the engine with the accessory
drive belt removed, the coolant pump will not
be operating and the engine may overheat if
left unsupervised even for a short period.
NOTE
There may also be a number of DTCs set when
running the engine with the accessory drive belt
removed.
4 Confirms an accessory drive component does not have a se ized bearing. With the belt removed, test the bearings
in the accessory drive co mponents spin free and smooth.
5 Confirms the drive belt tensioner is operating correctly. If the drive belt tensioner is not operating correctly, drive
belt tension will not be maintained, resulting in a belt squealing noise
6 Confirms the belt is not too long, which would prevent the tensioner from working as intended. Also, if an
excessively long belt has been fitted, it may also be r outed incorrectly and may be turning an accessory drive
component in the wrong direction.
7 Misalignment of the pulleys may be caused by one of the following:
• Incorrect mounting of an accessory drive component,
• Incorrect installation of an accessory drive pulley or,
• Bent or damaged pulley.
Test for a misaligned pulley using a straight edge in the pulley grooves across 2 or 3 pulleys. If a misaligned pulley is found, refer to the relevant component service info rmation for the correct installation and removal procedures.
8 This test is to confirm the pulleys are the correct di ameter and/or width. Using a known good vehicle, compare the
pulley sizes.
Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1
Did you review the information provided in 2.2 Symptoms, and
perform the required inspections. Go to Step 2 Go to
2.2 Symptoms
2 Confirm the customer compla int. Is there a squealing noise?
Go to Step 3 Refer to Diagnostic
Aids in this Section
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2839 of 6020
Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–62
Page 6A1–62
Drive Belt Falls Off
Definition
The drive belt falls off during normal operation or does not ride correctly on the accessory drive pulleys.
Diagnostic Aids
If the accessory drive belt repeatedly falls off the drive pulleys, this is most likely due to pulley misalignment.
An extra load that is quickly applied and released by an a ccessory drive component (e.g. A/C compressor) may cause
the accessory drive belt to fall off. In th is circumstance, confirm the fault by operating the accessory drive components in
turn, noting which one caused the belt to fall off.
Lack of drive belt tension may also cause the belt to fall o ff the pulleys. Low drive belt tension could be caused by one of
the following:
• an incorrect drive belt length,
• a faulty drive belt tensioner, or
• a stretched or faulty drive belt.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to steps in the diagnostic table.
2 Confirms the condition of t he drive belt. Damage may have occurred to the dr ive belt when it first fell off or it may
have been damaged which caused the belt to fall off.
4 Misalignment of the pulleys may be caused by:
• the incorrect installation or mount ing of an accessory drive component,
• the incorrect installation of an a ccessory drive component pulley, or
• a damaged or bent accessory drive pulley.
Test for a misaligned pulley using a suitable straight edge in the pulley grooves across two or more pulleys. If a
misaligned pulley is found, refer to the service informa tion for the particular component, for the correct pulley
replacement procedures.
5 Inspecting the pulleys should include an inspection for dents or other damage that would prevent the drive belt from
seating correctly in all of the pulley grooves or on the smooth surface of a pulley when the back side of the belt is
used.
6 Accessory drive component mounting brackets that are bent will cause the drive belt to fall off.
7 Inspection of the fasteners can eliminat e the possibility that an incorrect fastener was installed. Missing, loose or
incorrect fasteners may cause pulley misalignment from the fasteners moving under load. Over-tightening of the
fasteners may cause deflection of mounting brackets and result in misaligned accessory drive pulleys.
Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1
Did you review the information provided in 2.2 Symptoms, and
perform the required inspections. Go to Step 2 Go to
2.2 Symptoms
2 Inspect for a damaged accessory drive belt.
Did you find any damage on the drive belt? Go to Step 3 Go to Step 4
3 Install a new accessory drive belt, re
fer to 3.5 Accessory Drive Belt.
Does the drive belt continue to fall off? Go to Step 4 Go to Step 12
4 Inspect the accessory drive system pulleys for misalignment
Did you find and repair any misaligned drive system pulleys? Go to Step 12 Go to Step 5
5 Inspect for a dented or cracked accessory drive system pulley.
Did you find and repair any dented or cracked drive system? Go to Step 12 Go to Step 6
6 Inspect for bent accessory drive component mounting brackets.
Did you find and repair any bent mounting brackets? Go to Step 12 Go to Step 7
7 Inspect for incorrect, loose, missing or damaged fasteners.
Did you find any incorrect, loose, missing or damaged fasteners? Go to Step 8 Go to Step 9
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2865 of 6020
Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–88
Page 6A1–88
Clean
CAUTION
Due to the aluminium alloy construction of
the intake manifold, wire brushes and steel
scrapers must not be used during the
cleaning process, as damage to sealing
surfaces may occur. Use of a wooden or
plastic scraper is preferred.
1 Clean mating surfaces ensuring any gasket material is removed.
2 Clean the manifold using a suitable solvent
Safety glasses must be worn when using
compressed air.
3 Dry the timing components with compressed air.
Inspect
1 Inspect the intake manifold for the following fault conditions:
• Damaged sealing and mating surfaces.
• Damaged lower intake manifold gasket.
• Damage or excessive debris on the threaded and through holes.
• Cracks or damage to the intake manifold body.
NOTE
If the lower intake manifold is cracked or
damaged, it must be repl aced. No welding or
patching of the intake manifold should be
performed.
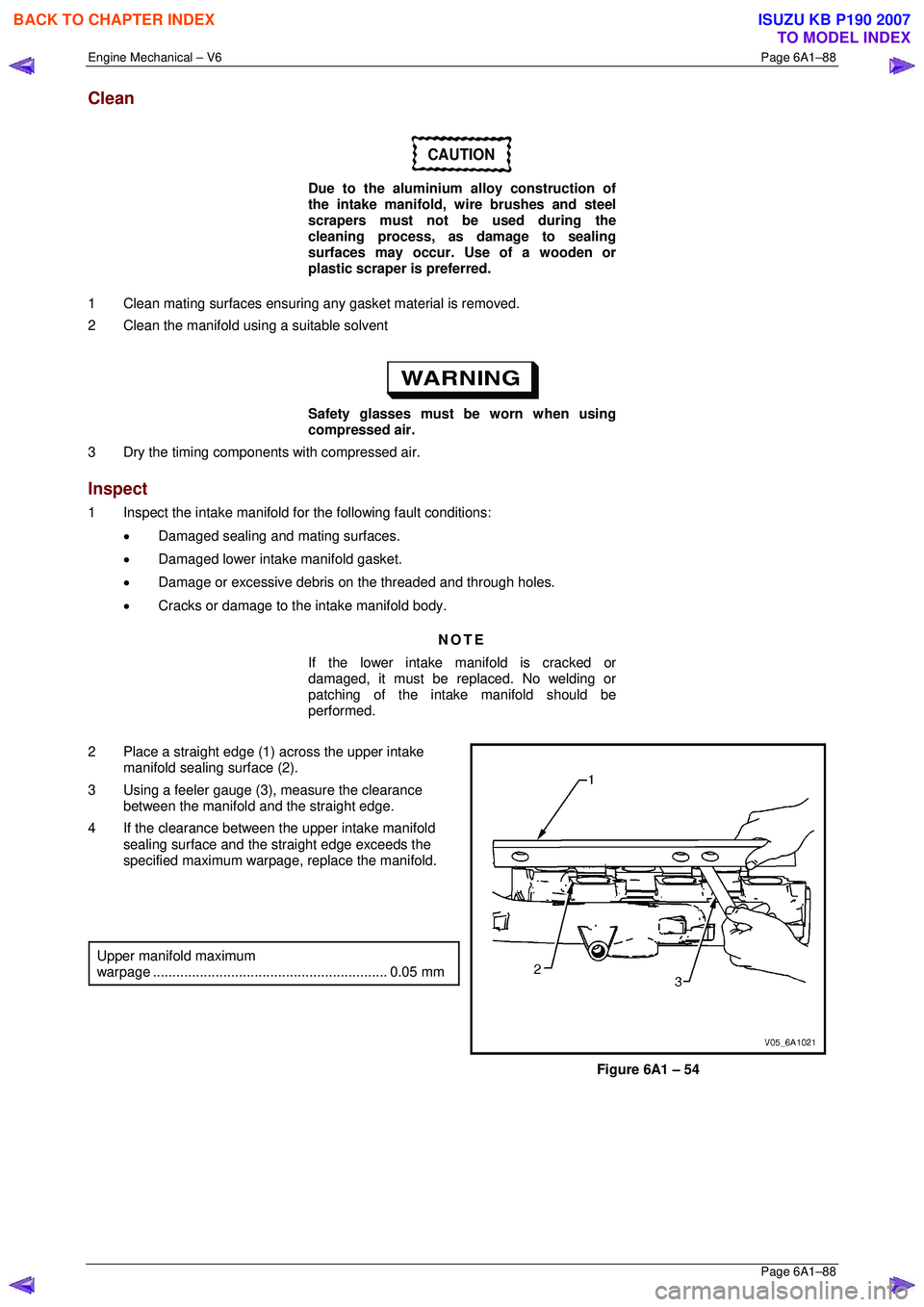
2 Place a straight edge (1) across the upper intake manifold sealing surface (2).
3 Using a feeler gauge (3), measure the clearance
between the manifold and the straight edge.
4 If the clearance between the upper intake manifold sealing surface and the straight edge exceeds the
specified maximum warpage, replace the manifold.
Upper manifold maximum
warpage ............................................................ 0.05 mm
Figure 6A1 – 54
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2878 of 6020
Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–101
Page 6A1–101
Clean and Inspect
1 Using a suitable non-corrosive cleaning solvent and a soft bristled parts cleaning brush, clean the crankshaft
balancer assembly.
Safety glasses must be worn when using
compressed air.
2 Dry the crankshaft balancer assembly using compressed air.
3 Inspect the crankshaft balancer assemb ly for the following fault conditions:
• Hub to crankshaft inner surface for wear or damage,
• Sealing surface for wear, grooving or scoring,
• Rubber ring between the hub and the pulley for wear, chunking and general deterioration, and
• Drive belt ribs of the pulley for damage.
Reinstall
CAUTION
Do not lubricate the crankshaft front oil seal
or crankshaft balancer sealing surfaces. The
crankshaft balancer must be installed onto a
dry seal.
1 Lubricate the crankshaft balancer assembly hub bore.
2 Partially install the crankshaft balancer assembly onto the crankshaft.
Figure 6A1 – 78
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2884 of 6020
Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–107
Page 6A1–107
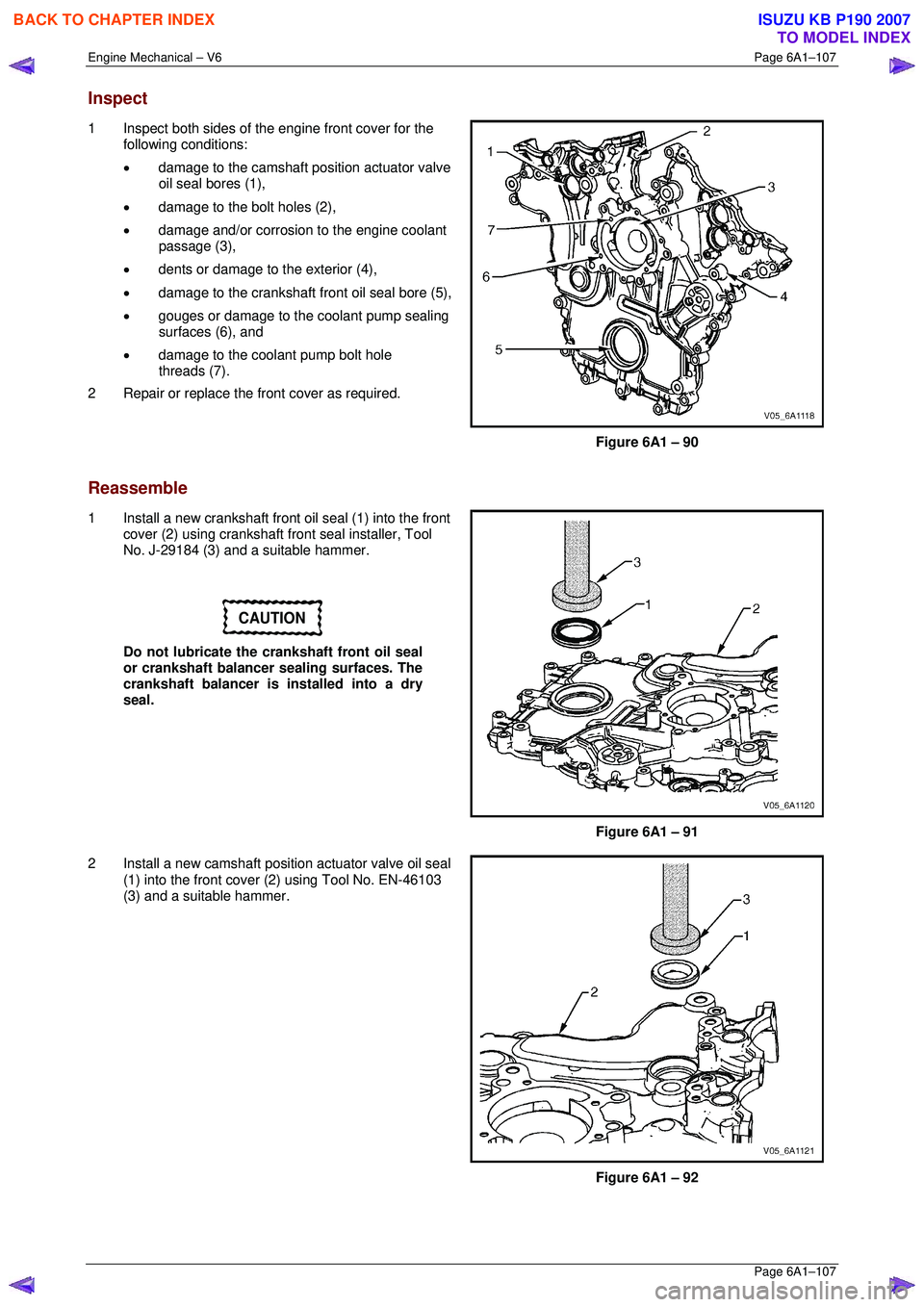
Inspect
1 Inspect both sides of the engine front cover for the
following conditions:
• damage to the camshaft position actuator valve
oil seal bores (1),
• damage to the bolt holes (2),
• damage and/or corrosion to the engine coolant
passage (3),
• dents or damage to the exterior (4),
• damage to the crankshaft front oil seal bore (5),
• gouges or damage to the coolant pump sealing
surfaces (6), and
• damage to the coolant pump bolt hole
threads (7).
2 Repair or replace the fr ont cover as required.
Figure 6A1 – 90
Reassemble
1 Install a new crankshaft front oil seal (1) into the front cover (2) using crankshaft front seal installer, Tool
No. J-29184 (3) and a suitable hammer.
CAUTION
Do not lubricate the crankshaft front oil seal
or crankshaft balancer sealing surfaces. The
crankshaft balancer is installed into a dry
seal.
Figure 6A1 – 91
2 Install a new camshaft positi on actuator valve oil seal
(1) into the front cover (2) using Tool No. EN-46103
(3) and a suitable hammer.
Figure 6A1 – 92
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007