2007 ISUZU KB P190 Harness
[x] Cancel search: HarnessPage 3317 of 6020
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–39
Injector Coil Test – With Special Tool J39021
1 Depressurise the fuel system, refer to 6C Fuel System – V6.
2 Turn the ignition OFF.
NOTE
After removing the upper intake manifold, plug
the lower manifold opening to prevent dirt and
other contaminants from entering.
3 Remove the upper intake manifold assembly, refer to 6A1 Engine Mechanical – V6.
4 Using Tech 2, observe the engine coolant temperature (ECT). If the ECT is 10 – 32 °C, refer to Engine Coolant
Temperature Between 10 – 32 °C, or if the ECT is outside this range, refer to Engine Coolant Temperature Outside
10 – 32 °C.
Engine Coolant Temperature Between 10 – 32 °
°°
°
C
Step Action Value(s) Yes No
1 1 Set the amperage supply selector switch on the
fuel injector tester (1), special tool J 39021 to the
Coil Test 0.5 A position. Refer to
Figure 6C1-2 – 11.
2 Connect the fuel injector tester leads (4 and 5) to B+ and ground.
3 Connect the digital multimeter (2) positive and negative lead to the fuel injector tester. Set the
multimeter to read DC Voltage.
4 Connect the fuel injector tester, using fuel injector harness adapter, special tool J44602 to a fuel
injector.
5 Press the Push to Start Test button on the fuel injector tester.
6 Observe and record the voltage reading on the digital multimeter.
NOTE
The voltage reading may rise during the
test. Record the voltage reading after one
second of the test.
7 Repeat steps 4 through 6 for each fuel injector. NOTE
The table in Figure 6C1-2 – 12 shows an
example of the results from a fuel injector
coil test.
Did any fuel injector have an erratic voltage reading
(large fluctuations in voltage that did not stabilise), or
voltage readings outside of the specified value? 5.5 – 6.6 V Replace the faulty
fuel injector/s. Refer to 2.13 Fuel Rail
Assembly, in 6C1-3 Engine
Management – V6 – Service Operations. System OK
When all repairs are completed, check the system for fuel leaks and correct operation.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3318 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–40
Engine Coolant Temperature Outside 10 – 32°
°°
°
C
Step Action Value(s) Yes No
1 1 Set the amperage supply selector switch on the
fuel injector tester (1), special tool J 39021 to the
Coil Test 0.5 A position. Refer to
Figure 6C1-2 – 11.
2 Connect the fuel injector tester leads (4 and 5) to B+ and ground.
3 Connect the digital multimeter (2) positive and negative lead to the fuel injector tester. Set the
multimeter to read DC Voltage.
4 Connect the fuel injector tester, using injector harness adapter, special tool J44602 to a fuel
injector.
5 Press the Push to Start Test button on the fuel injector tester.
6 Observe and record the voltage reading on the digital multimeter.
NOTE
The voltage reading may rise during the
test. Record the voltage reading after one
second of the test.
7 Repeat steps 4 through 6 for each fuel injector.
8 Identify the highest voltage reading recorded from the six fuel injectors tested that is 9.5 V or less.
NOTE
Disregard those voltage readings that are
greater than 9.5 V. Voltage readings greater
than 9.5 V indicate a faulty fuel injector.
9 Subtract the remaining voltage readings recorded in Step 8, from the highest voltage reading.
Are any of the values recorded in Step 9 greater than
the specified value? 0.6 V
Go to Step 2 System OK
2 1 Replace any fuel injector that has any of the
following:
− a subtracted value exceeding 0.6 V,
− an initial reading greater than 9.5 V, and
− an erratic reading.
NOTE
The table in Figure 6C1-2 – 13 shows an
example of the results from a fuel injector
coil test.
Has the repair been completed? – System OK. –
When all repairs are completed, check the system for fuel leaks and correct operation.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3319 of 6020
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–41
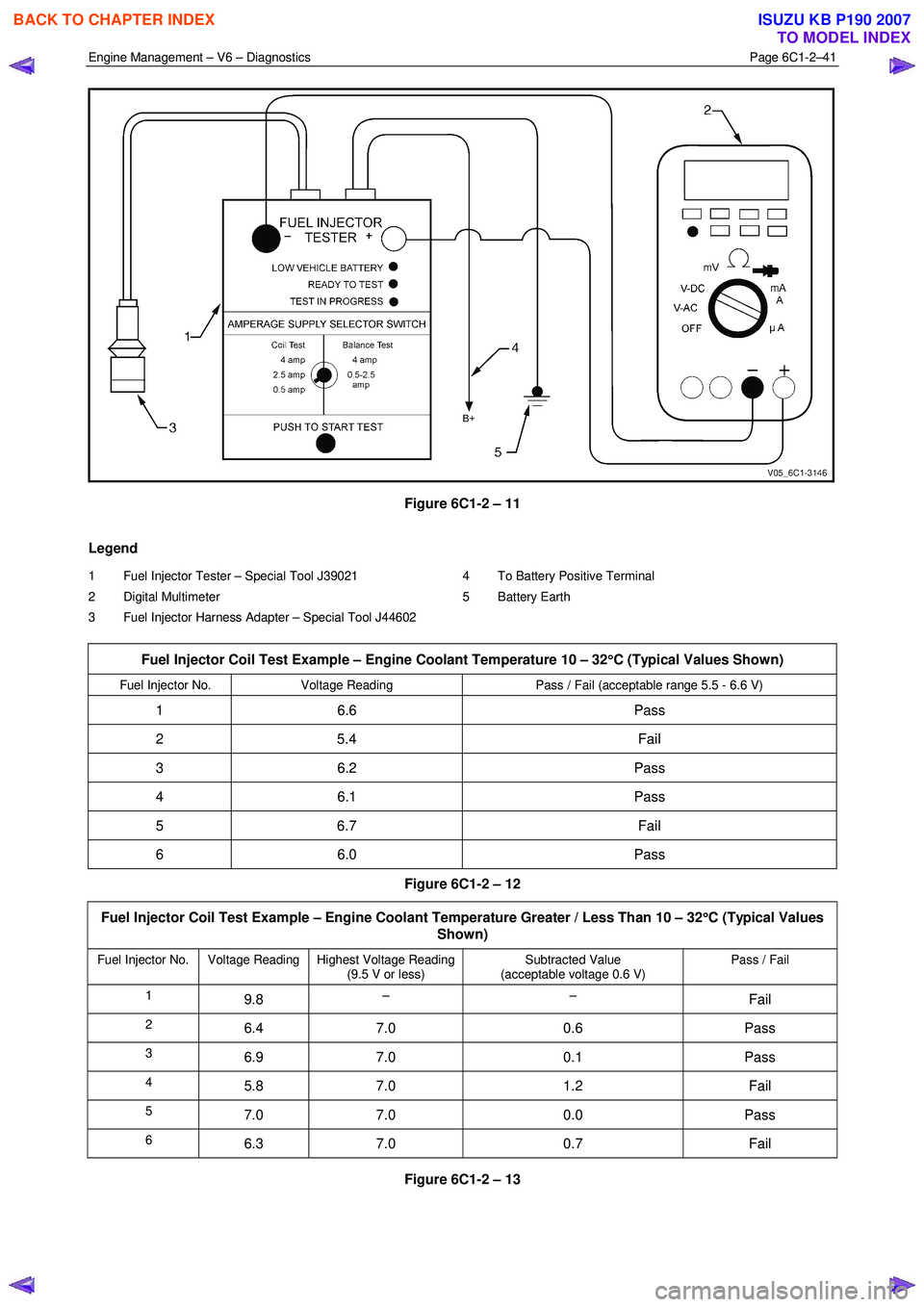
Figure 6C1-2 – 11
Legend
1 Fuel Injector Tester – Special Tool J39021
2 Digital Multimeter
3 Fuel Injector Harness Adapter – Special Tool J44602 4 To Battery Positive Terminal
5 Battery Earth
Fuel Injector Coil Test Example – Engine Coolant Temperature 10 – 32 °
°°
°
C (Typical Values Shown)
Fuel Injector No. Voltage Reading Pass / Fail (acceptable range 5.5 - 6.6 V)
1 6.6 Pass
2 5.4 Fail
3 6.2 Pass
4 6.1 Pass
5 6.7 Fail
6 6.0 Pass
Figure 6C1-2 – 12
Fuel Injector Coil Test Example – Engine Coolant Temperature Greater / Less Than 10 – 32 °
°°
°
C (Typical Values
Shown)
Fuel Injector No. Voltage Reading Highest Voltage Reading (9.5 V or less) Subtracted Value
(acceptable voltage 0.6 V) Pass / Fail
1 9.8 – – Fail
2 6.4 7.0 0.6 Pass
3 6.9 7.0 0.1 Pass
4 5.8 7.0 1.2 Fail
5 7.0 7.0 0.0 Pass
6 6.3 7.0 0.7 Fail
Figure 6C1-2 – 13
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3321 of 6020
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–43
6 Remove the upper intake manifold assembly, refer to 6A1 Engine Mechanical – V6.
NOTE
After removing the upper intake manifold, plug
the lower manifold opening to prevent dirt and
other contaminants from entering.
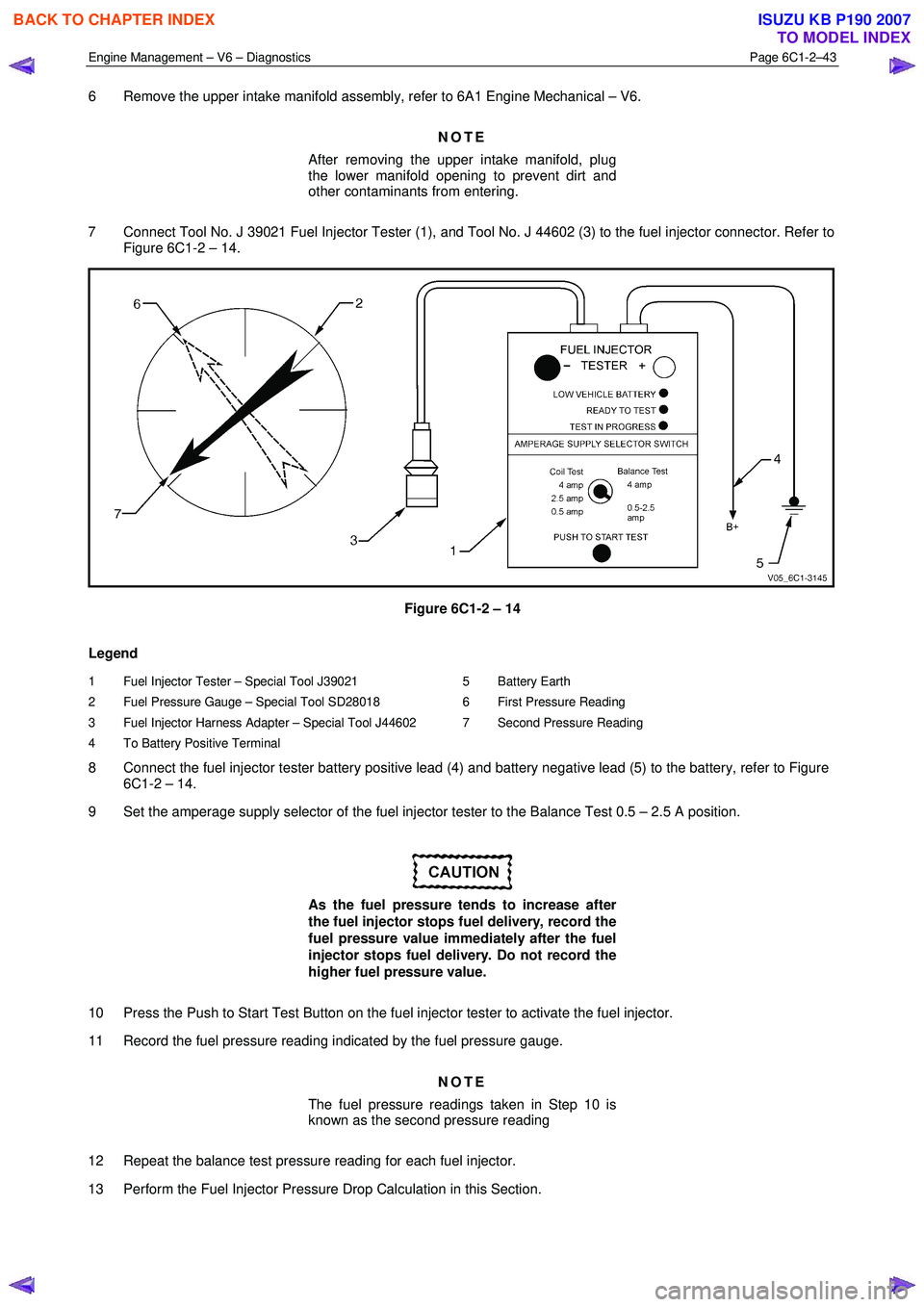
7 Connect Tool No. J 39021 Fuel Injector Tester (1), and Tool No. J 44602 (3) to the fuel injector connector. Refer to Figure 6C1-2 – 14.
Figure 6C1-2 – 14
Legend
1 Fuel Injector Tester – Special Tool J39021
2 Fuel Pressure Gauge – Special Tool SD28018
3 Fuel Injector Harness Adapter – Special Tool J44602
4 To Battery Positive Terminal 5 Battery Earth
6 First Pressure Reading
7 Second Pressure Reading
8 Connect the fuel injector tester battery positive lead (4) and battery negative lead (5) to the battery, refer to Figure 6C1-2 – 14.
9 Set the amperage supply selector of the fuel injector tester to the Balance Test 0.5 – 2.5 A position.
As the fuel pressure tends to increase after
the fuel injector stops fuel delivery, record the
fuel pressure value immediately after the fuel
injector stops fuel delivery. Do not record the
higher fuel pressure value.
10 Press the Push to Start Test Button on the fuel injector tester to activate the fuel injector.
11 Record the fuel pressure reading indicated by the fuel pressure gauge.
NOTE
The fuel pressure readings taken in Step 10 is
known as the second pressure reading
12 Repeat the balance test pressure reading for each fuel injector.
13 Perform the Fuel Injector Pressure Drop Calculation in this Section.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3323 of 6020
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–45
Clean around the area where the fuel
injectors enter the lower intake manifold.
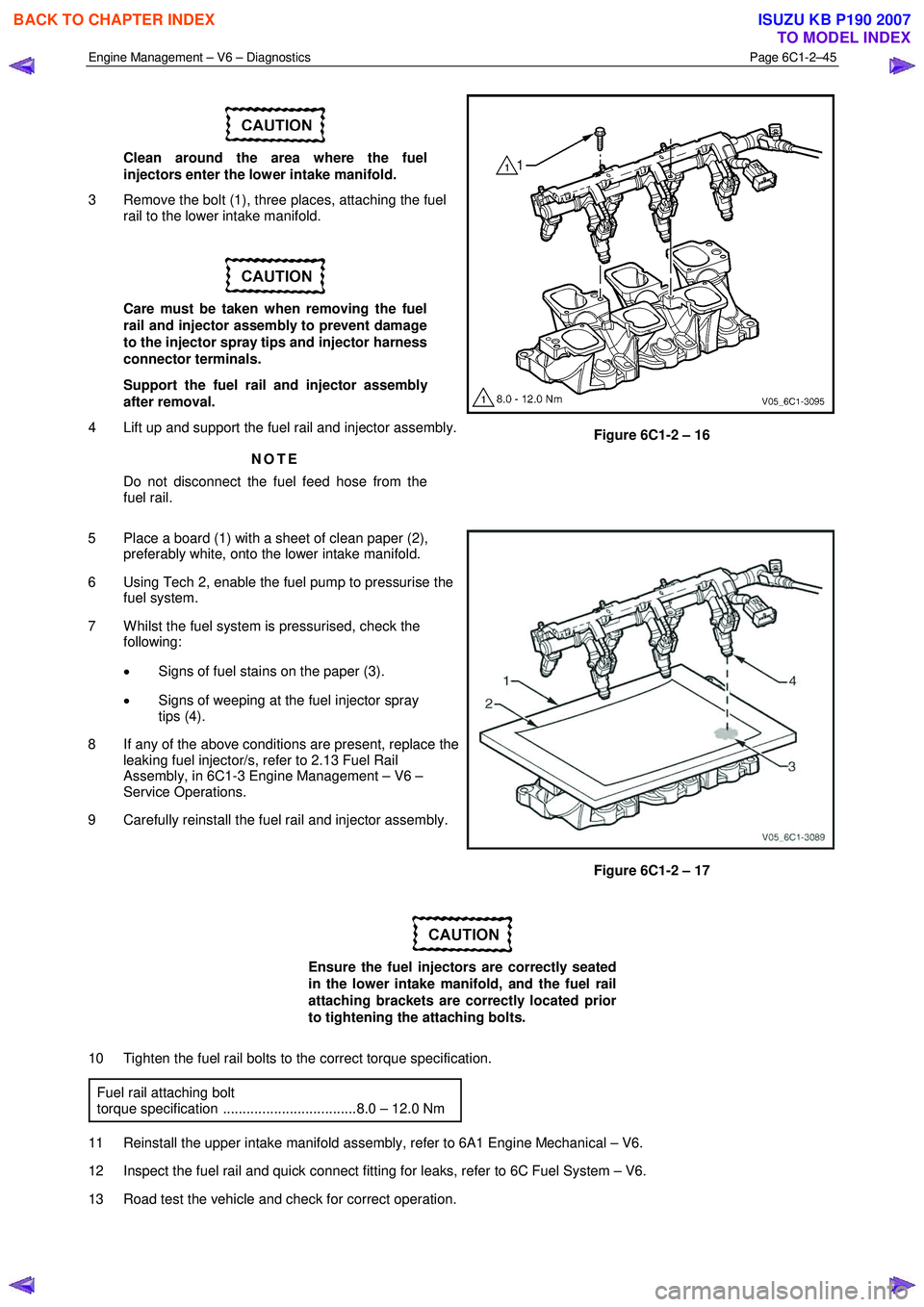
3 Remove the bolt (1), three places, attaching the fuel rail to the lower intake manifold.
Care must be taken when removing the fuel
rail and injector assembly to prevent damage
to the injector spray tips and injector harness
connector terminals.
Support the fuel rail and injector assembly
after removal.
4 Lift up and support the fuel rail and injector assembly.
NOTE
Do not disconnect the fuel feed hose from the
fuel rail.
Figure 6C1-2 – 16
5 Place a board (1) with a sheet of clean paper (2), preferably white, onto the lower intake manifold.
6 Using Tech 2, enable the fuel pump to pressurise the fuel system.
7 W hilst the fuel system is pressurised, check the following:
• Signs of fuel stains on the paper (3).
• Signs of weeping at the fuel injector spray
tips (4).
8 If any of the above conditions are present, replace the leaking fuel injector/s, refer to 2.13 Fuel Rail
Assembly, in 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
9 Carefully reinstall the fuel rail and injector assembly.
Figure 6C1-2 – 17
Ensure the fuel injectors are correctly seated
in the lower intake manifold, and the fuel rail
attaching brackets are correctly located prior
to tightening the attaching bolts.
10 Tighten the fuel rail bolts to the correct torque specification. Fuel rail attaching bolt
torque specification ..................................8.0 – 12.0 Nm
11 Reinstall the upper intake manifold assembly, refer to 6A1 Engine Mechanical – V6.
12 Inspect the fuel rail and quick connect fitting for leaks, refer to 6C Fuel System – V6.
13 Road test the vehicle and check for correct operation.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3326 of 6020
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–48
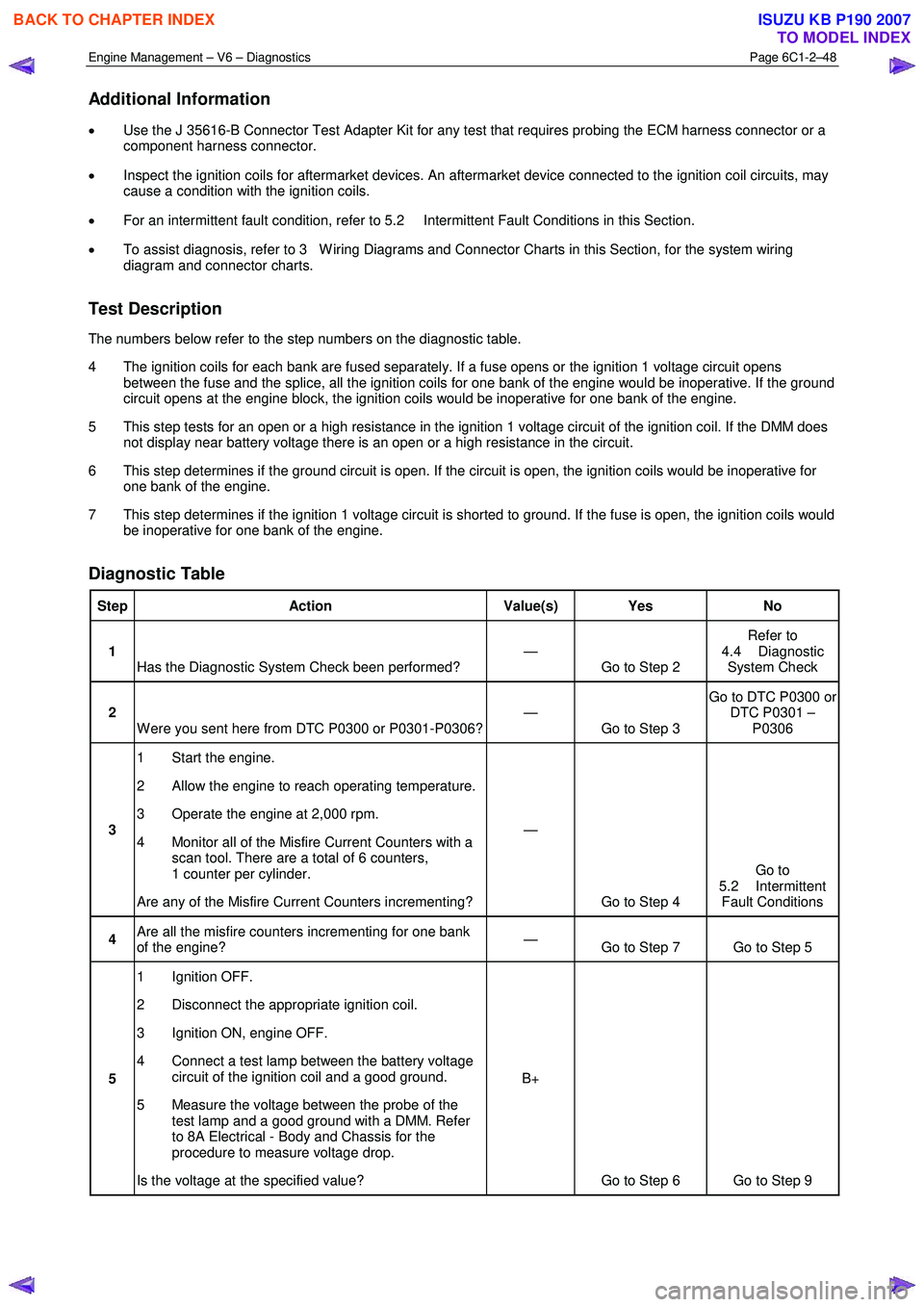
Additional Information
• Use the J 35616-B Connector Test Adapter Kit for any test that requires probing the ECM harness connector or a
component harness connector.
• Inspect the ignition coils for aftermarket devices. An aftermarket device connected to the ignition coil circuits, may
cause a condition with the ignition coils.
• For an intermittent fault condition, refer to 5.2 Intermittent Fault Conditions in this Section.
• To assist diagnosis, refer to 3 W iring Diagrams and Connector Charts in this Section, for the system wiring
diagram and connector charts.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to the step numbers on the diagnostic table.
4 The ignition coils for each bank are fused separately. If a fuse opens or the ignition 1 voltage circuit opens between the fuse and the splice, all the ignition coils for one bank of the engine would be inoperative. If the ground
circuit opens at the engine block, the ignition coils would be inoperative for one bank of the engine.
5 This step tests for an open or a high resistance in the ignition 1 voltage circuit of the ignition coil. If the DMM does not display near battery voltage there is an open or a high resistance in the circuit.
6 This step determines if the ground circuit is open. If the circuit is open, the ignition coils would be inoperative for one bank of the engine.
7 This step determines if the ignition 1 voltage circuit is shorted to ground. If the fuse is open, the ignition coils would be inoperative for one bank of the engine.
Diagnostic Table
Step Action Value(s) Yes No
1
Has the Diagnostic System Check been performed? —
Go to Step 2 Refer to
4.4 Diagnostic System Check
2 W ere you sent here from DTC P0300 or P0301-P0306? —
Go to Step 3 Go to DTC P0300 or
DTC P0301 – P0306
3 1 Start the engine.
2 Allow the engine to reach operating temperature.
3 Operate the engine at 2,000 rpm.
4 Monitor all of the Misfire Current Counters with a scan tool. There are a total of 6 counters,
1 counter per cylinder.
Are any of the Misfire Current Counters incrementing? —
Go to Step 4 Go to
5.2 Intermittent Fault Conditions
4 Are all the misfire counters incrementing for one bank
of the engine? —
Go to Step 7 Go to Step 5
5 1 Ignition OFF.
2 Disconnect the appropriate ignition coil.
3 Ignition ON, engine OFF.
4 Connect a test lamp between the battery voltage circuit of the ignition coil and a good ground.
5 Measure the voltage between the probe of the test lamp and a good ground with a DMM. Refer
to 8A Electrical - Body and Chassis for the
procedure to measure voltage drop.
Is the voltage at the specified value? B+
Go to Step 6 Go to Step 9
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3342 of 6020
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–64
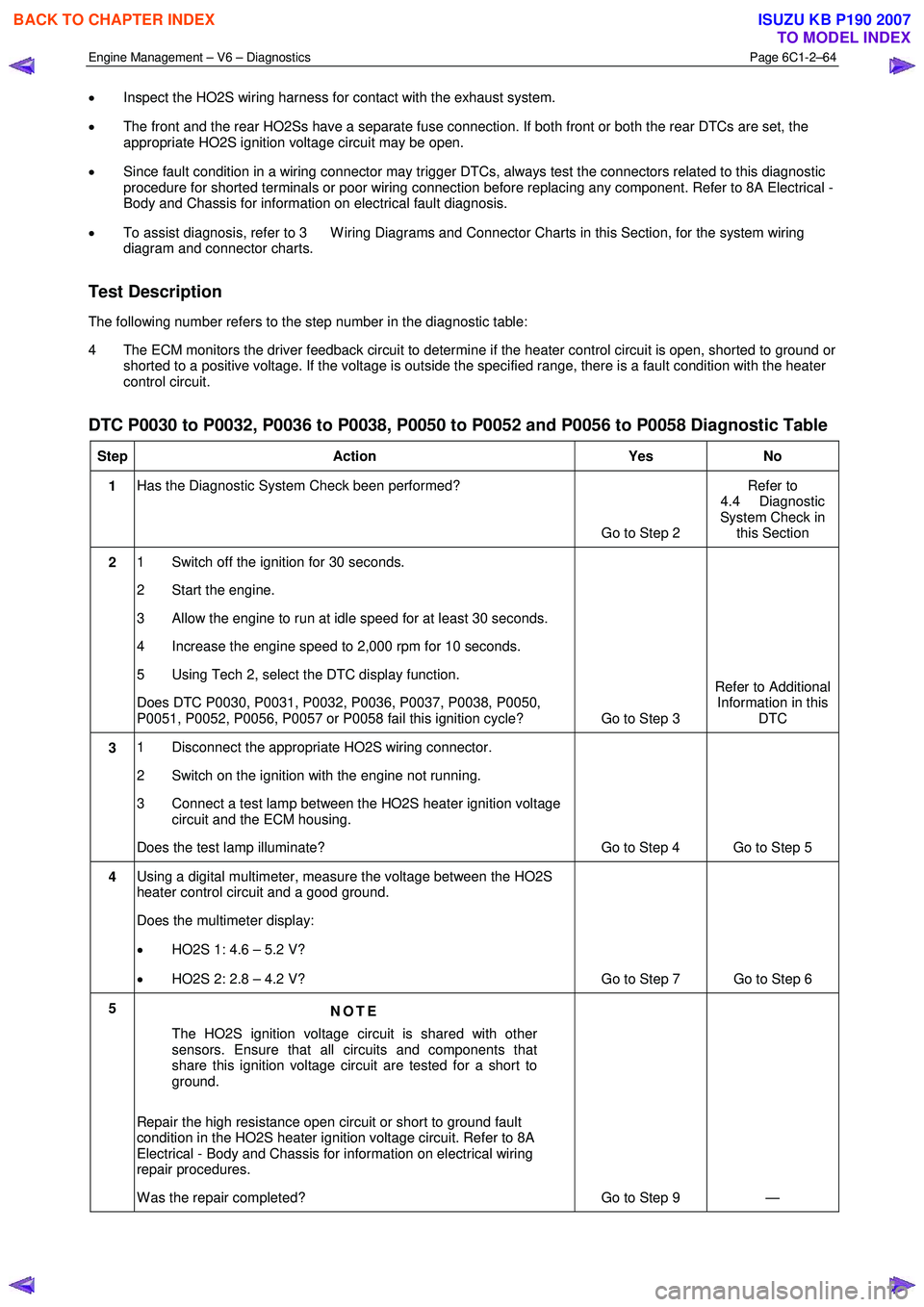
• Inspect the HO2S wiring harness for contact with the exhaust system.
• The front and the rear HO2Ss have a separate fuse connection. If both front or both the rear DTCs are set, the
appropriate HO2S ignition voltage circuit may be open.
• Since fault condition in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this diagnostic
procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component. Refer to 8A Electrical -
Body and Chassis for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
• To assist diagnosis, refer to 3 W iring Diagrams and Connector Charts in this Section, for the system wiring
diagram and connector charts.
Test Description
The following number refers to the step number in the diagnostic table:
4 The ECM monitors the driver feedback circuit to determine if the heater control circuit is open, shorted to ground or shorted to a positive voltage. If the voltage is outside the specified range, there is a fault condition with the heater
control circuit.
DTC P0030 to P0032, P0036 to P0038, P0050 to P0052 and P0056 to P0058 Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1 Has the Diagnostic System Check been performed?
Go to Step 2 Refer to
4.4 Diagnostic
System Check in this Section
2 1 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
2 Start the engine.
3 Allow the engine to run at idle speed for at least 30 seconds.
4 Increase the engine speed to 2,000 rpm for 10 seconds.
5 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does DTC P0030, P0031, P0032, P0036, P0037, P0038, P0050,
P0051, P0052, P0056, P0057 or P0058 fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 3 Refer to Additional
Information in this DTC
3 1 Disconnect the appropriate HO2S wiring connector.
2 Switch on the ignition with the engine not running.
3 Connect a test lamp between the HO2S heater ignition voltage circuit and the ECM housing.
Does the test lamp illuminate? Go to Step 4 Go to Step 5
4 Using a digital multimeter, measure the voltage between the HO2S
heater control circuit and a good ground.
Does the multimeter display:
• HO2S 1: 4.6 – 5.2 V?
• HO2S 2: 2.8 – 4.2 V? Go to Step 7 Go to Step 6
5
NOTE
The HO2S ignition voltage circuit is shared with other
sensors. Ensure that all circuits and components that
share this ignition voltage circuit are tested for a short to
ground.
Repair the high resistance open circuit or short to ground fault
condition in the HO2S heater ignition voltage circuit. Refer to 8A
Electrical - Body and Chassis for information on electrical wiring
repair procedures.
W as the repair completed? Go to Step 9 —
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3348 of 6020
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–70
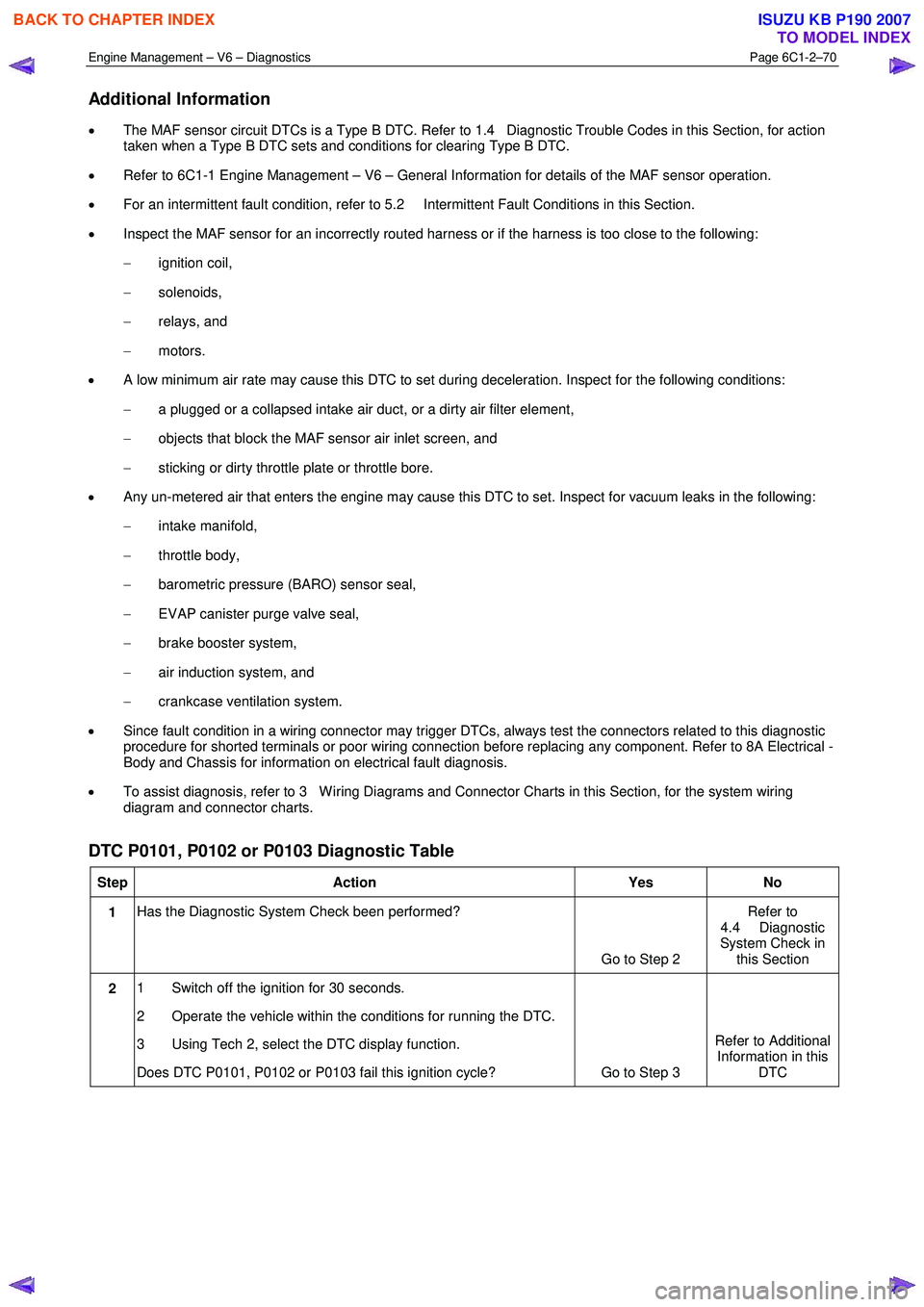
Additional Information
• The MAF sensor circuit DTCs is a Type B DTC. Refer to 1.4 Diagnostic Trouble Codes in this Section, for action
taken when a Type B DTC sets and conditions for clearing Type B DTC.
• Refer to 6C1-1 Engine Management – V6 – General Information for details of the MAF sensor operation.
• For an intermittent fault condition, refer to 5.2 Intermittent Fault Conditions in this Section.
• Inspect the MAF sensor for an incorrectly routed harness or if the harness is too close to the following:
− ignition coil,
− solenoids,
− relays, and
− motors.
• A low minimum air rate may cause this DTC to set during deceleration. Inspect for the following conditions:
− a plugged or a collapsed intake air duct, or a dirty air filter element,
− objects that block the MAF sensor air inlet screen, and
− sticking or dirty throttle plate or throttle bore.
• Any un-metered air that enters the engine may cause this DTC to set. Inspect for vacuum leaks in the following:
− intake manifold,
− throttle body,
− barometric pressure (BARO) sensor seal,
− EVAP canister purge valve seal,
− brake booster system,
− air induction system, and
− crankcase ventilation system.
• Since fault condition in a wiring connector may trigger DTCs, always test the connectors related to this diagnostic
procedure for shorted terminals or poor wiring connection before replacing any component. Refer to 8A Electrical -
Body and Chassis for information on electrical fault diagnosis.
• To assist diagnosis, refer to 3 W iring Diagrams and Connector Charts in this Section, for the system wiring
diagram and connector charts.
DTC P0101, P0102 or P0103 Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1 Has the Diagnostic System Check been performed?
Go to Step 2 Refer to
4.4 Diagnostic
System Check in this Section
2 1 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
2 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
3 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does DTC P0101, P0102 or P0103 fail this ignition cycle? Go to Step 3 Refer to Additional
Information in this DTC
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007