2007 ISUZU KB P190 Harness
[x] Cancel search: HarnessPage 3303 of 6020
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–25
Checks Actions
Fuel System
• Check the fuel system for the following fault conditions. Refer to 6C Fuel System
– V6 – V6.
• restricted fuel filter,
• incorrect fuel pressure, and
• contaminated fuel.
• Check the operation of the fuel injectors. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management –
V6 – Service Operations.
• Perform the fuel injector balance test, refer to 6.3 Fuel Injector Balance
Test in this Section.
• Check the items that can cause an engine to run lean.
• Check the items that cause an engine to run rich.
Ignition System
• Check for an intermittent ignition circuit malfunction.
• Inspect for moisture or corrosion around the spark plug / ignition coil area.
• Test the ignition coil voltage output. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
• Remove and inspect the spark plugs. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
NOTE
If the spark plugs are fouled, determine the cause of the fouling before
replacing the spark plugs. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
• Check for loose ignition coil ground circuit.
Engine Cooling System Check the engine for over-heating. Refer to 6B1 Engine Cooling – V6.
Engine Mechanical Check for the following engine fault conditions. Refer to 6A1 Engine Mechanical – V6.
• low compression, and
• worn valve train components.
Additional Checks
• Check the exhaust system for possible restrictions. Refer to 6F Exhaust System –
V6.
• Electromagnetic interference (EMI) on the crankshaft position (CKP) sensor can
cause an engine misfire condition.
Using Tech 2, monitor the engine speed parameter. A sudden increase in the engine speed parameters without moving the throttle position indicates that an
Electromagnetic Interference fault may be present.
W iring harness routing which may be positioned very close to a high voltage or high current device such as the following may induce EMI:
• secondary ignition components, or
• motors and generators.
Dirty starter motor commutator or brushes can mask the crankshaft position sensor signal.
• Check the torque converter clutch (TCC) operation. A TCC that applies too soon
can cause engine detonation, which will trigger spark retard activity. Refer to 7C1
Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – General Information.
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3306 of 6020
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–28
Checks Actions
Additional Checks
• Check the exhaust system for possible restrictions. Refer to 6F Exhaust System –
V6.
• Electromagnetic interference (EMI) on the crankshaft position (CKP) sensor can
cause an engine misfire condition.
Using Tech 2, monitor the engine speed parameter. A sudden increase in the engine speed parameters without moving the throttle position indicates that an
electromagnetic interference fault may be present.
• W iring harness routing which may be positioned very close to a high voltage or
high current device such as the following may induce EMI:
• secondary ignition components, or
• motors and generators.
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
5.6 Detonation / Spark Knock
Description
The engine produces sharp rapid metallic knocks that are more audible during acceleration.
Checks Actions
Preliminary Perform the preliminary checks. Refer to 4.3 Preliminary Checks in this Section.
Sensor System Use Tech 2 to monitor the knock sensor system.
Fuel System
• Check the fuel system for the following fault conditions. Refer to 6C Fuel System
– V6.
• restricted fuel filter,
• incorrect fuel pressure, and
• contaminated fuel.
• Check the operation of the fuel injectors. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management –
V6 – Service Operations.
• Perform the fuel injector balance test, refer to 6.3 Fuel Injector Balance
Test in this Section.
• Ensure the fuel tank is filled with petrol that has a minimum octane reading of 92.
• Check for fault conditions that can cause an engine to run lean.
Ignition System Check the spark plugs for proper heat range. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6
– Service Operations.
Engine Mechanical • Check the combustion chambers for excessive carbon build-up. Refer to 6A1
Engine Mechanical – V6.
• Check the camshaft timing. Refer to 6A1 Engine Mechanical – V6.
Additional Checks
• Check the torque converter clutch (TCC) operation. The TCC applying too soon
can cause the engine to spark knock. Refer to 7C2 Automatic Transmission –
4L60E – Electrical Diagnosis.
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
5.7 Dieseling, Run-on
Description
The engine continues to run after the ignition is switched off but runs very roughly and then stalls.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3308 of 6020
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–30
Checks Actions
Ignition System
• Inspect for moisture or corrosion around the spark plug / ignition coil area.
• Test the ignition coil voltage output. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
• Remove and inspect the spark plugs. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
NOTE
If the spark plugs are fouled, determine the cause of the fouling before
replacing the spark plugs. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
• Check for loose ignition coil ground circuit.
Engine Mechanical
• Check for excessive oil in combustion chamber. Refer to 6A1 Engine Mechanical
– V6.
• Check for the following engine fault conditions. Refer to 6A1 Engine Mechanical –
V6.
• low compression, and
• worn valve train components.
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
5.9 Hesitation, Sag and Stumble
Description
Momentary lack of response or hesitation as the accelerator is depressed. This condition is usually more severe when
first trying to make the vehicle move from a standing start but can occur at any vehicle speed.
Checks Actions
Preliminary • Perform the preliminary checks. Refer to 4.3 Preliminary Checks in this
Section.
• Check the air filter element and intake air ducts for blockages.
Sensor / System
• Using Tech 2, check the heated oxygen sensor (HO2s) operating parameters.
The HO2s should respond quickly to different throttle positions.
• Inspect the accelerator pedal position (APP) sensor harness connector for correct
connection. Poor connection of this connector will not set a DTC.
Fuel System • Check the fuel system for the following fault conditions. Refer to 6C Fuel System
– V6.
• restricted fuel filter,
• incorrect fuel pressure, and
• contaminated fuel.
• Check the operation of the fuel injectors. Refer to 6C Fuel System – V6.
• Perform the fuel injector balance test, refer to 6.3 Fuel Injector Balance
Test in this Section.
• Check for fault conditions that cause an engine to run rich or to run lean.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3309 of 6020
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–31
Checks Actions
Ignition System
• Inspect for moisture or corrosion around the spark plug / ignition coil area.
• Test the ignition coil voltage output. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
• Remove and inspect the spark plugs. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
NOTE
If the spark plugs are fouled, determine the cause of the fouling before
replacing the spark plugs. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
• Check for loose ignition coil ground circuit.
Engine Cooling System Check the engine thermostat for correct operation and heat range. Refer to 6B1 Engine
Cooling – V6.
Additional Checks • Check the generator output voltage. Refer to 6D1-1 Charging System – V6.
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
5.10 Lack of Power, Sluggishness or
Sponginess
Description
The engine delivers less than normal power. There is little or no increase in vehicle speed when the accelerator pedal is
partially depressed.
Checks Actions
Preliminary • Perform the preliminary checks. Refer to 4.3 Preliminary Checks in this
Section.
• Check the air filter element and intake air ducts for blockages.
Sensor / System
• Use Tech 2 to monitor the knock sensor system for excessive spark retard
activity. Check for items that cause spark retard activity.
• Inspect the accelerator pedal position (APP) sensor harness connector for correct
connection. Poor connection of this connector will not set a DTC.
Fuel System • Check the fuel system for the following fault conditions. Refer to 6C Fuel System
– V6.
• restricted fuel filter,
• incorrect fuel pressure, and
• contaminated fuel.
• Check the operation of the fuel injectors. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management –
V6 – Service Operations.
• Perform the fuel injector balance test, refer to 6.3 Fuel Injector Balance
Test in this Section.
• Check for fault conditions that can cause the engine to run rich or run lean.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3312 of 6020
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–34
Checks Actions
Additional Checks
• Check the exhaust system for possible restrictions. Refer to 6F Exhaust System –
V6.
• Electromagnetic interference (EMI) on the crankshaft position (CKP) sensor can
cause an engine misfire condition.
Using Tech 2, monitor the engine speed parameter. A sudden increase in the engine speed parameters without moving the throttle position indicates that an
Electromagnetic Interference fault may be present.
W iring harness routing which may be positioned very close to a high voltage or high current device such as the following may induce EMI:
• secondary ignition components, and
• motors and generators.
• Check the torque converter clutch (TCC) operation. A TCC that applies too soon
can cause engine detonation, which will trigger spark retard activity. Refer to 7C2
Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – Electrical Diagnosis.
• Test for other TCM related faults that may cause the transmission to operate in
the default mode. Refer to 7C2 Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – Electrical
Diagnosis.
• Check for transmission mechanical faults such as slipping clutch. Refer to 7C3
Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – Hydraulic and Mechanical Diagnosis.
• Check the brake system including the parking brake for sticking or incorrect
operation.
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
5.12 Rough, Unstable, Incorrect Idle or
Stalling
Description
Engine idle speed fluctuates causing the engine to run unevenly. If the engine idle speed drops too low, the engine may
stall.
Checks Actions
Preliminary • Perform the preliminary checks. Refer to 4.3 Preliminary Checks in this
Section.
• Check the air filter element and intake air ducts for blockages.
Sensor / System
• Check the throttle actuator control (TAC) system. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine
Management – V6 – Service Operations.
• Check the air intake system and crankcase for air leaks. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine
Management – V6 – Service Operations.
• Check the PCV System for correct operation. Refer to 6A1 Engine Mechanical –
V6.
• Use Tech 2 to monitor the knock sensor system for excessive spark retard
activity. Check for items that cause spark retard activity.
• Using Tech 2, check the heated oxygen sensor (HO2s) operating parameters.
The HO2s sensor should respond quickly to different throttle positions.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3314 of 6020
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–36
Checks Actions
Fuel System
• Check the fuel system for the following fault conditions. Refer to 6C Fuel System
– V6.
• restricted fuel filter,
• incorrect fuel pressure, and
• contaminated fuel.
• Check the operation of the fuel injectors. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management –
V6 – Service Operations.
• Perform the fuel injector balance test, refer to 6.3 Fuel Injector Balance
Test in this Section.
• Check the items that cause an engine to run rich.
• Check for fault conditions that can cause an engine to run lean.
Ignition System
• Inspect for moisture or corrosion around the spark plug / ignition coil area.
• Test the ignition coil voltage output. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
• Remove and inspect the spark plugs. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
NOTE
If the spark plugs are fouled, determine the cause of the fouling before
replacing the spark plugs. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
• Check for loose ignition coil ground circuit.
Additional Checks
• Check the torque converter clutch (TCC) operation. A TCC that applies too soon
can cause engine detonation, which will trigger spark retard activity. Refer to 7C2
Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – Electrical Diagnosis.
• Test the A/C clutch for correct operation. Refer to 2A Heater and Air-conditioning.
• Check the evaporative emission (EVAP) canister purge solenoid for the following
conditions: Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 – Service Operations.
− stuck open condition, and
− charcoal contamination.
• Check the exhaust system for possible restrictions. Refer to 6F Exhaust System –
V6.
• Electromagnetic interference (EMI) on the crankshaft position (CKP) sensor can
cause an engine misfire condition.
Using Tech 2, monitor the engine speed parameter. A sudden increase in the engine speed parameters without moving the throttle position indicates that an
Electromagnetic Interference fault may be present.
W iring harness routing which may be positioned very close to a high voltage or high current device such as the following may induce EMI:
• secondary ignition components, or
• motors and generators.
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3315 of 6020
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–37
6 Functional Checks
6.1 General Information
The items detailed in the following pages are to be used when there is a customer complaint and there are no diagnostic
trouble codes set, or one or more of the Tech 2 data values are not within the typical values. They are also to be used
when instructed from a DTC table. Before using these tables, you should refer to 5 Symptoms Diagnostics in this
Section, which may direct you to using the following functional checks.
The purpose of these tables is to diagnose engine control module (ECM) controlled components or sub-systems that do
not have diagnostic trouble codes assigned to them. Another purpose of these tables is for Technicians who feel
confident that a particular part of the sub-system is not operating properly and wants only to check that particular item
for proper operation without going through lengthy diagnostic procedures.
6.2 Fuel Injector Coil Test
The fuel injector coil test is divided into two parts. Begin by performing the fuel injector coil quick test. Then only perform
the Injector Coil Test – W ith Special Tool J39021 procedure if the quick test determines that there is a faulty fuel injector.
Fuel Injector Coil Quick Test
Test Description
The following numbers refer to the step numbers in the diagnostic table:
1 This step checks if the engine coolant temperature is within the correct range.
2 This step tests each fuel injector resistance within a specific temperature range.
3 This step determines if all of the fuel injectors are within 3 ohms of each other.
Step Action Value(s) Yes No
1 Using Tech 2, observe the engine coolant temperature
(ECT).
Is the ECT within the specified range? 10 – 32 °C Go to Step 2 Go to Step 3
2 1 Disconnect the fuel injector harness connector,
refer to 2.13 Fuel Rail Assembly, in 6C1-3 Engine
Management – V6 – Service Operations.
2 Using a digital ohmmeter and connector test adaptor kit J 35616-A, measure the resistance of
each fuel injector between the ignition voltage
circuit and the fuel injector control circuit. Refer to
8A Electrical - Body and Chassis for information
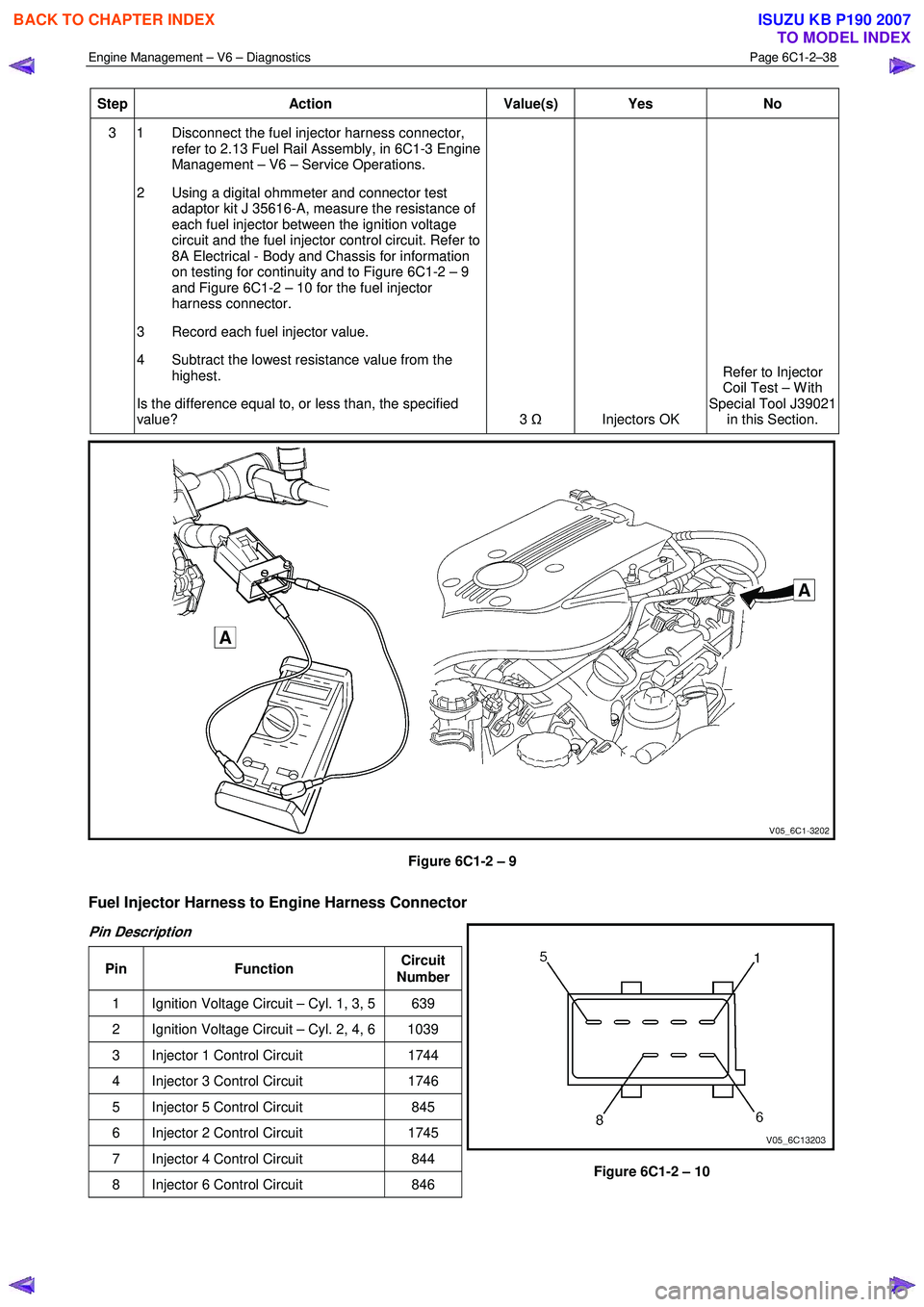
on testing for continuity and to Figure 6C1-2 – 9
and Figure 6C1-2 – 10 for the fuel injector
harness connector.
Do any of the fuel injectors display a resistance outside
the specified range? 11 – 14 ΩRefer to Injector
Coil Test – W ith
Special Tool J39021 in this Section Injectors OK
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3316 of 6020
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–38
Step Action Value(s) Yes No
3 1 Disconnect the fuel injector harness connector,
refer to 2.13 Fuel Rail Assembly, in 6C1-3 Engine
Management – V6 – Service Operations.
2 Using a digital ohmmeter and connector test adaptor kit J 35616-A, measure the resistance of
each fuel injector between the ignition voltage
circuit and the fuel injector control circuit. Refer to
8A Electrical - Body and Chassis for information
on testing for continuity and to Figure 6C1-2 – 9
and Figure 6C1-2 – 10 for the fuel injector
harness connector.
3 Record each fuel injector value.
4 Subtract the lowest resistance value from the highest.
Is the difference equal to, or less than, the specified
value? 3
Ω
Injectors OK Refer to Injector
Coil Test – W ith
Special Tool J39021 in this Section.
Figure 6C1-2 – 9
Fuel Injector Harness to Engine Harness Connector
Pin Description
Pin Function Circuit
Number
1 Ignition Voltage Circuit – Cyl. 1, 3, 5 639
2 Ignition Voltage Circuit – Cyl. 2, 4, 6 1039
3 Injector 1 Control Circuit 1744
4 Injector 3 Control Circuit 1746
5 Injector 5 Control Circuit 845
6 Injector 2 Control Circuit 1745
7 Injector 4 Control Circuit 844
8 Injector 6 Control Circuit 846
Figure 6C1-2 – 10
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007