2007 ISUZU KB P190 key
[x] Cancel search: keyPage 1957 of 6020
6E-340 ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM (4JK1/4JJ1)
Abnormal Combustion Noise
ChecksAction
Definition:
A mild to severe ping, usually worse under acceleration. The engine makes sharp metallic knocks that change with the throttle
opening.
Preliminary Checks • Diagnostic System Check - Engine Controls.
• Ensure the vehicle has an actual problem.
• Inspect for smoke associated with the combustion noise.
• Inspect the fuel quality (cetane index).
• Inspect the programmed fuel injector ID code for each cylinder.
• Inspect the Scan Tool Data List in this section.
• Inspect the Service Bulletin.
Sensor Checks Inspect the engine control sensors for the following conditions. Refer to the Scan Tool
Data List in this section.
• Compare the Coolant Temperature with the Intake Air Temperature (IAT) and Fuel Temperature (FT) parameters on a cold engine condition. If the difference among
temperature reading is more than 5 °C (9 °F) on a cold engine, check for high
resistance in each circuit or for a skewed sensor.
Notice: The mass air flow (MAF) sensor is heated and as a result the IAT may indicate
a higher than normal intake air temperature if the ignition switch is being ON.
• Observe the Fuel Rail Pressure (FRP) Sensor parameter with the engine OFF. The FRP Sensor should read 0.9 to 1.0 volt with the key ON and engine OFF after the
engine has stopped running for a minimum of 1 minute. If not, check for high
resistance in each circuit or for a skewed sensor.
• Observe the Fuel Rail Pressure and Desired Fuel Rail Pressure parameter between idle and W.O.T. (accelerator pedal full travel) in Neutral. Fuel Rail Pressure
parameter should follow within ± 5 MPa ( ± 725 psi) quick enough.
• Crankshaft position (CKP) sensor is tight and the sensor rotor is not damaged.
Fuel System Checks • If excessive smoke is present, check for a stuck open fuel injector. Inspect for fuel
leakage into the combustion chamber.
• Inspect the fuel injectors. Remove the injectors and visually inspect.
• Perform the Cylinder Balance Test with a scan tool.
• Perform the Injector Force Drive with a scan tool.
• Observe the Fuel Compensation for each cylinder at idle on the scan tool.
Engine Mechanical Checks Inspect the engine mechanical for the following conditions. Refer to the Engine
Mechanical section.
• Poor cylinder compression.
• Incorrect basic engine parts such as camshaft, cylinder head, pistons, etc..
• Inspect for any excessive oil entering combustion chamber.
Additional Checks • Inspect other possible causes that can make similar noise such as loose component
parts, bracket, mount and weak clutch damper spring.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1960 of 6020
ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM (4JK1/4JJ1) 6E-343
Excessive Smoke (Black Smoke)
ChecksAction
Definition:
Black smoke under load, idle or start up hot or cold.
Preliminary Check • Ensure the vehicle has an actual problem.
• Inspect the ECM grounds for being clean, tight, and in their proper locations.
• Remove the air cleaner and check for dirt, or for air ducts being plugged or restricted. Replace as necessary.
• Inspect the fuel quality (cetane index).
• Inspect the engine oil level and quality.
• Inspect the programmed fuel injector ID code for each cylinder.
• Inspect the Scan Tool Data List in this section.
• Inspect the Service Bulletin.
Sensor Checks Inspect the engine control sensors for the following conditions. Refer to the Scan Tool
Data List in this section.
• Compare the Coolant Temperature with the Intake Air Temperature (IAT) and Fuel Temperature (FT) parameters on a cold engine condition. If the difference among
temperature reading is more than 5 °C (9 °F) on a cold engine, check for high
resistance in each circuit or for a skewed sensor.
Notice: The mass air flow (MAF) sensor is heated and as a result the IAT may indicate
a higher than normal intake air temperature if the ignition switch is being ON.
• Observe the MAF parameter for a skewed or slow MAF sensor.
• Observe the Fuel Rail Pressure (FRP) Sensor parameter with the engine OFF. The FRP Sensor should read 0.9 to 1.0 volt with the key ON and engine OFF after the
engine has stopped running for a minimum of 1 minute. If not, check for high
resistance in each circuit or for a skewed sensor.
• Observe the Fuel Rail Pressure and Desired Fuel Rail Pressure parameter between idle and W.O.T. (accelerator pedal full travel) in Neutral. Fuel Rail Pressure
parameter should follow within ±5 MPa ( ±725 psi) quick enough.
• Observe the Barometric Pressure (BARO) parameter. The BARO parameter should indicate near surrounding barometric pressure. Refer to Altitude vs. Barometric
Pressure. (Standard output)
• Observe the Boost Pressure and BARO with ignition ON and engine OFF. Both parameters should be within the 7.0 kPa (1.0 psi) each other. (High output)
Fuel System Checks Inspect the fuel system for the following conditions. Refer to the Fuel System section.
• Fuel injectors. Remove the injectors and visually inspect.
• Perform the Cylinder Balance Test with a scan tool.
• Perform the Pilot Injection Control with a scan tool.
• Observe the Fuel Compensation for each cylinder at idle on the scan tool.
Air Intake System Checks Inspect the air intake system for the following conditions.
• Air cleaner, air intake ducts and charge air cooler for a restriction, holes, or leaks.
• A restriction in the turbocharger inlet duct.
• Intake throttle valve for a stuck condition.
• A restriction or leak in the intake manifold.
• A restriction or damaged at MAF sensor.
• A worn or damaged turbocharger turbine wheel, shaft or compressor wheel. Refer to turbocharger inspection in the Engine Mechanical section.
Exhaust System Checks Inspect the exhaust system for a possible restriction. Refer to the Exhaust System
section.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1962 of 6020
ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM (4JK1/4JJ1) 6E-345
Excessive Smoke (White Smoke)
ChecksAction
Difinition:
White smoke under load, idle or start up hot or cold.
Preliminary Check • Ensure the vehicle has an actual problem.
• Inspect the ECM grounds for being clean, tight, and in their proper locations.
• Inspect the fuel quality (cetane index).
• Inspect the programmed fuel injector ID code for each cylinder.
• Inspect the Scan Tool Data List in this section.
• Inspect the Service Bulletin.
Sensor Checks Inspect the engine control sensors for the following conditions. Refer to the Scan Tool
Data List in this section.
• Compare the Coolant Temperature with the Intake Air Temperature (IAT) and Fuel Temperature (FT) parameters on a cold engine condition. If the difference among
temperature reading is more than 5 °C (9 °F) on a cold engine, check for high
resistance in each circuit or for a skewed sensor.
Notice: The mass air flow (MAF) sensor is heated and as a result the IAT may indicate
a higher than normal intake air temperature if the ignition switch is being ON.
• Observe the Fuel Rail Pressure (FRP) Sensor parameter with the engine OFF. The FRP Sensor should read 0.9 to 1.0 volt with the key ON and engine OFF after the
engine has stopped running for a minimum of 1 minute. If not, check for high
resistance in each circuit or for a skewed sensor.
• Observe the Fuel Rail Pressure and Desired Fuel Rail Pressure parameter between idle and W.O.T. (accelerator pedal full travel) in Neutral. Fuel Rail Pressure
parameter should follow within ± 5 MPa ( ± 725 psi) quick enough.
• Observe the Accelerator Pedal Position (APP). APP parameter should change linearly from 0 to 100% according to the accelerator pedal operation.
• Observe the Boost Pressure and Barometric Pressure (BARO) with ignition ON and engine OFF. Both parameters should be within the 7.0 kPa (1.0 psi) each other.
• Crankshaft position (CKP) sensor is tight and the sensor rotor is not damaged.
Fuel System Checks • If excessive smoke is present, check for a stuck open fuel injector. Inspect for fuel
leakage into the combustion chamber.
• Fuel injectors. Remove the injectors and visually inspect.
• Perform the Cylinder Balance Test with a scan tool.
• Perform the Pilot Injection Control with a scan tool.
• Observe the Fuel Compensation for each cylinder at idle on the scan tool.
Air Intake System Checks Inspect the air intake system for the following conditions.
• Air cleaner, air intake ducts and charge air cooler for a restriction, holes, or leaks.
• A restriction in the turbocharger inlet duct.
• Intake throttle valve for a stuck condition.
• A restriction or leak in the intake manifold.
• A restriction or damaged at MAF sensor.
• Perform the Swirl Control Solenoid Test with a scan tool. Inspect the diaphragm valve operation when it commanded ON/ OFF.
• A worn or damaged turbocharger turbine wheel, shaft or compressor wheel. Oil leak from turbocharger. Refer to turbocharger inspection in the Engine Mechanical
section.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1966 of 6020

ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM (4JK1/4JJ1) 6E-349
4. In order to get programming approval, the on-screen displays a message to user. Get
programming approval from the TIS 2000 using
the following procedure:
a. Connect a scan tool to the terminal that installed TIS 2000 with the latest software and
the hardware key is plugged into port.
b. Turn ON the scan tool and keep at title screen.
c. Launch the TIS application.
d. Select the Security Access at the main screen.
e. Highlight the “Tech 2” on the Diagnostic Tool Selection screen and click “Next”.
f. Click “Close” on the Security Access Enabled screen.
g. Turn OFF the scan tool.
h. Disconnect the scan tool from the terminal.
5. Install a scan tool to the vehicle.
6. Turn ON the ignition, with the engine OFF.
7. Select Diagnostics > appropriate vehicle identification > 4JK1 or 4JJ1 > Programming >
Program ECU.
8. Verify the VIN on the screen if programmed at previously described SPS. If not programmed or
incorrect VIN, input correct VIN.
9. Input 24 digits of each fuel injector ID code.
10. After complete the programming, turn OFF the ignition for 30 seconds.
11. Start the engine and let idle.
12. Inspect for a proper engine running condition and for no DTC's. Refer to the Diagnostic System
Check - Engine Controls if needed.
G. Supply Pump Relearn 1. Install a scan tool.
2. Start the engine and let idle until engine coolant temperature reads 65 °C (149 °F) or higher while
observing the Supply Pump Status parameter with
a scan tool. The scan tool parameter changes
status Not Learn > Learning > Learned.
3. If the ECM has correctly learned the fuel supply pump current adjustment, the Supply Pump Status
parameter on the scan tool will repeatedly indicate
Learning and Learned.Service Programming System (SPS)
Description
The service programming system (SPS) allows a
technician to program a control module through the
data link connector (DLC). The information transfer
circuit that is used at the DLC is the same serial data
circuit used by the scan tool for retrieving DTCs,
displaying data, clearing DTCs etc. This procedure
offers the ability to install software/ calibrations
matched to a particular vehicle.
Most control modules have two types of memory. The
software/ calibrations reside in the flash memory. The
two types of memory are listed below:
• Electrically Erasable Programmable Read Only Memory (EEPROM)
This type of memory allows selected portions of
memory to be programmed while other portions
remain unchanged.
Certain learned values reside in the EEPROM,
such as:
- The vehicle identification number (VIN)
- The software/ calibrations identification numbers
- The control module security information
• Flash Read Only Memory-Flash Memory Flash memory has increased memory storage
capacity. During programming, all information
within this type of memory is erased, and then
replaced with entirely new information.
Service Programming Methods
The two methods of programming an ECM are listed
below:
• Remote Programming
• Pass Thru Programming
For information on programming an ECM using one of
the methods listed above, refer to Service
Programming System (SPS) (Remote Procedure) or
Service Programming System (SPS) (Pass-Thru
Procedure).
Before Programming a Control Module
Important: DO NOT program an existing ECM with the
identical software/ calibration package. This procedure is not
a short cut to correct the driveability condition. This is an
ineffective repair. An ECM should only be programmed when
the following occurs:
• When a service procedure instructs you to replace the ECM.
• An updated software/ calibrations is released.
Ensure that the following conditions are met before
programming an ECM:
• The scan tool PCMCIA card is programmed with the latest software.
• The TIS 2000 is installed with the latest software.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1967 of 6020

6E-350 ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM (4JK1/4JJ1)
• The hardware key is plugged into the computerport.
• Vehicle system voltage: - There are no charging system concerns. Allcharging system concerns must be repaired
before programming the ECM.
- The battery voltage is greater than 12 volts but less than 16 volts. The battery must be fully
charged before programming the ECM.
- A battery charger is NOT connected to the vehicles battery. Incorrect system voltage or
voltage fluctuations from a battery charger may
cause programming failure or ECM damage.
- Turn OFF or disable any system that may put a load on the vehicles battery. Turn OFF or
disable systems such as:
◊ Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning
(HVAC) systems
◊ Headlights
◊ Room lights
◊ Accessory equipment
• The ignition switch is in the proper position. The scan tool prompts you to turn ON the ignition, with
the engine OFF. DO NOT change the position of
the ignition switch during the programming
procedure unless instructed to do so.
• All tool connections are secure: - The RS-232 cable
- The connection at the DLC
- The voltage supply circuits
• DO NOT disturb the tool harnesses while programming. If an interruption occurs during the
programming procedure, programming failure or
ECM damage may occur.
• If you are performing the Pass-Thru programming procedure using a notebook computer without the
power cord, ensure that the internal battery is fully
charged.
Service Programming System (SPS)
(Remote Procedure)
Notice: Some module will not accept SPS remote
procedure using 10MB PCMCIA card. In such case,
use 32MB PCMCIA card or SPS pass-thru procedure.
The Remote SPS method is a three-step process that
involves the following procedures:
1. Connecting the scan tool to the vehicle and obtaining the information from the ECM.
2. Connecting the scan tool to the terminal and downloading a new calibration file from the
terminal into the scan tool memory.
3. Reconnecting the scan tool to the vehicle and uploading the new calibration file into the ECM. Performing the Remote Procedure
1. Connect a scan tool to the vehicle and obtain the ECM information using the following procedure:
Notice: Ensure the ECM is installed in the vehicle and
the battery is fully charged before programming.
a. Install a scan tool.
b. Turn ON the ignition, with the engine OFF.
c. Select Service Programming System (SPS) > Request Info.
d. If there is already stored in the scan tool, the existing data is displayed on the screen. The
scan tool asks user to keep existing data "Keep
Data" or "Continue" to request new vehicle
information from the ECM. If there is no data in
the scan tool, it will immediately start vehicle
identification.
e. Select the vehicle description by following the on-screen instructions based on stamped VIN
or affixed VIN plate on the vehicle.
f. During obtaining information, the scan tool is receiving information from all modules at the
same time. But only ECM information is
displayed on the screen.
g. Turn OFF all accessories and press "Okay".
h. Verify that the correct VIN is displayed on the scan tool. If the VIN is incorrect or no VIN,
record the correct VIN.
2. Turn OFF the ignition.
3. Turn OFF the scan tool and disconnect from the vehicle.
4. Transfer the data from the terminal to the scan tool using the following procedure:
Notice: The TIS supports service programming with
the Tech 2 scan tool only.
a. Connect the scan tool to the terminal.
b. Launch the TIS application.
c. Select the Service Programming System at the main screen.
d. Highlight the following information on the Select Diagnostic Tool and Programming Process
screen, then click "Next".
• Select Diagnostic Tool - Tech 2
• Select Programming Process - Identify whether an existing ECM is being
reprogrammed or an ECM is being replaced
with a new one
• Select ECU Location - Vehicle
e. Verify the connections on the Preparing for Communication screen, then click "Next".
f. Verify the VIN on the Validate Vehicle Identification Number (VIN) screen, then click
"Next".
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1981 of 6020

6E-364 ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM (4JK1/4JJ1)
Fuel Injection System Description
Fuel Injection Quantity Control
This control determines the fuel injection quantity by
adding coolant temperature, fuel temperature, intake
air temperature, barometric pressure, mass air flow and
some switch inputs information corrections to the basic
injection quantity is calculated by the ECM based on
the engine operating conditions (engine speed,
accelerator pedal pressing amount and boost pressure
sensor). More fuel rate indicates if the engine load is
increased as the accelerator pedal is stepped on at
constant engine speed.
Combined with high pressure injection of atomized fuel,
this control improves exhaust gas and ensures proper
fuel consumption. Compared with conventional
mechanical governors, an electronic control system
provides higher degree of freedom of fuel injection
quantity control, thereby presenting high accelerator
response (acceleration feeling and pressing feeling).
Starting Injection Quantity Control
At the engine starting (after the key switch is turned to
the START position to start the engine, up to return of
key switch to the ON position), optimum fuel injection
quantity is controlled based on the information on the
engine speed and coolant temperature. At low
temperature, the fuel injection quantity increases.
When the engine started completely, this boosted
quantity mode at the starting is cancelled and normal
running mode is restored.
Idle Speed Control
A control is made so as to achieve stable idling speed
at all time regardless of engine secular changes or
engine condition variations. The ECM sets target idling
speed and controls the fuel injection quantity according
to the engine conditions (actual engine speed, coolant
temperature and engine load) to follow actual engine
speed to the target idling speed so as to ensure stable
idling speed.
Idle Vibration Control
A control is made so as to reduce the engine vibration
caused by torque variations between cylinders due to
variations in fuel injection quantity of each cylinder or
injector performance. The ECM corrects the injection
quantity between cylinders based on the revolution
signals from the crankshaft position (CKP) sensor.
Normal range of correction quantity between cylinders
is within ±5 mm
3.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2129 of 6020
ENGINE FUEL (C24SE) 6C-11
140R100028
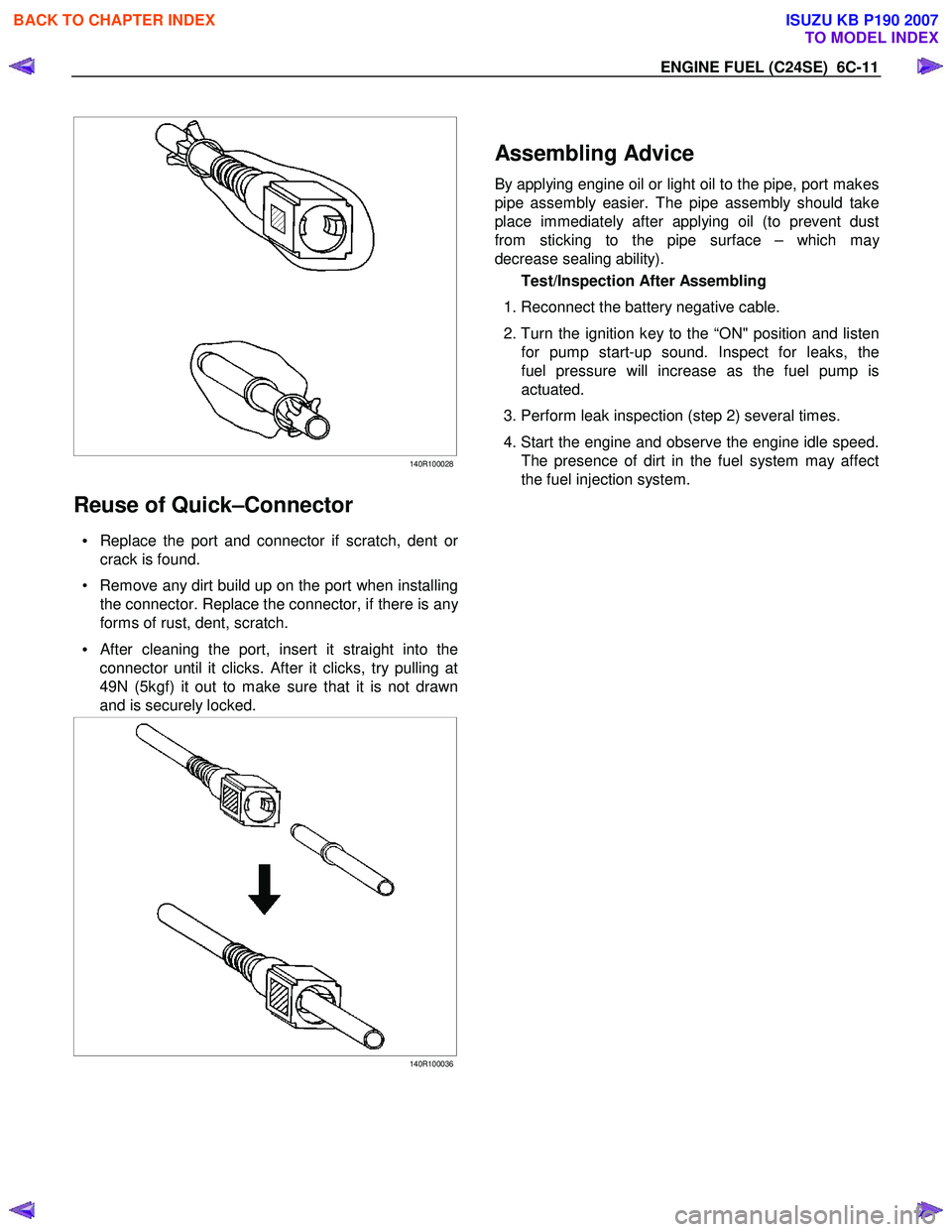
Reuse of Quick–Connector
• Replace the port and connector if scratch, dent or
crack is found.
• Remove any dirt build up on the port when installing the connector. Replace the connector, if there is an
y
forms of rust, dent, scratch.
•
After cleaning the port, insert it straight into the
connector until it clicks. After it clicks, try pulling at
49N (5kgf) it out to make sure that it is not drawn
and is securely locked.
140R100036
Assembling Advice
By applying engine oil or light oil to the pipe, port makes
pipe assembly easier. The pipe assembly should take
place immediately after applying oil (to prevent dust
from sticking to the pipe surface – which ma
y
decrease sealing ability).
Test/Inspection After Assembling
1. Reconnect the battery negative cable.
2. Turn the ignition key to the “ON" position and listen
for pump start-up sound. Inspect for leaks, the
fuel pressure will increase as the fuel pump is
actuated.
3. Perform leak inspection (step 2) several times.
4. Start the engine and observe the engine idle speed.
The presence of dirt in the fuel system may affect
the fuel injection system.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2162 of 6020

6D3-14 STARTING AND CHARGING SYSTEM
7. To remove the pulley, mount an 8mm Allen key in the vice
with the short end upwards, place a 24mm ring spanner on
the puley nut, position the internal hexagon of the roto
r
shaft onto the Allen ken, loosen the nut and remove the
pulley.
Note: the pulley has an integral boss which locks up against
the bearing,
therefore no thrust collar is provided.
8. Removing the rotor assembly. Remove the four retaining screws from the drive end housing, withdraw the roto
r
complete with the bearing.
Note: the rotor must not be pressed from the drive end housing
using a press as the bearing retaining plate and drive end
housing will be damaged or distorted. Parts removed in this
way must be replaced if the integrity of the generator is to be
maintained.
9. Remove the drive end bearing from the rotor shaft using a
chuck type puler, take care not to distort the fan assembl
y
during this process.
10. Remove the slipring end bearing using the same meghod as in 9.
Clean
Thoroughly clean all components except the rotor and stator
with an approved cleaning agent. Ensure that all traced of oil
and dirt are removed. If an abrasive cleaner is used to remove
scale and paint from the housings take care not to abrade the
bearing and mounting spigot surfaces. The rotor and stator
must be cleaned with compressed air only, the use of solvents
could cause damage to the insulating materials.
Inspection
1. Rectifier assembly
The following test equipment is required.
The recitifier assembly is not repairable and must be replaced
if a faulty diode is detected during inspection.
(a)
Adiode tester where the DC output at the test probes does
not exceed 14 volts or in the case of AC testers 12 volts
RMS. This is to ensue that when inspection rectifiers fitted
with zener power diodes the forward and reverse checks
are completer and are not masked by the diode turning on
due to the zener breakdown voltage.
(b) A zenere diode tester with a DC output in excess of 30 volts, the tester should also incorporate internal current
limiting set to 5 Ma. to prevent high currents during
inspection.
(c) Diodes can be destroyed during service due to high temperature and overload, open circuits are usually a result
of excessive voltage.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007