2007 ISUZU KB P190 torque
[x] Cancel search: torquePage 2514 of 6020
Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–35
2.11 Engine Noise Under Load
NOTE
A cold piston knock which disappears in
approximately 1.5 minutes from start up, should
be considered acceptable. A cold engine knock
usually disappears when the specific cylinder’s
secondary ignition circuit is grounded out during
diagnosis.
A light rattle/tapping noise may indicate a valve train/upper engine concern, while a low rumble/knocking may indicate a
crankshaft, piston or lower engine concern.
Cause Correction
Low oil pressure. 1 Perform an oil pressure test, refer to 2.19
Engine Oil Pressure Diagnosis.
2 Repair or replace the engine oil pump as required, refer to 3.17 Oil Pump Assembly.
Detonation or spark knock. Confirm the correct operation of the ignition system, refer to
6C1-2 Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics.
Loose torque converter bolts. Inspect and tighten the torque converter bolts to the correct
torque specification, refer to 7C1 Automatic – 4L60E –
General Information – 4L60E – General Information.
Cracked flexplate. Replace the flywheel/flex-plate as required, refer to 4.3
Flexplate Assembly.
Excessive connecting rod bearing clearance. Inspect the connecting rod, crankshaft and bearings and
repair/replace components as required, refer to 4.5
Pistons, Pins, Rings, Connecting Rods and Big-
end Bearings and 4.6 Crankshaft and Main Bearings.
Excessive crankshaft bearing clearance Inspect the crankshaft, cylinder block journals, main
bearings and main bearing caps and repair/replace
components as required, refer to 4.6 Crankshaft
and Main Bearings and 4.7Cylinder Block.
2.12 Engine Will Not Crank – Crankshaft Will Not Rotate
Cause Correction
Seized accessory drive system component. 1 Remove the accessory drive belt, refer to 3.5
Accessory Drive Belt.
2 Rotate the crankshaft by hand at the balancer pulley or flywheel.
3 Repair or replace accessory drive system components as required.
Hydraulically locked cylinder caused by:
• coolant in cylinder,
• oil in cylinder, or
• fuel in cylinder. 1 Remove the spark plugs and check for fluid, refer to
6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 – Service
Operations.
2 Inspect for broken head gasket/s.
3 Inspect for cracked engine block or cylinder head.
4 Inspect for sticking fuel injector.
5 Repair or replace components as required.
Seized torque converter. 1 Remove the torque converter bolts, refer to 7C1
Automatic – 4L60E – General Information – 4L60E –
General Information.
2 Rotate the crankshaft by hand at the balancer pulley or flywheel.
3 Repair or replace torque converter as required.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2524 of 6020
Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–45
Step Action Yes No
10 Inspect for missing, loose or incorrect fasteners.
Did you find any missing, loose or incorrect fasteners? Go to Step 11 Go to Step 12
11 Tighten any loose fasteners to the torque specification as provided in
provided in 6. Torque W rench Specifications.
Replace any incorrect or missing fasteners.
Did you complete the repairs? Go to Step 15 —
12 Inspect for a bent pulley. Did you find any bent pulleys? Go to Step 13 Go to Step 14
13 Replace bent pulleys as required. Did you complete the repair? Go to Step 15 —
14 Replace the accessory drive belt, refer to 3.5 Accessory Drive Belt.
Did you complete the repair? Go to Step 15 —
15 Reinstall the accessory drive belt and operate the system to confirm the repair.
Did you correct the chirp noise? Accessory drive
system OK Go to 2.2
Symptoms, and restart the
diagnosis
Drive Belt Squeal
Definition
Accessory drive belt squealing can be defined as a loud screeching noise caused by a slipping drive belt. Belt squeal is
unusual in multi-rib belts. Drive belt squeal generally occurs when a heavy load is applied to the drive belt, such as an
air-conditioning compressor engagement, snapping the throttle, seized pulley or a faulty accessory drive component.
Diagnostic Aids
If the noise is intermittent, confirm the accessory drive components by varying their loads, making sure they are operated
to their maximum capacity. An overcharged A/C system, restrictions in the power steering pressure circuit or a faulty
generator or coolant pump are likely causes of accessory drive belt squeal.
A loose or incorrectly installed body component, suspension component or other item may be the cause of the noise.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to steps in the diagnostic table.
2 The noise may not be engine related. This step is to confirm the engine is making the noise. If the engine is not making the noise, do not proceed further with this diagnostic procedure.
3 The noise may be an internal engine noise. Removing the drive belt and operating the engine briefly will confirm whether or not the noise is related to the drive belt.
CAUTION
When running the engine with the accessory
drive belt removed, the coolant pump will not
be operating and the engine may overheat if
left unsupervised even for a short period.
NOTE
There may also be a number of DTCs set when
running the engine with the accessory drive belt
removed.
4 Confirms an accessory drive component does not have a seized bearing. W ith the belt removed, test the bearings in the accessory drive components spin free and smooth.
5 Confirms the drive belt tensioner is operating correctly. If the drive belt tensioner is not operating correctly, drive belt tension will not be maintained, resulting in a belt squealing noise
6 Confirms the belt is not too long, which would prevent the tensioner from working as intended. Also, if an excessively long belt has been fitted, it may also be routed incorrectly and may be turning an accessory drive
component in the wrong direction.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2529 of 6020

Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–50
Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1 Did you review the information provided in 2.2 Symptoms, and
perform the required inspections. Go to Step 2 Go to 2.2
Symptoms
2 Confirm the customer complaint. Is there a rumbling noise? Go to Step 3 Refer to Diagnostic
Aids in this Section
3 1 Remove the drive belt, refer to 3.5 Accessory Drive Belt.
2 Operate the engine for no more than 40 seconds.
Does the vibration noise still exist? Accessory drive
system OK.
Go to 4.2
Symptoms, and
restart the diagnosis Go to Step 4
4 Inspect the accessory drive belt for damage, wear, debris build-up or
sections of missing ribs.
Did you find any damage, wear, debris build-up or missing ribs? Go to Step 5 Go to Step 6
5 Install a new accessory drive belt, refer to 3.5 Accessory Drive Belt.
Did you replace the accessory drive belt? Go to Step 10 —
6 Inspect for incorrect, loose, missing or damaged fasteners. Did you find any incorrect, loose, missing or damaged fasteners? Go to Step 7 Go to Step 8
7 Tighten any loose fasteners to the correct torque specification, refer to
6 Torque W rench Specifications.
Replace any incorrect or missing fasteners.
Did you complete the repairs? Go to Step 10 —
8 Inspect the coolant pump for a bent shaft, refer to 6B1 Engine Cooling – V6.
Did you find and repair a bent coolant pump shaft? Go to Step 10 Go to Step 9
9 Inspect for bent, cracked or damaged accessory drive component mounting brackets.
Did you find and repair any bent brackets? Go to Step 10 Refer to Diagnostic
Aids in this Section
10 If required, reinstall the accessory drive belt and operate the system to
confirm the repair.
Did you correct the vibration? Accessory drive
system OK Refer to Diagnostic
Aids in this Section
Drive Belt Falls Off
Definition
The drive belt falls off during normal operation or does not ride correctly on the accessory drive pulleys.
Diagnostic Aids
If the accessory drive belt repeatedly falls off the drive pulleys, this is most likely due to pulley misalignment.
An extra load that is quickly applied and released by an accessory drive component (e.g. A/C compressor) may cause
the accessory drive belt to fall off. In this circumstance, confirm the fault by operating the accessory drive components in
turn, noting which one caused the belt to fall off.
Lack of drive belt tension may also cause the belt to fall off the pulleys. Low drive belt tension could be caused by one of
the following:
• an incorrect drive belt length,
• a faulty drive belt tensioner, or
• a stretched or faulty drive belt.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to steps in the diagnostic table.
2 Confirms the condition of the drive belt. Damage may have occurred to the drive belt when it first fell off or it may have been damaged which caused the belt to fall off.
4 Misalignment of the pulleys may be caused by:
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2530 of 6020
Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–51
• the incorrect installation or mounting of an accessory drive component,
• the incorrect installation of an accessory drive component pulley, or
• a damaged or bent accessory drive pulley.
Test for a misaligned pulley using a suitable straight edge in the pulley grooves across two or more pulleys. If a misaligned pulley is found, refer to the service information for the particular component, for the correct pulley
replacement procedures.
5 Inspecting the pulleys should include an inspection for dents or other damage that would prevent the drive belt from seating correctly in all of the pulley grooves or on the smooth surface of a pulley when the back side of the belt is
used.
6 Accessory drive component mounting brackets that are bent will cause the drive belt to fall off.
7 Inspection of the fasteners can eliminate the possibility that an incorrect fastener was installed. Missing, loose or incorrect fasteners may cause pulley misalignment from the fasteners moving under load. Over-tightening of the
fasteners may cause deflection of mounting brackets and result in misaligned accessory drive pulleys.
Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1 Did you review the information provided in 2.2 Symptoms, and
perform the required inspections. Go to Step 2 Go to 2.2
Symptoms
2 Inspect for a damaged accessory drive belt.
Did you find any damage on the drive belt? Go to Step 3 Go to Step 4
3 Install a new accessory drive belt, refer to 3.5 Accessory Drive Belt.
Does the drive belt continue to fall off? Go to Step 4 Go to Step 12
4 Inspect the accessory drive system pulleys for misalignment
Did you find and repair any misaligned drive system pulleys? Go to Step 12 Go to Step 5
5 Inspect for a dented or cracked accessory drive system pulley. Did you find and repair any dented or cracked drive system? Go to Step 12 Go to Step 6
6 Inspect for bent accessory drive component mounting brackets.
Did you find and repair any bent mounting brackets? Go to Step 12 Go to Step 7
7 Inspect for incorrect, loose, missing or damaged fasteners. Did you find any incorrect, loose, missing or damaged fasteners? Go to Step 8 Go to Step 9
8 Tighten any loose fasteners to the correct torque specification, refer to 6 Torque W rench Specifications.
Replace any incorrect or missing fasteners.
Does the drive belt continue to fall off? Go to Step 9 Go to Step 12
9 Test the accessory drive belt tensioner for correct operation, refer to
Accessory Drive Belt Tensioner Diagnosis in this Section.
Did you accessory drive belt tensioner operate correctly? Go to Step 11 Go to Step 10
10 Replace the drive belt tensioner, refer to
3.7 Accessory Drive Belt Tensioner Assembly.
Does the drive belt continue to fall off? Go to Step 11 Go to Step 12
11 Inspect for a failed drive belt idler and drive belt tensioner bearings.
Did you find and repair any failed bearings? Go to Step 12 Refer to Diagnostic
Aids in this Section
12 If required, reinstall the accessory drive belt and operate the system to confirm the repair.
Does the drive belt continue to fall off? Go to Step 2 Accessory drive
system OK
Drive Belt Excessive Wear
Definition
Excessive wear can be defined as wear at the outside ribs of the drive belt (frayed edges), usually caused by an
incorrectly installed drive belt
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2531 of 6020
Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–52
Diagnostic Aids
Excessive wear of a drive belt is usually caused by an incorrect installation or an incorrect drive belt fitted. Minor pulley
misalignment will not cause excessive wear, but will cause the drive belt to fall off. Major pulley misalignment may cause
excessive wear, but would also result in the drive belt falling off.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to steps in the diagnostic table.
2 Confirms the drive belt is correctly installed onto all of the accessory drive system pulleys. W ear on the drive belt may be caused by incorrectly positioning the drive belt by one or more grooves to a particular pulley.
3 The installation of the drive belt that is the incorrect width will cause wear on the drive belt. The drive belt ribs should match all the grooves on all the pulleys in the accessory drive system.
4 Confirms the drive belt is not contacting any parts of the engine or body while the engine is running. There should be sufficient clearance when the accessory drive component loads varies. The drive belt should not come into
contact with any engine or body parts.
Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1 Did you review the information provided in 2.2 Symptoms, and
perform the required inspections. Go to Step 2 Go to 2.2
Symptoms
2 Inspect the accessory drive belt for correct installation.
Is the drive belt installed correctly? Go to Step 5 Go to Step 3
3 Ensure that the drive belt is the correct one for the application. Is the correct drive belt installed? Go to Step 5 Go to Step 4
4 Is the drive belt contacting any engine or body components with the engine running? Go to Step 6 Refer to Diagnostic
Aids in this Section
5 Install a new accessory drive belt, refer to 3.5 Accessory Drive Belt.
Did you replace the accessory drive belt? Go to Step 6 —
6 If required, reinstall the accessory drive belt and operate the system to confirm the repair.
Did you correct the excessive wear? Accessory drive
system OK Go to Step 2
Accessory Drive Belt Tensioner Diagnosis
Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1 1 Remove the accessory drive belt.
2 Inspect the drive belt tensioner pulley.
Is the drive belt tensioner pulley loose or misaligned? Go to Step 4 Go to Step 2
2 Rotate the drive belt tensioner.
Does the drive belt tensioner rotate freely, without any unusual
resistance or binding? Go to Step 3 Go to Step 4
3 1 Using a suitable torque wrench, measure the torque required to
lift the drive belt tensioner off the stop.
2 Using a known good tensioner, measure the torque required to lift the drive belt tensioner off the stop.
Is the first torque reading within 10% of the second reading?
Accessory drive belt tensioner OK Go to Step 4
4 Replace the drive belt tensioner, refer to
3.7 Accessory Drive Belt Tensioner Assembly.
Is the repair complete?
Accessory drive belt tensioner OK —
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2532 of 6020

Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–53
3 Minor Service Operations
ATTENTION
The V6 engine is a combination of numerous components, containing machined, honed, polished and lapped
surfaces manufactured on the latest, high technology production equipment. Many of the components
contain tolerances measured in thousandths of a millimetre. Consequently, when any engine component is to
be serviced, care and cleanliness are extremely important.
Prior to re-assembly of the engine, all components must be cleaned and inspected in accordance with the
relevant clean and inspect procedures throughout this Section, and replaced or repaired where required.
In addition to cleaning and inspecting components, a liberal coating of engine oil should be applied to friction
surfaces during assembly to protect and lubricate the surfaces on initial operation.
When performing any service operation, it should be understood that correct cleaning and protection of
machined surfaces and friction areas is part of the repair procedure. This is considered standard workshop
practice, even if not specifically stated. Torque values must be used as specified during reassembly to
ensure correct retention of all components.
Through out this section, fastener torque wrench specifications may be accompanied with the following
identification marks:
■ Fasteners must be replaced after loosening.
Fasteners either have micro encapsulated sealant applied or incorporate a mechanical thread lock and
should only be re-used once. If in doubt, replacement is recommended.
If one of these identification marks is present alongside a fastener torque wrench specification, the
recommendation regarding that fastener must be adhered to.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2534 of 6020
Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–55
Figure 6A1 – 24
6 Once the oil has completely drained, reinstall the drain plug and tighten to the correct torque specification.
Oil pan drain plug
torque specification ............................................25.0 Nm
7 Replace the oil filter, refer to 3.2 Oil Filter.
8 Lower the vehicle to the ground and fill with the specified amount of SAE 5W 30 lubricant.
Engine Oil Capacity:
With Oil Filter Change ........................................6.5 litres
9 Install the oil fill cap.
10 Start the engine and check for leaks.
Pressure Check
1 Run the engine to bring it to normal operating temperature.
2 Park the vehicle on a level surface. A vehicle not level will affect the accuracy of the level reading.
3 Stop the engine and wait 5 to 10 minutes to allow the oil to drain back into the oil pan.
4 Check the oil level and top up with the recommended engine oil as required, refer to Check, in this Section.
5 Remove the engine oil pressure sensor (1), refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 – Service
Operations.
6 Install the oil pressure gauge adaptor, Tool No. J36648-A into the oil pressure sender hole in the oil
filter housing.
7 Install a suitable oil pressure gauge into the adaptor.
8 Start the engine.
9 Measure and record the pressure reading on the gauge at idle and 2000 r.p.m. Compare the results
with the specification.
Minimum engine oil pressure
@ idle................................................................... 69 kPa
@ 2000 r.p.m. .................................................... 138 kPa
10 If the engine oil pressure is not to specification, refer to 2.19 Engine Oil Pressure Diagnosis.
11 After completing the engine oil pressure check, stop the engine and remove the oil pressure gauge.
Figure 6A1 – 25
12 Reinstall the oil pressure sensor, refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 – Service Operations.
13 Start the engine and check for leaks.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2536 of 6020
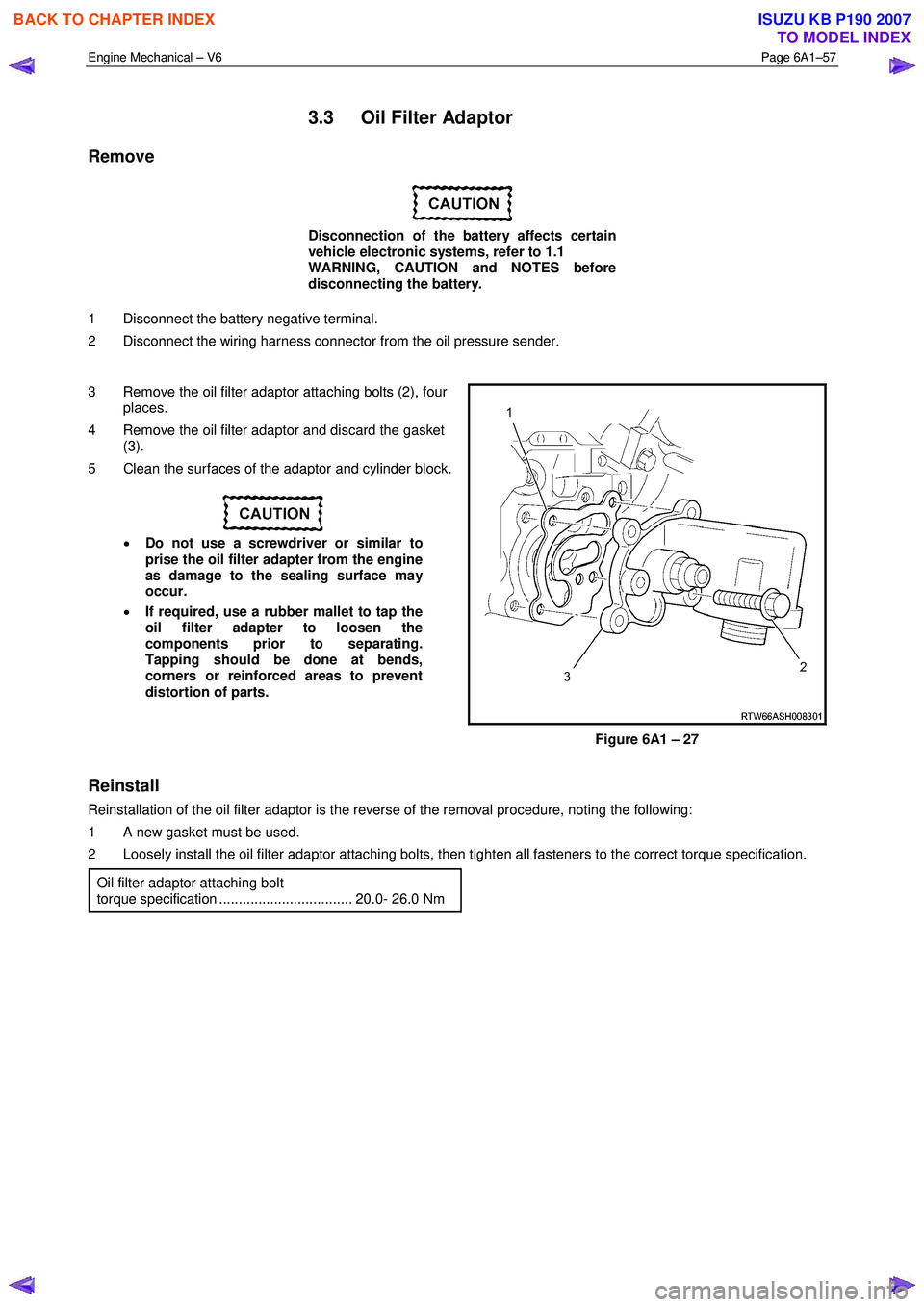
Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–57
3.3 Oil Filter Adaptor
Remove
Disconnection of the battery affects certain
vehicle electronic systems, refer to 1.1
WARNING, CAUTION and NOTES before
disconnecting the battery.
1 Disconnect the battery negative terminal.
2 Disconnect the wiring harness connector from the oil pressure sender.
3 Remove the oil filter adaptor attaching bolts (2), four places.
4 Remove the oil filter adaptor and discard the gasket (3).
5 Clean the surfaces of the adaptor and cylinder block.
• Do not use a screwdriver or similar to
prise the oil filter adapter from the engine
as damage to the sealing surface may
occur.
• If required, use a rubber mallet to tap the
oil filter adapter to loosen the
components prior to separating.
Tapping should be done at bends,
corners or reinforced areas to prevent
distortion of parts.
Figure 6A1 – 27
Reinstall
Reinstallation of the oil filter adaptor is the reverse of the removal procedure, noting the following:
1 A new gasket must be used.
2 Loosely install the oil filter adaptor attaching bolts, then tighten all fasteners to the correct torque specification.
Oil filter adaptor attaching bolt
torque specification .................................. 20.0- 26.0 Nm
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007