2007 ISUZU KB P190 engine mount
[x] Cancel search: engine mountPage 3479 of 6020
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–201
18 1 Replace the ECM. Refer to Engine Control
Module (ECM) Remove, Reinstall and ECM
Reset in 6C1- Engine Management – V6 Service
Operations.
Did you complete the replacement? —
Go to Step 19 —
19 1 Clear the DTCs, using Tech 2.
2 Turn OFF the ignition for 30 seconds.
3 Start the engine.
4 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
Does DTC P2195 or P2197 fail this ignition cycle? —
Go to Step 2 Go to Step 20
20 1 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does Tech 2 display any DTC? —
Go to the
appropriate DTC Table in this Section System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, clear all DTCs and verify correct operation
7.56 P2196 or P2198
DTC Descriptors
This diagnostic procedure supports the following DTCs:
• DTC P2196 – B1S1 O2 Sensor – System Too Rich (Bank 1 Sensor 1)
• DTC P2198 – B2S1 O2 Sensor – System Too Rich (Bank 2 Sensor 1)
Circuit Description
The wide band heated oxygen sensor 1 (HO2S1) measures the amount of oxygen in the exhaust system and provides
more information than the switching style HO2S2. The wide band sensor consists of an oxygen sensing cell, an oxygen
pumping cell, and a heater. The exhaust gas sample passes through a diffusion gap between the sensing cell and the
pumping cell. The engine control module (ECM) supplies a voltage to the HO2S and uses this voltage as a reference to
the amount of oxygen in the exhaust system. An electronic circuit within the ECM controls the pump current through the
oxygen pumping cell, maintaining a constant voltage in the oxygen sensing cell.
The ECM monitors the voltage variation in the sensing cell and attempts to keep the voltage constant by increasing or
decreasing the amount of current flow, or oxygen ion flow, to the pumping cell. By measuring the amount of current
required to maintain the voltage in the sensing cell, the ECM can determine the concentration of oxygen in the exhaust.
The HO2S voltage is displayed as a lambda value. A lambda value of 1 is equal to a stoichiometric air fuel ratio of
14.7:1.
Under normal operating conditions, the lambda value will remain around 1. W hen the fuel system is lean, the oxygen
level will be high and the lambda signal will be high or more than 1. W hen the fuel system is rich, the oxygen level will
be low, and the lambda signal will be low or less than 1. The ECM uses this information to maintain the correct air / fuel
ratio.
Conditions for Running the DTC
• Before the ECM can report DTC P2196 or P2198 failed, DTCs P0137, P0138, P0140, P0141, P0157, P0158,
P0160, P0161, P2270, P2271, P2272, and P2273 must run and pass.
• The front and rear heated oxygen sensors are at operating temperature.
• The rear HO2S voltage signal is more than 150 mV.
• The front HO2S is more than 0.92 lambda.
• The Loop Status for both the front and rear sensors is Closed Loop.
• DTCs P2196 and P2198 run continuously once the above conditions are met.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3493 of 6020
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–215
10 1 Replace the appropriate HO2S. Refer to 6C1-3
Engine Management – V6 – Service Operations.
W as the repair completed? —
Go to Step 12 —
11 1 Replace the ECM. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine
Management – V6 – Service Operations.
W as the repair completed? —
Go to Step 12 —
12 1 Using Tech 2, clear the DTCs.
2 Switch off the ignition for 30 seconds.
3 Start the engine.
4 Operate the vehicle within the conditions for running the DTC.
Does any of the HO2S pumping current control circuit
DTCs fail this ignition cycle? —
Go to Step 2 Go to Step 13
12 Using Tech 2, select the DTC display function.
Does Tech 2 display any DTCs? —
Go to the
appropriate DTC Table in this Section System OK
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, clear all DTCs and verify correct operation
7.60 DTC P2626, P2627, P2628, P2629, P2630
or P2631
DTC Descriptors
• DTC P2626 – O2 Sensor Pump Current Trim Circuit Malfunction (Bank 1, Sensor 1)
• DTC P2627 – O2 Sensor Pump Current Trim Circuit Low Voltage (Bank 1, Sensor 1)
• DTC P2628 – O2 Sensor Pump Current Trim Circuit High Voltage (Bank 1, Sensor 1)
• DTC P2629 – O2 Sensor Pump Current Trim Circuit Malfunction (Bank 2, Sensor 1)
• DTC P2630 – O2 Sensor Pump Current Trim Circuit Low Voltage (Bank 2, Sensor 1)
• DTC P2631 – O2 Sensor Pump Current Trim Circuit High Voltage (Bank 2, Sensor 1)
Circuit Description
The wide band heated oxygen sensor (HO2S) measures the amount of oxygen in the exhaust system and provides
more information than the switching style HO2S. The wide band sensor consists of an oxygen sensing cell, an oxygen
pumping cell, and a heater. The exhaust gas sample passes through a diffusion gap between the sensing cell and the
pumping cell. The engine control module (ECM) supplies a voltage to the HO2S and uses this voltage as a reference to
the amount of oxygen in the exhaust system.
An electronic circuit within the ECM controls the pump current through the oxygen pumping cell in order to maintain a
constant voltage in the oxygen sensing cell. The ECM monitors the voltage variation in the sensing cell and attempts to
keep the voltage constant by increasing or decreasing the amount of current flow, or oxygen ion flow, to the pumping
cell. By measuring the amount of current required to maintain the voltage in the sensing cell, the ECM can determine
the concentration of oxygen in the exhaust.
The HO2S voltage is displayed as a lambda value. A lambda value of 1 is equal to a stoichiometric air fuel ratio of
14.7:1. Under normal operating conditions, the lambda value will remain around 1. W hen the fuel system is lean, the
oxygen level will be high and the lambda signal will be high or more than 1. W hen the fuel system is rich, the oxygen
level will be low, and the lambda signal will be low or less than 1. The ECM uses this information to maintain the correct
air / fuel ratio.
Conditions for Running the DTC
• Before the ECM can report DTC P2626 or P2629 failed, DTCs P0101, P0121, P0122, P0123, P0221, P0222,
P0223, P0336, and P0338 must run and pass.
• The engine is operating.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3517 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–239
B1/B2 S1 O2 Sensor 1 (Bank 1 or Bank 2 Sensor 1): This parameter displays the lambda output from the HO2S to the
ECM. A lambda below 1.0 indicates a rich exhaust, while a lambda above 1.0 indicates a lean exhaust.
B1/B2 S2 O2 Sensor 2 (Bank 1 or Bank 2 Sensor 2): This parameter displays the mV output from the HO2S to the
ECM. A lower voltage indicates a lean exhaust, while a higher voltage indicates a rich exhaust.
B1/B2 S1 O2 Sensor Heater (Bank 1 or Bank 2 Sensor 1): This parameter displays the resistance of the sensing
element within the ECM. The front sensors are normally regulated to 80 ohms.
B1/B2 S1/S2 O2 Sensor Heater Circuit Status (Bank 1 or Bank 2 Sensor 1 or Sensor 2): The parameter displays
‘Fault’ if the oxygen sensor heater control circuit is open, shorted to ground, or shorted to voltage. The parameter
displays ‘Undefined’ until the circuit has been commanded ON.
Barometric Pressure: This parameter displays the barometric pressure in kPa. The ECM uses the barometric pressure
for fuel control to compensate for altitude differences.
Barometric Pressure: This parameter displays the barometric pressure voltage. The control module uses the
barometric pressure for fuel control to compensate for altitude differences.
Brake Lamp Switch: This parameter displays the status of the brake lamp switch. W hen the brake pedal is pressed the
switch contacts close causing the vehicles brake lamps to illuminate.
Brake Switch Signal Status: This parameter displays the position of the torque converter clutch (TCC) brake pedal
switch input to the ECM.
Calculated ECT – Closed Loop Fuel Control (Engine Coolant Temperature): This parameter displays the modelled
temperature that the control module calculates from air entering the engine, coolant temperature, and ambient air
temperature. If the actual engine coolant temperature does not reach this calculated temperature within a predetermined
amount of time, a DTC will set.
Calculated ECT – Thermostat Diagnosis (Engine Coolant Temperature): This parameter displays the modelled
temperature that the control module calculates from air entering the engine, coolant temperature, and ambient air
temperature. If the actual engine coolant temperature does not reach this calculated temperature within a predetermined
amount of time, a DTC will set.
Calculated Pedal Position: This parameter displays the angle of the accelerator pedal position (APP) as calculated by
the ECM, using the signals from the APP sensors, as a percentage of throttle opening.
Calculated Throttle Position: This parameter displays the percentage of throttle opening, based on the two TP sensor
inputs to the ECM.
Catalyst Protection Mode: This parameter displays if the control module is commanding catalytic converter protection
or not.
Catalyst Temperature (Bank 1 or Bank 2): This parameter displays the catalytic converter temperature as calculated
by the control module.
Clutch Pedal Switch: This parameter displays the state of the clutch pedal as determined by the ECM from the clutch
start switch position.
Clutch Pedal Switch: This parameter displays the state of the clutch pedal as determined by the ECM from the clutch
pedal switch.
Commanded Exhaust Camshaft Position (Bank 1 or Bank 2): This parameter displays the exhaust camshaft position
in percent of range as commanded by the control module.
Commanded Exhaust Camshaft Position (Bank 1 or Bank 2): This parameter displays the exhaust camshaft position
in crankshaft degrees, as commanded by the ECM.
Commanded Intake Camshaft Position (Bank 1 or Bank 2): This parameter displays the intake camshaft position in
crankshaft degrees, as commanded by the ECM.
Commanded B1/B2 S1 O2 Sensor Heater (Bank 1 or Bank 2 Sensor 1): This parameter displays the state of the
oxygen sensor heater control circuit, as a percentage.
Commanded B1/B2 S1 O2 Sensor Value (Bank 1 or Bank 2 Sensor 1): This parameter displays the lambda output
from the HO2S to the ECM. A lambda below 1.0 indicates a rich exhaust, while a lambda above 1.0 indicates a lean
exhaust.
Coolant Temperature: This parameter displays the temperature of the engine coolant based on input to the control
module from the engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor.
Crank Request: This parameter displays whether the ignition switch has been cycled to the crank position, requesting
the ECM to activate the starter relay.
Cruise Control Active: This parameter displays the status of the cruise control system as determined by the ECM.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3519 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–241
Cooling Fan Relay Circuit Status: This parameter displays the state of the fan relay control circuit. The parameter
displays ‘Fault’ if the fan relay control circuit is open, shorted to ground, or shorted to voltage. The parameter displays
‘Undefined’ until the relay control circuit has been determined as being ‘OK’.
Fuel Level: This parameter displays the amount of fuel in the fuel tank in litres, as calculated by the ECM from data
received from the fuel level sensor.
Fuel Level Sensor: This parameter displays the voltage received from the fuel level sensor in the fuel tank, by the ECM.
Fuel Pump Relay Circuit Status: This parameter displays the state of the fuel pump relay control circuit. The
parameter displays ‘Fault’ if the fuel pump relay control circuit is open, shorted to ground, or shorted to voltage. The
parameter displays ‘Undefined’ until the relay control circuit has been determined as being ‘OK’.
Fuel Pump Relay: This parameter displays the ECM commanded state of the fuel pump relay control circuit.
Fuel Trim Learn: This parameter displays ‘Enabled’ when conditions are appropriate for enabling long term fuel trim
corrections. This indicates that the long term fuel trim is adapting continuing amounts of short term fuel trim. If Tech 2
displays ‘Disabled’, then long term fuel trim will not respond to changes in short term fuel trim.
Ignition Accessory Signal: This parameter displays ‘On’ when the control module detects a voltage at the
ignition ‘ACC’ terminal, X1-4 of the ignition switch.
Ignition On Signal: This parameter displays ‘On’ when the control module detects a voltage at the ignition ‘IGN’
terminal X1-3 of the ignition switch.
Initial Brake Apply Signal: This parameter displays the status of the brake lamp switch. Before the cruise control can
be activated, this switch contact must be open circuit when the brake pedal is pressed.
Injection Time Cylinder 1 – 6: This parameter displays the amount of fuel injector On-time or pulse width as
commanded by the ECM.
Intake Air Temperature: This parameter displays the temperature of the air entering the air induction system based on
input to the ECM from the intake air temperature (IAT) sensor.
Knock Sensor Signal (Bank 1 or Bank 2): This parameters displays the voltage input to the control module from the
knock sensor (KS).
Knock Retard: This parameter indicates the amount of spark advance in crankshaft degrees, that the ECM removes
from the ignition control (IC) spark advance in response to the signal from the knock sensors.
Knock Retard Cylinder 1 – 6: This parameter displays the knock retard as commanded by the ECM for cylinders 1-6.
Each cylinder is controlled individually based on both knock sensor signal inputs.
Loop Status B1S1 / B2S1 (Bank 1 or Bank 2 Sensor 1): This parameter displays the state of the fuel control system
as commanded by the ECM. ‘Closed’ Loop operation indicates that the ECM is controlling the fuel delivery based on the
oxygen sensors input signal. In ‘Open’ Loop operation the ECM ignores the oxygen sensor input signal and bases the
amount of fuel to be delivered on other sensor inputs.
LTFT Idle/Deceleration (Bank 1 or Bank 2) (Long Term Fuel Trim): This parameter displays the commanded Long
Term Fuel Trim correction by the ECM for bank 1 or bank 2 for idle and deceleration conditions.
LTFT Cruise/Acceleration (Bank 1 or Bank 2) (Long Term Fuel Trim): This parameter displays the commanded Long
Term Fuel Trim correction by the ECM for bank 1 or bank 2 for cruise and acceleration conditions.
Malfunction Indicator (MI): This parameter displays the commanded (‘On, ‘Off’ or ‘Flashing’) state of the malfunction
indicator lamp (MIL) control circuit by the ECM.
Malfunction Indicator (MI) Circuit Status: This parameter displays the state of the MIL control circuit. The parameter
displays ‘Fault’ if the MIL control circuit is open, shorted to ground, or shorted to voltage. This parameter displays
‘Undefined Status’ until the circuit has been determined as being ‘OK’.
Mass Air Flow: This parameter displays the measured quantity (g/s) of air flowing into the engine during all operating
conditions.
Mass Air Flow Sensor: This parameter displays the signal voltage from the mass air flow (MAF) sensor to the ECM.
Misfire Current Cyl. #1 – #6: Tech 2 displays a range of 0 – 200 counts. This parameter displays the number of
misfires that have been detected during the last 200 cylinder firing events. The counters may normally display some
activity, but the activity should be nearly equal for all of the cylinders, and in low numbers.
Misfire History Cyl. #1 – #6: Tech 2 displays a range of 0 – 65,535 counts. The misfire history counters display the total
level of misfire that has been detected on each cylinder. The misfire history counters will not update or show any activity
until a misfire DTC P0300 has become active. The misfire history counters will update every 200 cylinder firing events.
Oil Level: W hen the ECM receives information from the engine oil level switch, where the engine oil level is within
preset parameters, Tech 2 will display ‘Normal’. If not within preset parameters, the display will show ‘Low’.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3520 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–242
Oil Temperature Sensor: This parameter displays the engine oil temperature in degrees C.
Power Enrichment: This parameter displays the status of the operating mode of the ECM used to increase fuel delivery
during certain acceleration conditions.
Reduced Engine Power: This parameter displays when the ECM is commanding reduced engine power due to a
throttle actuator control (TAC) system condition.
Requested Torque: This parameter displays the calculated amount torque requested of the ECM by the Transmission
Control Module (TCM).
Short Term Fuel Trim (Bank 1 or Bank 2): This parameter displays the short-term correction to the fuel delivery by the
ECM in response to oxygen sensor 1 or 2. If the oxygen sensor indicates a lean air/fuel mixture, the control module will
add fuel, increasing the short term fuel trim above 0. If the oxygen sensor indicates a rich air/fuel mixture, the control
module will reduce fuel decreasing the short term fuel trim below 0.
Spark Advance: This parameter displays the amount of spark advance the ECM is commanding on the ignition control
circuits. The ECM determines the desired advance.
Starter Relay: This parameter displays the Em’s commanded state of the starter motor relay control circuit.
Starter Relay Circuit Status: This parameter displays the state of the starter relay control circuit. The parameter
displays ‘Fault’ if the starter relay control circuit is open, shorted to ground, or shorted to voltage. The parameter
displays Undefined Status’ until the circuit has been determined as being ‘OK’. This parameter may not change if Tech 2
is used to command the relay control circuit ON.
Start Up ECT (Engine Coolant Temperature): This parameter displays the temperature of the engine coolant on start
up based on input to the ECM from the ECT sensor.
Start Up IAT (Intake Air Temperature): This parameter displays the temperature of the intake air at start in the air
induction system based on input to the ECM from the IAT sensor.
Time Since Engine Off: This parameter displays the amount of time (hours:minutes:seconds) that has elapsed since
the engine was last cycled OFF.
Total Fuel Trim (Bank 1 or Bank 2): This parameter displays the overall fuel trim from the idle/decel cell and the
cruise/accel cell.
Total Misfire: This parameter displays the total number of cylinder firing events that the control module detected as
misfires for the last 200 crankshaft revolution sample period.
TP Sensor 1 (Throttle Position): This parameter displays the actual voltage on the TP sensor 1 signal circuit as
measured by the ECM.
TP Sensor 1 Learned Lower Position (Throttle Position): This parameter displays the learned minimum value of TP
sensor 1 as recorded by the ECM during the last learn procedure.
TP Sensor 2 (Throttle Position): This parameter displays the actual voltage on the TP sensor 2 signal circuit as
measured by the ECM.
TP Sensor 2 Learned Lower Position (Throttle Position): This parameter displays the learned minimum value of TP
sensor 2 as recorded by the ECM during the last learn procedure.
TP Sensor 1-2 Correlation (Throttle Position): This parameter displays ‘Fault’ when the ECM detects that TP sensor 1
voltage signal is not within the correct relationship to TP sensor 2. Tech 2 displays ‘Okay’ under normal operating
conditions.
Transmission Gear: This parameter displays the position of the transmission gear selector that is transmitted over the
serial data circuit from the TCM.
Transmission Gear Selector Signal: This parameter displays the position of the transmission gear selector that is
transmitted over the serial data circuit from the TCM.
Vehicle Speed: This parameter displays the speed of the vehicle as calculated by the TCM from information received
from the vehicle speed sensor (VSS).
Volumetric Efficiency: This parameter displays the volumetric efficiency of the engine as calculated by the control
module.
8.5 OBD Data
Typical Values Tech 2 Display Units Displayed
Ignition On Engine Running
B1S1 O2 Sensor (Bank 1 Sensor 1) mA 0.008 0
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3522 of 6020

Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–244
Precondition: Ignition ‘On’.
Cooling Fan (PWM)
Take care that no-one can access the engine
compartment during these tests!
This test allows the Technician to turn the cooling fan on in increments to its maximum speed.
Precondition: Ignition ‘On’ Air conditioning is ‘Off’..
Alternator L Terminal
This test allows the Technician to turn ‘On’ and ‘Off’, the commanded state of the voltage regulator in the alternator. ‘On’
displays a commanded state of 99%, while ‘Off’ displays a commanded state of 0%.
Precondition: Engine running.
EVAP Purge Solenoid
This test allows the Technician to control the EVAP purge solenoid valve. The normal commanded state is ‘0%’. The
system will increase or decrease the amount of purge by changing the duty cycle of the purge valve in 10% increments
within a range of 0 – 100%. The system will remain in the commanded state until cancelled by Tech 2.
NOTE
The EVAP Purge Solenoid Command parameter
may not change states when using this output
control.
Precondition: Ignition ‘On’, engine ‘Off’.
Engine Speed Control
Other DTCs may set when the Engine Speed
Control function is used. Disregard those
DTCs that set under this condition.
Allows the increase / decrease of the engine speed in 20 – 30 rpm increments from the base idle speed, up to 1,600
rpm.
NOTE
If the engine coolant temperature is below the
prescribed minimum, a message to that effect is
displayed and access to engine speed control is
blocked.
Preconditions: Engine running, engine temperature above 80 °C, transmission in Park or Neutral.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3533 of 6020
Engine Management – V6 – Service Operations Page 6C1-3–9
2 General Service Operations
2.1 Accelerator Pedal Position Sensor
Remove
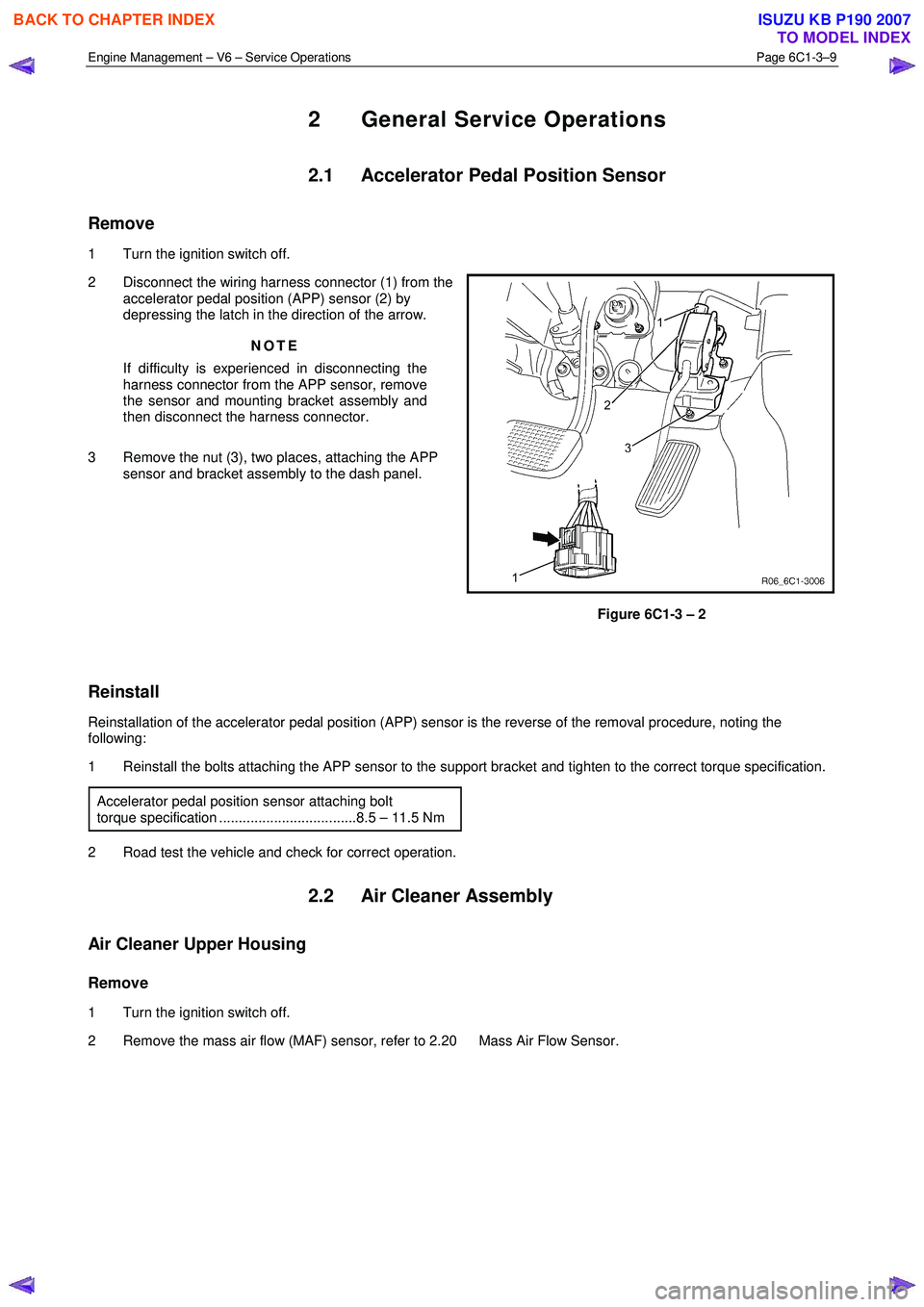
1 Turn the ignition switch off.
2 Disconnect the wiring harness connector (1) from the accelerator pedal position (APP) sensor (2) by
depressing the latch in the direction of the arrow.
NOTE
If difficulty is experienced in disconnecting the
harness connector from the APP sensor, remove
the sensor and mounting bracket assembly and
then disconnect the harness connector.
3 Remove the nut (3), two places, attaching the APP sensor and bracket assembly to the dash panel.
Figure 6C1-3 – 2
Reinstall
Reinstallation of the accelerator pedal position (APP) sensor is the reverse of the removal procedure, noting the
following:
1 Reinstall the bolts attaching the APP sensor to the support bracket and tighten to the correct torque specification.
Accelerator pedal position sensor attaching bolt
torque specification ...................................8.5 – 11.5 Nm
2 Road test the vehicle and check for correct operation.
2.2 Air Cleaner Assembly
Air Cleaner Upper Housing
Remove
1 Turn the ignition switch off.
2 Remove the mass air flow (MAF) sensor, refer to 2.20 Mass Air Flow Sensor.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3543 of 6020
Engine Management – V6 – Service Operations Page 6C1-3–19
Remove
If replacing the ECM, it must be reset prior to
removal. Failure to perform this procedure
will result in the inability to test the ECM for
warranty purposes, refer to ECM Reset in this
Section.
1 Turn the ignition switch off.
2 Disconnect the battery.
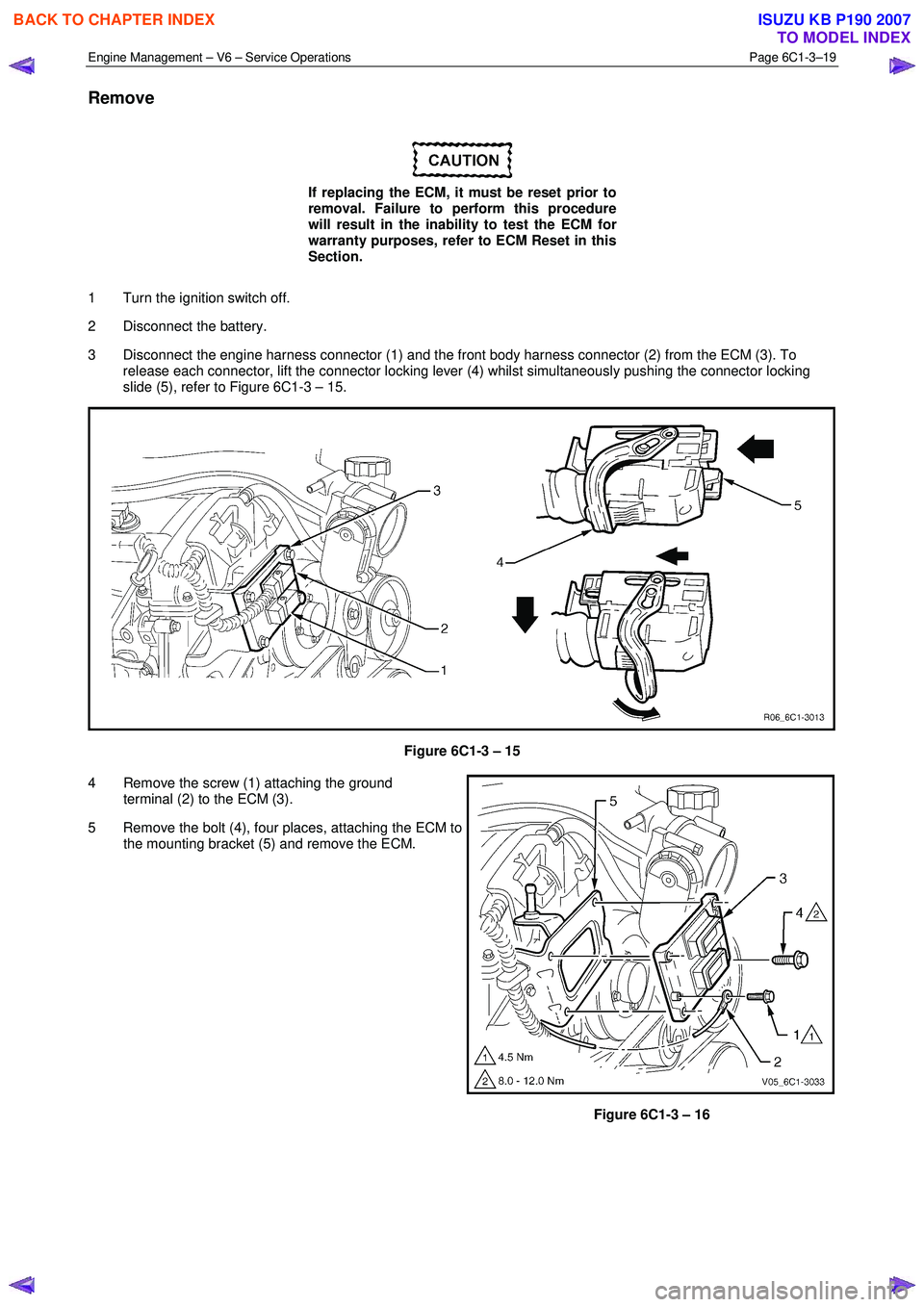
3 Disconnect the engine harness connector (1) and the front body harness connector (2) from the ECM (3). To release each connector, lift the connector locking lever (4) whilst simultaneously pushing the connector locking
slide (5), refer to Figure 6C1-3 – 15.
Figure 6C1-3 – 15
4 Remove the screw (1) attaching the ground terminal (2) to the ECM (3).
5 Remove the bolt (4), four places, attaching the ECM to the mounting bracket (5) and remove the ECM.
Figure 6C1-3 – 16
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007