2007 ISUZU KB P190 wheel
[x] Cancel search: wheelPage 2110 of 6020

6B-6 ENGINE COOLING
Draining and Refilling Cooling
System
Before draining the cooling system, inspect the system and
perform any necessary service to ensure that it is clean, does
not leak and is in proper working order. The engine coolant
level should be between the "MIN" and "MAX" lines of reserve
tank when the engine is cold. If low, check for leakage and add
engine coolant up to the "MAX" line. There should not be any
excessive deposit of rust or scales around the radiator cap or
radiator filler hole, and the engine coolant should also be free
from oil.
Replace the engine coolant if excessively dirty.
1. Completely drain the cooling system by opening the drain
plug at the bottom of the radiator.
2. Remove the radiator cap.
WARNING: TO AVOID THE DANGER OF BEING BURNED,
DO NOT REMOVE THE CAP WHILE THE ENGINE AND
RADIATOR ARE STILL HOT. SCALDING FLUID AND
STEAM CAN BE BLOWN OUT UNDER PRESSURE.
3. Disconnect all hoses from the engine coolant reserve tank.
Scrub and clean the inside of the reserve tank with soap and water. Flush it well with clean water, then drain it. Install
the reserve tank and hoses.
4. Refill the cooling system with the engine coolant using a solution that is at least 50 percent antifreeze.
5. Fill the radiator to the base of the filler neck.
Fill the engine coolant reserve tank to "MAX" line when the engine is cold.
6. Block the drive wheels and firmly apply the parking brake and place the shift lever in the "NEUTRAL" position.
7. Remove the radiator cap. Start the engine and warm it up at 2,500 - 3,000 rpm for about 30 minutes.
8. W hen the air comes out from the radiator filler neck and the engine coolant level has gone down, replenish with the
engine coolant. Repeat this procedure until the engine
coolant level does not go down. Then stop the engine and
install the radiator cap. Let the engine cool down.
9. After the engine has cooled, replenish with engine coolant up to the "MAX" line of the reserve tank.
10. Start the engine. W ith the engine running at 3,000 rpm, make sure there is no running water sound from the heate
r
core (behind the center console).
11. If the running water sound is heard, repeat steps 8 to 10.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2132 of 6020

6C-14 ENGINE FUEL (C24SE)
Removal
CAUTION: When repair to the fuel system has been
completed, start engine and check the fuel system
for loose connection or leakage. For the fuel system
diagnosis, see Section “Driveability and Emission".
1. Disconnect battery ground cable.
2. Loosen slowly the fuel filler cap.
NOTE: To prevent spouting out fuel to change the
pressure in the fuel tank.
NOTE: Cover opening of the filler neck to prevent an
y
dust entering.
3. Jack up the vehicle.
4. Support underneath of the fuel tank with a lifter.
5. Remove the inner liner of the wheel house on rea
r
left side.
6. Remove fasten bolt to the filler neck from the body.
7. Disconnect the quick connector (8) into the fuel
tube from the fuel pipe and the evapo tube from
evapo joint connector.
NOTE: Cover the quick connector to prevent any dust
entering and fuel leaking.
NOTE: Refer to “Fuel Tube/Quick Connector Fittings” in
this section when performing any repairs.
8. Remove fasten bolt (1) to the tank band and the tank band (2).
9. Disconnect the pump and sender connector on the
fuel pump and remove the harness from weld clip
on the fuel tank.
10. Lower the fuel tank (6).
NOTE: W hen the fuel tank is lowered from the vehicle,
don’t scratch each hose and tube by around other pars.
Installation
1. Rise the fuel tank into position.
NOTE: Ensure hoses and tubes do not foul on othe
r
component. 2. Connect the pump and sender connector to the
fuel pump and install harness to into the plastic clip
welded to the top of the fuel tank..
NOTE: The connector must be certainly connected
against stopper.
Ensure tank band anchor mates with guide hole on
frame.
3. Install the tank band to fasten bolt.
Torque: 68 N ⋅
⋅⋅
⋅
m (6.9kg ⋅
⋅⋅
⋅
m/50 lb ft)
NOTE: The anchor of the tank band must be certainl
y
installed to guide hole on frame. 4. Connect the quick connector from the fuel tube to
the fuel pipe and the evapo tube from evapo joint
connector.
NOTE: Pull off the left checker into the fuel pipe.
NOTE: Refer to “Fuel Tube/Quick Connector Fittings” in
this section when performing any repairs.
5. Install the filler neck to the body by bolt.
6. Install the inner liner of the wheel house on rea
r
side.
7. Remove lifter to support underneath of the fuel tank.
8. Put back the vehicle.
9. Tigten the filler cap until at least three clicks are
heard.
10. Connect the battery ground cable.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2354 of 6020
6E–184 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
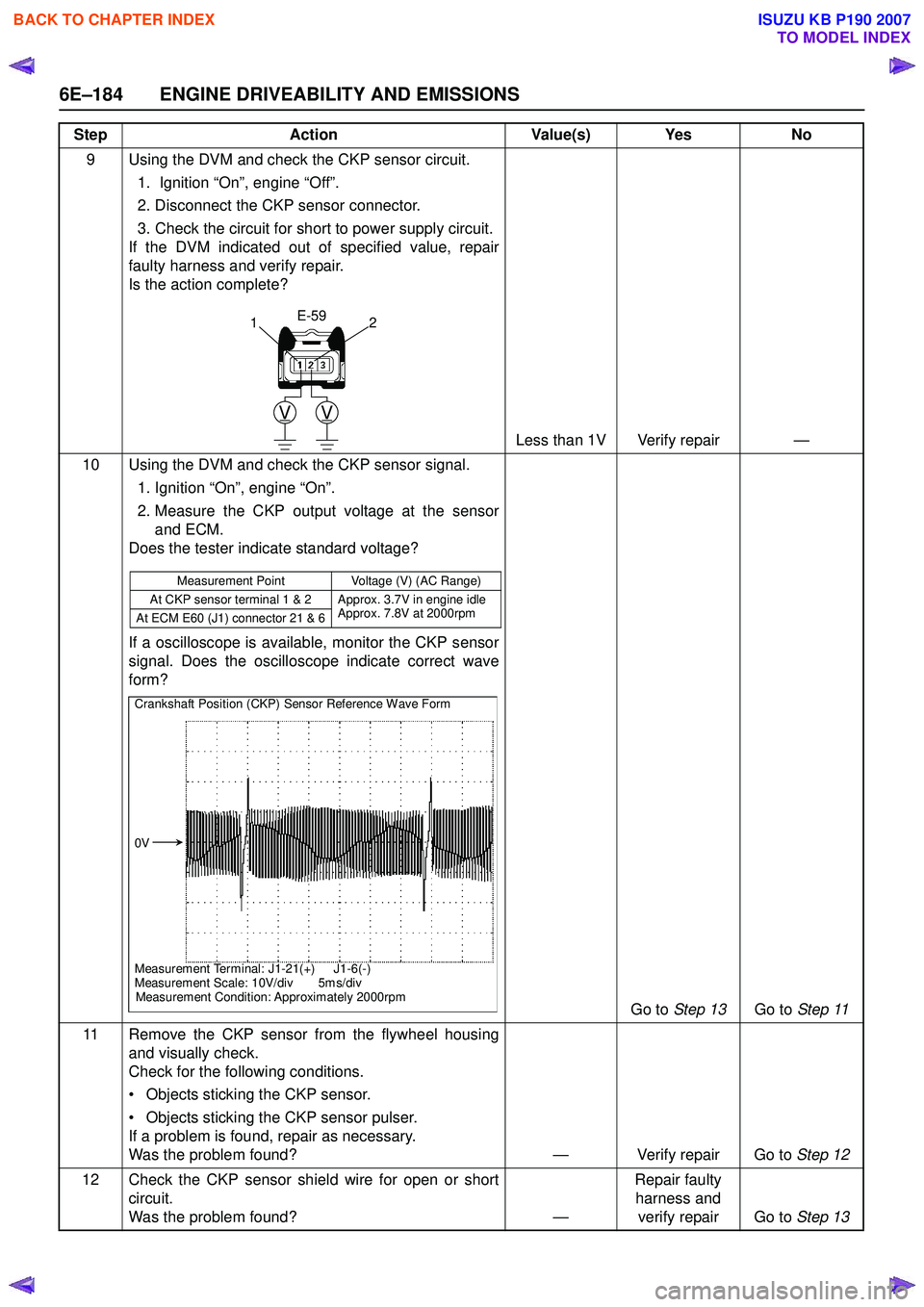
9 Using the DVM and check the CKP sensor circuit.1. Ignition “On”, engine “Off”.
2. Disconnect the CKP sensor connector.
3. Check the circuit for short to power supply circuit.
If the DVM indicated out of specified value, repair
faulty harness and verify repair.
Is the action complete?
Less than 1V Verify repair —
10 Using the DVM and check the CKP sensor signal. 1. Ignition “On”, engine “On”.
2. Measure the CKP output voltage at the sensor and ECM.
Does the tester indicate standard voltage?
If a oscilloscope is available, monitor the CKP sensor
signal. Does the oscilloscope indicate correct wave
form?
Go to Step 13 Go to Step 11
11 Remove the CKP sensor from the flywheel housing and visually check.
Check for the following conditions.
• Objects sticking the CKP sensor.
• Objects sticking the CKP sensor pulser.
If a problem is found, repair as necessary.
Was the problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 12
12 Check the CKP sensor shield wire for open or short circuit.
Was the problem found? —Repair faulty
harness and verify repair Go to Step 13
Step
Action Value(s) Yes No
VV
E-59
21
Measurement Point Voltage (V) (AC Range)
At CKP sensor terminal 1 & 2 Approx. 3.7V in engine idle Approx. 7.8V at 2000rpm
At ECM E60 (J1) connector 21 & 6
Crankshaft Position (CKP) Sensor Reference Wave Form
0V
Measurement Terminal: J1-21(+) J1-6(-)
Measurement Scale: 10V/div 5m s/div
Measurement Condition: Approximately 2000rpm
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2487 of 6020
Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–8
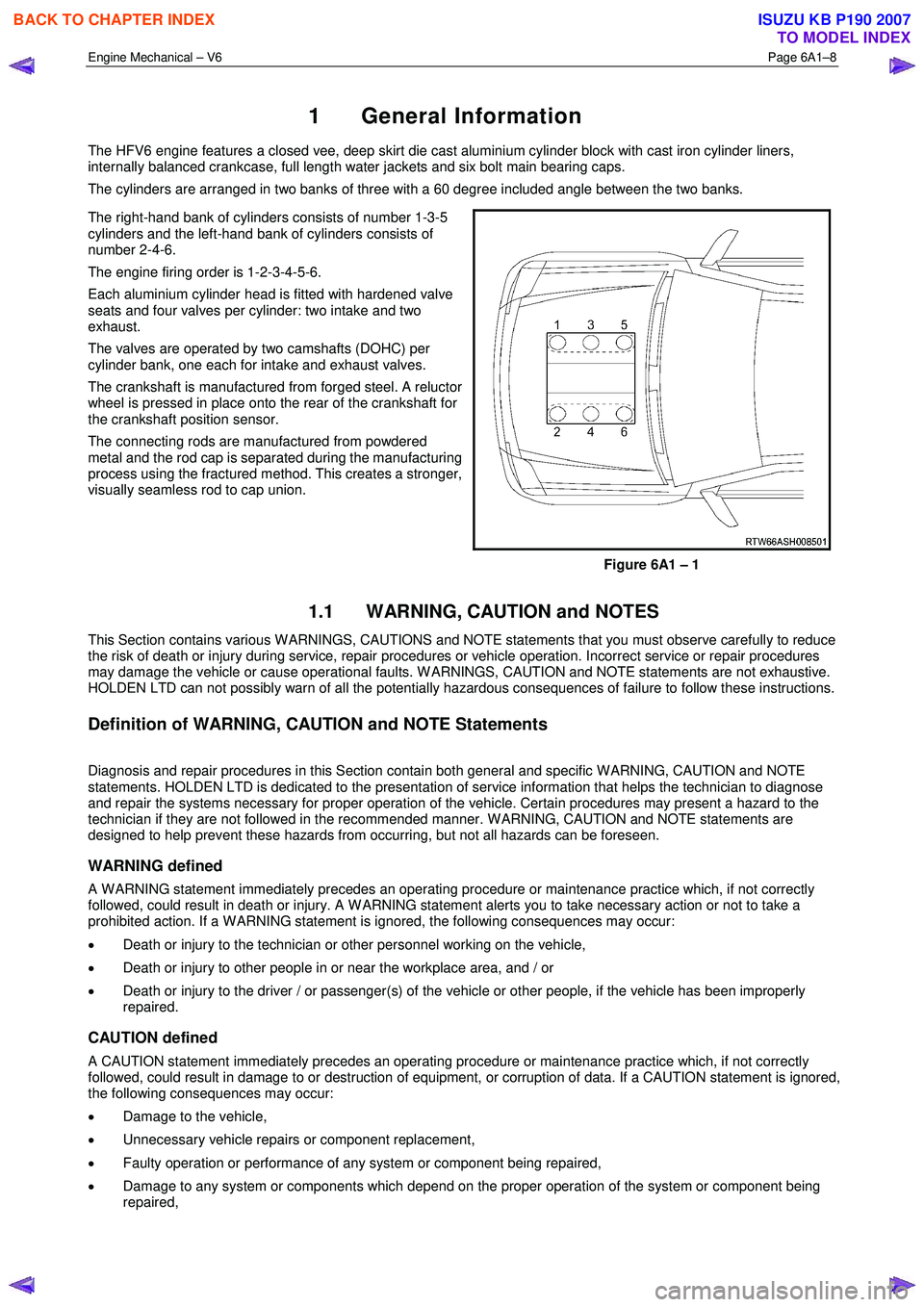
1 General Information
The HFV6 engine features a closed vee, deep skirt die cast aluminium cylinder block with cast iron cylinder liners,
internally balanced crankcase, full length water jackets and six bolt main bearing caps.
The cylinders are arranged in two banks of three with a 60 degree included angle between the two banks.
The right-hand bank of cylinders consists of number 1-3-5
cylinders and the left-hand bank of cylinders consists of
number 2-4-6.
The engine firing order is 1-2-3-4-5-6.
Each aluminium cylinder head is fitted with hardened valve
seats and four valves per cylinder: two intake and two
exhaust.
The valves are operated by two camshafts (DOHC) per
cylinder bank, one each for intake and exhaust valves.
The crankshaft is manufactured from forged steel. A reluctor
wheel is pressed in place onto the rear of the crankshaft for
the crankshaft position sensor.
The connecting rods are manufactured from powdered
metal and the rod cap is separated during the manufacturing
process using the fractured method. This creates a stronger,
visually seamless rod to cap union.
Figure 6A1 – 1
1.1 WARNING, CAUTION and NOTES
This Section contains various W ARNINGS, CAUTIONS and NOTE statements that you must observe carefully to reduce
the risk of death or injury during service, repair procedures or vehicle operation. Incorrect service or repair procedures
may damage the vehicle or cause operational faults. W ARNINGS, CAUTION and NOTE statements are not exhaustive.
HOLDEN LTD can not possibly warn of all the potentially hazardous consequences of failure to follow these instructions.
Definition of WARNING, CAUTION and NOTE Statements
Diagnosis and repair procedures in this Section contain both general and specific W ARNING, CAUTION and NOTE
statements. HOLDEN LTD is dedicated to the presentation of service information that helps the technician to diagnose
and repair the systems necessary for proper operation of the vehicle. Certain procedures may present a hazard to the
technician if they are not followed in the recommended manner. W ARNING, CAUTION and NOTE statements are
designed to help prevent these hazards from occurring, but not all hazards can be foreseen.
WARNING defined
A W ARNING statement immediately precedes an operating procedure or maintenance practice which, if not correctly
followed, could result in death or injury. A W ARNING statement alerts you to take necessary action or not to take a
prohibited action. If a W ARNING statement is ignored, the following consequences may occur:
• Death or injury to the technician or other personnel working on the vehicle,
• Death or injury to other people in or near the workplace area, and / or
• Death or injury to the driver / or passenger(s) of the vehicle or other people, if the vehicle has been improperly
repaired.
CAUTION defined
A CAUTION statement immediately precedes an operating procedure or maintenance practice which, if not correctly
followed, could result in damage to or destruction of equipment, or corruption of data. If a CAUTION statement is ignored,
the following consequences may occur:
• Damage to the vehicle,
• Unnecessary vehicle repairs or component replacement,
• Faulty operation or performance of any system or component being repaired,
• Damage to any system or components which depend on the proper operation of the system or component being
repaired,
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2489 of 6020
Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–10
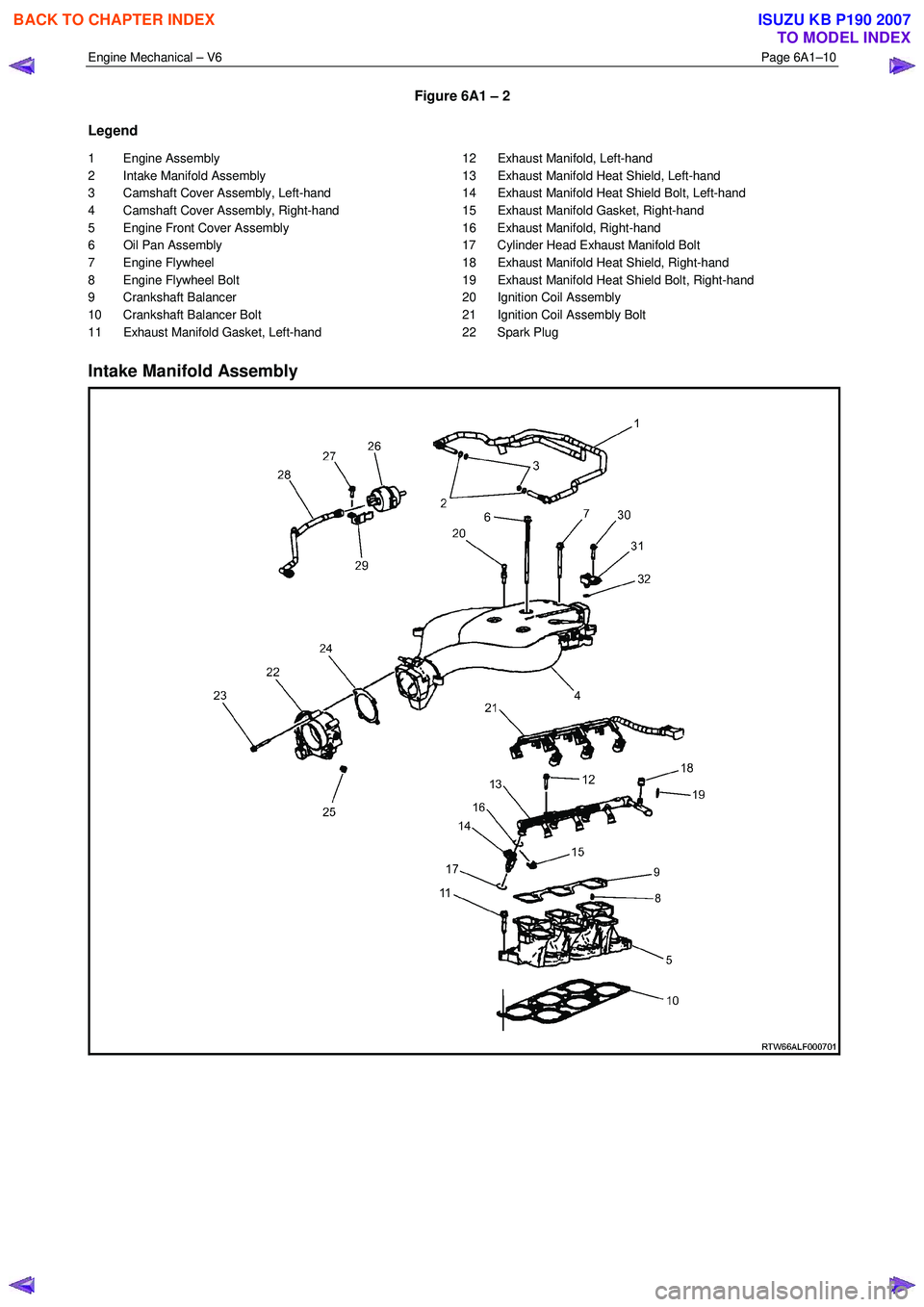
Figure 6A1 – 2
Legend
1 Engine Assembly
2 Intake Manifold Assembly
3 Camshaft Cover Assembly, Left-hand
4 Camshaft Cover Assembly, Right-hand
5 Engine Front Cover Assembly
6 Oil Pan Assembly
7 Engine Flywheel
8 Engine Flywheel Bolt
9 Crankshaft Balancer
10 Crankshaft Balancer Bolt
11 Exhaust Manifold Gasket, Left-hand 12 Exhaust Manifold, Left-hand
13 Exhaust Manifold Heat Shield, Left-hand
14 Exhaust Manifold Heat Shield Bolt, Left-hand
15 Exhaust Manifold Gasket, Right-hand
16 Exhaust Manifold, Right-hand
17 Cylinder Head Exhaust Manifold Bolt
18 Exhaust Manifold Heat Shield, Right-hand
19 Exhaust Manifold Heat Shield Bolt, Right-hand
20 Ignition Coil Assembly
21 Ignition Coil Assembly Bolt
22 Spark Plug
Intake Manifold Assembly
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2501 of 6020

Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–22
Crankshaft
The crankshaft is a forged steel design with four main bearings. The number three main bearing controls crankshaft
thrust. A crankshaft position reluctor wheel is pressed onto the rear of the crankshaft, in front of the rear main journal.
The crankshaft is internally balanced with an integral oil pump drive machined into the nose in front of the front main
journal.
Pistons, Pins and Connecting Rods
The piston assembly (1) is fitted with two low tension
compression rings and one multi-piece oil control ring. The
top compression ring is plasma sprayed, while the second
compression ring is cast iron Napier.
The oil control ring incorporates a steel expander and two
chrome plated steel rails.
The connecting rods are sinter forged steel and have full
floating piston pins. The piston pins are a slip-fit type, into
the bronze bushed connecting rods. Round wire retainers
are used to retain the piston pin into the piston.
The cast aluminium pistons incorporate a polymer coated
skirt to reduce friction.
Figure 6A1 – 17
Camshaft Drive System
Three timing chains are fitted:
• primary (1),
• right-hand secondary (2), and
• left-hand secondary (3), refer to Figure 6A1 – 18 for the HFV6 engine.
The primary timing chain connects the crankshaft sprocket (4) with the left-hand and right-hand intermediate drive shaft
sprockets (5).
Each oil pressure fed intermediate sprocket drives the secondary timing chains, which subsequently drive the respective
cylinder head camshaft position actuators (6).
Two stationary timing chain guides (7) and movable timing chain shoes (8) control secondary timing chain backlash.
Each secondary timing chain shoe is under tension from an oil pressure hydraulically operated tensioner (9). To control
backlash on the primary chain, two stationary timing chain guides (10) and an oil pressure hydraulically actuated
tensioner with built in shoe (11) are fitted.
The tensioners minimise timing chain noise and provide accurate valve action by keeping slack out of the timing chains,
while continuously adjusting for timing chain wear. The tensioners incorporate a plunger that adjusts outward with wear,
minimising backlash. The tensioners are equipped with oiling jets to spray oil onto the timing components during engine
operation. Each tensioner is sealed to the head or block using a rubber coated steel gasket. The gasket traps an
adequate oil reserve to ensure quiet start-up.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2509 of 6020
Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–30
Cause Correction
Faulty cylinder head gasket and/or cracking or other
damage to the cylinder head and cylinder block coolant
passages.
Coolant consumption may or may not cause the engine to
overheat. 1 Inspect the spark plugs for coolant saturation, refer to
6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 – Service
Operations.
2 Inspect the cylinder heads, cylinder block and/or head gaskets, refer to 3.22 Cylinder Head Assembly and/or
4.7 Cylinder Block.
3 Repair or replace components as required.
W orn piston rings.
Oil consumption may or may not cause the engine to
misfire. 1 Inspect the spark plugs for oil deposits, refer to 6C1-3
Engine Management – V6 – Service Operations.
2 Check the cylinders for a loss of compression, refer to 2.15 Engine Compression Test.
3 Perform compression testing to identify the cause of low compression.
4 Repair or replace components as required.
A damaged crankshaft reluctor wheel.
A damaged crankshaft reluctor wheel can result in different
symptoms depending on the severity and location of the
damage.
Systems with severe reluctor ring damage may exhibit
periodic loss of crankshaft position, stop delivering a signal,
and then re-sync the crankshaft position.
Systems with slight reluctor ring damage may exhibit no
loss of crankshaft position and no misfire may occur,
however, a DTC may set. Replace the crankshaft as required, refer to 4.6
Crankshaft and Main Bearings.
Refer to 6C1-2 Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics to
check for DTCs
2.4 Engine Misfire with Abnormal Internal Lower Engine Noises
Cause Correction
Abnormalities, severe cracking, bumps or missing areas in
the accessory drive belt.
Abnormalities in the accessory drive system and/or
components may cause engine speed variations that result
in a misfire diagnostic trouble code (DTC). A misfire code
may be present without an actual misfire condition. Replace the accessory drive belt, refer to 3.5
Accessory
Drive Belt.
Refer to 6C1-2 Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics to
check for DTCs
W orn, damaged or misaligned accessory drive components
and excessive pulley run-out may lead to a misfire DTC.
A misfire code may be present without an actual misfire
condition. Inspect the components and repair or replace as required.
Refer to 6C1-2 Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics to
check for DTCs
Loose or Incorrectly fitted flexplate or crankshaft balancer
assembly.
A misfire code may be present without an actual misfire
condition. Repair or replace the flexplate or crankshaft balancer as
required, refer to 3.13 Crankshaft Balancer Assembly
or 4.3 Flexplate Assembly.
W orn or broken piston rings.
Oil consumption may or may not cause an actual misfire. 1 Inspect the spark plugs for oil deposits, refer to 6C1-3
Engine Management – V6 – Service Operations.
2 Check the cylinders for a loss of compression, refer to 2.15 Engine Compression Test.
3 Perform compression testing to identify the cause of low compression.
4 Repair or replace components as required.
W orn crankshaft thrust bearing.
Severely worn thrust surfaces on the crankshaft and/or
thrust bearing may permit fore and aft movement of the
crankshaft and create a DTC without an actual misfire
condition being present. Replace the crankshaft and/or bearings as required, refer to
4.6 Crankshaft and Main Bearings.
Refer to 6C1-2 Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics to
check for DTCs
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2514 of 6020
Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–35
2.11 Engine Noise Under Load
NOTE
A cold piston knock which disappears in
approximately 1.5 minutes from start up, should
be considered acceptable. A cold engine knock
usually disappears when the specific cylinder’s
secondary ignition circuit is grounded out during
diagnosis.
A light rattle/tapping noise may indicate a valve train/upper engine concern, while a low rumble/knocking may indicate a
crankshaft, piston or lower engine concern.
Cause Correction
Low oil pressure. 1 Perform an oil pressure test, refer to 2.19
Engine Oil Pressure Diagnosis.
2 Repair or replace the engine oil pump as required, refer to 3.17 Oil Pump Assembly.
Detonation or spark knock. Confirm the correct operation of the ignition system, refer to
6C1-2 Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics.
Loose torque converter bolts. Inspect and tighten the torque converter bolts to the correct
torque specification, refer to 7C1 Automatic – 4L60E –
General Information – 4L60E – General Information.
Cracked flexplate. Replace the flywheel/flex-plate as required, refer to 4.3
Flexplate Assembly.
Excessive connecting rod bearing clearance. Inspect the connecting rod, crankshaft and bearings and
repair/replace components as required, refer to 4.5
Pistons, Pins, Rings, Connecting Rods and Big-
end Bearings and 4.6 Crankshaft and Main Bearings.
Excessive crankshaft bearing clearance Inspect the crankshaft, cylinder block journals, main
bearings and main bearing caps and repair/replace
components as required, refer to 4.6 Crankshaft
and Main Bearings and 4.7Cylinder Block.
2.12 Engine Will Not Crank – Crankshaft Will Not Rotate
Cause Correction
Seized accessory drive system component. 1 Remove the accessory drive belt, refer to 3.5
Accessory Drive Belt.
2 Rotate the crankshaft by hand at the balancer pulley or flywheel.
3 Repair or replace accessory drive system components as required.
Hydraulically locked cylinder caused by:
• coolant in cylinder,
• oil in cylinder, or
• fuel in cylinder. 1 Remove the spark plugs and check for fluid, refer to
6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 – Service
Operations.
2 Inspect for broken head gasket/s.
3 Inspect for cracked engine block or cylinder head.
4 Inspect for sticking fuel injector.
5 Repair or replace components as required.
Seized torque converter. 1 Remove the torque converter bolts, refer to 7C1
Automatic – 4L60E – General Information – 4L60E –
General Information.
2 Rotate the crankshaft by hand at the balancer pulley or flywheel.
3 Repair or replace torque converter as required.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007