2007 ISUZU KB P190 wheel
[x] Cancel search: wheelPage 1956 of 6020
ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM (4JK1/4JJ1) 6E-339
Fuel System ChecksInspect the fuel system for the following conditions. Refer to Fuel System Check Chart
and appropriate procedure in the Fuel System section.
• Air in the fuel system.
• Water contamination in the fuel.
• Fuel waxing or icing.
• Fuel filter indicator lamp is continuously or frequently turned ON with engine run.
• External fuel leaks or high engine oil level.
• In-tank fuel pump operation. Refer to In-tank Fuel Pump System Check in this section.
• Fuel leak off from the fuel pressure limiter valve and fuel injectors.
• Fuel lines between the fuel tank and fuel supply pump for being crushed, kinked, tightness, cracks and plugged.
• A plugged fuel tank vent valve and hose.
• Inside the fuel tank for any foreign material that may be getting drawn into the fuel line pickup causing a blocked condition.
• Fuel supply pump operation.
Notice: The fuel supply pump must be timed to the engine and adjustment value must
be learned to the ECM.
• Perform the Cylinder Balance Test with a scan tool.
• Perform the Injector Force Drive with a scan tool.
• Observe the Fuel Compensation for each cylinder at idle on the scan tool.
Air Intake System Checks Inspect the air intake system for the following conditions.
• Air cleaner, air intake ducts and charge air cooler for a restriction, holes, or leaks.
• A restriction in the turbocharger inlet duct.
• Intake throttle valve for a stuck condition.
• A restriction or leak in the intake manifold.
• A restriction or damaged at MAF sensor.
• Perform the Swirl Control Solenoid Test with a scan tool. Inspect the diaphragm valve operation when it commanded ON/ OFF.
• A worn or damaged turbocharger turbine wheel, shaft or compressor wheel. Refer to turbocharger inspection in the Engine Mechanical section.
• Turbocharger wastegate valve operation. Refer to wastegate valve inspection in the Engine Mechanical section. (Standard output)
• Turbocharger nozzle control actuator operation. Refer to Turbocharger Control System Check in this section. (High output)
Exhaust System Checks Inspect the exhaust system for a possible restriction. Refer to the Exhaust System
section.
Engine Mechanical Checks Inspect the engine mechanical for the following conditions. Refer to the Engine
Mechanical section.
• Poor cylinder compression.
• Improper valve gap.
• Broken or weak valve springs.
• Worn camshaft lobes.
Additional Checks • Inspect the EGR system operating correctly. Refer to EGR Control System Check in
this section.
• Inspect for an engine overheat condition. Refer to Engine Cooling section.
• Inspect the A/C operation.
• Inspect the torque converter clutch (TCC) operation. (A/T only)
Checks
Action
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1959 of 6020
6E-342 ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM (4JK1/4JJ1)
Air Intake System ChecksInspect the air intake system for the following conditions.
• Air cleaner, air intake ducts and charge air cooler for a restriction, holes, or leaks.
• A restriction in the turbocharger inlet duct.
• Intake throttle valve for a stuck condition.
• A restriction or leak in the intake manifold.
• A restriction or damaged at MAF sensor.
• Perform the Swirl Control Solenoid Test with a scan tool. Inspect the diaphragm valve operation when it commanded ON/ OFF.
• A worn or damaged turbocharger turbine wheel, shaft or compressor wheel. Refer to turbocharger inspection in the Engine Mechanical section.
• Turbocharger wastegate valve operation. Refer to wastegate valve inspection in the Engine Mechanical section. (Standard output)
• Turbocharger nozzle control actuator operation. Refer to Turbocharger Control System Check in this section. (High output)
Exhaust System Checks Inspect the exhaust system for a possible restriction. Refer to the Exhaust System
section.
Engine Mechanical Checks Inspect the engine mechanical for the following conditions. Refer to the Engine
Mechanical section.
• Poor cylinder compression.
• Improper valve gap.
• Broken or weak valve springs.
• Worn camshaft lobes.
Checks
Action
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1960 of 6020
ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM (4JK1/4JJ1) 6E-343
Excessive Smoke (Black Smoke)
ChecksAction
Definition:
Black smoke under load, idle or start up hot or cold.
Preliminary Check • Ensure the vehicle has an actual problem.
• Inspect the ECM grounds for being clean, tight, and in their proper locations.
• Remove the air cleaner and check for dirt, or for air ducts being plugged or restricted. Replace as necessary.
• Inspect the fuel quality (cetane index).
• Inspect the engine oil level and quality.
• Inspect the programmed fuel injector ID code for each cylinder.
• Inspect the Scan Tool Data List in this section.
• Inspect the Service Bulletin.
Sensor Checks Inspect the engine control sensors for the following conditions. Refer to the Scan Tool
Data List in this section.
• Compare the Coolant Temperature with the Intake Air Temperature (IAT) and Fuel Temperature (FT) parameters on a cold engine condition. If the difference among
temperature reading is more than 5 °C (9 °F) on a cold engine, check for high
resistance in each circuit or for a skewed sensor.
Notice: The mass air flow (MAF) sensor is heated and as a result the IAT may indicate
a higher than normal intake air temperature if the ignition switch is being ON.
• Observe the MAF parameter for a skewed or slow MAF sensor.
• Observe the Fuel Rail Pressure (FRP) Sensor parameter with the engine OFF. The FRP Sensor should read 0.9 to 1.0 volt with the key ON and engine OFF after the
engine has stopped running for a minimum of 1 minute. If not, check for high
resistance in each circuit or for a skewed sensor.
• Observe the Fuel Rail Pressure and Desired Fuel Rail Pressure parameter between idle and W.O.T. (accelerator pedal full travel) in Neutral. Fuel Rail Pressure
parameter should follow within ±5 MPa ( ±725 psi) quick enough.
• Observe the Barometric Pressure (BARO) parameter. The BARO parameter should indicate near surrounding barometric pressure. Refer to Altitude vs. Barometric
Pressure. (Standard output)
• Observe the Boost Pressure and BARO with ignition ON and engine OFF. Both parameters should be within the 7.0 kPa (1.0 psi) each other. (High output)
Fuel System Checks Inspect the fuel system for the following conditions. Refer to the Fuel System section.
• Fuel injectors. Remove the injectors and visually inspect.
• Perform the Cylinder Balance Test with a scan tool.
• Perform the Pilot Injection Control with a scan tool.
• Observe the Fuel Compensation for each cylinder at idle on the scan tool.
Air Intake System Checks Inspect the air intake system for the following conditions.
• Air cleaner, air intake ducts and charge air cooler for a restriction, holes, or leaks.
• A restriction in the turbocharger inlet duct.
• Intake throttle valve for a stuck condition.
• A restriction or leak in the intake manifold.
• A restriction or damaged at MAF sensor.
• A worn or damaged turbocharger turbine wheel, shaft or compressor wheel. Refer to turbocharger inspection in the Engine Mechanical section.
Exhaust System Checks Inspect the exhaust system for a possible restriction. Refer to the Exhaust System
section.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1962 of 6020
ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM (4JK1/4JJ1) 6E-345
Excessive Smoke (White Smoke)
ChecksAction
Difinition:
White smoke under load, idle or start up hot or cold.
Preliminary Check • Ensure the vehicle has an actual problem.
• Inspect the ECM grounds for being clean, tight, and in their proper locations.
• Inspect the fuel quality (cetane index).
• Inspect the programmed fuel injector ID code for each cylinder.
• Inspect the Scan Tool Data List in this section.
• Inspect the Service Bulletin.
Sensor Checks Inspect the engine control sensors for the following conditions. Refer to the Scan Tool
Data List in this section.
• Compare the Coolant Temperature with the Intake Air Temperature (IAT) and Fuel Temperature (FT) parameters on a cold engine condition. If the difference among
temperature reading is more than 5 °C (9 °F) on a cold engine, check for high
resistance in each circuit or for a skewed sensor.
Notice: The mass air flow (MAF) sensor is heated and as a result the IAT may indicate
a higher than normal intake air temperature if the ignition switch is being ON.
• Observe the Fuel Rail Pressure (FRP) Sensor parameter with the engine OFF. The FRP Sensor should read 0.9 to 1.0 volt with the key ON and engine OFF after the
engine has stopped running for a minimum of 1 minute. If not, check for high
resistance in each circuit or for a skewed sensor.
• Observe the Fuel Rail Pressure and Desired Fuel Rail Pressure parameter between idle and W.O.T. (accelerator pedal full travel) in Neutral. Fuel Rail Pressure
parameter should follow within ± 5 MPa ( ± 725 psi) quick enough.
• Observe the Accelerator Pedal Position (APP). APP parameter should change linearly from 0 to 100% according to the accelerator pedal operation.
• Observe the Boost Pressure and Barometric Pressure (BARO) with ignition ON and engine OFF. Both parameters should be within the 7.0 kPa (1.0 psi) each other.
• Crankshaft position (CKP) sensor is tight and the sensor rotor is not damaged.
Fuel System Checks • If excessive smoke is present, check for a stuck open fuel injector. Inspect for fuel
leakage into the combustion chamber.
• Fuel injectors. Remove the injectors and visually inspect.
• Perform the Cylinder Balance Test with a scan tool.
• Perform the Pilot Injection Control with a scan tool.
• Observe the Fuel Compensation for each cylinder at idle on the scan tool.
Air Intake System Checks Inspect the air intake system for the following conditions.
• Air cleaner, air intake ducts and charge air cooler for a restriction, holes, or leaks.
• A restriction in the turbocharger inlet duct.
• Intake throttle valve for a stuck condition.
• A restriction or leak in the intake manifold.
• A restriction or damaged at MAF sensor.
• Perform the Swirl Control Solenoid Test with a scan tool. Inspect the diaphragm valve operation when it commanded ON/ OFF.
• A worn or damaged turbocharger turbine wheel, shaft or compressor wheel. Oil leak from turbocharger. Refer to turbocharger inspection in the Engine Mechanical
section.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1983 of 6020
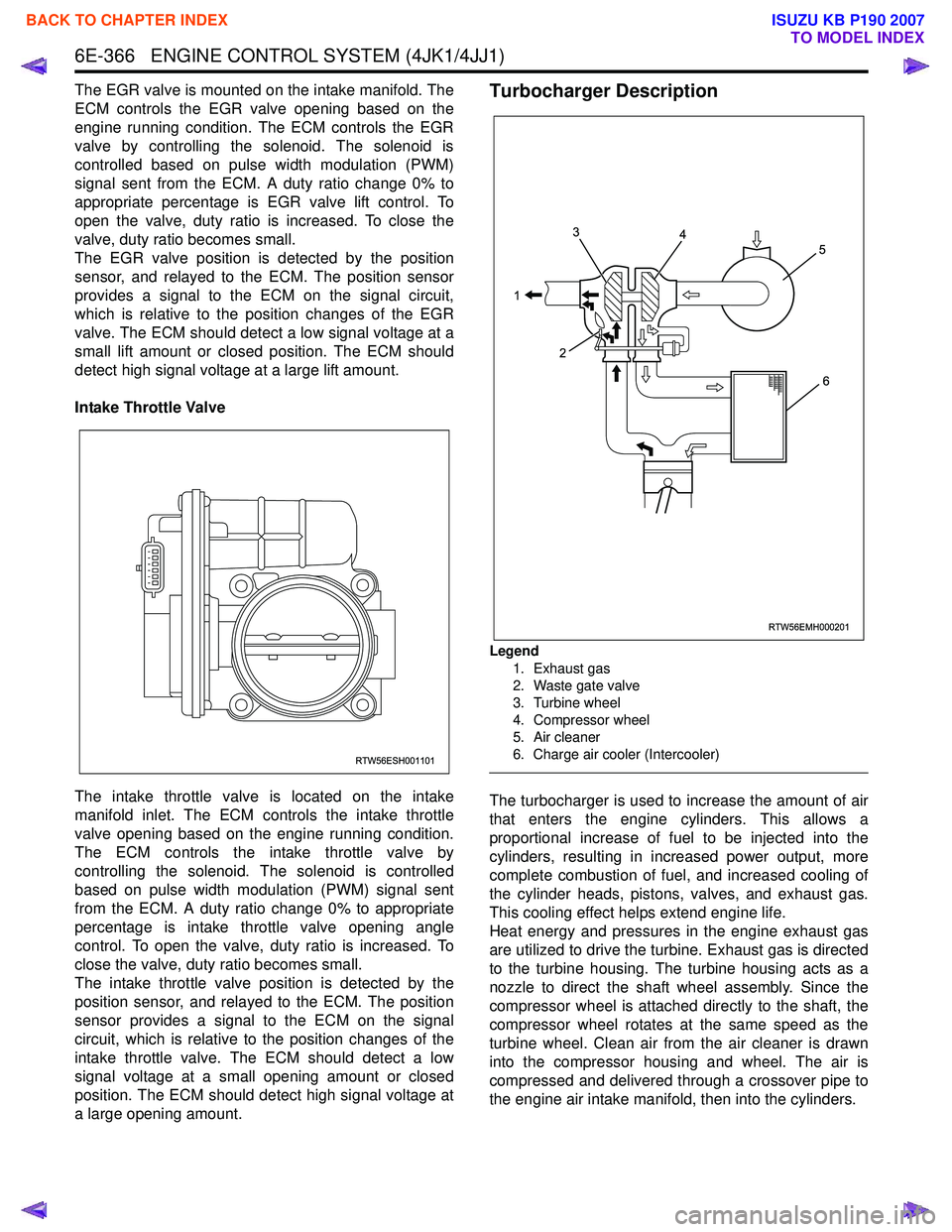
6E-366 ENGINE CONTROL SYSTEM (4JK1/4JJ1)
The EGR valve is mounted on the intake manifold. The
ECM controls the EGR valve opening based on the
engine running condition. The ECM controls the EGR
valve by controlling the solenoid. The solenoid is
controlled based on pulse width modulation (PWM)
signal sent from the ECM. A duty ratio change 0% to
appropriate percentage is EGR valve lift control. To
open the valve, duty ratio is increased. To close the
valve, duty ratio becomes small.
The EGR valve position is detected by the position
sensor, and relayed to the ECM. The position sensor
provides a signal to the ECM on the signal circuit,
which is relative to the position changes of the EGR
valve. The ECM should detect a low signal voltage at a
small lift amount or closed position. The ECM should
detect high signal voltage at a large lift amount.
Intake Throttle Valve
The intake throttle valve is located on the intake
manifold inlet. The ECM controls the intake throttle
valve opening based on the engine running condition.
The ECM controls the intake throttle valve by
controlling the solenoid. The solenoid is controlled
based on pulse width modulation (PWM) signal sent
from the ECM. A duty ratio change 0% to appropriate
percentage is intake throttle valve opening angle
control. To open the valve, duty ratio is increased. To
close the valve, duty ratio becomes small.
The intake throttle valve position is detected by the
position sensor, and relayed to the ECM. The position
sensor provides a signal to the ECM on the signal
circuit, which is relative to the position changes of the
intake throttle valve. The ECM should detect a low
signal voltage at a small opening amount or closed
position. The ECM should detect high signal voltage at
a large opening amount.Turbocharger Description
Legend
1. Exhaust gas
2. Waste gate valve
3. Turbine wheel
4. Compressor wheel
5. Air cleaner
6. Charge air cooler (Intercooler)
The turbocharger is used to increase the amount of air
that enters the engine cylinders. This allows a
proportional increase of fuel to be injected into the
cylinders, resulting in increased power output, more
complete combustion of fuel, and increased cooling of
the cylinder heads, pistons, valves, and exhaust gas.
This cooling effect helps extend engine life.
Heat energy and pressures in the engine exhaust gas
are utilized to drive the turbine. Exhaust gas is directed
to the turbine housing. The turbine housing acts as a
nozzle to direct the shaft wheel assembly. Since the
compressor wheel is attached directly to the shaft, the
compressor wheel rotates at the same speed as the
turbine wheel. Clean air from the air cleaner is drawn
into the compressor housing and wheel. The air is
compressed and delivered through a crossover pipe to
the engine air intake manifold, then into the cylinders.
RTW56ESH001101
RTW56EMH000201
1 3
2 4
5
6
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2010 of 6020
6-10 ENGINE DIAGNOSIS (C24SE)
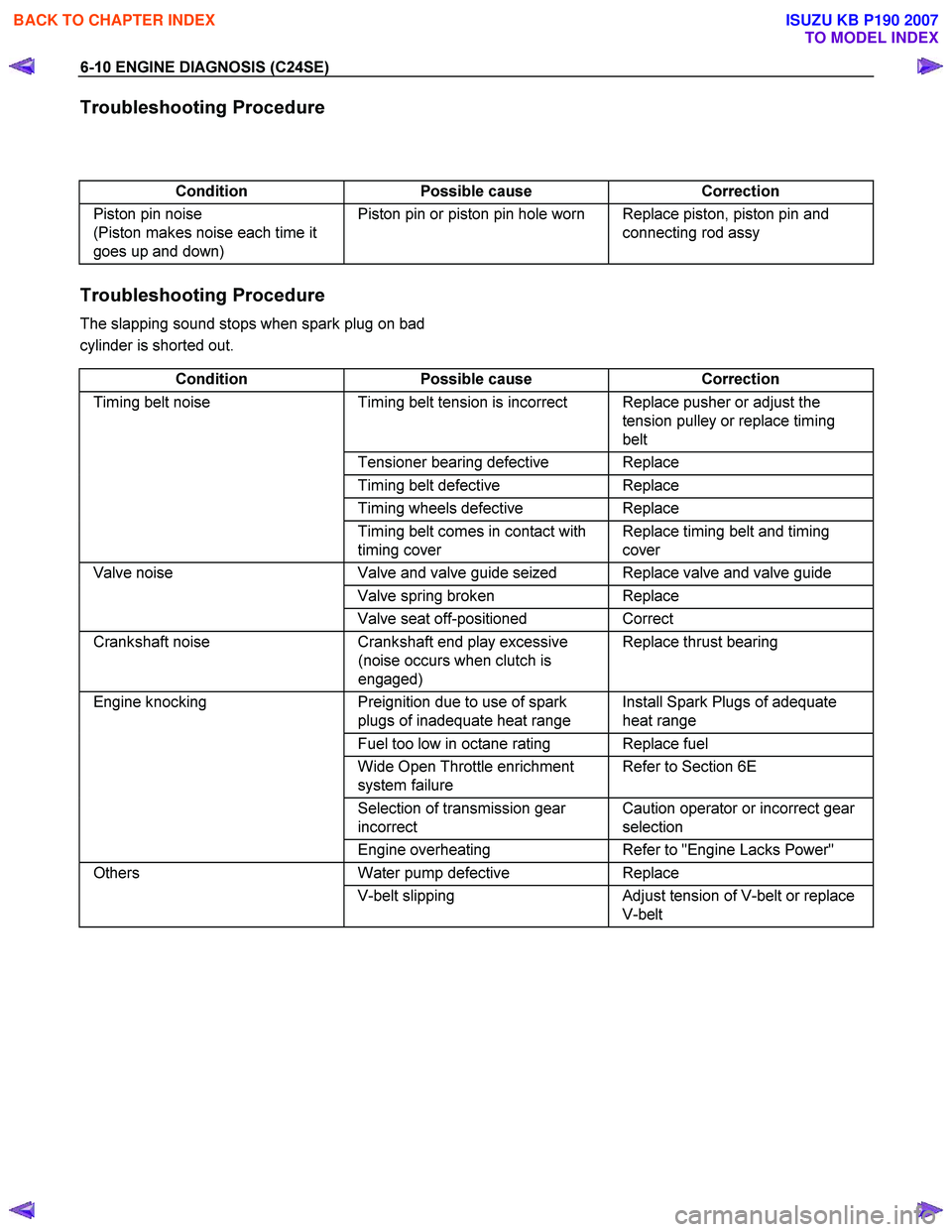
Troubleshooting Procedure
Condition Possible cause Correction
Piston pin noise
(Piston makes noise each time it
goes up and down) Piston pin or piston pin hole worn Replace piston, piston pin and
connecting rod assy
Troubleshooting Procedure
The slapping sound stops when spark plug on bad
cylinder is shorted out.
Condition Possible cause Correction
Timing belt noise Timing belt tension is incorrect Replace pusher or adjust the
tension pulley or replace timing
belt
Tensioner bearing defective Replace
Timing belt defective Replace
Timing wheels defective Replace
Timing belt comes in contact with
timing cover Replace timing belt and timing
cover
Valve noise Valve and valve guide seized Replace valve and valve guide
Valve spring broken Replace
Valve seat off-positioned Correct
Crankshaft noise Crankshaft end play excessive
(noise occurs when clutch is
engaged) Replace thrust bearing
Engine knocking
Preignition due to use of spark
plugs of inadequate heat range Install Spark Plugs of adequate
heat range
Fuel too low in octane rating Replace fuel
Wide Open Throttle enrichment
system failure Refer to Section 6E
Selection of transmission gear
incorrect Caution operator or incorrect gear
selection
Engine overheating Refer to "Engine Lacks Power"
Others Water pump defective Replace
V-belt slipping Adjust tension of V-belt or replace
V-belt
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2016 of 6020

6A-2 ENGINE MECHANICAL (C24SE)
PAGE
Camshaft Housing, Check for Plance Surface ......................................................... 6A-39
Cylinder Head, Removal and Installation.................................................................. 6A-39
Cylinder Head, Disassemble and Assemble............................................................. 6A-42
Valve, Grind ................................................................................................................. 6 A-44
Valve Guide, Ream .................................................................................................... 6A-44
Valve Seating, Mill ...................................................................................................... 6A-45
Cylinder Head, Overhaul ............................................................................................ 6A-45
Flywheel....................................................................................................................... 6A-46
Starter Ring Gear(Manual Transmission) ................................................................. 6A-47
Seal Ring, Crankshaft................................................................................................. 6A-48
Seal Ring, Crankshaft Rear ........................................................................................ 6A-48
Oil Pan and Bearing Bridge ....................................................................................... 6A-49
OPERATIONS ON CRANK DRIVE ................................................................................... 6A-51 Con-Rod Bearing ........................................................................................................ 6A-51
Piston with Con-Rod................................................................................................... 6A-51
Con-Rod....................................................................................................................... 6A-52
Pistion Rings ............................................................................................................... 6A -53
OPERATIONS ON REMOVED ENGINE........................................................................... 6A-55 Crankshaft ................................................................................................................... 6 A-55
Bearing Free Play Measurement ............................................................................... 6A-57
Plastigage Method ...................................................................................................... 6A-57
Micrometer and gauge method.................................................................................. 6A-58
Bypass Valve ............................................................................................................... 6A- 59
Oil Filter ..................................................................................................................... .. 6A-59
Oil Pump ...................................................................................................................... 6A-59
Oil Pump Safety Valve ................................................................................................ 6A-60
Oil Pump(Overhaul) .................................................................................................... 6A-60
OPERATIONS ON OIL CIRCULATION ............................................................................ 6A-61 Cylinder Head Safety Valve ........................................................................................ 6A-61
OPERATIONS ON COOLING SYSYTEM ......................................................................... 6A-63 Cooling System, Check for Leakes ........................................................................... 6A-63
Cooling System, Fill Up and Bleed ............................................................................ 6A-63
Refill Coolant............................................................................................................... 6 A-64
Ignition Timing, Check ............................................................................................... 6A-64
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2060 of 6020
6A-46 ENGINE MECHANICAL (C24SE)
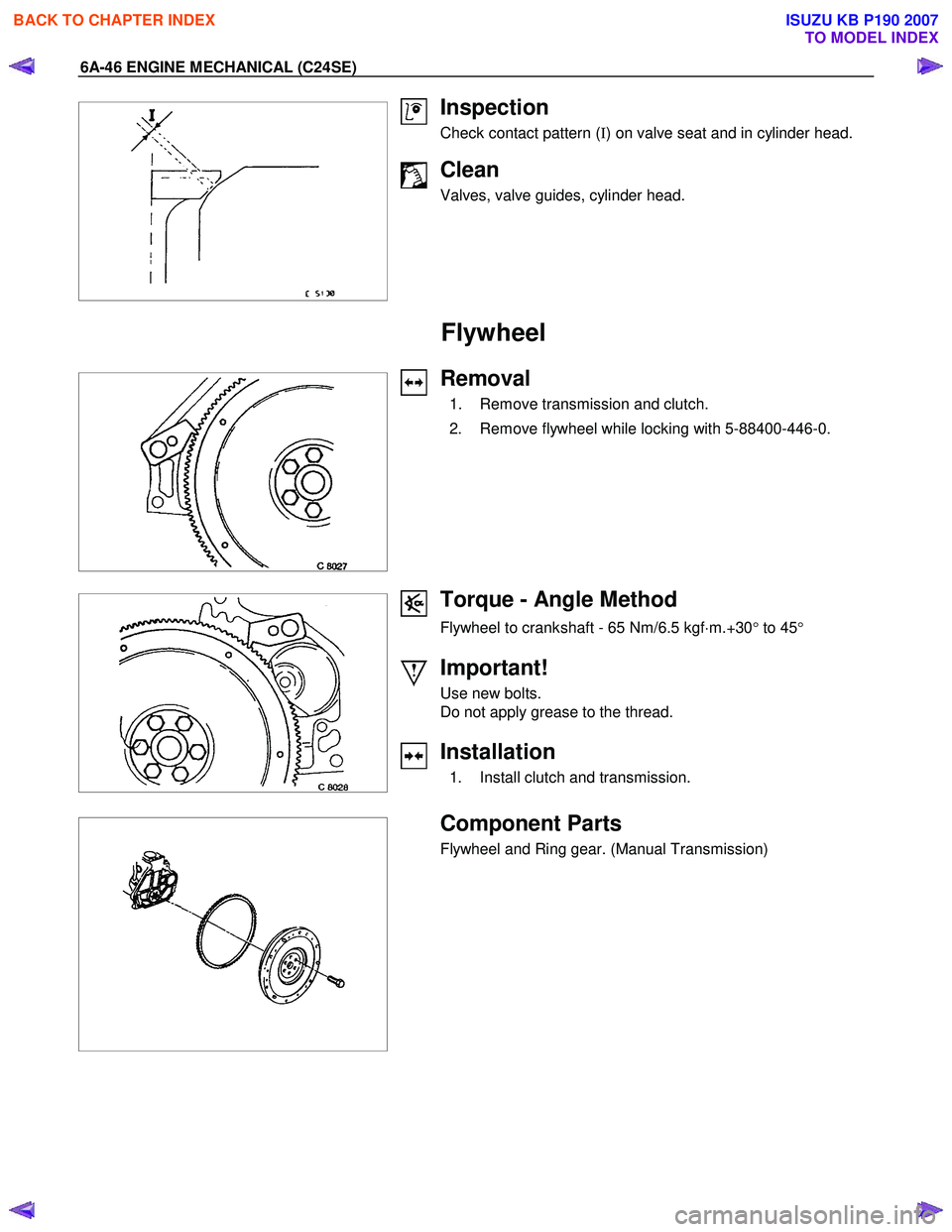
Inspection
Check contact pattern ( I) on valve seat and in cylinder head.
Clean
Valves, valve guides, cylinder head.
Flywheel
Removal
1. Remove transmission and clutch.
2. Remove flywheel while locking with 5-88400-446-0.
Torque - Angle Method
Flywheel to crankshaft - 65 Nm/6.5 kgf ⋅m.+30 ° to 45 °
Important!
Use new bolts.
Do not apply grease to the thread.
Installation
1. Install clutch and transmission.
Component Parts
Flywheel and Ring gear. (Manual Transmission)
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007