2007 ISUZU KB P190 engine overheat
[x] Cancel search: engine overheatPage 2523 of 6020
Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–44
CAUTION
When running the engine with the accessory
drive belt removed, the coolant pump will not
be operating and the engine may overheat if
left unsupervised even for a short period.
NOTE
There may also be a number of DTCs set when
running the engine with the accessory drive belt
removed.
4 Inspect all drive pump pulleys for pilling. NOTE
Pilling is the small balls (pills) or strings of rubber
in the belt grooves caused by the accumulation of
rubber dust.
6 Misalignment of the accessory drive system pulleys may be caused by incorrect mounting of an accessory drive component (A/C compressor, generator etc.) or pulley. Misalignment may also be caused by incorrect installation of
a pulley during a previous repair. Test for a misaligned pulley using a straight edge in the pulley grooves across
two or three pulleys. If a misaligned pulley is found, refer to the relevant component service information for the
correct installation and removal procedures.
10 Inspecting the fasteners can eliminate the possibility that an incorrect fastener has been installed.
12 Inspecting the pulleys for being bent should include inspecting for a dent or other damage that would prevent the drive belt from not seating correctly in all of the pulley grooves or on the smooth surface when the back end of the
belt is used as the driving surface.
14 Replacing the drive belt when it is not damaged and there is no excessive pilling will only be a temporary repair.
Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1 Did you review the information provided in 2.2 Symptoms, and
perform the required inspections. Go to Step 2 Go to 2.2
Symptoms
2 Confirm the customer complaint. Is there a chirping noise? Go to Step 3 Refer to Diagnostic
Aids in this Section
3 1 Remove the drive belt, refer to 3.5 Accessory Drive Belt.
2 Operate the engine for no more than 40 seconds.
Does the chirping noise still exist? Accessory drive
system OK.
Go to 2.2
Symptoms, and restart the
diagnosis of the noise Go to Step 4
4 Inspect for severe pilling, i.e. in excess of 33% of the belt groove
depth.
Do the belt grooves have pilling? Go to Step 5 Go to Step 6
5 Clean the drive belt pulleys with a wire brush. Are the belt pulleys clean? Go to Step 15 Go to Step 6
6 Inspect for misalignment of the pulleys. Are the pulleys misaligned? Go to Step 7 Go to Step 8
7 Replace or repair misaligned pulleys. Did you complete the repair? Go to Step 15 —
8 Inspect for any bent or damaged accessory drive component mounting brackets.
Did you find any bent or damaged brackets? Go to Step 9 Go to Step 10
9 Replace or repair any bent or damaged Brackets. Did you complete the repairs? Go to Step 15 —
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2524 of 6020
Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–45
Step Action Yes No
10 Inspect for missing, loose or incorrect fasteners.
Did you find any missing, loose or incorrect fasteners? Go to Step 11 Go to Step 12
11 Tighten any loose fasteners to the torque specification as provided in
provided in 6. Torque W rench Specifications.
Replace any incorrect or missing fasteners.
Did you complete the repairs? Go to Step 15 —
12 Inspect for a bent pulley. Did you find any bent pulleys? Go to Step 13 Go to Step 14
13 Replace bent pulleys as required. Did you complete the repair? Go to Step 15 —
14 Replace the accessory drive belt, refer to 3.5 Accessory Drive Belt.
Did you complete the repair? Go to Step 15 —
15 Reinstall the accessory drive belt and operate the system to confirm the repair.
Did you correct the chirp noise? Accessory drive
system OK Go to 2.2
Symptoms, and restart the
diagnosis
Drive Belt Squeal
Definition
Accessory drive belt squealing can be defined as a loud screeching noise caused by a slipping drive belt. Belt squeal is
unusual in multi-rib belts. Drive belt squeal generally occurs when a heavy load is applied to the drive belt, such as an
air-conditioning compressor engagement, snapping the throttle, seized pulley or a faulty accessory drive component.
Diagnostic Aids
If the noise is intermittent, confirm the accessory drive components by varying their loads, making sure they are operated
to their maximum capacity. An overcharged A/C system, restrictions in the power steering pressure circuit or a faulty
generator or coolant pump are likely causes of accessory drive belt squeal.
A loose or incorrectly installed body component, suspension component or other item may be the cause of the noise.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to steps in the diagnostic table.
2 The noise may not be engine related. This step is to confirm the engine is making the noise. If the engine is not making the noise, do not proceed further with this diagnostic procedure.
3 The noise may be an internal engine noise. Removing the drive belt and operating the engine briefly will confirm whether or not the noise is related to the drive belt.
CAUTION
When running the engine with the accessory
drive belt removed, the coolant pump will not
be operating and the engine may overheat if
left unsupervised even for a short period.
NOTE
There may also be a number of DTCs set when
running the engine with the accessory drive belt
removed.
4 Confirms an accessory drive component does not have a seized bearing. W ith the belt removed, test the bearings in the accessory drive components spin free and smooth.
5 Confirms the drive belt tensioner is operating correctly. If the drive belt tensioner is not operating correctly, drive belt tension will not be maintained, resulting in a belt squealing noise
6 Confirms the belt is not too long, which would prevent the tensioner from working as intended. Also, if an excessively long belt has been fitted, it may also be routed incorrectly and may be turning an accessory drive
component in the wrong direction.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2526 of 6020

Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–47
3 The noise may be an internal engine noise. Removing the drive belt and operating the engine briefly will confirm
whether or not the noise is related to the drive belt.
CAUTION
When running the engine with the accessory
drive belt removed, the coolant pump will not
be operating and the engine may overheat if
left unsupervised even for a short period.
NOTE
There may also be a number of DTCs set when
running the engine with the accessory drive belt
removed.
4 The inspection of bearings should include the following accessory drive components: • drive belt tensioners,
• drive belt idlers,
• generator,
• power steering pump,
• coolant pump, and
• A/C compressor.
The drive belt may need to be installed and the accessory drive components operated separately, at varying loads to confirm the location of the faulty bearing, refer to the relevant Sections for component inspection and repair
procedures.
Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1 Did you review the information provided in 2.2 Symptoms, and
perform the required inspections. Go to Step 2 Go to 2.2
Symptoms
2 Confirm the customer complaint. Is there a whining noise? Go to Step 3 Refer to Diagnostic
Aids in this Section
3 1 Remove the drive belt, refer to 3.5 Accessory Drive Belt.
2 Operate the engine for no more than 40 seconds.
Does the whining noise still exist? Accessory drive
system OK
Go to 2.2
Symptoms, and restart the diagnosis Go to Step 4
4 Inspect the accessory drive components for a faulty or seized
bearings and general malfunctions.
Did you find and correct any faulty/seized bearings or general
malfunctions in the accessory drive system? Go to Step 5 Refer to Diagnostic
Aids in this Section
5 Reinstall the accessory drive belt and operate the system to confirm the repair.
Did you correct the whine? Accessory drive
system OK Go to 2.2
Symptoms, and restart the diagnosis
Drive Belt Rumble
Definition
Accessory drive belt rumble can be defined as a low pitch tapping, knocking or thumping noise heard at or just above idle,
once per rotation of the drive belt or a specific component. Drive belt rumble is generally caused by one of the following:
• pilling or strings in the drive belt grooves,
• separation of the drive belt, or
• a damaged or faulty drive belt.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2527 of 6020
Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–48
NOTE
Pilling is the small balls (pills) or strings of rubber
in the belt grooves caused by the accumulation of
rubber dust.
Diagnostic Aids
Vibration from the engine may cause a body component or other parts to emit a rumbling noise.
The drive belt may have a condition that cannot be seen or felt. Sometimes the replacement of the belt may be the only
way to confirm the belt is faulty.
If the drive belt has been replaced and the diagnostic table completed, but the rumble is still present only when the drive
belt is installed, an accessory drive component such as the A/C compressor may be the cause. Varying the load to each
accessory drive component in turn, should help isolate which component is causing the noise.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to steps in the diagnostic table.
2 Confirms the symptom exists at the time of diagnosis. Other vehicle components may be causing the noise.
3 Confirms the accessory drive belt is the cause of the noise. Drive belt rumbling is often confused with an internal engine noise due to the similarity in the description. Removing the drive belt and operating the engine briefly will
confirm whether or not the noise is related to the drive belt.
CAUTION
When running the engine with the accessory
drive belt removed, the coolant pump will not
be operating and the engine may overheat if
left unsupervised even for a short period.
NOTE
There may also be a number of DTCs set when
running the engine with the accessory drive belt
removed.
4 Inspecting the drive belt is to ensure that it is not causing the noise. Small cracks across the ribs of the drive belt will not cause the noise and are not justification alone to replace the belt. Belt separation can be identified by the
ply of the belt separating and may be seen at the edge of the belt or felt as lumps under the belt.
5 Small amounts of pilling is a normal condition and is deemed acceptable. W hen the pilling is severe (33% of the belt groove depth), the belt does not have a smooth surface to run on and should be replaced.
Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1 Did you review the information provided in 2.2 Symptoms, and
perform the required inspections. Go to Step 2 Go to 2.2
Symptoms
2 Confirm the customer complaint. Is there a rumbling noise? Go to Step 3 Refer to Diagnostic
Aids in this Section
3 1 Remove the drive belt, refer to 3.5 Accessory Drive Belt.
2 Operate the engine for no more than 40 seconds.
Does the rumbling noise still exist? Accessory drive
system OK
Go to 2.2
Symptoms,
and restart the diagnosis Go to Step 4
4 Inspect the accessory drive belt for damage, separation or sections of missing ribs.
Did you find any damaged, separated or missing ribs? Go to Step 7 Go to Step 5
5 Inspect the accessory drive belt for severe pilling (exceeding 33% of the belt groove depth).
Did you find sever pilling? Go to Step 6 Go to Step 5
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2528 of 6020

Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–49
Step Action Yes No
6 Clean the drive belt using a suitable wire brush and reinstall to the
engine, refer to 3.5 Accessory Drive Belt.
Did you complete the repairs? Go to Step 8 —
7 Install a new accessory drive belt, refer to 3.5 Accessory Drive Belt.
Did you replace the accessory drive belt? Go to Step 8
—
8 If required, reinstall the accessory drive belt and operate the system to
confirm the repair.
Did you correct the rumbling noise? Accessory drive
system OK Refer to Diagnostic
Aids in this Section
Drive Belt Vibration
Definition
Accessory drive belt vibration can be defined as a drive belt that jumps, shakes or rattles. Accessory drive belt vibration
is usually indicated by one of the following:
• the vibration is engine speed related, or
• the vibration is sensitive to accessory drive system load.
Diagnostic Aids
The accessory drive components such as the A/C compressor or generator can have an affect on engine vibration.
To aid in locating which component is causing the vibration, vary the load to each accessory drive component in turn and
note the effect it has on the vibration if any.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to steps in the diagnostic table.
2 Confirms the symptom exists at the time of diagnosis. Other vehicle components may be causing the noise.
3 Confirms the accessory drive belt is the cause of the noise. Drive belt rumbling is often confused with an internal engine noise due to the similarity in the description. Removing the drive belt and operating the engine briefly will
confirm whether or not the noise is related to the drive belt.
CAUTION
When running the engine with the accessory
drive belt removed, the coolant pump will not
be operating and the engine may overheat if
left unsupervised even for a short period.
NOTE
There may also be a number of DTCs set when
running the engine with the accessory drive belt
removed.
4 The drive belt may cause a vibration. Inspecting the drive belt is considerably easier while the drive belt is removed.
6 Inspecting the fasteners can eliminate the possibility that an incorrect fastener has been installed.
8 This step should only be performed if the coolant pump is driven by the drive belt. Inspect the coolant pump for a bent shaft. Also inspect the coolant pump bearings for smooth operation and excessive play. Compare the coolant
pump with a known good pump.
9 Accessory drive component brackets that are bent, cracked or loose may put extra strain on the accessory component causing it to vibrate.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2538 of 6020
Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–59
3.5 Accessory Drive Belt
RWD Vehicle
Remove
1 Remove the air intake duct from between the air flow meter and the throttle body, refer to 6C1-3 Engine
Management – V6 – Service Operations.
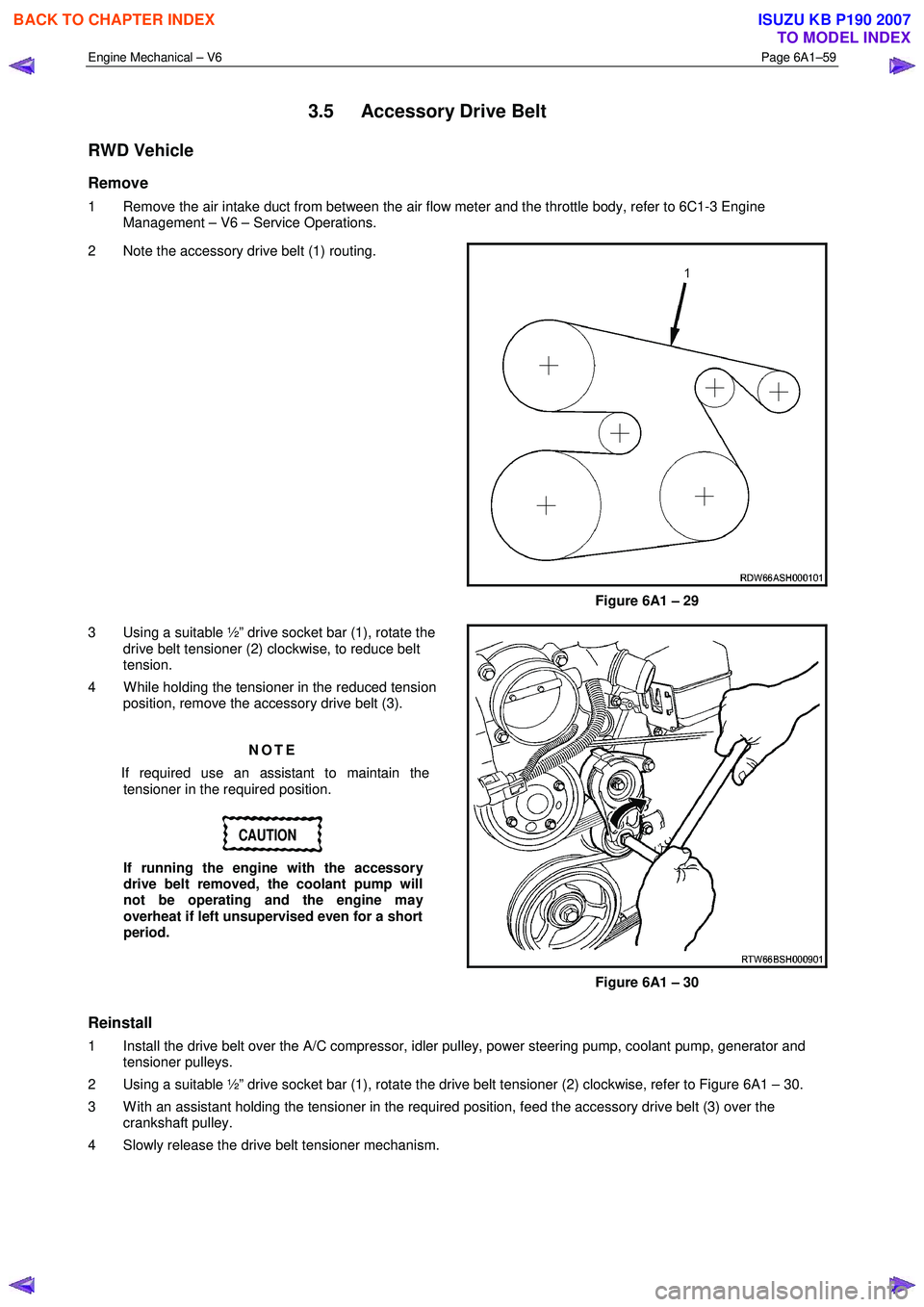
2 Note the accessory drive belt (1) routing.
Figure 6A1 – 29
3 Using a suitable ½” drive socket bar (1), rotate the drive belt tensioner (2) clockwise, to reduce belt
tension.
4 W hile holding the tensioner in the reduced tension position, remove the accessory drive belt (3).
NOTE
If required use an assistant to maintain the tensioner in the required position.
CAUTION
If running the engine with the accessory
drive belt removed, the coolant pump will
not be operating and the engine may
overheat if left unsupervised even for a short
period.
Figure 6A1 – 30
Reinstall
1 Install the drive belt over the A/C compressor, idler pulley, power steering pump, coolant pump, generator and tensioner pulleys.
2 Using a suitable ½” drive socket bar (1), rotate the drive belt tensioner (2) clockwise, refer to Figure 6A1 – 30.
3 W ith an assistant holding the tensioner in the required position, feed the accessory drive belt (3) over the crankshaft pulley.
4 Slowly release the drive belt tensioner mechanism.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2629 of 6020
Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–150
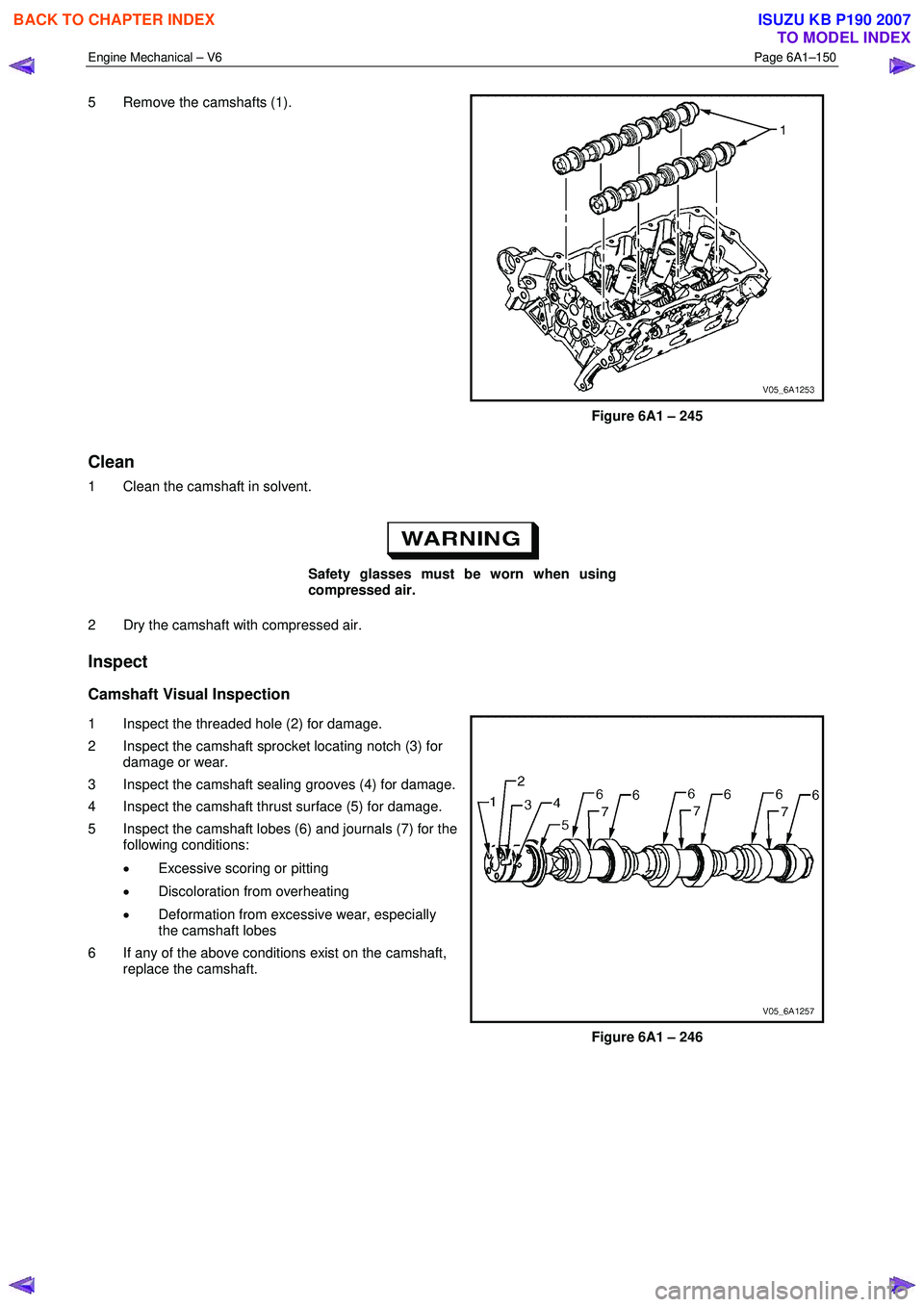
5 Remove the camshafts (1).
Figure 6A1 – 245
Clean
1 Clean the camshaft in solvent.
Safety glasses must be worn when using
compressed air.
2 Dry the camshaft with compressed air.
Inspect
Camshaft Visual Inspection
1 Inspect the threaded hole (2) for damage.
2 Inspect the camshaft sprocket locating notch (3) for damage or wear.
3 Inspect the camshaft sealing grooves (4) for damage.
4 Inspect the camshaft thrust surface (5) for damage.
5 Inspect the camshaft lobes (6) and journals (7) for the following conditions:
• Excessive scoring or pitting
• Discoloration from overheating
• Deformation from excessive wear, especially
the camshaft lobes
6 If any of the above conditions exist on the camshaft, replace the camshaft.
Figure 6A1 – 246
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2646 of 6020
Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–167
Inspect
Visual Inspection
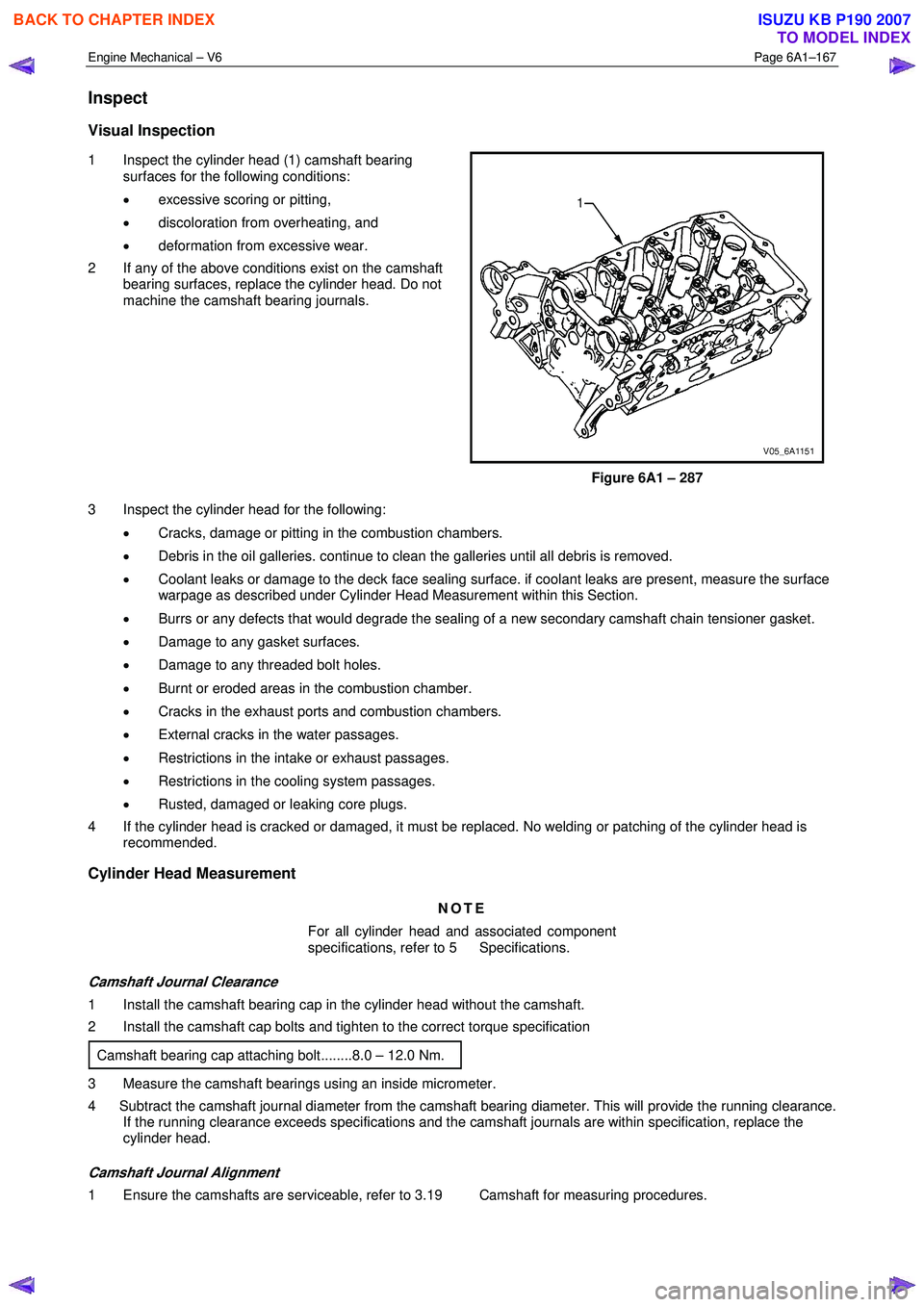
1 Inspect the cylinder head (1) camshaft bearing
surfaces for the following conditions:
• excessive scoring or pitting,
• discoloration from overheating, and
• deformation from excessive wear.
2 If any of the above conditions exist on the camshaft bearing surfaces, replace the cylinder head. Do not
machine the camshaft bearing journals.
Figure 6A1 – 287
3 Inspect the cylinder head for the following: • Cracks, damage or pitting in the combustion chambers.
• Debris in the oil galleries. continue to clean the galleries until all debris is removed.
• Coolant leaks or damage to the deck face sealing surface. if coolant leaks are present, measure the surface
warpage as described under Cylinder Head Measurement within this Section.
• Burrs or any defects that would degrade the sealing of a new secondary camshaft chain tensioner gasket.
• Damage to any gasket surfaces.
• Damage to any threaded bolt holes.
• Burnt or eroded areas in the combustion chamber.
• Cracks in the exhaust ports and combustion chambers.
• External cracks in the water passages.
• Restrictions in the intake or exhaust passages.
• Restrictions in the cooling system passages.
• Rusted, damaged or leaking core plugs.
4 If the cylinder head is cracked or damaged, it must be replaced. No welding or patching of the cylinder head is recommended.
Cylinder Head Measurement
NOTE
For all cylinder head and associated component
specifications, refer to 5 Specifications.
Camshaft Journal Clearance
1 Install the camshaft bearing cap in the cylinder head without the camshaft.
2 Install the camshaft cap bolts and tighten to the correct torque specification
Camshaft bearing cap attaching bolt........8.0 – 12.0 Nm.
3 Measure the camshaft bearings using an inside micrometer.
4 Subtract the camshaft journal diameter from the camshaft bearing diameter. This will provide the running clearance. If the running clearance exceeds specifications and the camshaft journals are within specification, replace the
cylinder head.
Camshaft Journal Alignment
1 Ensure the camshafts are serviceable, refer to 3.19 Camshaft for measuring procedures.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007