2007 ISUZU KB P190 engine overheat
[x] Cancel search: engine overheatPage 2810 of 6020
Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–33
Page 6A1–33
Cause Correction
Faulty cylinder head gasket and/or cracking or other
damage to the cylinder head and cylinder block coolant
passages.
Coolant consumption may or may not cause the engine to
overheat. 1 Inspect the spark plugs for
coolant saturation, refer to
6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 – Service
Operations.
2 Inspect the cylinder heads, cylinder block and/or head gaskets, refer to 3.22 Cylinder Head Assembly
and/or 4.7 Cylinder Block.
3 Repair or replace components as required.
Worn piston rings.
Oil consumption may or ma y not cause the engine to
misfire. 1 Inspect the spark plugs for oil deposits, refer to 6C1-3
Engine Management – V6 – Service Operations.
2 Check the cylinders for a loss of compression, refer to 2.15 Engine Compression Test.
3 Perform compression testing to identify the cause of
low compression.
4 Repair or replace components as required.
A damaged crankshaft reluctor wheel.
A damaged crankshaft reluctor wheel can result in different
symptoms depending on the severity and location of the
damage.
Systems with severe relu ctor ring damage may exhibit
periodic loss of crankshaft posit ion, stop delivering a signal,
and then re-sync the crankshaft position.
Systems with slight reluctor ring damage may exhibit no
loss of crankshaft position and no misfire may occur,
however, a DTC may set. Replace the crankshaft as required, refer to 4.6 Crankshaft
and Main Bearings.
Refer to 6C1-2 Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics to
check for DTCs
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2813 of 6020

Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–36
Page 6A1–36
2.6 Engine Misfire with Coolant
Consumption
Cause Correction
Faulty cylinder head gasket and/or cracking or other
damage to the cylinder heads and cylinder block coolant
passages.
Coolant consumption may or may not cause the engine to
overheat. 1 Inspect the spark plugs for
coolant saturation, refer to
6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 – Service
Operations.
2 Inspect the cylinder heads, cylinder block and/or head gaskets, refer to 3.22 Cylinder Head Assembly
and/or 4.7 Cylinder Block.
3 Repair or replace components as required.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2830 of 6020

Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–53
Page 6A1–53
Drive Belt Chirp
Definition
Accessory drive belt chirping can be defined as a high-pitched noise that is heard once per revolution of the drive belt or
a pulley.
NOTE
Chirping during start-up in cold damp conditions
that abates once the engine reaches operating
temperature is considered normal.
Diagnostic Aids
The symptom may be intermittent due to moisture on the driv e belts or pulleys. It may be necessary to spray a small
amount of water on the drive belt to dup licate and confirm a customers concern. If spraying water onto the drive belt
system duplicates the symptom, cleaning the belt pulleys may be the solution.
A loose or incorrectly installed body component, suspension component or other item may be the cause of the noise.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to steps in the diagnostic table.
2 The noise may not be engine related. This step is to confirm the engine is making t he noise. If the engine is not
making the noise, do not proceed further with this diagnostic procedure.
3 The noise may be an internal engine noise. Removing the drive belt and operating the engine briefly will confirm
whether or not the noise is related to the drive belt.
CAUTION
When running the engine with the accessory
drive belt removed, the coolant pump will not
be operating and the engine may overheat if
left unsupervised even for a short period.
NOTE
There may also be a number of DTCs set when
running the engine with the accessory drive belt
removed.
4 Inspect all drive pump pulleys for pilling. NOTE
Pilling is the small balls (p ills) or strings of rubber
in the belt grooves caused by the accumulation of
rubber dust.
6 Misalignment of the accessory drive system pulleys ma y be caused by incorrect mounting of an accessory drive
component (A/C compressor, generator etc.) or pulley. Misa lignment may also be caused by incorrect installation of
a pulley during a previous repair. Test for a misaligned pulley using a straight edge in the pulley grooves across
two or three pulleys. If a misaligned pulley is found, refer to the relevant component service information for the
correct installation and removal procedures.
10 Inspecting the fasteners can elim inate the possibility that an incorrect fastener has been installed.
12 Inspecting the pulleys for being bent should include inspec ting for a dent or other damage that would prevent the
drive belt from not seating correctly in all of the pulley grooves or on the smooth surface when the back end of the
belt is used as the driving surface.
14 Replacing the drive belt when it is not damaged and there is no excessive p illing will only be a temporary repair.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2832 of 6020

Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–55
Page 6A1–55
Drive Belt Squeal
Definition
Accessory drive belt squealing can be defined as a loud screeching noise caused by a slipping drive belt. Belt squeal is
unusual in multi-rib belts. Drive belt squeal generally occurs when a heavy load is applied to the drive belt, such as an
air-conditioning compressor engagement, snapping the throttle, se ized pulley or a faulty accessory drive component.
Diagnostic Aids
If the noise is intermittent, confirm the accessory drive components by varying t heir loads, making sure they are operated
to their maximum capacity. An overcharged A/C system, restrictions in the power steering pressure circuit or a faulty
generator or coolant pump are likely c auses of accessory drive belt squeal.
A loose or incorrectly installed body component, suspension component or other item may be the cause of the noise.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to steps in the diagnostic table.
2 The noise may not be engine related. This step is to confirm the engine is making t he noise. If the engine is not
making the noise, do not proceed further with this diagnostic procedure.
3 The noise may be an internal engine noise. Removing the drive belt and operating the engine briefly will confirm
whether or not the noise is related to the drive belt.
CAUTION
When running the engine with the accessory
drive belt removed, the coolant pump will not
be operating and the engine may overheat if
left unsupervised even for a short period.
NOTE
There may also be a number of DTCs set when
running the engine with the accessory drive belt
removed.
4 Confirms an accessory drive component does not have a se ized bearing. With the belt removed, test the bearings
in the accessory drive co mponents spin free and smooth.
5 Confirms the drive belt tensioner is operating correctly. If the drive belt tensioner is not operating correctly, drive
belt tension will not be maintained, resulting in a belt squealing noise
6 Confirms the belt is not too long, which would prevent the tensioner from working as intended. Also, if an
excessively long belt has been fitted, it may also be r outed incorrectly and may be turning an accessory drive
component in the wrong direction.
7 Misalignment of the pulleys may be caused by one of the following:
• Incorrect mounting of an accessory drive component,
• Incorrect installation of an accessory drive pulley or,
• Bent or damaged pulley.
Test for a misaligned pulley using a straight edge in the pulley grooves across 2 or 3 pulleys. If a misaligned pulley is found, refer to the relevant component service info rmation for the correct installation and removal procedures.
8 This test is to confirm the pulleys are the correct di ameter and/or width. Using a known good vehicle, compare the
pulley sizes.
Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1
Did you review the information provided in 2.2 Symptoms, and
perform the required inspections. Go to Step 2 Go to
2.2 Symptoms
2 Confirm the customer compla int. Is there a squealing noise?
Go to Step 3 Refer to Diagnostic
Aids in this Section
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2834 of 6020
Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–57
Page 6A1–57
Drive Belt Whine
Definition
Accessory drive belt whine can be defined as a high-pitched continuous noise that is most likely to be caused by a failed
bearing in one of the acce ssory drive components.
Diagnostic Aids
The drive belts themselves will not caus e a whine. If the noise is intermittent, confirm the accessory drive components by
varying their loads, making sure they are operated to their maximum capacity. An overcharged A/C system, restrictions
in the power steering pressure circuit or a faulty generator or coolant pump ar e likely causes of accessory drive belt
whine.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to steps in the diagnostic table.
3 The noise may be an internal engine noise. Removing the drive belt and operating the engine briefly will confirm
whether or not the noise is related to the drive belt.
CAUTION
When running the engine with the accessory
drive belt removed, the coolant pump will not
be operating and the engine may overheat if
left unsupervised even for a short period.
NOTE
There may also be a number of DTCs set when
running the engine with the accessory drive belt
removed.
4 The inspection of bearings should include the following accessory drive components:
• drive belt tensioners,
• drive belt idlers,
• generator,
• power steering pump,
• coolant pump, and
• A/C compressor.
The drive belt may need to be installed and the accessory drive components operated separ ately, at varying loads
to confirm the location of the faulty bearing, refer to the relevant Sections for component inspection and repair
procedures.
Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1
Did you review the information provided in 2.2 Symptoms, and
perform the required inspections. Go to Step 2 Go to
2.2 Symptoms
2 Confirm the customer compla int. Is there a whining noise?
Go to Step 3 Refer to Diagnostic
Aids in this Section
3 1 Remove the drive belt, refer to 3.5 Accessory Drive Belt.
2 Operate the engine for no more than 40 seconds.
Does the whining noise still exist? Accessory drive
system OK
Go to 2.2
Symptoms, and
restart the diagnosis Go to Step 4
4 Inspect the accessory drive components for a faulty or seized
bearings and general malfunctions.
Did you find and correct any faulty/seized bearings or general
malfunctions in the accessory drive system? Go to Step 5 Refer to Diagnostic
Aids in this Section
5 Reinstall the accessory drive belt and operate the system to confirm
the repair.
Did you correct the whine? Accessory drive
system OK Go to 2.2
Symptoms, and
restart the diagnosis
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2835 of 6020
Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–58
Page 6A1–58
Drive Belt Rumble
Definition
Accessory drive belt rumble can be defined as a low pitch tapping, knocking or thumping noise heard at or just above
idle, once per rotation of the drive belt or a specific co mponent. Drive belt rumble is generally caused by one of the
following:
• pilling or strings in the drive belt grooves,
• separation of the drive belt, or
• a damaged or faulty drive belt.
NOTE
Pilling is the small balls (p ills) or strings of rubber
in the belt grooves caused by the accumulation of
rubber dust.
Diagnostic Aids
Vibration from the engine may cause a body component or other parts to emit a rumbling noise.
The drive belt may have a condition that cannot be seen or felt. Sometimes the replacement of the belt may be the only
way to confirm the belt is faulty.
If the drive belt has been replaced and the di agnostic table completed, but the rumble is still present only when the drive
belt is installed, an accessory drive component such as t he A/C compressor may be the cause. Varying the load to each
accessory drive component in turn, should help isolate which component is causing the noise.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to steps in the diagnostic table.
2 Confirms the symptom exists at the time of di agnosis. Other vehicle components may be causing the noise.
3 Confirms the accessory drive belt is the cause of the noise. Drive belt rumbling is often confused with an internal
engine noise due to the similarity in the description. Removing the drive belt and operating the engine briefly will
confirm whether or not the noise is related to the drive belt.
CAUTION
When running the engine with the accessory
drive belt removed, the coolant pump will not
be operating and the engine may overheat if
left unsupervised even for a short period.
NOTE
There may also be a number of DTCs set when
running the engine with the accessory drive belt
removed.
4 Inspecting the drive belt is to ensure t hat it is not causing the noise. Small cracks across the ribs of the drive belt
will not cause the noise and are not just ification alone to replace the belt. Belt separation can be identified by the
ply of the belt separating and may be seen at the edge of the belt or felt as lumps under the belt.
5 Small amounts of pilling is a normal condition and is deemed acceptable. When the pilling is severe (33% of the
belt groove depth), the belt does not have a smoot h surface to run on and should be replaced.
Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1
Did you review the information provided in 2.2 Symptoms, and
perform the required inspections. Go to Step 2 Go to
2.2 Symptoms
2 Confirm the customer compla int. Is there a rumbling noise?
Go to Step 3 Refer to Diagnostic
Aids in this Section
3 1 Remove the drive belt, refer to 3.5 Accessory Drive Belt.
2 Operate the engine for no more than 40 seconds.
Does the rumbling noise still exist? Accessory drive
system OK
Go to 2.2
Symptoms, and
restart the diagnosis Go to Step 4
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2837 of 6020
Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–60
Page 6A1–60
Drive Belt Vibration
Definition
Accessory drive belt vibration can be defined as a drive belt that jumps, shakes or rattles. Accessory drive belt vibration
is usually indicated by one of the following:
• the vibration is engine speed related, or
• the vibration is sensitive to accessory drive system load.
Diagnostic Aids
The accessory drive components such as the A/C compre ssor or generator can have an affect on engine vibration.
To aid in locating which component is causing the vibration, vary the load to each accessory drive component in turn and
note the effect it has on the vibration if any.
Test Description
The numbers below refer to steps in the diagnostic table.
2 Confirms the symptom exists at the time of di agnosis. Other vehicle components may be causing the noise.
3 Confirms the accessory drive belt is the cause of the noise. Drive belt rumbling is often confused with an internal
engine noise due to the similarity in the description. Removing the drive belt and operating the engine briefly will
confirm whether or not the noise is related to the drive belt.
CAUTION
When running the engine with the accessory
drive belt removed, the coolant pump will not
be operating and the engine may overheat if
left unsupervised even for a short period.
NOTE
There may also be a number of DTCs set when
running the engine with the accessory drive belt
removed.
4 The drive belt may cause a vibration. Inspecting the drive belt is considerably easier while the drive belt is
removed.
6 Inspecting the fasteners can eliminate the possibility that an inco rrect fastener has been installed.
8 This step should only be performed if t he coolant pump is driven by the drive belt. Inspect the coolant pump for a
bent shaft. Also inspect the coolant pump bearings for smooth operation and excessive play. Compare the coolant
pump with a known good pump.
9 Accessory drive component brackets that are bent, cra cked or loose may put extra strain on the accessory
component causing it to vibrate.
Diagnostic Table
Step Action Yes No
1
Did you review the information provided in 2.2 Symptoms, and
perform the required inspections. Go to Step 2 Go to
2.2 Symptoms
2 Confirm the customer compla int. Is there a rumbling noise?
Go to Step 3 Refer to Diagnostic
Aids in this Section
3 1 Remove the drive belt, refer to 3.5 Accessory Drive Belt.
2 Operate the engine for no more than 40 seconds.
Does the vibration noise still exist? Accessory drive
system OK.
Go to 4.2
Symptoms, and
restart the diagnosis Go to Step 4
4 Inspect the accessory drive belt for damage, wear, debris build-up or
sections of missing ribs.
Did you find any damage, wear, debris build-up or missing ribs? Go to Step 5 Go to Step 6
5 Install a new accessory drive belt, refer to 3.5 Accessory Drive Belt.
Did you replace the accessory drive belt? Go to Step 10 —
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2849 of 6020
Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–72
Page 6A1–72
3.5 Accessory Drive Belt
RWD Vehicle
Remove
1 Remove the air intake duct from between the air flow meter and the throttle body, refer to
Section 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 – Service Operations.
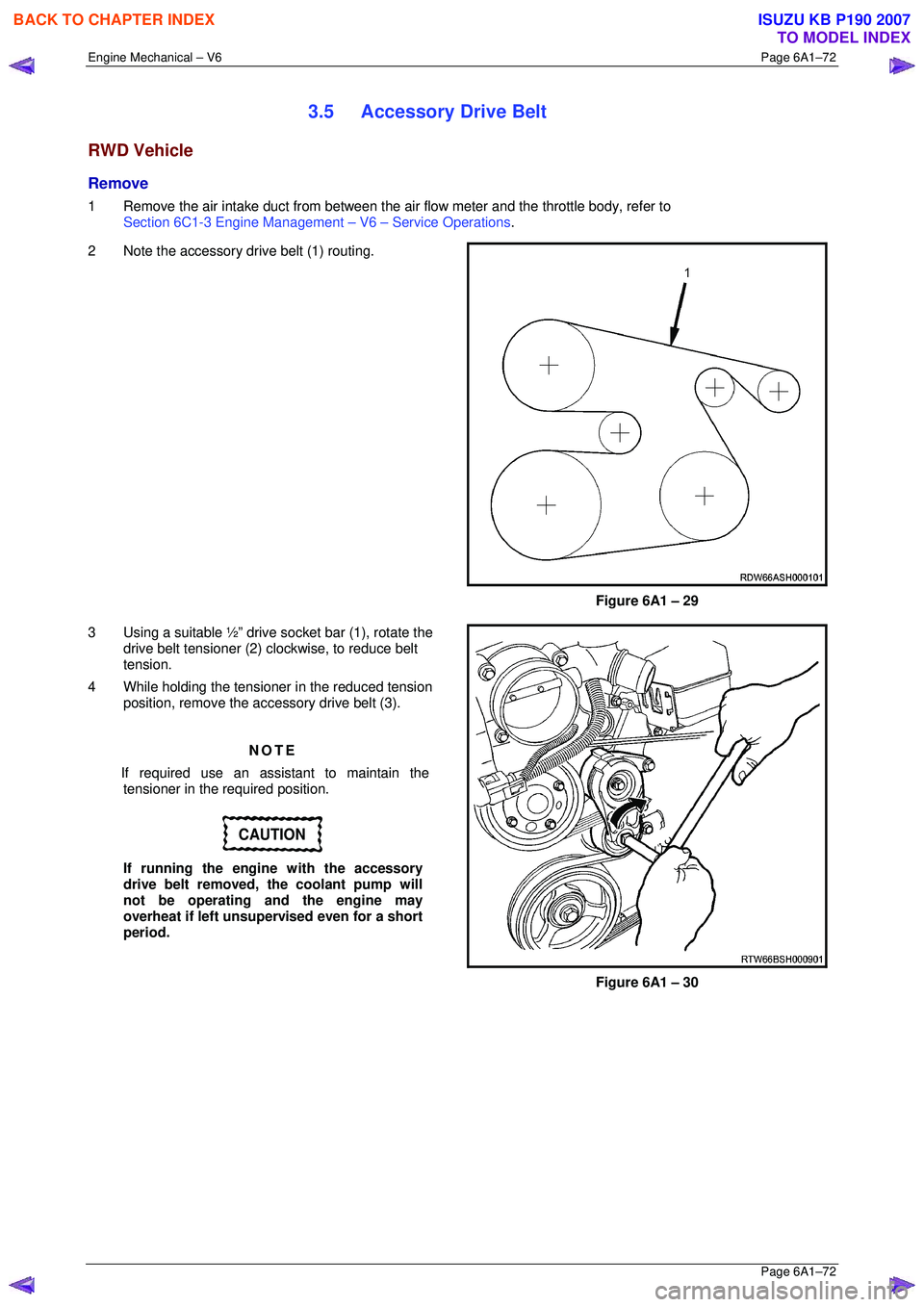
2 Note the accessory drive belt (1) routing.
Figure 6A1 – 29
3 Using a suitable ½” drive socket bar (1), rotate the drive belt tensioner (2) clockwise, to reduce belt
tension.
4 While holding the tensioner in the reduced tension
position, remove the accessory drive belt (3).
NOTE
If required use an assistant to maintain the tensioner in the required position.
CAUTION
If running the engine with the accessory
drive belt removed, the coolant pump will
not be operating and the engine may
overheat if left unsupervised even for a short
period.
Figure 6A1 – 30
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007