2007 ISUZU KB P190 wheel
[x] Cancel search: wheelPage 974 of 6020

6C – 10 FUEL SYSTEM
5. Install the filler neck to the body with bolt.
6. Install the inner liner of the wheel house at rear left side.
7. Remove lifter from the fuel tank.
8. Lower the vehicle.
9. Tigten the filler cap until at least three clicks.
10. Connect the battery ground cable.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1020 of 6020
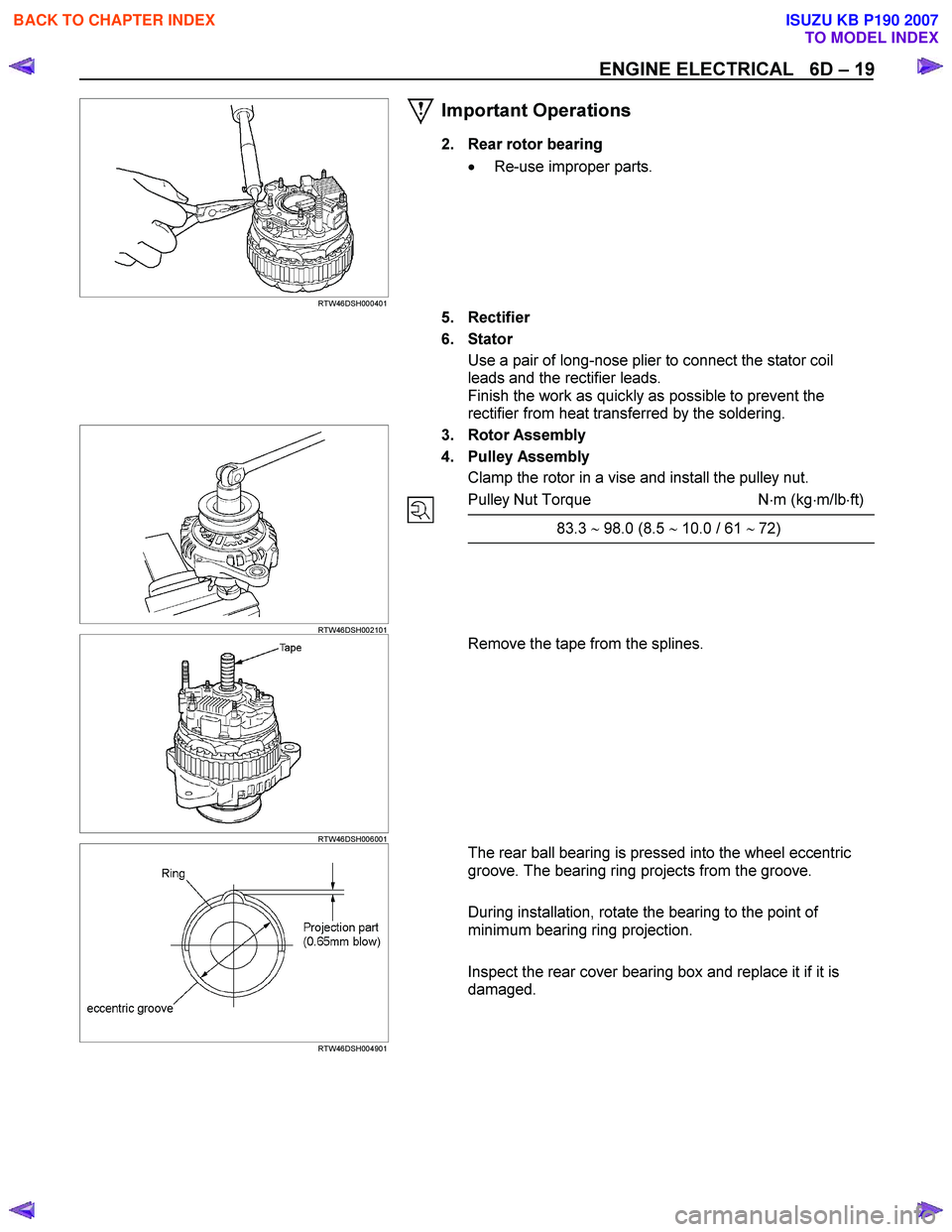
ENGINE ELECTRICAL 6D – 19
RTW46DSH000401
Important Operations
2. Rear rotor bearing
• Re-use improper parts.
5. Rectifier
6. Stator Use a pair of long-nose plier to connect the stator coil
leads and the rectifier leads.
Finish the work as quickly as possible to prevent the
rectifier from heat transferred by the soldering.
RTW46DSH002101
3. Rotor Assembly
4. Pulley Assembly Clamp the rotor in a vise and install the pulley nut.
Pulley Nut Torque N ⋅m (kg ⋅m/lb ⋅ft)
83.3 ∼ 98.0 (8.5 ∼ 10.0 / 61 ∼ 72)
RTW46DSH006001
Remove the tape from the splines.
RTW46DSH004901
The rear ball bearing is pressed into the wheel eccentric
groove. The bearing ring projects from the groove.
During installation, rotate the bearing to the point of
minimum bearing ring projection.
Inspect the rear cover bearing box and replace it if it is
damaged.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1083 of 6020
Engine Control System (4JH1) 6E-49
Step Action Value(s) Yes No
7 1. Disconnect the fuel hose that connects to the
fuel injection pump suction side. In order to
measure the discharged fuel amount, put the
hose into a bottle or a container.
2. Pump the priming pump on the fuel filter.
Notice: If there is a leak on the suction side of the
fuel system, the fuel from the disconnected hose will
not flow out sufficiently and fuel leakage may occur.
Also if there is a restriction on the suction side of the
fuel system, the fuel from the disconnected hose will
not flow out sufficiently that is most likely caused by
clogged fuel filter or kinked fuel hose or pipe.
3. Draw fuel from the fuel tank at the fuel line (as close to the fuel tank as possible) going to the
fuel pickup tube to verify a clean stream of fuel
comes out (use the hand-held vacuum pump 5-
8840-0279-0/J-23738-A with a clear hose or
equivalent). This will ensure the fuel pickup tube
is not cracked drawing air into the fuel line.
4. Repair any fuel system leaks and restrictions as necessary.
Did you find and correct the condition?
Go to Step 10 Go to Step 8
8 1. Other possible causes for the no-start condition: • Fuel injection pump mechanical timing
incorrect
• Flywheel installed incorrectly causing the
crankshaft position (CKP) sensor to be
incorrectly timed to the engine. Disconnect
sensor and attempt to start engine to verify.
• Heavily restricted intake, exhaust or
catalytic converter plugged solid
• Poor engine compression
• W ater or gasoline contamination in fuel
2. Repair or replace as necessary.
Did you find and correct the condition?
Go to Step 10 Go to Step 9
9 Important: The fuel injection pump must be timed to
the engine.
Replace the fuel injection pump. Refer to Fuel
Injection Pump Replacement in engine mechanical
section.
Did you complete the replacement?
Go to Step 10
10 1. Reconnect all previously disconnected harness
connector(s).
2. Turn OFF the ignition for 30 seconds.
3. Attempt to start the engine.
Does the engine start and continue to run?
Go to Step 11 Go to Step 2
11 Observe the DTC Information with the scan tool. Are there any DTCs that you have not diagnosed? Go to Diagnostic
Trouble Code (DTC) List System OK
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1089 of 6020
Engine Control System (4JH1) 6E-55
DTC
(Symptom Code) Flash
Code MIL
Status DTC Name on
scan tool Condition for
Running the DTC Condition for
Setting the DTC Possible Cause
P0251
(E) 53 ON Injection Pump
Fuel Metering
Control •
The ignition switch
is ON. •
The ECM detects
communication
message from the
PCU is not received
for longer than 1
second.
•
CAN high circuit is open circuit,
high resistance, short to ground,
short to battery or ignition
voltage.
• CAN low circuit is open circuit,
high resistance, short to ground,
short to battery or ignition
voltage.
• Electrical interference.
• Magnetic interference.
• Faulty PCU.
• Faulty ECM.
P0335 (B) 43 ON
Crankshaft
Position (CKP)
Sensor Circuit •
The ignition switch
is ON.
• The engine speed
is higher than 665
RPM.
•
The ECM detects
extra or missing
CKP sensor signals
while engine is
running. •
Sensor signal circuit is open
circuit, high resistance, short to
ground, short to battery or short
to ignition voltage.
• Sensor low reference circuit is
open circuit, high resistance,
short to ground, short to battery
or short to ignition voltage.
• Sensor shield ground is open
circuit, high resistance, short to
ground, short to battery or short
to ignition voltage.
• Faulty CKP sensor.
• Faulty ECM.
• Electrical interference.
• Magnetic interference.
• Faulty sensor installation.
• Faulty flywheel circumference.
P0335 (D) 43 ON
Crankshaft
Position (CKP)
Sensor Circuit •
DTC P0335
(Symptom Code B)
is not set.
• The ignition switch
is ON.
• The fuel injection
pump CMP sensor
signal is generated.
• The CAN
communication
between the ECM
and PCU is normal.
•
The ECM detects
that the CKP sensor
signals are not
generated when
doubled fuel
injection pump
rotation speed is
higher than 50
RPM.
•
Sensor signal circuit is open
circuit, high resistance, short to
ground, short to battery or short
to ignition voltage.
• Sensor low reference circuit is
open circuit, high resistance,
short to ground, short to battery
or short to ignition voltage.
• Sensor shield ground is open
circuit, high resistance, short to
ground, short to battery or short
to ignition voltage.
• Faulty CKP sensor.
• Faulty ECM.
• Electrical interference.
• Magnetic interference.
• Faulty sensor installation.
• Faulty flywheel circumference.
P0335 (E) 43 ON Crankshaft
Position (CKP)
Sensor Circuit •
Ignition switch is
ON.
•
The ECM detects
that the engine
speed is higher
than 5700 RPM for
0.2 seconds. •
Engine overrun.
• Faulty CKP sensor.
• Faulty ECM.
• Electrical interference.
• Magnetic interference.
• Faulty flywheel circumference.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1160 of 6020
6E-126 Engine Control System (4JH1)
Step Action Value(s) Yes No
4 1. Observe the Engine Speed parameter with the
scan tool.
2. Accelerate the engine between idle and W .O.T. (accelerator pedal full travel) many times while
observing the scan tool.
Does the Engine Speed parameter indicate correct
engine speed?
Go to Step 9 Go to Step 5
5 1. Inspect the crankshaft position (CKP) sensor for tightness.
2. Remove the CKP sensor and check for damage, metal particles on magnet and for flywheel
circumference damage.
Did you find and correct the condition?
Go to Step 10 Go to Step 6
6 1. Turn OFF the ignition.
2. Disconnect the CKP sensor harness connector.
3. Inspect for an intermittent, for poor connections and corrosion on the CKP sensor terminal (pins
1, 2 and 3 of E-9 connector).
4. Repair the connection(s) as necessary.
Did you find and correct the condition.
Go to Step 10 Go to Step 7
7 1. Turn OFF the ignition. 2. Disconnect the fuel injection pump control unit (PCU) harness connector.
3. Inspect for an intermittent, for a poor connection and corrosion on the CKP sensor signal input at
the harness connector of the PCU (pin 8 of E-6
connector).
4. Repair the connection(s) as necessary.
Did you find and correct the condition?
Go to Step 10 Go to Step 8
8 1. Turn OFF the ignition. Disconnect the engine control module (ECM)
harness connector.
2. Inspect for an intermittent, for poor connections and corrosion on at the harness connector of the
ECM (pins 90, 91, 98 and 101 of C-57
connector).
3. Repair the connection(s) as necessary.
Did you find and correct the condition?
Go to Step 10 Go to Step 9
9 Important: The fuel injection pump must be timed to
the engine.
Replace the fuel injection pump. Refer to Fuel
Injection Pump Replacement in engine mechanical
section.
Did you complete the replacement?
Go to Step 10
10 1. Reconnect all previously disconnected harness
connector(s).
2. Clear the DTCs with the scan tool.
3. Turn OFF the ignition for 30 seconds.
4. Start the engine.
5. Accelerate the engine between idle and W .O.T. (accelerator pedal full travel) many times while
observing the DTC Information with the scan
tool.
Does the DTC fail this ignition?
Go to Step 2 Go to Step 11
11 Observe the DTC Information with the scan tool. Are there any DTCs that you have not diagnosed? Go to Diagnostic
Trouble Code (DTC) List System OK
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1164 of 6020
6E-130 Engine Control System (4JH1)
DTC P0335 (Symptom Code B, D) (Flash Code 43)
Circuit Description
The crankshaft position (CKP) sensor is located on top
of the flywheel housing. There are 4 slits spaced 90 °
on the flywheel circumference. The CKP sensor is a
magnetic coil type sensor, which generates an AC
signal voltage based on the crankshaft rotational speed.
The engine control module (ECM) monitors both the
CKP sensor and injection pump camshaft position
(CMP) sensor signals to ensure they correlate with each
other.
If the ECM receives extra or missing CKP sensor signal
pulses, this DTC will set. (Symptom Code B)
If the ECM receives a certain amount of injection pump
CMP sensor signal pulses without a CKP sensor signal,
this DTC will set. (Symptom Code D)
Condition for Running the DTC
Symptom Code B • The ignition switch is ON.
• The engine speed is higher than 665 RPM
Symptom Code D • DTC P0335 (Symptom Code B) is not set.
• The ignition switch is ON.
• The fuel injection pump CMP sensor signal is
generated.
• The controller area network (CAN) communication
between the ECM and PCU is normal.
Condition for Setting the DTC
Symptom Code B • The ECM detects extra or missing CKP senso
r
signals while engine is running.
Symptom Code D
• The ECM detects that the CKP sensor signals are
not generated when doubled fuel injection pump
rotation speed is higher than 50 RPM.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
• The ECM illuminates the malfunction indicato
r
lamp (MIL) when the diagnostic runs and fails.
The ECM uses an engine speed substitution o
f
doubled fuel injection pump speed for engine
control.
Condition for Clearing the MIL/DTC
• The ECM turns OFF the MIL when the diagnostic
runs and does not fail.
• A history DTC clears after 40 consecutive driving
cycles without a fault. Or clear with the scan tool.
Diagnostic Aids
• If an intermittent condition is suspected, refer to
Intermittent Conditions in this section.
• Ensure the sensor is tight and the flywheel
circumference is not damaged.
DTC P0335 (Symptom Code B, D) (Flash Code 43)
Schematic Reference: Engine Controls Schematics
Connector End View Reference: Engine Controls
Connector End Views or Engine Control Module (ECM)
Connector End Views
Step Action Value(s) Yes No
1 Did you perform the Diagnostic System Check-
Engine Controls?
Go to Step 2 Go to Diagnostic
System Check-
Engine Controls
2 1. Install the scan tool. 2. Turn OFF the ignition for 30 seconds.
3. Start the engine (Note a slight start delay may be noticed).
4. Monitor the Diagnostic Trouble Code (DTC) Information with the scan tool.
Does the DTC fail this ignition?
Go to Step 3 Go to Diagnostic
Aids
3 1. Turn OFF the ignition. 2. Disconnect the crankshaft position sensor (CKP) harness connector.
3. Connect a DMM across the CKP sensor terminals (pins 1 and 2 of E-9 connector).
4. Measure the resistance across the CKP sensor.
Is the CKP sensor resistance within the specified
value? 870 – 930
Ω
Go to Step 4 Go to Step 20
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1167 of 6020
Engine Control System (4JH1) 6E-133
Step Action Value(s) Yes No
19 1. Inspect the CKP sensor for tightness.
2. Retest if the sensor was loose.
3. Remove the CKP sensor and check for damage, metal particles on magnet and for flywheel
circumference damage.
Did you find and correct the condition?
Go to Step 22 Go to Step 20
20 Replace the CKP sensor. Refer to Crankshaft Position Sensor Replacement in this section.
Did you complete the replacement?
Go to Step 22
21 Important: Replacement ECM must be
programmed.
Replace the ECM. Refer to Engine Control Module
(ECM) Replacement in this section.
Did you complete the replacement?
Go to Step 22
22 1. Reconnect all previously disconnected harness
connector(s).
2. Clear the DTCs with the scan tool.
3. Turn OFF the ignition for 30 seconds.
4. Start the engine.
5. Monitor the DTC Information with the scan tool.
Did the DTC fail this ignition?
Go to Step 3 Go to Step 23
23 Observe the DTC Information with the scan tool. Are there any DTCs that you have not diagnosed? Go to Diagnostic
Trouble Code (DTC) List System OK
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 1168 of 6020
6E-134 Engine Control System (4JH1)
DTC P0335 (Symptom Code E) (Flash Code 43)
Circuit Description
The crankshaft position (CKP) sensor is located on top
of the flywheel housing. The engine control module
(ECM) calculates the engine speed and exact position
of the crankshaft based on the signal from the CKP
sensor. If the ECM detects an engine overrun condition,
this DTC will set.
Condition for Running the DTC
• The ignition switch is ON.
Condition for Setting the DTC • The ECM detects that the engine speed is highe
r
than 5700 RPM for 0.2 seconds.
Action Taken When the DTC Sets
• The ECM illuminates the malfunction indicato
r
lamp (MIL) when the diagnostic runs and fails.
• The ECM cuts fuel injection.
Condition for Clearing the MIL/DTC
• The ECM turns OFF the MIL when the diagnostic
runs and does not fail.
• A history DTC clears after 40 consecutive driving
cycles without a fault. Or clear with the scan tool.
Diagnostic Aids
• Ensure the sensor is tight and the flywheel
circumference is not damaged.
Notice:
• This DTC is caused by an engine over speed
condition, which was most likely caused by drive
r
error (i.e. downshifting a manual transmission on a
steep grade). Ensure there are no signs of engine
damage. Excessive engine over speed ma
y
damage internal engine components.
DTC P0335 (Symptom Code E) (Flash Code 43)
Step Action Value(s) Yes No
1 Did you perform the Diagnostic System Check-
Engine Controls?
Go to Step 2 Go to Diagnostic
System Check-
Engine Controls
2 1. Install the scan tool. 2. Start the engine.
3. Observe the Engine Speed parameter with the scan tool.
4. Accelerate the engine between idle and W .O.T. (accelerator pedal full travel) many times while
observing the scan tool.
Does the Engine Speed parameter ever exceed the
specified value? 5000 RPM
Go to Step 4 Go to Step 3
3 Ask the driver if overrun is caused by gear slip-out, shift error, down-slope diving, etc. If engine overrun
has experienced, the engine must be inspected and
repaired as necessary.
Did you complete the action?
Go to Step 7
4 1. Remove the crankshaft position (CKP) sensor.
Refer to CKP Sensor replacement in this section.
2. Visually inspect the CKP sensor for the following conditions: • For physical damage
• For being loose
• For improper installation
Did you find and correct the condition?
Go to Step 7 Go to Step 5
5 Visually inspect the flywheel circumference for damage.
Did you find and correct the condition?
Go to Step 7 Go to Step 6
6 Important: Replacement ECM must be
programmed.
Replace the ECM. Refer to Engine Control Module
(ECM) Replacement in this section.
Did you complete the replacement?
Go to Step 7
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007