2007 ISUZU KB P190 cooling
[x] Cancel search: coolingPage 3264 of 6020
Engine Management – V6 – General Information Page 6C1-1–22
4.6 Clutch Pedal Switch Assembly – Manual
Vehicles Only
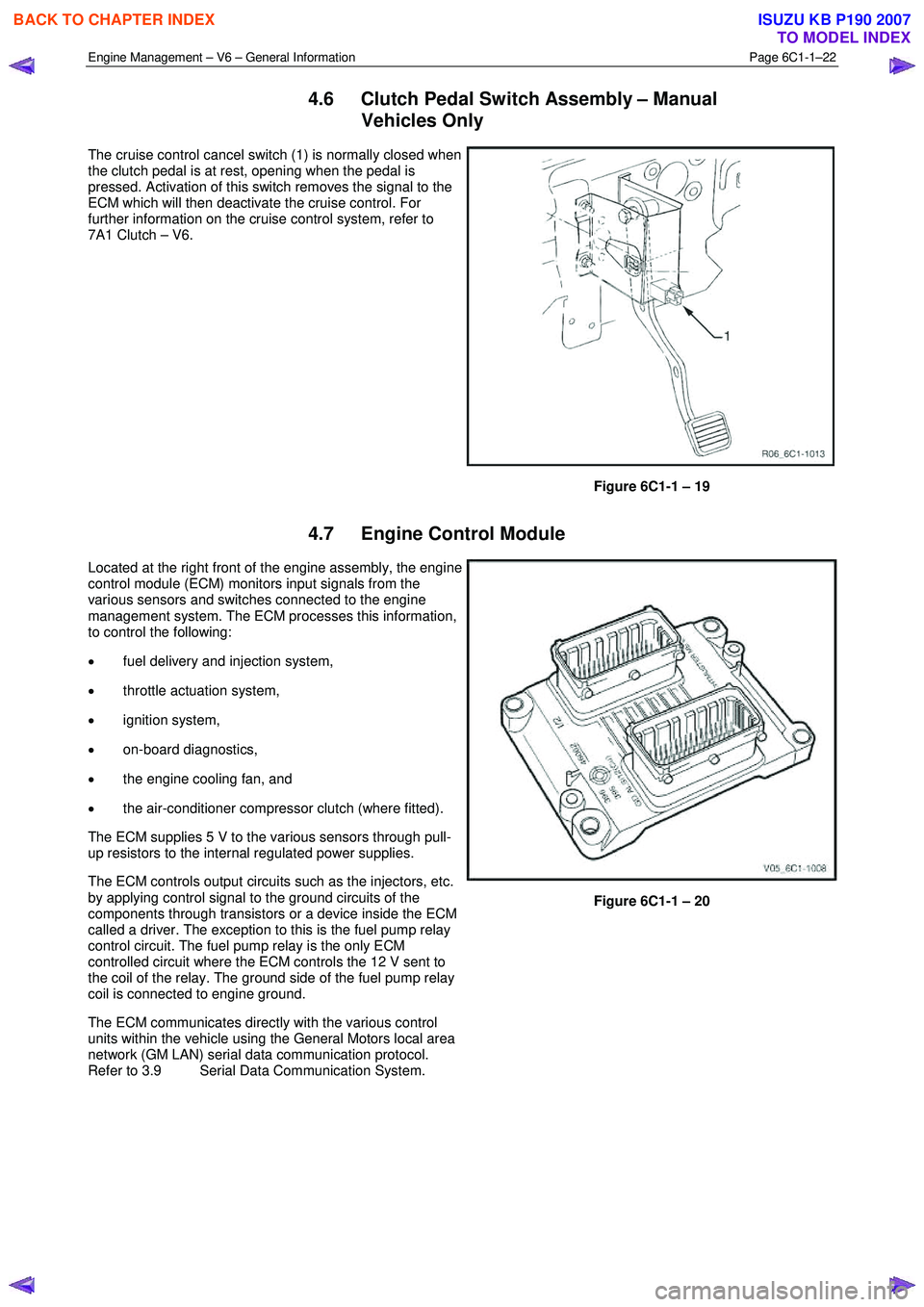
The cruise control cancel switch (1) is normally closed when
the clutch pedal is at rest, opening when the pedal is
pressed. Activation of this switch removes the signal to the
ECM which will then deactivate the cruise control. For
further information on the cruise control system, refer to
7A1 Clutch – V6.
Figure 6C1-1 – 19
4.7 Engine Control Module
Located at the right front of the engine assembly, the engine
control module (ECM) monitors input signals from the
various sensors and switches connected to the engine
management system. The ECM processes this information,
to control the following:
• fuel delivery and injection system,
• throttle actuation system,
• ignition system,
• on-board diagnostics,
• the engine cooling fan, and
• the air-conditioner compressor clutch (where fitted).
The ECM supplies 5 V to the various sensors through pull-
up resistors to the internal regulated power supplies.
The ECM controls output circuits such as the injectors, etc.
by applying control signal to the ground circuits of the
components through transistors or a device inside the ECM
called a driver. The exception to this is the fuel pump relay
control circuit. The fuel pump relay is the only ECM
controlled circuit where the ECM controls the 12 V sent to
the coil of the relay. The ground side of the fuel pump relay
coil is connected to engine ground.
The ECM communicates directly with the various control
units within the vehicle using the General Motors local area
network (GM LAN) serial data communication protocol.
Refer to 3.9 Serial Data Communication System.
Figure 6C1-1 – 20
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3265 of 6020
Engine Management – V6 – General Information Page 6C1-1–23
4.8 Engine Coolant Temperature Sensor
The engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor is a
thermistor, which is a resistor that changes it’s resistance
value based on temperature.
Figure 6C1-1 – 21
The ECT is mounted in the engine coolant stream and as it
is a negative temperature coefficient (NTC) type, low engine
coolant temperature produces a high sensor resistance
while high engine coolant temperature causes low sensor
resistance.
Legend
A Temperature
B Resistance
The ECM provides a 5 V reference signal to the ECT and
monitors the return signal which enables it to calculate the
engine temperature.
The ECM uses this signal to make corrections to the
operating parameters of the system based on changes in
engine coolant temperature.
Figure 6C1-1 – 22
4.9 Electric Cooling Fan
The ECM controls the operation of the electric engine
cooling fan. The ECM applies a pulse width modulated
(PW M) signal to the cooling fan motor to control the fan
speed based on current vehicle conditions. For further
information on cooling fan operation, refer to 6B1 Engine
Cooling – V6.
Figure 6C1-1 – 23
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3276 of 6020
Engine Management – V6 – General Information Page 6C1-1–34
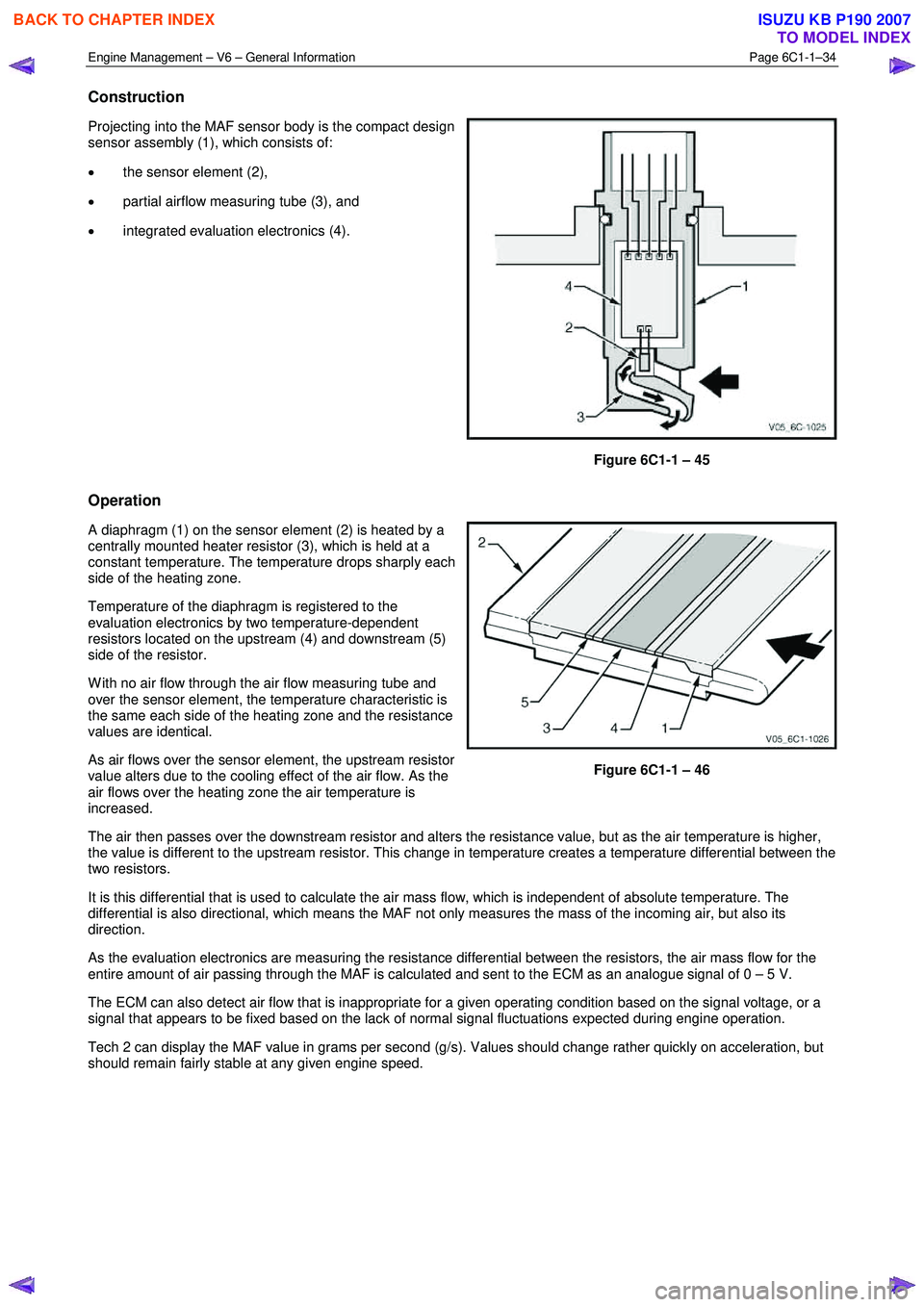
Construction
Projecting into the MAF sensor body is the compact design
sensor assembly (1), which consists of:
• the sensor element (2),
• partial airflow measuring tube (3), and
• integrated evaluation electronics (4).
Figure 6C1-1 – 45
Operation
A diaphragm (1) on the sensor element (2) is heated by a
centrally mounted heater resistor (3), which is held at a
constant temperature. The temperature drops sharply each
side of the heating zone.
Temperature of the diaphragm is registered to the
evaluation electronics by two temperature-dependent
resistors located on the upstream (4) and downstream (5)
side of the resistor.
W ith no air flow through the air flow measuring tube and
over the sensor element, the temperature characteristic is
the same each side of the heating zone and the resistance
values are identical.
As air flows over the sensor element, the upstream resistor
value alters due to the cooling effect of the air flow. As the
air flows over the heating zone the air temperature is
increased.
Figure 6C1-1 – 46
The air then passes over the downstream resistor and alters the resistance value, but as the air temperature is higher,
the value is different to the upstream resistor. This change in temperature creates a temperature differential between the
two resistors.
It is this differential that is used to calculate the air mass flow, which is independent of absolute temperature. The
differential is also directional, which means the MAF not only measures the mass of the incoming air, but also its
direction.
As the evaluation electronics are measuring the resistance differential between the resistors, the air mass flow for the
entire amount of air passing through the MAF is calculated and sent to the ECM as an analogue signal of 0 – 5 V.
The ECM can also detect air flow that is inappropriate for a given operating condition based on the signal voltage, or a
signal that appears to be fixed based on the lack of normal signal fluctuations expected during engine operation.
Tech 2 can display the MAF value in grams per second (g/s). Values should change rather quickly on acceleration, but
should remain fairly stable at any given engine speed.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3292 of 6020
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–14
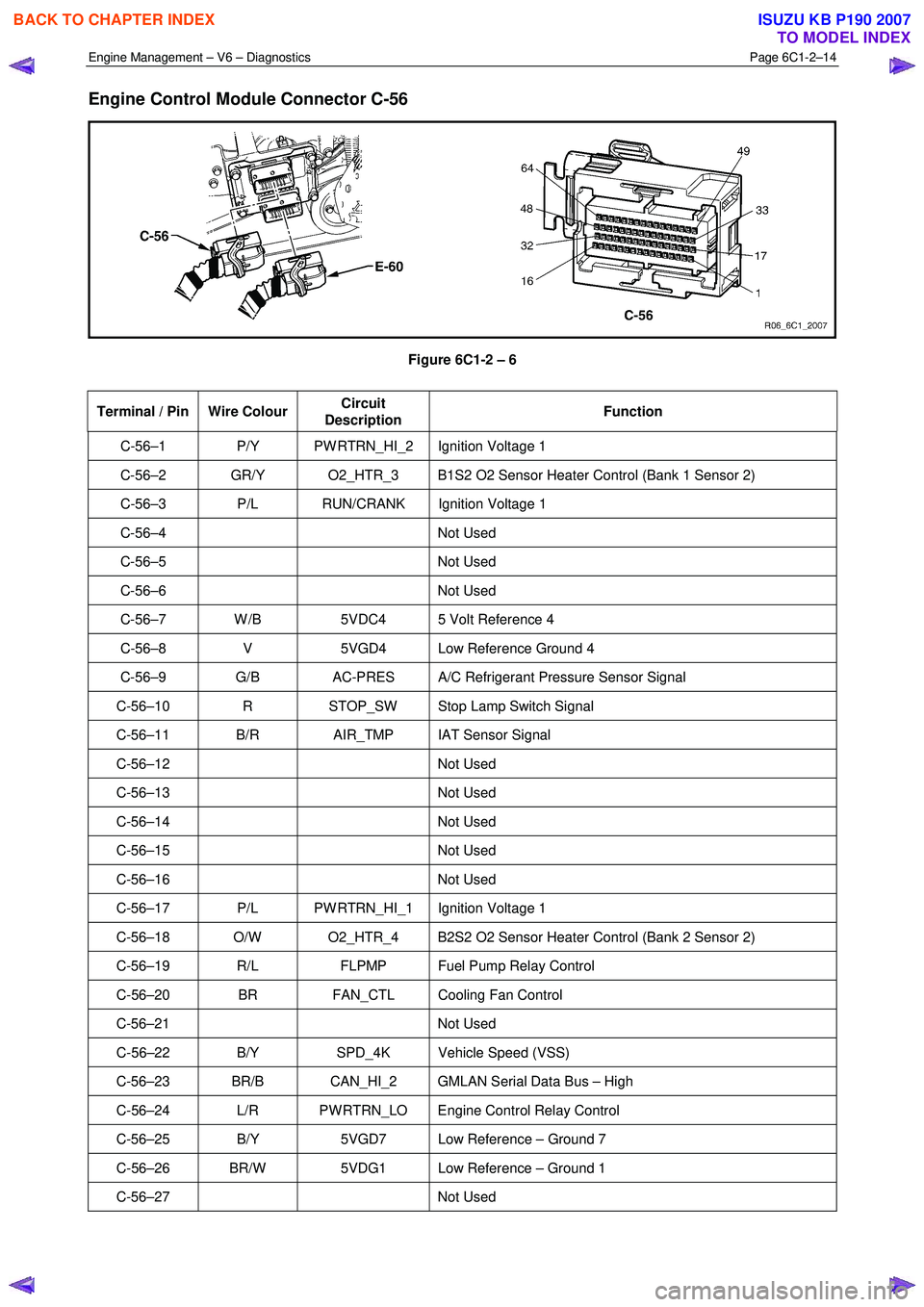
Engine Control Module Connector C-56
Figure 6C1-2 – 6
Terminal / Pin Wire Colour Circuit
Description Function
C-56–1 P/Y PW RTRN_HI_2 Ignition Voltage 1
C-56–2 GR/Y O2_HTR_3 B1S2 O2 Sensor Heater Control (Bank 1 Sensor 2)
C-56–3 P/L RUN/CRANK Ignition Voltage 1
C-56–4 Not
Used
C-56–5 Not Used
C-56–6 Not Used
C-56–7 W /B 5VDC4 5 Volt Reference 4
C-56–8 V 5VGD4 Low Reference Ground 4
C-56–9 G/B AC-PRES A/C Refrigerant Pressure Sensor Signal
C-56–10 R STOP_SW Stop Lamp Switch Signal
C-56–11 B/R AIR_TMP IAT Sensor Signal
C-56–12 Not Used
C-56–13 Not Used
C-56–14 Not Used
C-56–15 Not Used
C-56–16 Not Used
C-56–17 P/L PW RTRN_HI_1 Ignition Voltage 1
C-56–18 O/W O2_HTR_4 B2S2 O2 Sensor Heater Control (Bank 2 Sensor 2)
C-56–19 R/L FLPMP Fuel Pump Relay Control
C-56–20 BR FAN_CTL Cooling Fan Control
C-56–21 Not Used
C-56–22 B/Y SPD_4K Vehicle Speed (VSS)
C-56–23 BR/B CAN_HI_2 GMLAN Serial Data Bus – High
C-56–24 L/R PW RTRN_LO Engine Control Relay Control
C-56–25 B/Y 5VGD7 Low Reference – Ground 7
C-56–26 BR/W 5VDG1 Low Reference – Ground 1
C-56–27 Not Used
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3303 of 6020
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–25
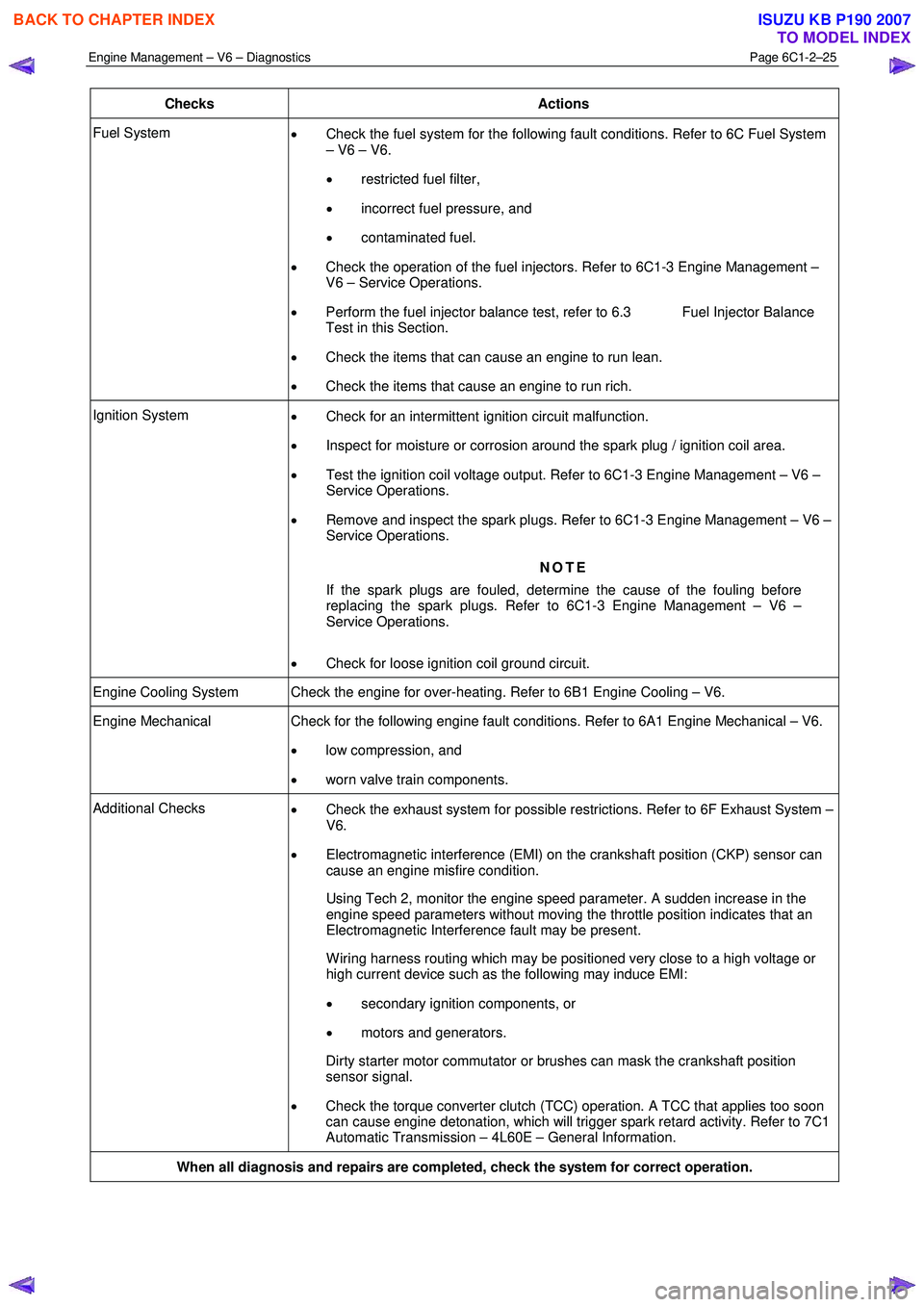
Checks Actions
Fuel System
• Check the fuel system for the following fault conditions. Refer to 6C Fuel System
– V6 – V6.
• restricted fuel filter,
• incorrect fuel pressure, and
• contaminated fuel.
• Check the operation of the fuel injectors. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management –
V6 – Service Operations.
• Perform the fuel injector balance test, refer to 6.3 Fuel Injector Balance
Test in this Section.
• Check the items that can cause an engine to run lean.
• Check the items that cause an engine to run rich.
Ignition System
• Check for an intermittent ignition circuit malfunction.
• Inspect for moisture or corrosion around the spark plug / ignition coil area.
• Test the ignition coil voltage output. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
• Remove and inspect the spark plugs. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
NOTE
If the spark plugs are fouled, determine the cause of the fouling before
replacing the spark plugs. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
• Check for loose ignition coil ground circuit.
Engine Cooling System Check the engine for over-heating. Refer to 6B1 Engine Cooling – V6.
Engine Mechanical Check for the following engine fault conditions. Refer to 6A1 Engine Mechanical – V6.
• low compression, and
• worn valve train components.
Additional Checks
• Check the exhaust system for possible restrictions. Refer to 6F Exhaust System –
V6.
• Electromagnetic interference (EMI) on the crankshaft position (CKP) sensor can
cause an engine misfire condition.
Using Tech 2, monitor the engine speed parameter. A sudden increase in the engine speed parameters without moving the throttle position indicates that an
Electromagnetic Interference fault may be present.
W iring harness routing which may be positioned very close to a high voltage or high current device such as the following may induce EMI:
• secondary ignition components, or
• motors and generators.
Dirty starter motor commutator or brushes can mask the crankshaft position sensor signal.
• Check the torque converter clutch (TCC) operation. A TCC that applies too soon
can cause engine detonation, which will trigger spark retard activity. Refer to 7C1
Automatic Transmission – 4L60E – General Information.
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3307 of 6020
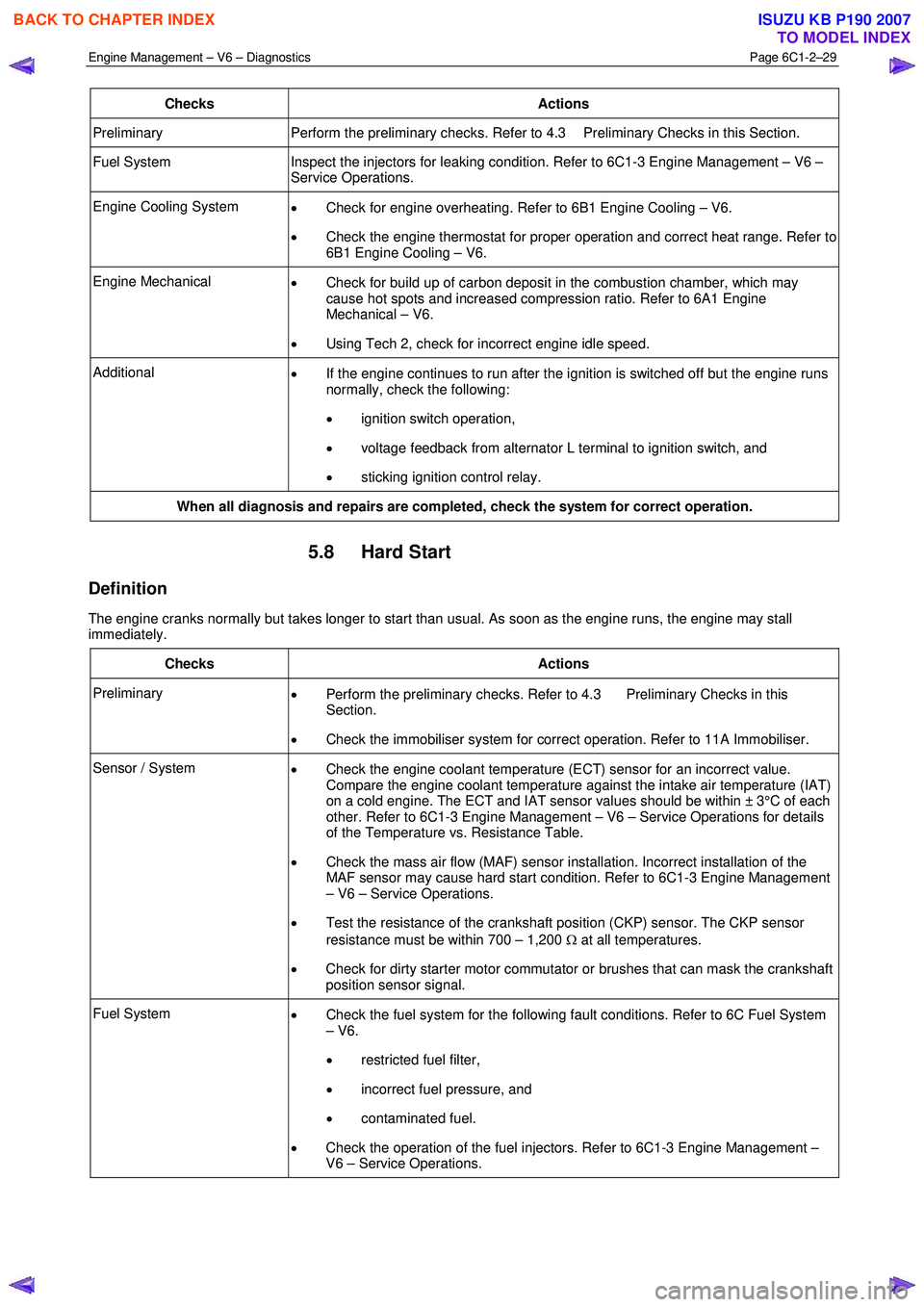
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–29
Checks Actions
Preliminary Perform the preliminary checks. Refer to 4.3 Preliminary Checks in this Section.
Fuel System Inspect the injectors for leaking condition. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
Engine Cooling System • Check for engine overheating. Refer to 6B1 Engine Cooling – V6.
• Check the engine thermostat for proper operation and correct heat range. Refer to
6B1 Engine Cooling – V6.
Engine Mechanical • Check for build up of carbon deposit in the combustion chamber, which may
cause hot spots and increased compression ratio. Refer to 6A1 Engine
Mechanical – V6.
• Using Tech 2, check for incorrect engine idle speed.
Additional
• If the engine continues to run after the ignition is switched off but the engine runs
normally, check the following:
• ignition switch operation,
• voltage feedback from alternator L terminal to ignition switch, and
• sticking ignition control relay.
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
5.8 Hard Start
Definition
The engine cranks normally but takes longer to start than usual. As soon as the engine runs, the engine may stall
immediately.
Checks Actions
Preliminary • Perform the preliminary checks. Refer to 4.3 Preliminary Checks in this
Section.
• Check the immobiliser system for correct operation. Refer to 11A Immobiliser.
Sensor / System
• Check the engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor for an incorrect value.
Compare the engine coolant temperature against the intake air temperature (IAT)
on a cold engine. The ECT and IAT sensor values should be within ± 3°C of each
other. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 – Service Operations for details
of the Temperature vs. Resistance Table.
• Check the mass air flow (MAF) sensor installation. Incorrect installation of the
MAF sensor may cause hard start condition. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management
– V6 – Service Operations.
• Test the resistance of the crankshaft position (CKP) sensor. The CKP sensor
resistance must be within 700 – 1,200 Ω at all temperatures.
• Check for dirty starter motor commutator or brushes that can mask the crankshaft
position sensor signal.
Fuel System • Check the fuel system for the following fault conditions. Refer to 6C Fuel System
– V6.
• restricted fuel filter,
• incorrect fuel pressure, and
• contaminated fuel.
• Check the operation of the fuel injectors. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management –
V6 – Service Operations.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3309 of 6020
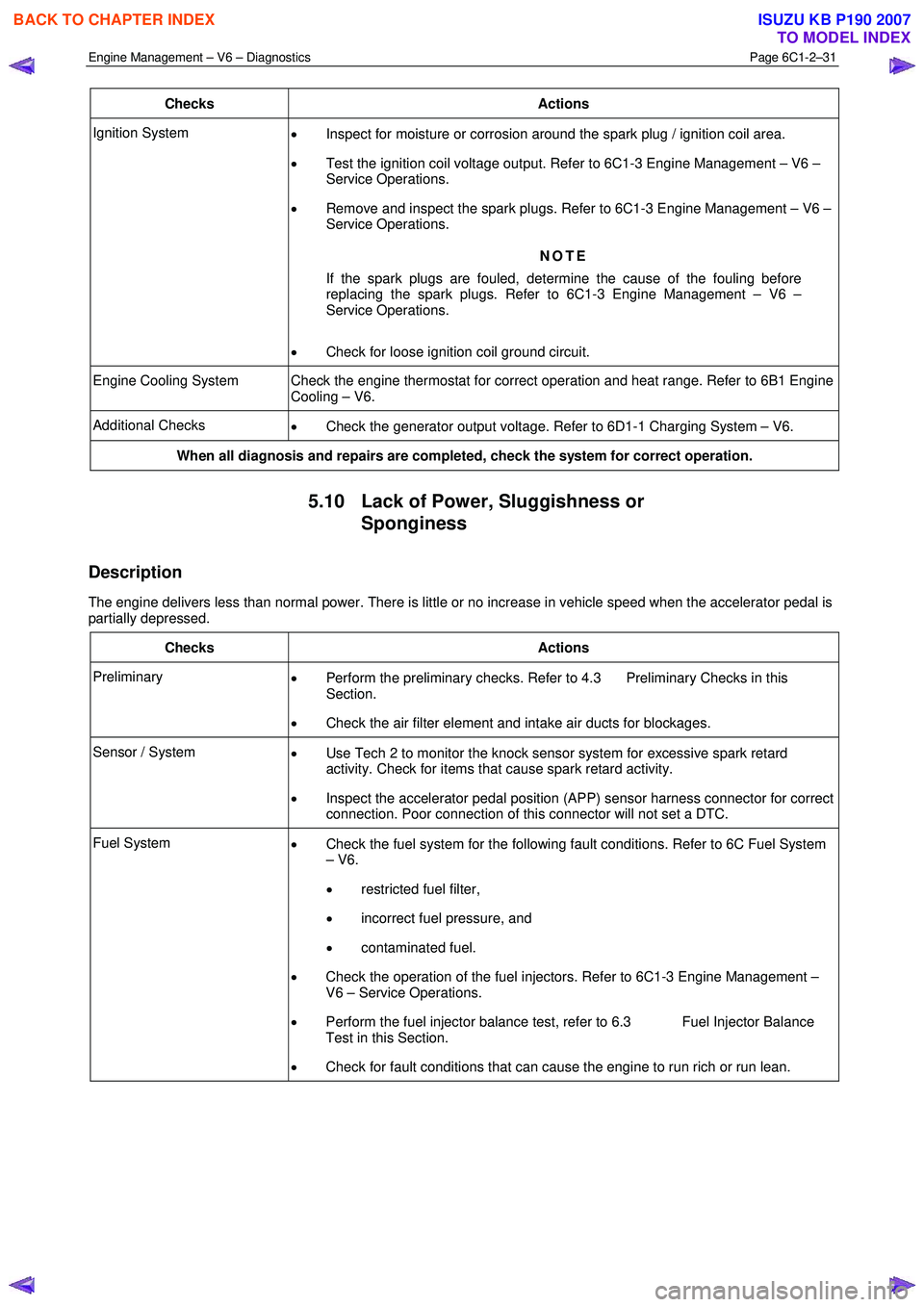
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–31
Checks Actions
Ignition System
• Inspect for moisture or corrosion around the spark plug / ignition coil area.
• Test the ignition coil voltage output. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
• Remove and inspect the spark plugs. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
NOTE
If the spark plugs are fouled, determine the cause of the fouling before
replacing the spark plugs. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
• Check for loose ignition coil ground circuit.
Engine Cooling System Check the engine thermostat for correct operation and heat range. Refer to 6B1 Engine
Cooling – V6.
Additional Checks • Check the generator output voltage. Refer to 6D1-1 Charging System – V6.
When all diagnosis and repairs are completed, check the system for correct operation.
5.10 Lack of Power, Sluggishness or
Sponginess
Description
The engine delivers less than normal power. There is little or no increase in vehicle speed when the accelerator pedal is
partially depressed.
Checks Actions
Preliminary • Perform the preliminary checks. Refer to 4.3 Preliminary Checks in this
Section.
• Check the air filter element and intake air ducts for blockages.
Sensor / System
• Use Tech 2 to monitor the knock sensor system for excessive spark retard
activity. Check for items that cause spark retard activity.
• Inspect the accelerator pedal position (APP) sensor harness connector for correct
connection. Poor connection of this connector will not set a DTC.
Fuel System • Check the fuel system for the following fault conditions. Refer to 6C Fuel System
– V6.
• restricted fuel filter,
• incorrect fuel pressure, and
• contaminated fuel.
• Check the operation of the fuel injectors. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management –
V6 – Service Operations.
• Perform the fuel injector balance test, refer to 6.3 Fuel Injector Balance
Test in this Section.
• Check for fault conditions that can cause the engine to run rich or run lean.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 3311 of 6020
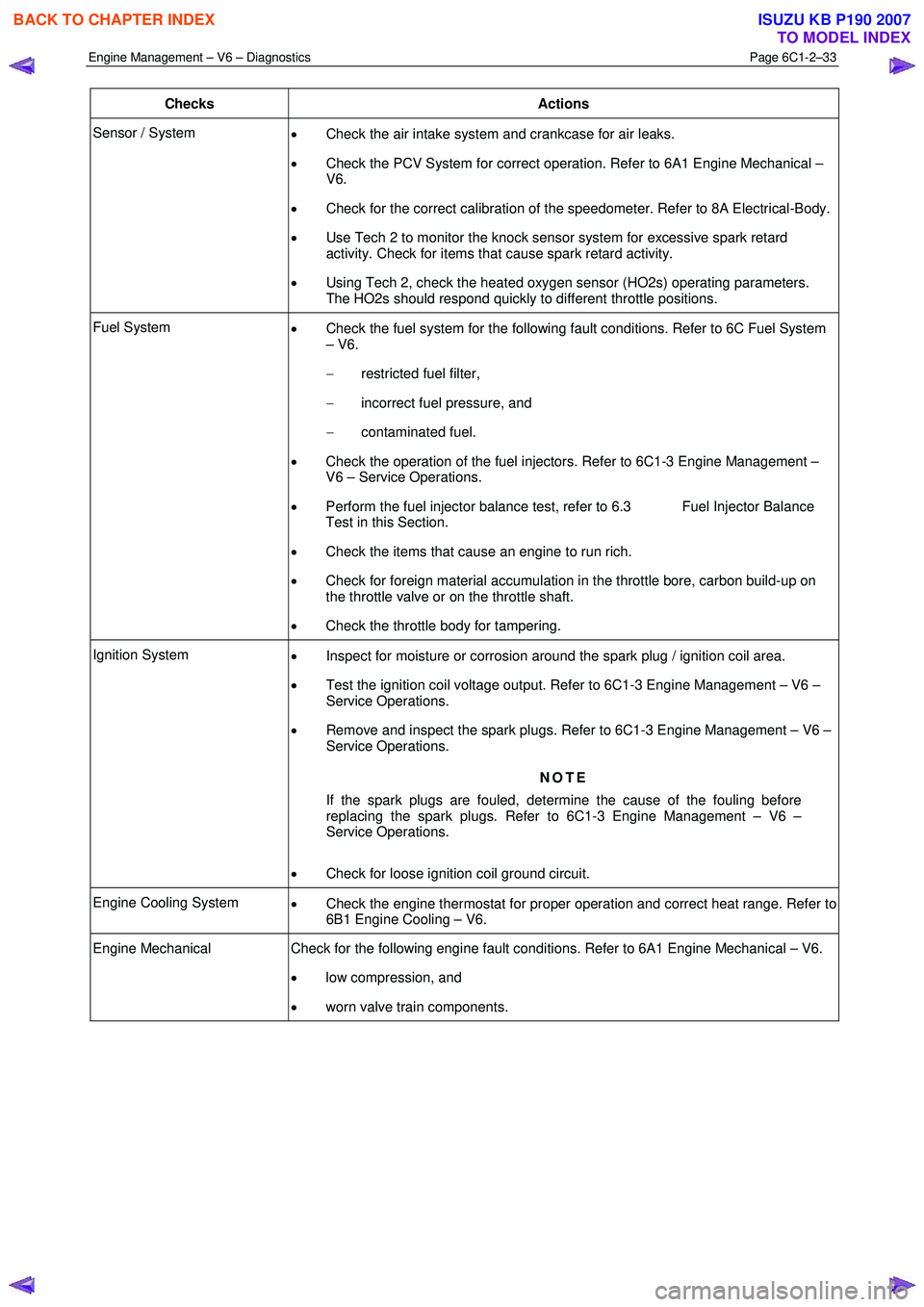
Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics Page 6C1-2–33
Checks Actions
Sensor / System
• Check the air intake system and crankcase for air leaks.
• Check the PCV System for correct operation. Refer to 6A1 Engine Mechanical –
V6.
• Check for the correct calibration of the speedometer. Refer to 8A Electrical-Body.
• Use Tech 2 to monitor the knock sensor system for excessive spark retard
activity. Check for items that cause spark retard activity.
• Using Tech 2, check the heated oxygen sensor (HO2s) operating parameters.
The HO2s should respond quickly to different throttle positions.
Fuel System • Check the fuel system for the following fault conditions. Refer to 6C Fuel System
– V6.
− restricted fuel filter,
− incorrect fuel pressure, and
− contaminated fuel.
• Check the operation of the fuel injectors. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management –
V6 – Service Operations.
• Perform the fuel injector balance test, refer to 6.3 Fuel Injector Balance
Test in this Section.
• Check the items that cause an engine to run rich.
• Check for foreign material accumulation in the throttle bore, carbon build-up on
the throttle valve or on the throttle shaft.
• Check the throttle body for tampering.
Ignition System
• Inspect for moisture or corrosion around the spark plug / ignition coil area.
• Test the ignition coil voltage output. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
• Remove and inspect the spark plugs. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
NOTE
If the spark plugs are fouled, determine the cause of the fouling before
replacing the spark plugs. Refer to 6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 –
Service Operations.
• Check for loose ignition coil ground circuit.
Engine Cooling System
• Check the engine thermostat for proper operation and correct heat range. Refer to
6B1 Engine Cooling – V6.
Engine Mechanical Check for the following engine fault conditions. Refer to 6A1 Engine Mechanical – V6.
• low compression, and
• worn valve train components.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007