2007 ISUZU KB P190 light
[x] Cancel search: lightPage 2416 of 6020
6E–246 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
10 Monitor “B1S1 (Bank 1 Sensor 1) Status ” on the Tech
2.
Is the “ B1S1 (Bank 1 Sensor 1) Status ” in the rich
condition? — Go to Step 11Go to Step 12
11 Check items that can cause the engine to run rich. Refer to DTC P1167 “Fuel Supply System Rich During
Deceleration Fuel Cut Off”.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 12
12 Check items that can cause the engine to run lean. Refer to DTC P1171 “Fuel Supply System Lean
During Power Enrichment”.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 13
13 Check for proper ignition voltage output with the spark tester.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 14
14 Check for a loose ignition control module ground. Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 15
15 Visually/physically inspect all spark plug high-tension cables. Check for the following conditions:
• Verify that the resistance of all spark plug high- tension cables are less than the specified value.
• Verify that the all spark plug high-tension cables are correctly fitted to eliminate cross-fitting.
• Verify that the all spark plug high-tension cables are not arcing to ground.
Spraying the spark plug high-tension cables with a
light mist of water may help locate an intermittent
problem.
Was a problem found? #1 cyl. 4.4k
Ω
#2 cyl. 3.6k Ω
#3 cyl. 3.1k Ω
#4 cyl. 2.8k ΩVerify repair Go to Step 16
16 1. Check the ignition coil secondary resistance. 2. Replace the coil if it is greater than the specifiedresistance.
Did the coil require replacement? 2.5kΩ Verify repair Go to Step 17
17 1. Remove the spark plugs and check for gas or oil fouling cracks, wear, improper gap, burned
electrodes, heavy deposits, or improper heat
range.
2. If spark plugs are fouled, the cause of fouling must be determined before replacing the spark plugs.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 18
18 Check the ECM grounds to verify that they are clean and tight. Refer to the ECM wiring diagrams.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 19
19 Visually/physically check the vacuum hose for splits, kinks and proper connections and routing.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 20
Step
Action Value(s) Yes No
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2418 of 6020
6E–248 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
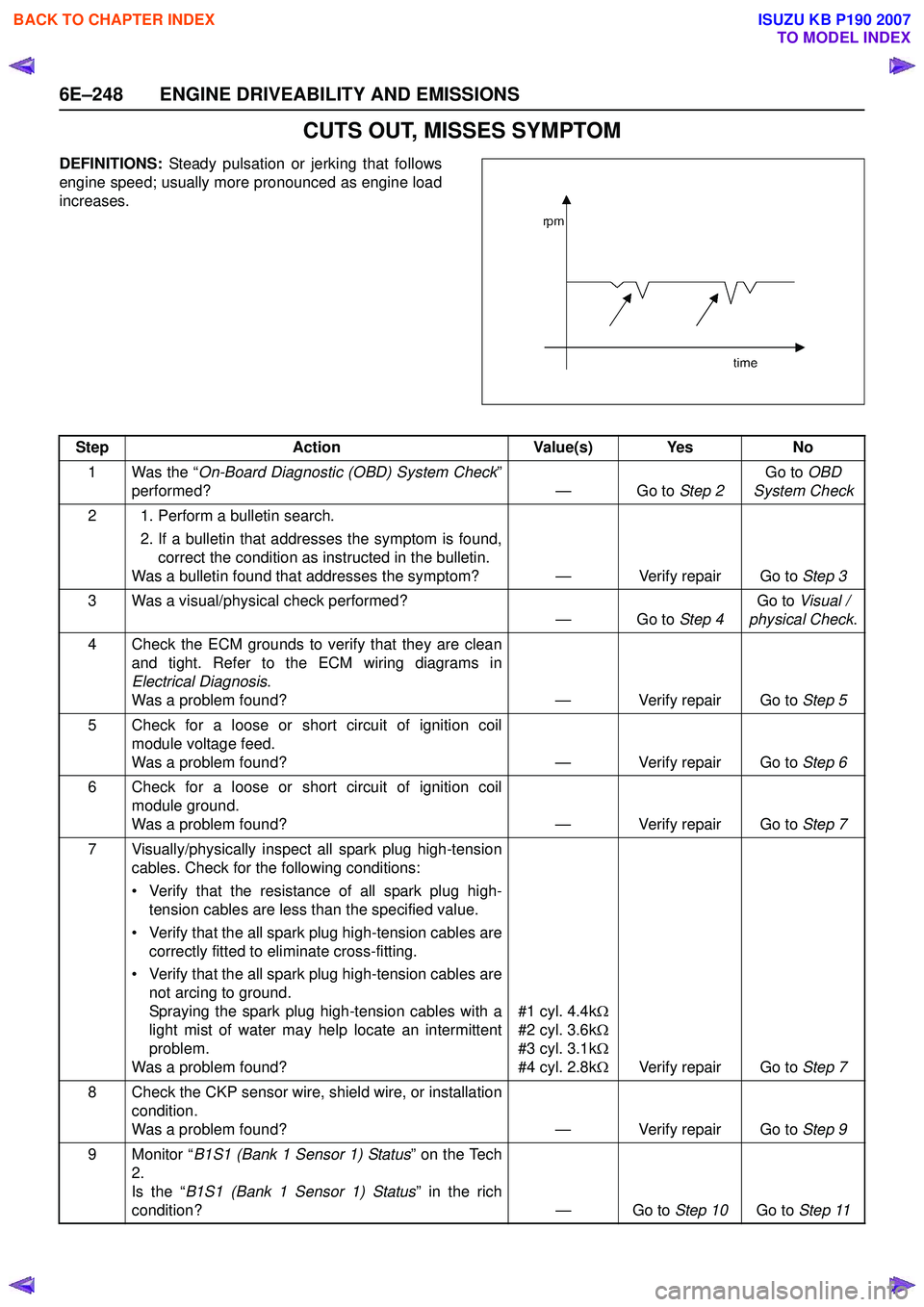
CUTS OUT, MISSES SYMPTOM
DEFINITIONS: Steady pulsation or jerking that follows
engine speed; usually more pronounced as engine load
increases.
Step Action Value(s) Yes No
1 Was the “ On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check ”
performed? — Go to Step 2Go to
OBD
System Check
2 1. Perform a bulletin search. 2. If a bulletin that addresses the symptom is found,correct the condition as instructed in the bulletin.
Was a bulletin found that addresses the symptom? — Verify repair Go to Step 3
3 Was a visual/physical check performed? —Go to Step 4Go to
Visual /
physical Check .
4 Check the ECM grounds to verify that they are clean and tight. Refer to the ECM wiring diagrams in
Electrical Diagnosis .
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 5
5 Check for a loose or short circuit of ignition coil module voltage feed.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 6
6 Check for a loose or short circuit of ignition coil module ground.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 7
7 Visually/physically inspect all spark plug high-tension cables. Check for the following conditions:
• Verify that the resistance of all spark plug high- tension cables are less than the specified value.
• Verify that the all spark plug high-tension cables are correctly fitted to eliminate cross-fitting.
• Verify that the all spark plug high-tension cables are not arcing to ground.
Spraying the spark plug high-tension cables with a
light mist of water may help locate an intermittent
problem.
Was a problem found? #1 cyl. 4.4k
Ω
#2 cyl. 3.6k Ω
#3 cyl. 3.1k Ω
#4 cyl. 2.8k ΩVerify repair Go to Step 7
8 Check the CKP sensor wire, shield wire, or installation condition.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 9
9 Monitor “ B1S1 (Bank 1 Sensor 1) Status ” on the Tech
2.
Is the “ B1S1 (Bank 1 Sensor 1) Status ” in the rich
condition? — Go to Step 10Go to Step 11
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2432 of 6020
6E–262 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
BACKFIRE SYMPTOM
DEFINITIONS: Fuel ignites in the intake manifold, or in the exhaust system, making a loud popping noise.
Step Action Value(s) Yes No
1 Was the “ On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System Check ”
performed? — Go to Step 2Go to
OBD
System Check
2 1. Perform a bulletin search. 2. If a bulletin that addresses the symptom is found,correct the condition as instructed in the bulletin.
Was a bulletin found that addresses the symptom? — Verify repair Go to Step 3
3 Was a visual/physical check performed? —Go to Step 4Go to
Visual /
physical Check .
4 Check for proper ignition voltage output with the spark tester.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 5
5 1. Remove the spark plugs and check for gas or oil fouling cracks, wear, improper gap, burned
electrodes, heavy deposits, or improper heat
range.
2. If spark plugs are fouled, the cause of fouling must be determined before replacing the spark plugs.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 6
6 Visually/physically inspect all spark plug high-tension cables. Check for the following conditions:
• Verify that the resistance of all spark plug high- tension cables are less than the specified value.
• Verify that the all spark plug high-tension cables are correctly fitted to eliminate cross-fitting.
• Verify that the all spark plug high-tension cables are not arcing to ground.
Spraying the spark plug high-tension cables with a
light mist of water may help locate an intermittent
problem.
Was a problem found? #1 cyl. 4.4k
Ω
#2 cyl. 3.6k Ω
#3 cyl. 3.1k Ω
#4 cyl. 2.8k ΩVerify repair Go to Step 7
7 Check the fuel pressure. Refer to 6E-108 page “Fuel
System Diagnosis” .
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 8
8 Check for an intermittent ignition system malfunction: • Intermittent CKP 58X signal
• Intermittent ignition feed circuit or sensor ground circuit to the crankshaft position sensor.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 9
9 Refer to 6E-108 page “Fuel System Diagnosis ” to
determine if there is a problem with fuel delivery.
Was a problem found? — Verify repair Go to Step 10
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2481 of 6020

Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–2
Visual / Physical Inspection ................................................................................................................................ 28
Intermittent ........................................................................................................................................................... 28
2.3 Engine Misfire without Internal Engine Noises .................................................................................. ............... 29
2.4 Engine Misfire with Abnormal Internal Lower Engine Noises...................................................................... .... 30
2.5 Engine Misfire with Abnormal Valve Train Noise .............................................................................................. 31
2.6 Engine Misfire with Coolant Consumption ........................................................................................................ 31
2.7 Engine Misfire with Excessive Oil Consumption .................................................................................. ............ 31
2.8 Engine Noise on Start-up, but only Lasting a Few Seconds ....................................................................... ..... 31
2.9 Upper Engine Noise, Regardless of Engine Speed........................................................................................... 33
2.10 Lower Engine Noise, Regardless of Engine Speed ................................................................................. ......... 34
2.11 Engine Noise Under Load ................................................................................................................................... 35
2.12 Engine Will Not Crank – Crankshaft Will Not Rotate ............................................................................. ........... 35
2.13 Coolant in Combustion Chamber ....................................................................................................................... 37
Definition .............................................................................................................................................................. 37
2.14 Coolant in Engine Oil.......................................................................................................... ................................. 37
Definition .............................................................................................................................................................. 37
2.15 Engine Compression Test ........................................................................................................ ........................... 38
Preliminary Steps................................................................................................................................................. 38
Engine Cylinder Compression Test ............................................................................................... .................... 38
Test Result Evaluation......................................................................................................................................... 38
2.16 Cylinder Leakage Test .......................................................................................................... ............................... 39
2.17 Engine Oil Consumption Diagnosis ............................................................................................... .................... 39
Definition .............................................................................................................................................................. 39
2.18 Engine Oil Leak Diagnosis ...................................................................................................... ............................ 40
Introduction .......................................................................................................................................................... 40
Locating and Identifying the Leak .............................................................................................. ........................ 40
Visual Inspection ................................................................................................................................................. 40
Powder Method .................................................................................................................. .................................. 40
Black Light and Dye Method ..................................................................................................... .......................... 40
Possible Causes for Engine Oil Leaks ........................................................................................... .................... 41
2.19 Engine Oil Pressure Diagnosis ........................................................................................................................... 42
2.20 Accessory Drive Belt Diagnosis ................................................................................................. ........................ 42
Tension Check ..................................................................................................................................................... 42
Inspect .................................................................................................................................................................. 42
Drive Belt Chirp .................................................................................................................................................... 43
Definition .......................................................................................................................................................... 43
Diagnostic Aids................................................................................................................................................. 43
Test Description ............................................................................................................... ................................ 43
Diagnostic Table............................................................................................................................................... 44
Drive Belt Squeal .............................................................................................................. ................................... 45
Definition .......................................................................................................................................................... 45
Diagnostic Aids................................................................................................................................................. 45
Test Description ............................................................................................................... ................................ 45
Diagnostic Table............................................................................................................................................... 46
Drive Belt Whine ............................................................................................................... ................................... 46
Definition .......................................................................................................................................................... 46
Diagnostic Aids................................................................................................................................................. 46
Test Description ............................................................................................................... ................................ 46
Diagnostic Table............................................................................................................................................... 47
Drive Belt Rumble .............................................................................................................. .................................. 47
Definition .......................................................................................................................................................... 47
Diagnostic Aids................................................................................................................................................. 48
Test Description ............................................................................................................... ................................ 48
Diagnostic Table............................................................................................................................................... 48
Drive Belt Vibration........................................................................................................... ................................... 49
Definition .......................................................................................................................................................... 49
Diagnostic Aids................................................................................................................................................. 49
Test Description ............................................................................................................... ................................ 49
Diagnostic Table............................................................................................................................................... 50
Drive Belt Falls Off ........................................................................................................... .................................... 50
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2488 of 6020
Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–9
• Faulty operation or performance of any systems or components which depend on the proper operation or
performance of the system or component under repair,
• Damage to fasteners, basic tools or special tools and / or
• Leakage of coolant, lubricant or other vital fluids.
NOTE defined
A NOTE statement immediately precedes or follows an operating procedure, maintenance practice or condition that
requires highlighting. A NOTE statement also emphasises necessary characteristics of a diagnostic or repair procedure.
A NOTE statement is designed to:
• Clarify a procedure,
• Present additional information for accomplishing a procedure,
• Give insight into the reasons for performing a procedure in the recommended manner, and / or
Present information that gives the technician the benefit of past experience in accomplishing a procedure with greater
ease.
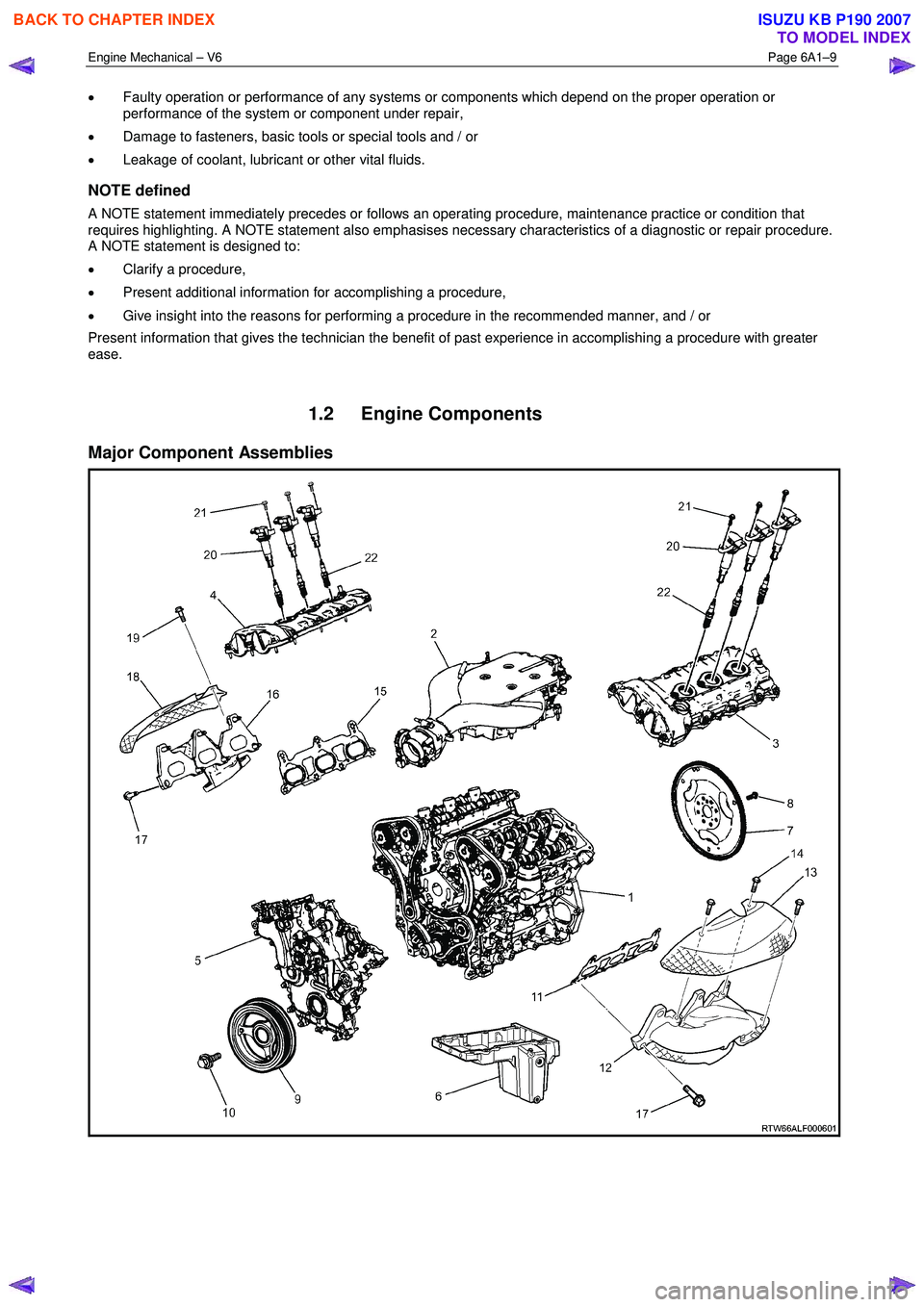
1.2 Engine Components
Major Component Assemblies
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2506 of 6020
Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–27
• A clean, well-lit, work area.
• A suitable parts cleaning tank.
• A compressed air supply.
• Trays or storage containers to keep parts and fasteners organised.
• An adequate set of hand tools.
• Approved engine repair stand.
• An approved engine lifting device that will adequately support the weight of the components.
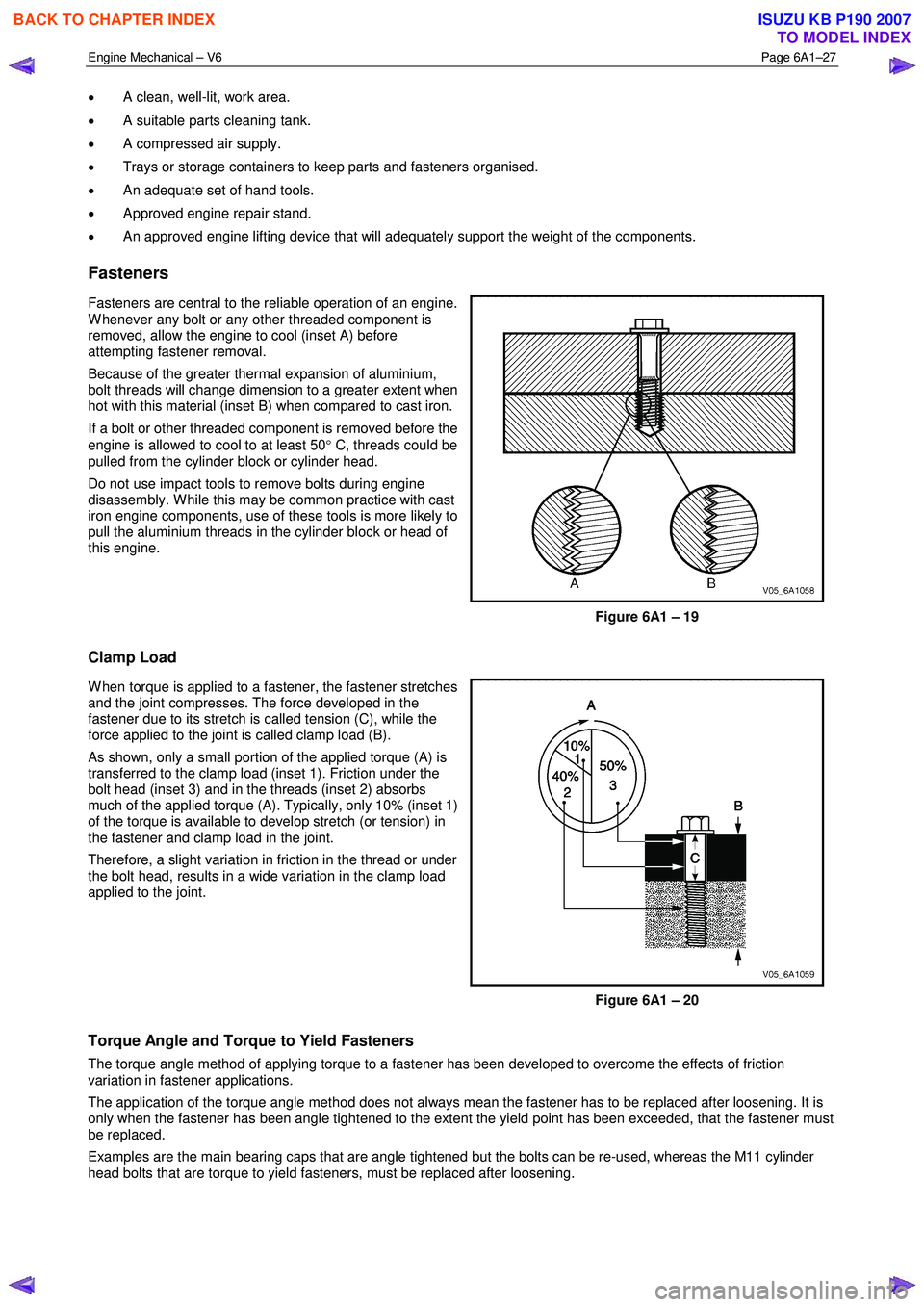
Fasteners
Fasteners are central to the reliable operation of an engine.
W henever any bolt or any other threaded component is
removed, allow the engine to cool (inset A) before
attempting fastener removal.
Because of the greater thermal expansion of aluminium,
bolt threads will change dimension to a greater extent when
hot with this material (inset B) when compared to cast iron.
If a bolt or other threaded component is removed before the
engine is allowed to cool to at least 50 ° C, threads could be
pulled from the cylinder block or cylinder head.
Do not use impact tools to remove bolts during engine
disassembly. W hile this may be common practice with cast
iron engine components, use of these tools is more likely to
pull the aluminium threads in the cylinder block or head of
this engine.
Figure 6A1 – 19
Clamp Load
W hen torque is applied to a fastener, the fastener stretches
and the joint compresses. The force developed in the
fastener due to its stretch is called tension (C), while the
force applied to the joint is called clamp load (B).
As shown, only a small portion of the applied torque (A) is
transferred to the clamp load (inset 1). Friction under the
bolt head (inset 3) and in the threads (inset 2) absorbs
much of the applied torque (A). Typically, only 10% (inset 1)
of the torque is available to develop stretch (or tension) in
the fastener and clamp load in the joint.
Therefore, a slight variation in friction in the thread or under
the bolt head, results in a wide variation in the clamp load
applied to the joint.
Figure 6A1 – 20
Torque Angle and Torque to Yield Fasteners
The torque angle method of applying torque to a fastener has been developed to overcome the effects of friction
variation in fastener applications.
The application of the torque angle method does not always mean the fastener has to be replaced after loosening. It is
only when the fastener has been angle tightened to the extent the yield point has been exceeded, that the fastener must
be replaced.
Examples are the main bearing caps that are angle tightened but the bolts can be re-used, whereas the M11 cylinder
head bolts that are torque to yield fasteners, must be replaced after loosening.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2509 of 6020
Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–30
Cause Correction
Faulty cylinder head gasket and/or cracking or other
damage to the cylinder head and cylinder block coolant
passages.
Coolant consumption may or may not cause the engine to
overheat. 1 Inspect the spark plugs for coolant saturation, refer to
6C1-3 Engine Management – V6 – Service
Operations.
2 Inspect the cylinder heads, cylinder block and/or head gaskets, refer to 3.22 Cylinder Head Assembly and/or
4.7 Cylinder Block.
3 Repair or replace components as required.
W orn piston rings.
Oil consumption may or may not cause the engine to
misfire. 1 Inspect the spark plugs for oil deposits, refer to 6C1-3
Engine Management – V6 – Service Operations.
2 Check the cylinders for a loss of compression, refer to 2.15 Engine Compression Test.
3 Perform compression testing to identify the cause of low compression.
4 Repair or replace components as required.
A damaged crankshaft reluctor wheel.
A damaged crankshaft reluctor wheel can result in different
symptoms depending on the severity and location of the
damage.
Systems with severe reluctor ring damage may exhibit
periodic loss of crankshaft position, stop delivering a signal,
and then re-sync the crankshaft position.
Systems with slight reluctor ring damage may exhibit no
loss of crankshaft position and no misfire may occur,
however, a DTC may set. Replace the crankshaft as required, refer to 4.6
Crankshaft and Main Bearings.
Refer to 6C1-2 Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics to
check for DTCs
2.4 Engine Misfire with Abnormal Internal Lower Engine Noises
Cause Correction
Abnormalities, severe cracking, bumps or missing areas in
the accessory drive belt.
Abnormalities in the accessory drive system and/or
components may cause engine speed variations that result
in a misfire diagnostic trouble code (DTC). A misfire code
may be present without an actual misfire condition. Replace the accessory drive belt, refer to 3.5
Accessory
Drive Belt.
Refer to 6C1-2 Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics to
check for DTCs
W orn, damaged or misaligned accessory drive components
and excessive pulley run-out may lead to a misfire DTC.
A misfire code may be present without an actual misfire
condition. Inspect the components and repair or replace as required.
Refer to 6C1-2 Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics to
check for DTCs
Loose or Incorrectly fitted flexplate or crankshaft balancer
assembly.
A misfire code may be present without an actual misfire
condition. Repair or replace the flexplate or crankshaft balancer as
required, refer to 3.13 Crankshaft Balancer Assembly
or 4.3 Flexplate Assembly.
W orn or broken piston rings.
Oil consumption may or may not cause an actual misfire. 1 Inspect the spark plugs for oil deposits, refer to 6C1-3
Engine Management – V6 – Service Operations.
2 Check the cylinders for a loss of compression, refer to 2.15 Engine Compression Test.
3 Perform compression testing to identify the cause of low compression.
4 Repair or replace components as required.
W orn crankshaft thrust bearing.
Severely worn thrust surfaces on the crankshaft and/or
thrust bearing may permit fore and aft movement of the
crankshaft and create a DTC without an actual misfire
condition being present. Replace the crankshaft and/or bearings as required, refer to
4.6 Crankshaft and Main Bearings.
Refer to 6C1-2 Engine Management – V6 – Diagnostics to
check for DTCs
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007
Page 2511 of 6020
Engine Mechanical – V6 Page 6A1–32
secondary ignition circuit is grounded out during
diagnosis.
A light rattle/tapping noise may indicate a valve train/upper engine concern, while a low rumble/knocking may indicate a
crankshaft, piston or lower engine concern.
Cause Correction
Oil filter anti-drain back valve faulty. Replace the oil filter adaptor, refer to 3.3 Oil Filter
Adaptor.
Incorrect oil viscosity. Drain the engine oil and replace with the correct viscosity
oil, refer to 3.1 Engine Oil.
High camshaft stationary hydraulic lash adjuster (SHLA)
leak down rate. Replace the SHLA as required, refer to 3.21 Stationary
Hydraulic Lash Adjuster.
W orn crankshaft thrust bearing. Inspect and replace the crankshaft and/or bearings as
required, refer to 4.6 Crankshaft and Main Bearings.
Damaged or faulty oil filter by-pass valve. 1 Inspect the oil filter by-pass valve for correct
operation.
2 Repair or replace the oil filter adaptor/by-pass valve as required.
BACK TO CHAPTER INDEX
TO MODEL INDEX
ISUZU KB P190 2007