2006 MERCEDES-BENZ SPRINTER lock
[x] Cancel search: lockPage 1574 of 2305

A relay cannot be repaired or adjusted and, if
faulty or damaged, it must be replaced.
OPERATION
The ISO relay consists of an electromagnetic coil, a
resistor and three (two fixed and one movable) elec-
trical contacts. The movable (common feed) relay con-
tact is held against one of the fixed contacts
(normally closed) by spring pressure. When the elec-
tromagnetic coil is energized, it draws the movable
contact away from the normally closed fixed contact,
and holds it against the other (normally open) fixed
contact.
When the electromagnetic coil is de-energized,
spring pressure returns the movable contact to the
normally closed position. The resistor is connected in
parallel with the electromagnetic coil in the relay,
and helps to dissipate voltage spikes that are pro-
duced when the coil is de-energized.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - RELAY
(1) Remove the relay from its mounting location.
(2) A relay in the de-energized position should
have continuity between terminals 87A and 30, and
no continuity between terminals 87 and 30. If OK, go
to Step 3. If not OK, replace the faulty relay.
(3) Resistance between terminals 85 and 86 (elec-
tromagnet) should be 60.7 - 80.3 ohms. If OK, go to
Step 4. If not OK, replace the faulty relay.
(4) Connect a battery to terminals 85 and 86.
There should now be continuity between terminals
30 and 87, and no continuity between terminals 87A
and 30. If OK, perform the Relay Circuit Test that
follows. If not OK, replace the faulty relay.
DIAGNOSIS AND TESTING - RELAY CIRCUIT TEST
(1) The relay common feed terminal cavity (30) of
the fuse block is connected to battery voltage and
should be hot at all times. Check for battery voltage
at the fused B(+) circuit cavity in the fuse block
receptacle for the relay. If OK, go to Step 2. If not
OK, repair the fused B(+) circuit to the fuse block
fuse as required.
(2) The relay normally closed terminal (87A) is
connected to terminal 30 in the de-energized position,
but is not used for this application. Go to Step 3.
(3) The relay normally open terminal (87) is con-
nected to the common feed terminal (30) in the ener-
gized position. This terminal supplies battery voltage
to the fused B(+) fuse in the fuse block that feeds the
accessory when the relay is energized by the ignition
switch. There should be continuity between the fuse
block cavity for relay terminal 87 and the fused B(+)
fuse in the fuse block at all times. If OK, go to Step
4. If not OK, repair the open fused B(+) circuit to the
fuse block fuse as required.(4) The coil ground terminal (85) is connected to
the electromagnet in the relay. It receives battery
feed to energize the relay when the ignition switch is
in the Accessory or Run positions. Turn the ignition
switch to the On position. Check for battery voltage
at the fused ignition switch output (acc/run) circuit
cavity for relay terminal 85 in the fuse block recep-
tacle for the relay. If OK, go to Step 5. If not OK,
repair the open fused ignition switch output (acc/run)
circuit to the ignition switch as required.
(5) The coil battery terminal (86) is connected to
the electromagnet in the relay. The fuse block cavity
for this terminal should have continuity to ground at
all times. If not OK, repair the open ground circuit to
ground as required.
REMOVAL
(1) Disconnect and isolate the negative battery
cable.
(2) Remove the relay by grasping it firmly and
pulling it straight out from its receptacle. A slight
back and fourth rocking motion may help the
removal process.
INSTALLATION
(1) Position the relay to the proper receptacle.
(2) Align the relay terminals with the terminal
cavities in the receptacle.
(3) Push firmly and evenly on the top of the relay
until the terminals are fully seated in the terminal
cavities in the receptacle.
(4) Connect the negative battery cable.
VA8W-97 POWER DISTRIBUTION 8W - 97 - 5
Page 1576 of 2305

ENGINE
TABLE OF CONTENTS
page page
ENGINE
DESCRIPTION..........................2
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - COMPRESSION
TESTING ENGINE......................3
STANDARD PROCEDURE - CYLINDER
LEAK DOWN TEST.....................3
STANDARD PROCEDURE - DETERMINING
CYLINDER PRESSURE LOSS.............4
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - ENGINE COVER.............4
REMOVAL............................5
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - ENGINE COVER..........9
INSTALLATION........................9
SPECIFICATIONS - TORQUE
SPECIFICATIONS.....................11
SPECIAL TOOLS.......................17
AIR CLEANER ELEMENT
REMOVAL.............................21
INSTALLATION.........................21
AIR CLEANER HOUSING
REMOVAL.............................21
INSTALLATION.........................22
CYLINDER HEAD
DESCRIPTION.........................22
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - CYLINDER
HEAD BOLT INSPECTION...............22
STANDARD PROCEDURE - MEASURE
CYLINDER HEAD SURFACE.............22
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - CYLINDER HEAD............23
REMOVAL - CYLINDER HEAD FRONT
COVER.............................25
REMOVAL - CYLINDER HEAD GUIDE RAIL . . 26
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - CYLINDER HEAD........26
INSTALLATION - CYLINDER HEAD FRONT
COVER.............................28
INSTALLATION - CYLINDER HEAD GUIDE
RAIL...............................28
CAMSHAFT(S)
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - CHECKING
CAMSHAFT POSITION.................28
STANDARD PROCEDURE - INSPECTING
TAPPET CLEARANCE..................30
REMOVAL.............................30
INSTALLATION.........................32CYLINDER HEAD COVER(S)
REMOVAL.............................33
INSTALLATION.........................34
VALVE STEM SEALS
DESCRIPTION.........................34
VALVE SPRINGS
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - VALVE SPRINGS............35
REMOVAL - VALVES...................36
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - VALVE SPRINGS........36
INSTALLATION - VALVES...............37
ENGINE BLOCK
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - REPLACING
ENGINE CORE AND OIL GALLERY PLUGS . . 37
STANDARD PROCEDURE - MEASURING
CYLINDER BORES....................38
CRANKSHAFT
DESCRIPTION.........................39
STANDARD PROCEDURE - MEASURE
CRANKSHAFT AND BLOCK JOURNALS....39
REMOVAL.............................40
INSTALLATION.........................40
CRANKSHAFT OIL SEAL - REAR
REMOVAL.............................41
INSTALLATION.........................42
CRANKSHAFT OIL SEAL - FRONT
REMOVAL.............................42
INSTALLATION.........................43
FLYWHEEL
REMOVAL.............................43
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION.......................44
INSTALLATION - CRANKSHAFT LOCK.....44
PISTON & CONNECTING ROD
DESCRIPTION.........................45
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - CHECKING AND
REPAIRING CONNECTING RODS.........46
STANDARD PROCEDURE - MEASURING
PISTON PROTRUSION.................47
REMOVAL.............................47
INSTALLATION.........................49
PISTON RINGS
STANDARD PROCEDURE - PISTON RING
FITTING.............................52
VIBRATION DAMPER
REMOVAL.............................53
INSTALLATION.........................54
VAENGINE 9 - 1
Page 1577 of 2305

VACUUM PUMP
DESCRIPTION.........................54
OPERATION...........................54
REMOVAL.............................55
INSTALLATION.........................55
LEFT MOUNT
REMOVAL.............................55
INSTALLATION.........................55
RIGHT MOUNT
REMOVAL.............................56
INSTALLATION.........................56
OIL
REMOVAL - OIL SEPARATOR..............56
INSTALLATION - OIL SEPARATOR..........56
OIL COOLER & LINES
REMOVAL.............................56
INSTALLATION.........................57
OIL FILTER
REMOVAL.............................57
INSTALLATION.........................57
OIL JET
DESCRIPTION.........................57
REMOVAL.............................58
INSTALLATION.........................58
OIL PAN
REMOVAL.............................58
INSTALLATION.........................60
OIL PUMP
REMOVAL
REMOVAL...........................61
REMOVAL- OIL PUMP CHAIN............61
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION.......................62INSTALLATION - OIL PUMP CHAIN........62
OIL SENSOR
DESCRIPTION.........................64
OPERATION...........................64
REMOVAL.............................65
INSTALLATION.........................65
INTAKE MANIFOLD
REMOVAL.............................65
INSTALLATION.........................68
EXHAUST MANIFOLD
REMOVAL.............................68
INSTALLATION.........................69
TIMING CHAIN COVER
REMOVAL.............................70
INSTALLATION.........................71
TIMING CHAIN AND SPROCKETS
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - TENSIONING AND SLIDE RAILS . 72
REMOVAL - INTERMEDIATE GEAR........73
REMOVAL - TIMING CHAIN TENSIONING
RAIL...............................74
REMOVAL - TIMING CHAIN..............74
INSTALLATION
INSTALLATION - TENSIONING AND SLIDE
RAIL...............................76
INSTALLATION - INTERMEDIATE GEAR....77
INSTALLATION - TIMING CHAIN
TENSIONING RAIL....................77
ADJUSTMENTS
INSTALLATION - TIMING CHAIN..........77
TIMING CHAIN TENSIONER
REMOVAL.............................81
INSTALLATION.........................81
ENGINE
DESCRIPTION
This 2.7 Liter five-cylinder Common Rail Diesel
Injection (CDI) engine is an in-line overhead valve
diesel engine. This engine utilizes a cast iron cylin-
der block and an aluminum cylinder head. The
engine is turbocharged and intercooled. This engine
also has for valve per cylinder and dual overhead
camshafts (Fig. 1).
Fig. 1 2.7L CDI ENGINE
9 - 2 ENGINEVA
Page 1578 of 2305

DESCRIPTION SPECIFICATION
Engine 2.7L CDI
Engine Description 5 Cylinder In-Line En-
gine With 4-Valve Tech-
nology
Air Intake Turbo-Charged Engine
with Charge Air Cooling
Fuel Injection System 2 nd. Generation Com-
mon Rail Direct Injection
(CDI)
Fuel Diesel
Firing Order 1-2-4-5-3
Rated Output 154 HP at 3800 RPM
Torque 243 ft. lbs. at 1600-2400
RPM
Maximum Speed 4800 RPM
Compression Ratio 18:1
Bore/Stroke 3.46/3.48
Eff. Displacement 2688 cm3
STANDARD PROCEDURE
STANDARD PROCEDURE - COMPRESSION
TESTING ENGINE
(1) Warm up engine to operating temperature
(approx. 80 ÉC, 176ÉF).
(2) Shut off engine.
(3) Remove engine cover (Refer to 9 - ENGINE -
REMOVAL).
(4) Remove glow plugs (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
IGNITION CONTROL/GLOW PLUG - REMOVAL).
(5) Crank engine several times with the starter to
eliminate combustion residues in the cylinders.
(6) Insert compression tester adapter #8927 (Refer
to 9 - ENGINE - SPECIAL TOOLS) with check valve
installed into glow plug hole of cylinder to be tested.
(7) Connect compression tester hose adapter #9295
to compression gauge and test compression pressure
by cranking engine with starter for at least 8 revolu-
tions.
(8) Carry out test procedure at the remaining cyl-
inders in the same way.
(9) Compare pressure readings obtained with the
specified pressures. If the pressure reading is below
the minimum compression pressure or if the permis-
sible difference between the individual cylinders is
exceeded. Refer to cylinder leak down test.
(10) Remove compression tester and adapter from
cylinder head.
(11) Install glow plugs (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
IGNITION CONTROL/GLOW PLUG - INSTALLA-
TION).(12) Install engine cover (Refer to 9 - ENGINE -
INSTALLATION).
COMPRESSION SPECIFICATIONS
Maximum Compression 29-35 bar (420-507 psi)
Minimum Compression 18bar (261 psi)
Permissible Difference
Between Cylinders 3bar ( 44 psi)
STANDARD PROCEDURE - CYLINDER LEAK
DOWN TEST
(1) Warm engine to operating temperature.
WARNING: DO NOT OPEN COOLING SYSTEM
UNLESS COOLANT TEMPERATURE IS BELOW 90C
(194ÉF). RISK OF INJURY TO SKIN AND EYES AS A
RESULT OF SCALDING WITH HOT COOLANT
WHICH SPLASHES OUT. RISK OF POISONING
FROM SWALLOWING COOLANT. OPEN CAP
SLOWLY AND RELEASE PRESSURE. STORE COOL-
ANT IN PROPER CONTAINERS ONLY. WEAR PRO-
TECTIVE GLOVES, CLOTHING AND EYE
PROTECTION.
NOTE: Turn cap carefully as far as first detent,
release pressure, then unscrew cap.
(2) Open cooling system cap at coolant recover
pressure container.
(3) Remove engine cover (Refer to 9 - ENGINE -
REMOVAL).
(4) Unscrew oil filler cap.
(5) Remove glow plugs (Refer to 8 - ELECTRICAL/
IGNITION CONTROL/GLOW PLUG - REMOVAL).
NOTE: Crank engine at crankshaft in direction of
rotation of the engine (clockwise).
(6) Position cylinder to be tested to ignition Top
Dead Center (DTC).
NOTE: Calibrate cylinder leak down tester and
remove check valve in screw-in fitting.
(7) Connect cylinder leak down tester and follow
INSPECTING Instruction.
INSPECTING
NOTE: If crankshaft rotates, install retaining lock for
crankshaft/ring gear.
(1) Pressurize cylinder with compressed air and
read off pressure loss at cylinder leak tester. If exces-
sive pressure loss exists, determine possible cause
(Refer to 9 - ENGINE - STANDARD PROCEDURE).
VAENGINE 9 - 3
Page 1579 of 2305

NOTE: If the retaining lock is installed, remove it,
rotate engine and install lock once again.
(2) Carry out test of other cylinders in the firing
order of engine.
CYLINDER LEAK DOWN VALUES
CYLINDER LEAK
DOWN PERMISSIBLE
TOTAL LOSS 25%
CYLINDER LEAK
DOWN PERMISSIBLE
LOSS AT VALVES AND
CYLINDER HEAD 10%
CYLINDER LEAK
DOWN PERMISSIBLE
LOSS AT PISTON AND
RINGS 20%
STANDARD PROCEDURE - DETERMINING CYL-
INDER PRESSURE LOSS
If an increased pressure loss was found with the
cylinder leak test, inspect the engine by listening at
the cylinder head gasket, air intake area, exhaust, oil
fill opening and where injectors and glow plugs enter
the cylinder head. Also check the engine coolant in
the radiator or expansion reservoir for the formation
of bubbles.
Possible causes for the pressure loss are:
POSSIBLE CAUSE FOR PRESSURE LOSS
CONDITION POSSIBLE
CAUSESCORRECTION
AIR LOSS
THROUGH
GLOW PLUG,
INJECTOR, AD-
JACENT CYL-
INDERS, OR
AIR BUBBLES
IN COOLANT1. Sealing Sur-
facesRepair Sealing
Surfaces
2. Gaskets 2. Replace
Component or
Gasket
3. Cylinder
Head Gasket3. Replace Cyl-
inder Head
Gasket
AIR LOSS
THROUGH AIR
INTAKE AREA1. Sealing Sur-
faces1. Remove Cyl-
inder Head for
Further Inspec-
tion
CONDITION POSSIBLE
CAUSESCORRECTION
2. Intake
Valves and
Seats2. Replace
Valves, Guides
or Seats
AIR LOSS
THROUGH EX-
HAUSTSealing Surfac-
esRemove Cylin-
der Head for
Further Inspec-
tion
2. Exhaust
Valves and
Seats2. Replace
Valves, Guides
or Seats
AIR LOSS
THROUGH OIL
FILL OPENING1. Sealing Sur-
facesRemove Engine
for Further In-
spection
2. Pistons, Pis-
ton Rings2. Replace Pis-
tons or Piston
Rings
It is possible to pin point the pressure loss of the
relevant cylinder by spraying with clean engine oil.
Engine oil seals off the gap between the piston and
cylinder wall briefly. If a reduced pressure loss now
occurs for a short time, the cause is very likely to be
the pistons, piston rings or cylinder contact surfaces
of the relevant cylinder.
Determining the cause can be falsified by the posi-
tion of the piston ring joints. If suspicion exists that
the loss of pressure is caused by the piston ring
joints being positioned directly one above the other,
fit the parts to the engine and repeat this test after
running the engine for a short time.
REMOVAL
REMOVAL - ENGINE COVER
(1) Remove the retaining screws and remove cover
(Fig. 2).
9 - 4 ENGINEVA
Page 1583 of 2305

(30) Disconnect the engine valley drain hose fas-
tener from the transmission (Fig. 5).
(31) Remove the steering gear mounting bolts.
(32) Disconnect the transmission cooler lines at
transmission and oil pan.
(33) Remove the torque converter access plate.
(34) Remove the torque converter bolts.
(35) Remove the crank position sensor.
(36) Remove the transmission housing to engine
mounting bolts.
(37) Remove the starter mounting bolts (Fig. 5).
(38) Support the transmission with a transmission
jack.
(39) Place a wood block between the transmission
housing and the front frame cross over.
(40) Remove the transmission jack.
(41) Remove the exhaust bracket (right side).
(42) Remove the engine ground strap (left side).
(43) Lower the vehicle.
(44) Remove the heater housing filter and lower
housing.(45) Connect the engine lifting fixture #9308 to the
engine lifting eyes.
(46) Remove the engine mount bolts.
(47) Remove the transmission oil level indicator
tube mounting bolt.
Fig. 5 2.7L CDI ENGINE
1 - INTAKE MANIFOLD 5 - FUEL FILTER
2 - ENGINE VALLEY DRAIN HOSE 6 - AIR CONDITIONING COMPRESSOR
3 - STARTER 7 - POWER STEERING PUMP
4 - ENGINE OIL LEVEL SENSOR 8 - EGR VALVE
9 - 8 ENGINEVA
Page 1585 of 2305

(11) Install the torque converter access plate. Refer
to (Refer to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANSAXLE/AU-
TOMATIC - NAG1 - INSTALLATION) for correct
sequence and torque specification.
(12) Install the transmission cooler lines to trans-
mission. (Refer to 21 - TRANSMISSION/TRANS-
AXLE/AUTOMATIC - NAG1 - INSTALLATION) for
correct sequence and torque specification.
(13) Connect the engine valley drain hose to the
transmission (Fig. 5).
(14) Install transmission electrical connector and
shifter hardware. Refer to (Refer to 21 - TRANSMIS-
SION/TRANSAXLE/AUTOMATIC - NAG1 - INSTAL-
LATION) for correct sequence and torque
specification.
(15) Install the steering gear and tighten in two
stages. 25 N´m (18.5 lbs. ft.), then 45 N´m (33 lbs. ft.)
plus 90É.
(16) Install the starter.
(17) Connect the ground strap (left side).
(18) Align and install the exhaust and bracket
(Refer to 11 - EXHAUST SYSTEM/EXHAUST PIPE -
INSTALLATION).
(19) Lower the vehicle.
(20) Install the lower heater housing and filter.
(21) Install the air inlet hose, CCV breather and
CCV heater at the turbocharger (Fig. 4).
(22) Connect the coolant supply and return hoses.
(23) Connect the brake booster vacuum hose at the
vacuum pump.(24) Connect the fuel lines at the filter assembly
(Fig. 9).
(25) Connect the power steering hoses.
(26) Install the radiator/charge air cooler and
hose(s) assemblies (Refer to 7 - COOLING/ENGINE/
RADIATOR - INSTALLATION).
(27) Install A/C condenser and fan assemblies Con-
nect the fan harness connector.
(28) Connect the refrigerant lines.
(29) Install a air conditioning receiver/drier (Refer
to 24 - HEATING & AIR CONDITIONING/PLUMB-
ING/RECEIVER / DRIER - INSTALLATION).
(30) Connect the upper and lower radiator hoses.
(31) Connect the transmission lines at the radia-
tor.
(32) Install air cleaner housing and connect the air
inlet duct and air flow sensor.
(33) Connect the charge air cooler hose at intake
manifold. (Refer to 9 - ENGINE/AIR INTAKE SYS-
TEM/AIR CLEANER HOUSING - INSTALLATION).
(34) Route the engine wiring harness inside the
vehicle and connect.
(35) Install the turbocharger heat shield.
(36) Install the front grille and fascia assembly.
(37) Connect the negative battery cable.
(38) Check and fill engine oil (Refer to LUBRICA-
TION & MAINTENANCE/FLUID TYPES - SPECIFI-
CATIONS).
Fig. 8 CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
1 - ENGINE BLOCK
2 - WIRING HARNESS CONNECTOR
3 - CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR
4 - STARTER SOLENOID
Fig. 9 FUEL FILTER
1 - FUEL SUPPLY FROM TANK
2 - FUEL SUPPLY TO HIGH PRESSURE PUMP
3 - POWER STEERING RESERVOIR
4 - FUEL FILTER
5 - OIL FILTER
6 - WATER IN FUEL SENSOR
9 - 10 ENGINEVA
Page 1588 of 2305
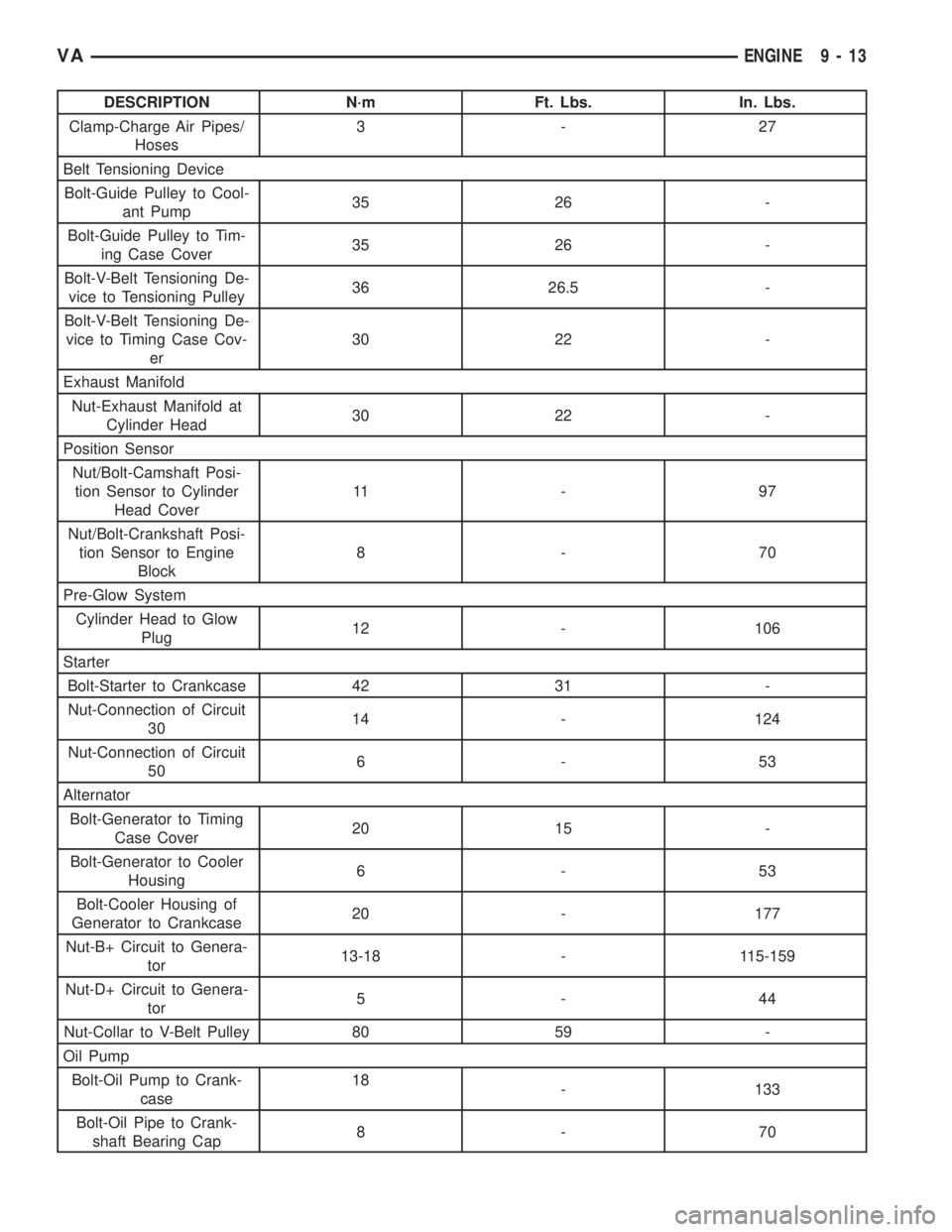
DESCRIPTION N´m Ft. Lbs. In. Lbs.
Clamp-Charge Air Pipes/
Hoses3-27
Belt Tensioning Device
Bolt-Guide Pulley to Cool-
ant Pump35 26 -
Bolt-Guide Pulley to Tim-
ing Case Cover35 26 -
Bolt-V-Belt Tensioning De-
vice to Tensioning Pulley36 26.5 -
Bolt-V-Belt Tensioning De-
vice to Timing Case Cov-
er30 22 -
Exhaust Manifold
Nut-Exhaust Manifold at
Cylinder Head30 22 -
Position Sensor
Nut/Bolt-Camshaft Posi-
tion Sensor to Cylinder
Head Cover11 - 9 7
Nut/Bolt-Crankshaft Posi-
tion Sensor to Engine
Block8-70
Pre-Glow System
Cylinder Head to Glow
Plug12 - 106
Starter
Bolt-Starter to Crankcase 42 31 -
Nut-Connection of Circuit
3014 - 124
Nut-Connection of Circuit
506-53
Alternator
Bolt-Generator to Timing
Case Cover20 15 -
Bolt-Generator to Cooler
Housing6-53
Bolt-Cooler Housing of
Generator to Crankcase20 - 177
Nut-B+ Circuit to Genera-
tor13-18 - 115-159
Nut-D+ Circuit to Genera-
tor5-44
Nut-Collar to V-Belt Pulley 80 59 -
Oil Pump
Bolt-Oil Pump to Crank-
case18
- 133
Bolt-Oil Pipe to Crank-
shaft Bearing Cap8-70
VAENGINE 9 - 13