2006 MERCEDES-BENZ SPRINTER coolant
[x] Cancel search: coolantPage 258 of 2305
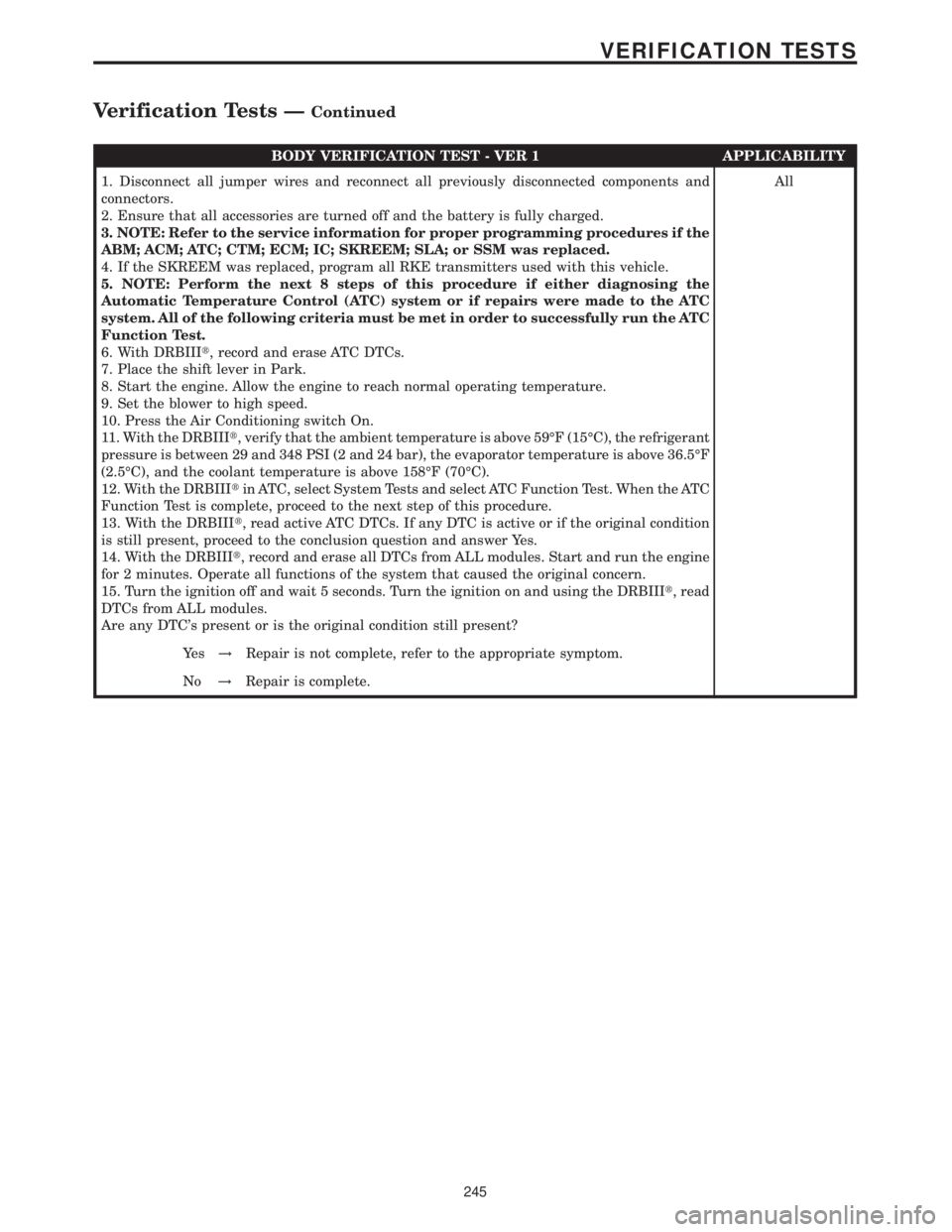
BODY VERIFICATION TEST - VER 1 APPLICABILITY
1. Disconnect all jumper wires and reconnect all previously disconnected components and
connectors.
2. Ensure that all accessories are turned off and the battery is fully charged.
3. NOTE: Refer to the service information for proper programming procedures if the
ABM; ACM; ATC; CTM; ECM; IC; SKREEM; SLA; or SSM was replaced.
4. If the SKREEM was replaced, program all RKE transmitters used with this vehicle.
5. NOTE: Perform the next 8 steps of this procedure if either diagnosing the
Automatic Temperature Control (ATC) system or if repairs were made to the ATC
system. All of the following criteria must be met in order to successfully run the ATC
Function Test.
6. With DRBIIIt, record and erase ATC DTCs.
7. Place the shift lever in Park.
8. Start the engine. Allow the engine to reach normal operating temperature.
9. Set the blower to high speed.
10. Press the Air Conditioning switch On.
11. With the DRBIIIt, verify that the ambient temperature is above 59ÉF (15ÉC), the refrigerant
pressure is between 29 and 348 PSI (2 and 24 bar), the evaporator temperature is above 36.5ÉF
(2.5ÉC), and the coolant temperature is above 158ÉF (70ÉC).
12. With the DRBIIItin ATC, select System Tests and select ATC Function Test. When the ATC
Function Test is complete, proceed to the next step of this procedure.
13. With the DRBIIIt, read active ATC DTCs. If any DTC is active or if the original condition
is still present, proceed to the conclusion question and answer Yes.
14. With the DRBIIIt, record and erase all DTCs from ALL modules. Start and run the engine
for 2 minutes. Operate all functions of the system that caused the original concern.
15. Turn the ignition off and wait 5 seconds. Turn the ignition on and using the DRBIIIt, read
DTCs from ALL modules.
Are any DTC's present or is the original condition still present?All
Ye s!Repair is not complete, refer to the appropriate symptom.
No!Repair is complete.
245
VERIFICATION TESTS
Verification Tests ÐContinued
Page 259 of 2305

HEATER VERIFICATION TEST - VER 1 APPLICABILITY
1. WARNING: NEVER OPERATE THE HEATER IN AN ENCLOSED AREA THAT DOES
NOT HAVE EXHAUST VENTILATION FACILITIES. ALWAYS VENT THE HEATER's
EXHAUST WHEN OPERATING THE HEATER. FAILURE TO FOLLOW THESE IN-
STRUCTIONS CAN RESULT IN PERSONAL INJURY OR DEATH.
2. WARNING: ALLOW THE HEATER ASSEMBLY TO COOL BEFORE PERFORMING A
COMPONENT INSPECTION/REPAIR/REPLACEMENT. FAILURE TO FOLLOW
THESE INSTRUCTIONS CAN RESULT IN PERSONAL INJURY OR DEATH.
3. NOTE: The heater's control unit will store up to five DTCs in its memory.
4. NOTE: If the heater's control unit detects a new fault in the system, one that is not
already stored in its memory, it will clear the oldest of the five stored DTCs, and it
will store the new fault's DTC.
5. NOTE: If the heater's control unit detects a reoccurrence of a stored fault, it will
overwrite that fault's DTC with the most recent occurrence.
6. Verify that the vehicle's battery is fully charged.
7. Verify that there is more than 1/8 of a tank of fuel in the vehicle's fuel tank. Add fuel, if
necessary.
8. Verify that all heater's coolant hoses and fuel lines are securely fastened to their respective
components.
9. Disconnect all jumper wires and reconnect all previously disconnected components and
connectors.
10. If a heater installation/cooling system service was performed, purge the coolant circuit of air
in accordance with the Service Information.
11. Turn the ignition on.
12. Verify that the Cabin Heater or Heater Booster is switched off.
13. Ensure that all accessories are turned off.
14. Set the blend control to the max heat position and the mode control to the floor position.
15. If a fuel system service requiring fuel to drain out of the heater's fuel line was performed,
prime the heater's Dosing Pump in accordance with the Service Information.
16. With the DRBIIIt, record and erase all DTCs from the Cabin Heater Module or Heater
Booster Module. Turn the ignition off, wait 5 seconds, then turn start the engine.
17. Allow the engine to idle.
18. NOTE: Do not disconnect the vehicle's battery or the heater's main power supply
while the heater is in operation or in run-down mode. Failure to follow these
instructions can result in excess emissions from the heater during heater operation.
19. Switch the Cabin Heater or Heater Booster on. Allow the heater to run through at least one
cycle of operation (approximately 10 minutes), and then turn the heater off.
20. With the DRBIIIt, read the Cabin Heater or Heater Booster Module's DTC.
21. Turn the engine off.
Are any DTC's present or is the original condition still present?All
Ye s!Repair is not complete, refer to the appropriate symptom.
No!Repair is complete.
246
VERIFICATION TESTS
Verification Tests ÐContinued
Page 292 of 2305

INSTRUMENT CLUSTER C1CAV CIRCUIT FUNCTION
1 20BR FUEL LEVEL SENSOR SIGNAL RETURN
2 20BR/DG AMBIENT TEMPERATURE SENSOR SIGNAL RETURN
4 20WT/GY K-IC/ATC/HBM/CHM
5 20BR/BK PARK BRAKE INDICATOR SIGNAL
7 20BK/DG RIGHT TURN SIGNAL
10 20BL/BK FUEL LEVEL SENSOR SIGNAL (+)
11 20BL/DG AMBIENT TEMPERATURE SENSOR SIGNAL (+)
14 20DG/WT/BL ENGINE COOLANT LEVEL SWITCH SIGNAL
15 20BR/WT FRONT COURTESY LAMPS CONTROL
16 20YL/RD SEAT BELT SWITCH SIGNAL
17 20DG CAN C BUS (-)
18 20DG/WT CAN C BUS (+)
INSTRUMENT CLUSTER C2 - WHITECAV CIRCUIT FUNCTION
1- -
2- -
3 20RD/YL FUSED B(+)
4 20BR/WT BRAKE WEAR SENSOR SIGNAL
5- -
6 18BR GROUND
7 20GY/DG/RD LAMP DRIVER
8 20BL/WT FUSED HIGH BEAM SWITCH OUTPUT
9 20BL/RD/WT VEHICLE SPEED SENSOR OUTPUT
10 20BK FUSED IGNITION SWITCH OUTPUT (RUN-START)
11 20BL/BK KEY-IN IGNITION SWITCH SIGNAL
12 - -
13 20BK/WT LEFT TURN SIGNAL
14 20BR/YL BRAKE FLUID LEVEL INDICATOR SIGNAL
15 20BL GENERATOR FIELD DRIVER
16 20YL AIRBAG WARNING INDICATOR DRIVER
17 - -
18 20BL/VT D(+) RELAY NO. 1 CONTROL
18 20BL/VT D(+) RELAY NO. 1 CONTROL
INTRUSION SENSOR NO. 1 - BLACKCAV CIRCUIT FUNCTION
1 20BR GROUND
2 20DG/BK INTRUSION SENSOR 1 SIGNAL
3 20DG/YL INTRUSION SENSOR INTERFACE
4 20RD/DG FUSED B(+)
INTRUSION SENSOR NO. 2 - BLACKCAV CIRCUIT FUNCTION
1 20BR GROUND
2 20GY/BK INTRUSION SENSOR 2 SIGNAL
3 20DG/YL INTRUSION SENSOR INTERFACE
4 20RD/DG FUSED B(+)
C
O
N
N
E
C
T
O
R
P
I
N
O
U
T
S
279
CONNECTOR PINOUTS
Page 401 of 2305
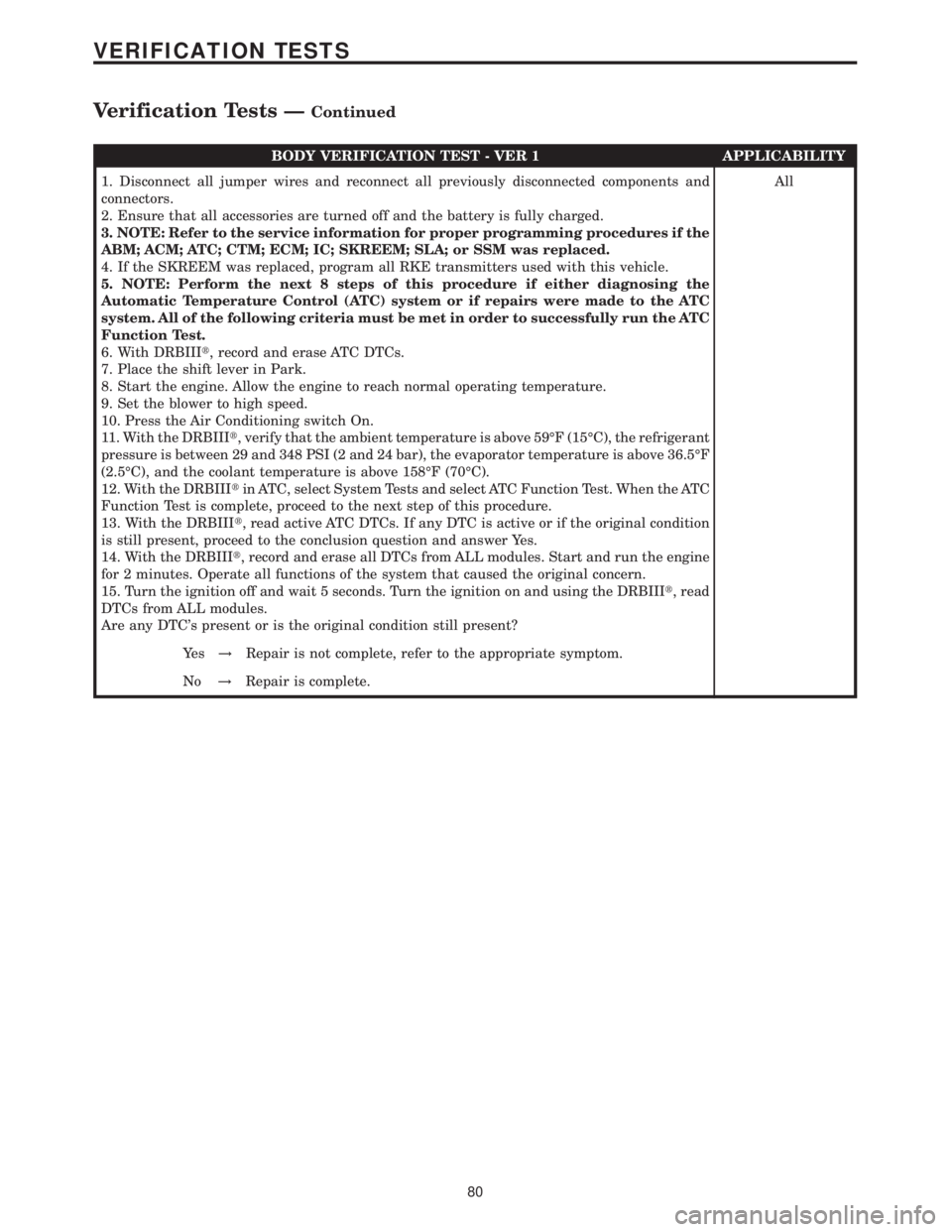
BODY VERIFICATION TEST - VER 1 APPLICABILITY
1. Disconnect all jumper wires and reconnect all previously disconnected components and
connectors.
2. Ensure that all accessories are turned off and the battery is fully charged.
3. NOTE: Refer to the service information for proper programming procedures if the
ABM; ACM; ATC; CTM; ECM; IC; SKREEM; SLA; or SSM was replaced.
4. If the SKREEM was replaced, program all RKE transmitters used with this vehicle.
5. NOTE: Perform the next 8 steps of this procedure if either diagnosing the
Automatic Temperature Control (ATC) system or if repairs were made to the ATC
system. All of the following criteria must be met in order to successfully run the ATC
Function Test.
6. With DRBIIIt, record and erase ATC DTCs.
7. Place the shift lever in Park.
8. Start the engine. Allow the engine to reach normal operating temperature.
9. Set the blower to high speed.
10. Press the Air Conditioning switch On.
11. With the DRBIIIt, verify that the ambient temperature is above 59ÉF (15ÉC), the refrigerant
pressure is between 29 and 348 PSI (2 and 24 bar), the evaporator temperature is above 36.5ÉF
(2.5ÉC), and the coolant temperature is above 158ÉF (70ÉC).
12. With the DRBIIItin ATC, select System Tests and select ATC Function Test. When the ATC
Function Test is complete, proceed to the next step of this procedure.
13. With the DRBIIIt, read active ATC DTCs. If any DTC is active or if the original condition
is still present, proceed to the conclusion question and answer Yes.
14. With the DRBIIIt, record and erase all DTCs from ALL modules. Start and run the engine
for 2 minutes. Operate all functions of the system that caused the original concern.
15. Turn the ignition off and wait 5 seconds. Turn the ignition on and using the DRBIIIt, read
DTCs from ALL modules.
Are any DTC's present or is the original condition still present?All
Ye s!Repair is not complete, refer to the appropriate symptom.
No!Repair is complete.
80
VERIFICATION TESTS
Verification Tests ÐContinued
Page 414 of 2305

TABLE OF CONTENTS - Continued
P0100-MASS AIR FLOW SENSOR SIGNAL VOLTAGE TOO LOW...............19
P2011-MASS AIR FLOW SENSOR PLAUSIBILITY AIR MASS TOO HIGH.........19
P2011-MASS AIR FLOW SENSOR PLAUSIBILITY AIR MASS TOO LOW..........19
P2024-MASS AIR FLOW SENSOR SIGNAL VOLTAGE TOO HIGH...............19
P2024-MASS AIR FLOW SENSOR SIGNAL VOLTAGE TOO LOW...............19
P2065-MASS AIR FLOW SENSOR SUPPLY VOLTAGE TOO HIGH...............19
P2065-MASS AIR FLOW SENSOR SUPPLY VOLTAGE TOO LOW...............19
P2067-MASS AIR FLOW SENSOR SIGNAL CIRCUIT OPEN OR SHORTED.......19
P2067-MASS AIR FLOW SENSOR SIGNAL VOLTAGE TOO HIGH...............19
P2067-MASS AIR FLOW SENSOR SIGNAL VOLTAGE TOO LOW...............19
P2068-MASS AIR FLOW SENSOR PLAUSIBILITY SIGNAL RATIO ERROR........19
P2633-MAF SENSOR SIGNAL PLAUSIBILITY................................19
P0105-INTAKE PRESSURE SENSOR CAN MESSAGE ERROR.................25
P0105-INTAKE PRESSURE SENSOR PLAUSIBILITY..........................25
P0105-INTAKE PRESSURE SENSOR SIGNAL VOLTAGE TOO HIGH.............28
P0105-INTAKE PRESSURE SENSOR SIGNAL VOLTAGE TOO LOW.............31
P0110-INTAKE AIR TEMP SENSOR SIGNAL VOLTAGE TOO HIGH..............34
P2063-INTAKE AIR TEMP SENSOR CIRCUIT SIGNAL VOLTAGE TOO HIGH......34
P0110-INTAKE AIR TEMP SENSOR SIGNAL VOLTAGE TOO LOW...............37
P2063-INTAKE AIR TEMP SENSOR CIRCUIT SIGNAL VOLTAGE TOO LOW......37
P0115-ENGINE COOLANT TEMP SENSOR CIRCUIT PLAUSIBILITY.............40
P2012-ENGINE COOLANT TEMP SENSOR CIRCUIT PLAUSIBILITY.............40
P0115-ENGINE COOLANT TEMP SENSOR CIRCUIT PLAUSIBILITY WITH ENGINE
OIL SENSOR...........................................................42
P0115-ENGINE COOLANT TEMP SENSOR CIRCUIT SIGNAL VOLTAGE TOO
HIGH.................................................................44
P2054-ENGINE COOLANT TEMP SENSOR CIRCUIT SIGNAL VOLTAGE TOO
HIGH.................................................................44
P2054-ENGINE COOLANT TEMP SENSOR CIRCUIT SIGNAL VOLTAGE TOO
LOW..................................................................44
P0115-ENGINE COOLANT TEMP SENSOR CIRCUIT SIGNAL VOLTAGE TOO
LOW..................................................................47
P0180-FUEL TEMPERATURE SENSOR CIRCUIT - SIGNAL VOLTAGE TOO HIGH. .49
P0180-FUEL TEMPERATURE SENSOR CIRCUIT - SIGNAL VOLTAGE TOO LOW . .51
P2625-FUEL TEMPERATURE SENSOR PLAUSIBILITY........................51
P0190-FUEL PRESS SENSOR CIRCUIT MALF SIGNAL VOLTAGE TOO HIGH.....53
P2008-FUEL PRESSURE SENSOR CIRCUIT SIGNAL VOLTAGE TOO HIGH......53
P0190-FUEL PRESS SENSOR CIRCUIT MALF SIGNAL VOLTAGE TOO LOW.....57
P2008-FUEL PRESSURE SENSOR CIRCUIT SIGNAL VOLTAGE TOO LOW.......57
P0201-CYLINDER 1-INJECTOR CIRCUIT EXCESSIVE CURRENT...............60
P0201-CYLINDER 1-INJECTOR CIRCUIT OPEN OR SHORTED TO GROUND.....60
P0201-CYLINDER 1-INJECTOR CIRCUIT SHORTED TO GROUND..............60
P0201-CYLINDER 1-INJECTOR CIRCUIT SHORTED TO VOLTAGE..............60
P0202-CYLINDER 2-INJECTOR CIRCUIT EXCESSIVE CURRENT...............60
P0202-CYLINDER 2-INJECTOR CIRCUIT OPEN OR SHORTED TO GROUND.....60
P0202-CYLINDER 2-INJECTOR CIRCUIT SHORTED TO GROUND..............60
P0202-CYLINDER 2-INJECTOR CIRCUIT SHORTED TO VOLTAGE..............60
P0203-CYLINDER 3-INJECTOR CIRCUIT EXCESSIVE CURRENT...............60
P0203-CYLINDER 3-INJECTOR CIRCUIT OPEN OR SHORTED TO GROUND.....60
P0203-CYLINDER 3-INJECTOR CIRCUIT SHORTED TO GROUND..............60
P0203-CYLINDER 3-INJECTOR CIRCUIT SHORTED TO VOLTAGE..............60
P0204-CYLINDER 4-INJECTOR CIRCUIT EXCESSIVE CURRENT...............60
P0204-CYLINDER 4-INJECTOR CIRCUIT OPEN OR SHORTED TO GROUND.....60
iii
Page 421 of 2305

TABLE OF CONTENTS - Continued
*CHECKING THE FUEL PRESSURE SOLENOID CIRCUITS...................233
*CHECKING THE FUEL QUANTITY SOLENOID CIRCUITS....................234
*CHECKING THE POWER AND GROUNDS................................235
*ENGINE CRANKS BUT WILL NOT START.................................239
*ENGINE WILL NOT CRANK.............................................242
VERIFICATION TESTS
VERIFICATION TESTS..................................................246
8.0 COMPONENT LOCATIONS..............................................249
8.1CONTROL MODULES.............................................249
8.2CONTROLS AND SOLENOIDS......................................249
8.3DATA LINK CONNECTOR..........................................250
8.4SENSORS.......................................................251
8.5SWITCHES......................................................253
9.0 CONNECTOR PINOUTS................................................255
ACCELERATOR PEDAL POSITION SENSOR (OBD).........................255
AIRBAG CONTROL MODULE - YELLOW...................................255
BOOST PRESSURE SENSOR (OBD)......................................255
BOOST PRESSURE SERVOMOTOR (OBD)................................256
CAMSHAFT POSITION SENSOR - BLACK.................................256
CONTROLLER ANTILOCK BRAKE........................................257
CRANKCASE HEATER - BLACK..........................................257
CRANKSHAFT POSITION SENSOR - BLACK...............................258
DATA LINK CONNECTOR - BLACK........................................258
EGR VALVE - BLACK...................................................258
ENGINE CONTROL MODULE C1 (OBD)...................................259
ENGINE CONTROL MODULE C2 (OBD)...................................260
ENGINE COOLANT TEMPERATURE SENSOR - BLACK......................260
ENGINE OIL SENSOR - BLACK..........................................261
FUEL INJECTOR NO. 1 - BLACK.........................................261
FUEL INJECTOR NO. 2 - BLACK.........................................261
FUEL INJECTOR NO. 3 - BLACK.........................................261
FUEL INJECTOR NO. 4 - BLACK.........................................262
FUEL INJECTOR NO. 5 - BLACK.........................................262
FUEL PRESSURE SENSOR - BLACK.....................................262
FUEL PRESSURE SOLENOID............................................262
FUEL PUMP (OBD).....................................................262
FUEL PUMP RELAY (OBD)..............................................263
FUEL QUANTITY CONTROL VALVE (OBD).................................263
FUEL TEMPERATURE SENSOR..........................................263
ENGINE CONTROL RELAY (FUSE BLOCK NO. 1)...........................265
FUSES (FUSE BLOCK NO. 1)............................................265
FUSES (FUSE BLOCK NO. 2)............................................267
FUSES (FUSE/RELAY BLOCK)...........................................269
STARTER MOTOR RELAY (FUSE/RELAY BLOCK)...........................269
GLOW PLUG CONTROL MODULE C1 - BLACK.............................270
GLOW PLUG CONTROL MODULE C2 - BLACK.............................270
INTAKE AIR PRESSURE SENSOR (OBD)..................................270
INTAKE AIR TEMPERATURE SENSOR - BLACK............................270
x
Page 425 of 2305

3.2.2 ECM OPERATING MODES
As input signals to the ECM change, the ECM
adjusts its response to the output devices. For
example, the ECM must calculate a different fuel
quantity and fuel timing for engine idle condition
than it would for a wide open throttle condition.
There are several different modes of operation that
determine how the ECM responds to the various
input signals.
Ignition Switch On (Engine Off)
When the ignition is turned on the ECM activates
the glow plug relay for a time period that is deter-
mined by engine coolant temperature, intake air
temperature and battery voltage.
Engine Start-Up Mode
The ECM uses the intake air temperature sensor,
engine temperature sensor and the crankshaft po-
sition sensor (engine speed) inputs to determine
fuel injection quantity.
Normal Driving Modes
Engine idle, warm-up, acceleration, deceleration
and wide open throttle modes are controlled based
on all of the sensor inputs to the ECM. The ECM
uses these sensor inputs to adjust fuel quantity and
fuel injector timing. EGR valve control is performed
using feedback from the oxygen sensor. An oxygen
sensor is located in the exhaust manifold to sample
oxygen content exiting the engine cylinders. The
ECM uses the O2 sensor, along with other sensor
inputs, to govern the amount of exhaust gas recir-
culation to reduce HC (HydroCarbons) and CO
(Carbon Monoxide). Engine coolant is routed
through the base of the EGR valve to provide
additional cooling of the exhaust gas, which further
helps the reductions of emissions. The EGR valve
has a self-cleaning function. When the engine is
shut off, the EGR valve rotates twice to reduce
carbon deposits at the valve seat.
Overheat Production Mode
If the engine temperature is above 105ÉC (221ÉF)
and vehicle speed is above 40 km/h (25 MPH) the
ECM will limit fuel quantity for engine protection.
Limp-In Mode
The ECM utilizes different degrees of engine
limp-in. The ECM is able to limit engine rpm,
engine power output (turbo boost reduction), acti-
vate engine cooling fan or all of these functions
based on the type of fault that is detected. Critical
engine performance faults such as accelerator pedal
position sensor fault will result in a fixed idle speed
of approximately 680 rpm regardless of actual pedalposition. Other less critical faults will result in
power reduction throughout the full range of driv-
ing conditions.
Overspeed Detection Mode
If the ECM detects engine RPM that exceeds
5200 RPM, the ECM will set a DTC in memory,
limit engine RPM to no more than 2500 RPM, and
illuminate the MIL until the DTC is cleared.
After-Run Mode
The ECM transfers RAM information to ROM
and performs an Input/Output state check.
3.2.3 MONITORED CIRCUITS
The ECM is able to monitor and identify most
driveability related trouble conditions. Some cir-
cuits are directly monitored through ECM feedback
circuitry. In addition, the ECM monitors the voltage
state of some circuits and compares those states
with expected values. Other systems are monitored
indirectly when the ECM conducts a rationality test
to identify problems.
Although most subsystems of the engine control
module are either directly or indirectly monitored,
there may be occasions when diagnostic trouble
codes are not immediately identified. For a trouble
code to set, a specific set of conditions must occur
and unless these conditions occur, a DTC will not
set.
3.2.4 SKREEM OVERVIEW
The sentry key remote entry module system
(SKREEM) is designed to prevent unauthorized
vehicle operation. The system consists of a sentry
key remote entry module (SKREEM), ignition
key(s) equipped with a transponder chip and the
ECM. When the ignition switch is turned on, the
SKREEM interrogates the ignition key. If the igni-
tion key is Valid or Invalid, the SKREEM sends a
message to the ECM indicating ignition key status.
Upon receiving this message the ECM will termi-
nate engine operation or allow the engine to con-
tinue to operate.
3.2.5 SKREEM ON-BOARD DIAGNOSTICS
The SKREEM has been programmed to transmit
and monitor many different coded messages as well
as CAN Bus messages. This monitoring is called
On-Board Diagnostics. Certain criteria must be met
for a DTC to be entered into SKREEM memory. The
criteria may be a range of; input voltage, CAN Bus
message or coded messages to the SKREEM. If all
the criteria for monitoring a circuit or function are
met and a fault is detected, a DTC will be stored in
the SKREEM memory and the START ERROR indi-
cator will be turned on in the instrument cluster.
2
GENERAL INFORMATION
Page 428 of 2305

ecm internal error 3
ecm internal error 4
ecm internal error 4
ecm internal error 5
ecm internal fault
ecm invalid coding
ecm invalid data
ecm read error
ecm read/write error
ecm supply voltage too low
ecm voltage supply is too high
ecm voltage supply is too low
ecm write error
egr flow rate is too high
egr flow rate is too low
egr valve excessive current
egr valve signal circuit open circuit
egr valve signal circuit shorted to ground
egr valve signal circuit shorted to ground
egr valve signal circuit shorted to voltage
engine control relay plausibility
engine control relay shuts off too early
engine control relay shuts off too late
engine coolant temp sensor circuit plausibility
engine coolant temp sensor circuit plausibility
engine coolant temp sensor circuit plausibility with
engine oil sensor
engine coolant temp sensor circuit signal voltage too
high
engine coolant temp sensor circuit signal voltage too
high
engine coolant temp sensor circuit signal voltage too
low
engine coolant temp sensor circuit signal voltage too
low
*engine cranks but will not start
engine oil sensor circuit invalid level
engine oil sensor circuit level out of range
engine oil sensor circuit level out of range
engine oil sensor monitoring error
engine oil sensor oil temperature plausibility
engine oil sensor open circuit
engine oil sensor poor oil quality
engine oil sensor quality measurement error
engine oil sensor quality plausibility
engine oil sensor signal error
engine oil sensor signal plausibility
engine oil sensor signal voltage is too high
engine oil sensor signal voltage is too low
engine oil sensor synchronization error
engine oil sensor water contamination
*engine will not crank
esm can message missing or incorrect
etc can message missing or incorrect
fuel injector 1 read too large
fuel injector 1 read too large
fuel injector 1 read too small
fuel injector 1 read too smallfuel injector 2 read too large
fuel injector 2 read too large
fuel injector 2 read too small
fuel injector 2 read too small
fuel injector 3 read too large
fuel injector 3 read too large
fuel injector 3 read too small
fuel injector 3 read too small
fuel injector 4 read too large
fuel injector 4 read too large
fuel injector 4 read too small
fuel injector 4 read too small
fuel injector 5 read too large
fuel injector 5 read too large
fuel injector 5 read too small
fuel injector 5 read too small
fuel press sensor circuit malf signal voltage too high
fuel press sensor circuit malf signal voltage too low
fuel press solenoid signal plausibility high
fuel press solenoid signal plausibility low
fuel pressure sensor circuit signal voltage too high
fuel pressure sensor circuit signal voltage too low
fuel pressure solenoid circuit excessive current
fuel pressure solenoid circuit open circuit
fuel pressure solenoid circuit shorted to ground or
b+
fuel pump relay circuit open circuit
fuel pump relay circuit shorted to ground
fuel pump relay circuit shorted to voltage
fuel pump relay excessive current
fuel quantity solenoid ecm thermal overload
fuel quantity solenoid open circuit
fuel quantity solenoid short to ground
fuel quantity solenoid short to ground
fuel quantity solenoid short to voltage
fuel rail pressure malfunction deceleration error
fuel rail pressure malfunction deceleration error
fuel rail pressure malfunction fuel flow below min-
imum quantity
fuel rail pressure malfunction maximum fuel flow
exceeded
fuel rail pressure malfunction maximum fuel pres-
sure exceeded
fuel rail pressure malfunction maximum fuel pres-
sure exceeded
fuel rail pressure malfunction maximum fuel pres-
sure exceeded
fuel rail pressure malfunction plausibility with fuel
pressure solenoid
fuel rail pressure malfunction rail pressure is too
high
fuel rail pressure malfunction rail pressure is too
low
fuel rail pressure malfunction rail pressure is too
low
fuel rail pressure malfunction rail pressure is too
low
fuel rail pressure malfunction rail pressure too high
5
GENERAL INFORMATION