2006 BMW MOTORRAD K 1200 S lock
[x] Cancel search: lockPage 72 of 163

to turn the handlebars to the
left or right. However, the mo-
torcycle is more stable on a
level surface with the handle-
bars turned to the left than
with the handlebars turned to
the right.
On level ground, always turn
the handlebars to the left to
set the steering lock.Turn the handlebars to full
left or right lock.
Check that the motorcycle
is standing firmly. On a gradient, the mo-
torcycle should always
face uphill; select 1st gear.
Lock the steering lock.Remove the motorcycle
from side standUnlock the steering lock.
From the left, grip the
handlebars with both hands. Pull the handbrake lever.
Swing your right leg over
the seat and lift the motor-
cycle to the upright position.
Hold the motorcycle upright
and balanced.
An extended side stand
can catch on the ground
when the motorcycle is mov-
ing and lead to a fall.
Retract the side stand before
moving the motorcycle.
Sit on the motorcycle and
use your left foot to retract
the side stand.
Place the motorcycle on
centre stand
OA
If the ground is soft or
uneven, there is no guar-
antee that the motorcycle will
rest firmly on the stand.
Always check that the ground
under the stand is level and
firm. Switch off the engine.
Dismount and keep your left
hand on the left handlebar
grip.
With your right hand, grip
the rear grab handle or the
rear frame.
Place your right foot on the
pin of the centre stand, and
press the stand down un-
til its curved feet touch the
ground.
Place your full body weight
on the centre stand and at
the same time pull the mo-
torcycle to the rear.
Excessive movements
could cause the centre
stand to retract, and the mo-
torcycle would topple in con-
sequence.
Do not lean or sit on the mo-
torcycle with the centre stand
extended.
570zRiding
Page 73 of 163

Check that the motorcycle
is standing firmly.
Lock the steering lock.Remove the motorcycle
from centre stand
OA
Unlock the steering lock.
Place your left hand on the
left handlebar grip.
With your right hand, grip
the rear grab handle or the
rear frame.
Push the motorcycle for-
ward off the centre stand.
Check that the centre stand
has fully retracted.Refuelling
Fuel is highly flammable.
A naked flame close to
the fuel tank can cause a fire
or explosion.
Do not smoke. Never bring
a naked flame near the fuel
tank. Fuel expands when hot.
Fuel escaping from an
overfilled tank could make its
way onto the rear tyre. This
could cause a fall.
Do not fill the tank past the
bottom edge of the filler
neck.
Fuel attacks plastics,
which become dull or
unsightly.
Wipe off plastic parts immedi-
ately if they come into contact
with fuel.
Leaded fuel will destroy
the catalytic converter.
Use only unleaded fuel.
Make sure the ground is
level and firm and place the
motorcycle on its stand. Open the protective cap.
Open the fuel tank cap with
the ignition key by turning it
counter-clockwise.
Refuel with fuel of the grade
stated below; do not fill the
tank past the bottom edge
of the filler neck.
Recommended fuel
grade
98 ROZ/RON (Premium
plus unleaded)
571zRiding
Page 76 of 163

Brake system with
BMW Motorrad
Integral ABSPartially integral brakesYour motorcycle is equipped
with partially integral brakes.
Both front and rear brakes
are applied when you pull the
handbrake lever. The foot-
brake lever acts only on the
rear brake.
When actively intervening
in the braking process, the
BMW Motorrad Integral ABS
adapts braking-force distri-
bution between front and rear
brakes to suit the load on the
motorcycle.The integral braking
function makes it
very difficult to spin the
rear wheel by opening
the throttle with the front
brake applied to keep the
motorcycle stationary (burn- out). Attempted burn-outs
can result in damage to the
rear brake and the clutch.
Do not attempt burn-outs.
How does ABS work?The amount of braking force
that can be transferred to
the road depends on factors
hat include the coefficient of
friction of the road surface.
Loose stones, ice and snow
or a wet road all have much
lower coefficients of friction
than a clean, dry asphalt sur-
face. The lower the coeffi-
cient of friction, the longer the
braking distance.
If the rider increases braking
pressure to the extent that
braking force exceeds the
maximum transferrable limit,
the wheels start to lock and
the motorcycle loses its dir-
ectional stability; a fall is im-
minent. Before this situation
can occur, ABS intervenes
and adapts braking pressure
to the maximum transferrable
braking force, so the wheels
continue to turn and direc-
tional stability is maintained
irrespective of the condition of
the road surface.
What are the effects of
surface irregularities?Humps and surface irregu-
larities can cause the wheels
to lose contact temporarily
with the road surface; if this
happens the braking force
that can be transmitted to
the road can drop to zero.
If the brakes are applied un-
der these circumstances the
ABS has to reduce braking
force to ensure that direc-
tional stability is maintained
when the wheels regain con-
tact with the road surface.
At this instant the BMW Mo-
574zRiding
Page 77 of 163

torrad Integral ABS must as-
sume an extremely low coef-
ficient of friction, so that the
wheels will continue to rotate
under all imaginable circum-
stances, because this is the
precondition for ensuring dir-
ectional stability. As soon as
is registers the actual circum-
stances, the system reacts
instantly and adjusts braking
force accordingly to achieve
optimum braking.What feedback does the
rider receive from the
BMW Motorrad Integral
ABS?If the ABS system has to re-
duce braking force on ac-
count of the circumstances
described above, vibration is
perceptible through the hand-
brake lever.
When the handbrake lever is
pulled, brake pressure is alsobuilt up at the rear wheel by
the integral function. If the
brake pedal is depressed
after the handbrake lever is
pulled, the brake pressure
built up beforehand is per-
ceptible as counter-pressure
sooner than is the case when
the brake pedal is depressed
either before or at the same
time as the brake lever is
pulled.
How can stopping
distance be minimised?Each time the brakes are
applied, a load distribution
shift takes place with the
load shifting forward from
the rear to the front wheel.
The sharper the motorcycle
decelerates, the more load
is shifted to the front wheel.
The higher the wheel load, the
more braking force can be
transmitted without the wheel
locking.
To optimise stopping dis-
tance, apply the front brakes
rapidly and keep on increas-
ing the force you apply to the
brake lever. This makes the
best possible use of the dy-
namic increase in load at the
front wheel. Remember to
pull the clutch at the same
time. In the "panic braking
situations" that are trained so
frequently braking force is ap-
plied as rapidly as possible
and with the rider's full force
applied to the brake levers;
under these circumstances
the dynamic shift in load dis-
tribution cannot keep pace
with the increase in decel-
eration and the tyres cannot
transmit the full braking force
to the surface of the road.
ABS has to intervene to keep
the front wheel from locking;
575zRiding
Page 78 of 163

this increases stopping dis-
tance.Rear wheel liftEven under severe braking,
a high level of tyre grip can
mean that the front wheel
does not lock up until very
late, if at all. Consequently,
ABS does not intervene until
very late, if at all. Under these
circumstances the rear wheel
can lift off the ground, and the
outcome can be a highsiding
situation in which the motor-
cycle can flip over.Severe braking can
cause the rear wheel to
lift off the ground.
When you brake, bear in mind
that ABS control cannot be
relied on in all circumstances
to prevent the rear wheel from
lifting clear of the ground.
What is the design
baseline for BMW
Motorrad Integral ABS?Within the limits imposed by
physics, the BMW Motorrad
Integral ABS ensures direc-
tional stability on any surface.
The system is not optimised
for special requirements that
apply under extreme compet-
itive situations off-road or on
the track.Special situationsThe speeds of the front and
rear wheels are compared
as one means of detecting a
wheel's incipient tendency to
lock. If the system registers
implausible values for a
lengthy period the ABS
function is deactivated
for safety reasons and
an ABS fault message is
issued. Self-diagnosis has to complete before fault
messages can be issued.
In addition to problems with
the BMW Motorrad Integ-
ral ABS, exceptional riding
conditions can lead to a fault
message being issued.
Exceptional riding
conditions:
Heating up with the motor-
cycle on the centre stand
or an auxiliary stand, en-
gine idling or with a gear
engaged.
Rear wheel locked by the
engine brake for a lengthy
period, for example while
descending off-road.
If a fault message is issued on
account of exceptional riding
conditions as outlined above,
you can reactivate the ABS
function by switching the igni-
tion off and on again.
576zRiding
Page 83 of 163

switched off. In order to en-
sure that the drain on the on-
board power supply system is
minimised, the supply to the
power socket is cut off ap-
proximately 15 minutes after
the ignition is switched off,
and it is also temporarily in-
terrupted during the start pro-
cedure.Cable routingThe cables from the power
socket to the auxiliary device
must be routed in such a way
that they:Do not impede the rider
Do not restrict or obstruct
the steering angle and
handling characteristics
Cannot be trapped
Incorrectly routed cables
can impede the rider.
Route the cables as
described above.
LuggageCorrect loading
Overloading and imbal-
anced loads can ad-
versely affect the motorcycle's
handling.
Do not exceed the permiss-
ible gross weight and be sure
to comply with the instruc-
tions on loading.
The maximum speed recom-
mended for riding with loaded
cases is 180 km/h.
Set spring preload, damping
characteristic and tyre pres-
sures to suit total weight.
Ensure that the case
volumes on the left and right
are equal.
Make sure that the weight
is uniformly distributed
between right and left. Pack heavy items at the
bottom and toward the in-
board side.
Max. load in each case (left
and right): 8 kg.
Max. load in tank rucksack
5 kg.
Case
OA
Release leversEach case has two levers,
one on each side of the lock.
The grey lever marked OPEN
is for opening and closing the
case.
The black lever marked RE-
LEASE is for removing and
attaching the case.
681zAccessories
Page 84 of 163

Opening casesTurn the lock barrel in the
OPEN direction.
Pull the grey release lever
(OPEN) up.
Lock straps1open. Pull the grey release lever
(OPEN) up again.
Pull case lid
2out of the re-
tainer.
Close the casePress catches 1of the case
lid into retainers 2.
The catches engage with an
audible click.
Press the catches on the
lock straps into retainers 2.
The catches engage with an
audible click.
Check that the catches are
locked securely into place.
Adjust the case volumeClose the case lid.
Turn the lock strap
buckles 1of the lock straps
out.
Pull the lock straps up and
out.
This expands the case to
maximum volume.
682zAccessories
Page 85 of 163
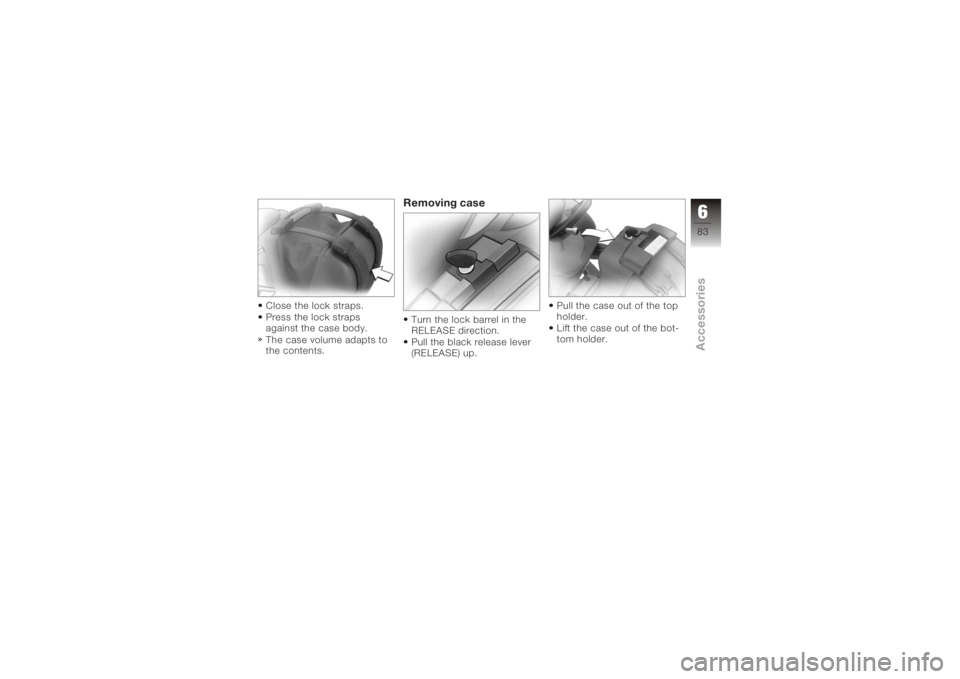
Close the lock straps.
Press the lock straps
against the case body.
The case volume adapts to
the contents.
Removing caseTurn the lock barrel in the
RELEASE direction.
Pull the black release lever
(RELEASE) up.Pull the case out of the top
holder.
Lift the case out of the bot-
tom holder.
683zAccessories