Page 3990 of 5135
05±842
±
DIAGNOSTICS ABS WITH EBD & BA & TRC & VSC SYSTEM
AVENSIS REPAIR MANUAL (RM1018E)
INSPECTION PROCEDURE
HINT:
Start the inspection from step 1 if you are using the hand±held tester and\
start from step 2 if you are not using
the hand±held tester.
1PERFORM ACTIVE TEST BY HAND±HELD TESTER(BRAKE WARNING LIGHT)
(a)Check that ºONº and ºOFFº of the Brake warning light is shown on \
the combination meter by the hand± held tester.
OKGo to step 4
NG
2CHECK DTC FOR ABS
(a)Check the DTC on page 05±756. YES REPAIR CIRCUIT INDICATED BY OUTPUTCODE
NO
3 INSPECT BRAKE WARNING LIGHT
(a)See combination meter troubleshooting on page 71±1. NG REPAIR OR REPLACE COMBINATION METERASSEMBLY
OK
4INSPECT PARKING BRAKE SWITCH ASSY(See page 71±3)
NG REPLACE PARKING BRAKE SWITCH ASSY
OK
5INSPECT BRAKE FLUID LEVEL WARNING SWITCH(See page 71±3)
NG REPLACE BRAKE MASTER CYLINDER RESERVOIR SUB±ASSY
OK
Page 3991 of 5135
±
DIAGNOSTICS ABS WITH EBD & BA & TRC & VSC SYSTEM
05±843
AVENSIS REPAIR MANUAL (RM1018E)
6CHECK HARNESS AND CONNECTOR(SKID CONTROL ECU ± PARKING BRAKE
SWITCH)
(a)Check for an open or short circuit in harness and connector between terminal \
PKB of the skid control
ECU and parking brake switch (See page 01±32).
NGREPAIR OR REPLACE HARNESS ORCONNECTOR
OK
7CHECK HARNESS AND CONNECTOR(SKID CONTROL ECU ± BRAKE FLUID LEVEL WARNING SWITCH)
(a)Check for an open or short circuit in harness and connector between terminal \
EBDW of the skid control
ECU and brake fluid level warning switch (See page 01±32).
NGREPAIR OR REPLACE HARNESS ORCONNECTOR
OK
8CHECK HARNESS AND CONNECTOR(SKID CONTROL ECU ± COMBINATION MERTER)
(a)Check for an open or short circuit in harness and connector between the skid \
control ECU and com-
bination meter (See page 01±32).
NGREPAIR OR REPLACE HARNESS ORCONNECTOR
OK
REPLACE ABS & TRACTION ACTUATOR ASSY(See page 32±57)
Page 3996 of 5135
![TOYOTA AVENSIS 2005 Service Repair Manual ± DIAGNOSTICSELECTRONIC CONTROLLED AUTOMATIC
TRANSAXLE [ECT] (U341E)05±989
AVENSIS REPAIR MANUAL (RM1018E)ItemDiagnostic Note Normal Condition Measurement Item/
Display (Range)
PNP SW [NSW]PNP SW TOYOTA AVENSIS 2005 Service Repair Manual ± DIAGNOSTICSELECTRONIC CONTROLLED AUTOMATIC
TRANSAXLE [ECT] (U341E)05±989
AVENSIS REPAIR MANUAL (RM1018E)ItemDiagnostic Note Normal Condition Measurement Item/
Display (Range)
PNP SW [NSW]PNP SW](/manual-img/14/57441/w960_57441-3995.png)
± DIAGNOSTICSELECTRONIC CONTROLLED AUTOMATIC
TRANSAXLE [ECT] (U341E)05±989
AVENSIS REPAIR MANUAL (RM1018E)ItemDiagnostic Note Normal Condition Measurement Item/
Display (Range)
PNP SW [NSW]PNP SW Status/
ON or OFFShift lever range is;
P or N: ON
Except P or N: OFF
The shift lever range and these
REVERSEPNP SW Status/
ON or OFFShift lever range is;
R: ON
Except R: OFFThe shift lever range and these
values are different, there are fail-
ures of the PNP switch or shift
cable adjustment
DRIVEPNP SW Status/
ON or OFFShift lever range is;
D and S: ON
Except D and S: OFFcable adjustment.
SOLENOID (SLT)Shift Solenoid SLT Status/
ON or OFFIG SW ON: ON�
AT FLUID TEMP
ATF Temp. Sensor Value/
min.: ±40�C (±40�F)
max.: 215�C (419�F)80�C (176�F)
(After Stall Test)If the value is º±40�C (±40�F)º or
º215�C (419�F)º, ATF temp. sen-
sor circuit is opened or shorted.
5. ACTIVE TEST
HINT:
Performing the ACTIVE TEST using the hand±held tester allows the relay, VSV, actuator and so on to oper-
ate without parts removal. Performing the ACTIVE TEST as the first step of troubleshooting is one of the
method to shorten the work time.
It is possible to display the DATA LIST during the ACTIVE TEST.
(a) Warm up the engine.
(b) Turn the ignition switch OFF.
(c) Connect the hand±held tester to the DLC3.
(d) Turn the ignition switch ON.
(e) According to the display on tester, perform the ºACTIVE TESTº.
ItemTest DetailsDiagnostic Note
LINE PRESS UP
[Test Details]
Operate the shift solenoid SLT and raise the line pressure.
[Vehicle Condition]
�Vehicle Stopped.
�IDL: ON
[Others]
ON: Line pressure up.
OFF: No action (normal operation)
±
LOCK UP
[Test Details]
Control the shift solenoid SL to set the ATM to the lock±up condition.
[Vehicle Condition]
Vehicle Speed: 60 km/h (37 mph) or more
Possible to check the SL opera-
tion.
SHIFT
[Test Details]
Operate the shift solenoid valve and set the each shift range by your-
self.
[Vehicle Condition]
Less than 50 km/h (31 mph)
[Others]
�Press � button: Shift up
�Press � button: Shift down
Possible to check the operation of
the shift solenoid values.
6. PROBLEM SYMPTOM CONFIRMATION
(a) Taking into consideration the results of the customer problem analysis, try to reproduce the symptoms
of the trouble. If the problem is that the transaxle does not shift up, shift down, or the shift point is too
high or too low, conduct the following road test referring to the automatic shift schedule and simulate
the problem symptoms.
Page 4000 of 5135
![TOYOTA AVENSIS 2005 Service Repair Manual G24063
SST
SST
± DIAGNOSTICSELECTRONIC CONTROLLED AUTOMATIC
TRANSAXLE [ECT] (U341E)05±993
AVENSIS REPAIR MANUAL (RM1018E)
9. HYDRAULIC TEST
(a) Measure the line pressure.
NOTICE:
�Do the test at n TOYOTA AVENSIS 2005 Service Repair Manual G24063
SST
SST
± DIAGNOSTICSELECTRONIC CONTROLLED AUTOMATIC
TRANSAXLE [ECT] (U341E)05±993
AVENSIS REPAIR MANUAL (RM1018E)
9. HYDRAULIC TEST
(a) Measure the line pressure.
NOTICE:
�Do the test at n](/manual-img/14/57441/w960_57441-3999.png)
G24063
SST
SST
± DIAGNOSTICSELECTRONIC CONTROLLED AUTOMATIC
TRANSAXLE [ECT] (U341E)05±993
AVENSIS REPAIR MANUAL (RM1018E)
9. HYDRAULIC TEST
(a) Measure the line pressure.
NOTICE:
�Do the test at normal operation ATF temperature 50 to 80�C (122 to 176�F).
�The line pressure test should always be carried out in pairs. One technician should observe
the conditions of wheels or wheel stopper outside the vehicle while the other is doing the test.
�Be careful to prevent SST's hose from interfering with the exhaust pipe.
(1) Warm up the ATF.
(2) Remove the test plug on the left side of the trans-
axle case and connect SST.
SST 09992±00095 (09992± 00231, 09992±00271)
(3) Fully apply the parking brake and chock the 4
wheels.
(4) Connect the hand±held tester to DLC3.
(5) Start the engine and check idling speed.
(6) Keep your left foot pressing firmly on the brake ped-
al and shift into D range.
(7) Measure the line pressure when the engine is idling.
(8) Depress the accelerator pedal all the way down.
Quickly read the highest line pressure when engine
speed reaches stall speed.
(9) In the same way, do the test in R range.
Specified line pressure:
ConditionD range kPa (kgf / cm2, psi)R range kPa (kgf / cm2, psi)
Idling370 to 410 (3.8 to 4.2, 54 to 60)540 to 640 (5.5 to 6.5, 78 to 92)
Stall1,110 to 1,230 (11.3 to 12.5, 161 to 178)1,700 to 1,810 (17.3 to 18.5, 246 to 263)
Evaluation:
ProblemPossible cause
If the measured values at all ranges are higher�Shift solenoid valve SLT defective
�Regulator valve detective
If the measured values at all ranges are lower
�Shift solenoid valve SLT defective
�Regulator valve detective
�Oil pump defective
If pressure is low in the D range only�D range circuit fluid leak
�Forward clutch defective
If pressure is low in the R range only
�R range circuit fluid leak
�Reverse clutch defective
�1st and reverse brake defective
Page 4001 of 5135
G24064
05±994± DIAGNOSTICSELECTRONIC CONTROLLED AUTOMATIC
TRANSAXLE [ECT] (U341E)
AVENSIS REPAIR MANUAL (RM1018E)
10. MANUAL SHIFTING TEST
HINT:
By this test, it can be determined whether the trouble is within
the electrical circuit or is a mechanical problem in the transaxle.
(a) Disconnect the transmission wire connector.
(b) Inspect the manual driving operation.
Check that the shift and gear ranges correspond to the
table below.
While driving, shift through the D range.
Check that the gear change corresponds to the shift
range.
Shift rangeGear position
D3rd
RReverse
PPawl Lock
HINT:
If the gear positions of the D are difficult to distinguish, do the
above road test.
If any abnormality is found in the above test, the problem is in
the transaxle itself.
(c) Connect the transmission wire connector.
(d) Clear the DTC.
Page 4050 of 5135
05−82
− DIAGNOSTICSSFI SYSTEM (2AZ−FSE)
AVENSIS Supplement (RM1045E)
DTC P0130 OXYGEN SENSOR CIRCUIT (BANK1
SENSOR1)
DTC P0150 OXYGEN SENSOR CIRCUIT MALFUNCTION
(BANK 2 SENSOR1)
DTC P2195 OXYGEN SENSOR SIGNAL STUCK LEAN
(BANK1SENSOR1)
DTC P2196 OXYGEN SENSOR SIGNAL STUCK RICH
(BANK1SENSOR1)
DTC P2197 OXYGEN SENSOR SIGNAL STUCK LEAN
(BANK 2 SENSOR1)
DTC P2198 OXYGEN SENSOR SIGNAL STUCK RICH
(BANK 2 SENSOR1)
05CK9−02
Page 4051 of 5135

A00798
Atmosphere
Housing
Platinum Electrode
Solid Electrolyte
(Zirconia Element)
Platinum Electrode
Heater
Coating (Ceramic)
Exhaust Gas CoverIdeal Air−Fuel Mixture
Output Voltage
Richer−Air Fuel Ratio−Leaner
− DIAGNOSTICSSFI SYSTEM (2AZ−FSE)
05−83
AVENSIS Supplement (RM1045E)
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
To obtain a high purification rate for the CO, HC and NOx components of the exhaust gas, a three−way cata-
lytic converter is used. For the most efficient use of the three−way catalytic converter, the air−fuel ratio must
be precisely controlled so that it is always close to the stoichiometric air−fuel ratio.
The heated oxygen sensor has the characteristic whereby its output voltage changes suddenly in the vicinity
of the stoichiometric air−fuel ratio. This is used to detect the oxygen concentration in the exhaust gas and
to provide the ECM with feedback to control the air−fuel ratio.
When the air−fuel ratio becomes LEAN, the oxygen concentration in the exhaust gas increases. And the
heated oxygen sensor informs the ECM of the LEAN condition (low voltage, i. e. less than 0.45 V).
When the air−fuel ratio is RICHER than the stoichiometric air−fuel ratio, the oxygen concentration in the ex-
haust gas is reduced. And the heated oxygen sensor informs the ECM of the RICH condition (high voltage,
i. e. more than 0.45 V). The ECM judges whether the air−fuel ratio is RICH or LEAN by voltage from the
heated oxygen sensor, and controls the injection timing accordingly. However, if the malfunction of the
heated oxygen sensor causes abnormal voltage output, the ECM becomes unable to perform the accurate
air−fuel ratio control.
The heated oxygen sensors include a heater which heats the zirconia element. The heater is controlled by
the ECM. When the intake air volume is low (the temperature of the exhaust gas is low), the current flows
to the heater in order to heat the sensor for the accurate oxygen concentration detection.
Page 4052 of 5135
05−84
− DIAGNOSTICSSFI SYSTEM (2AZ−FSE)
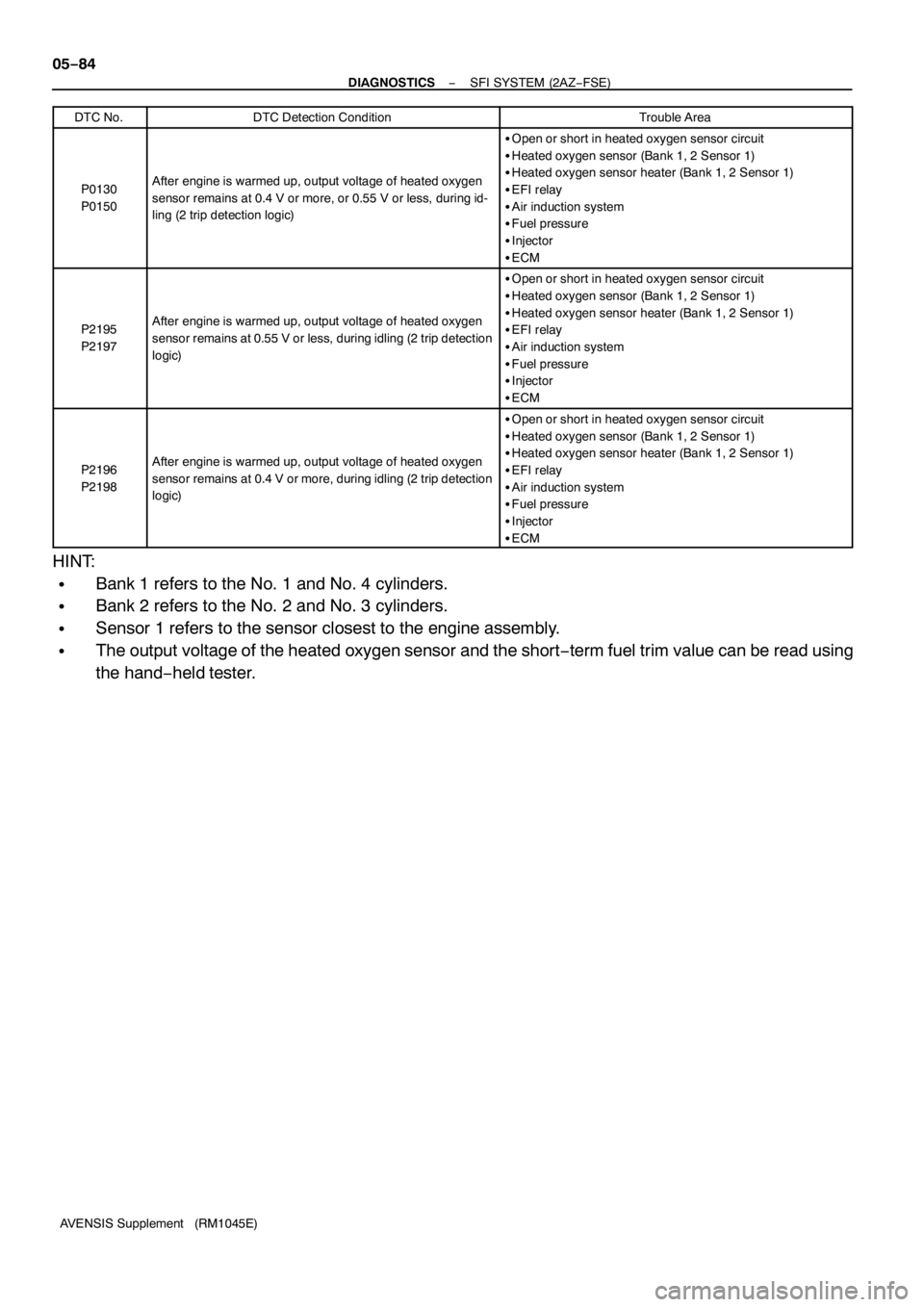
AVENSIS Supplement (RM1045E) DTC No.
DTC Detection ConditionTrouble Area
P0130
P0150After engine is warmed up, output voltage of heated oxygen
sensor remains at 0.4 V or more, or 0.55 V or less, during id-
ling (2 trip detection logic)
SOpen or short in heated oxygen sensor circuit
SHeated oxygen sensor (Bank1, 2 Sensor1)
SHeated oxygen sensor heater (Bank1, 2 Sensor1)
SEFI relay
SAir induction system
SFuel pressure
SInjector
SECM
P2195
P2197After engine is warmed up, output voltage of heated oxygen
sensor remains at 0.55 V or less, during idling (2 trip detection
logic)
SOpen or short in heated oxygen sensor circuit
SHeated oxygen sensor (Bank1, 2 Sensor1)
SHeated oxygen sensor heater (Bank1, 2 Sensor1)
SEFI relay
SAir induction system
SFuel pressure
SInjector
SECM
P2196
P2198After engine is warmed up, output voltage of heated oxygen
sensor remains at 0.4 V or more, during idling (2 trip detection
logic)
SOpen or short in heated oxygen sensor circuit
SHeated oxygen sensor (Bank1, 2 Sensor1)
SHeated oxygen sensor heater (Bank1, 2 Sensor1)
SEFI relay
SAir induction system
SFuel pressure
SInjector
SECM
HINT:
SBank1refers to the No.1and No. 4 cylinders.
SBank 2 refers to the No. 2 and No. 3 cylinders.
SSensor1refers to the sensor closest to the engine assembly.
SThe output voltage of the heated oxygen sensor and the short−term fuel trim value can be read using
the hand−held tester.