2005 SUZUKI JIMNY Connector
[x] Cancel search: ConnectorPage 427 of 687

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 6-70 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS
5 Check Fuel Injectors and Circuit.
1) Using sound scope (4) or such, check operating
sound of each injector (5) when engine is run-
ning. Cycle of operating sound should vary
according to engine speed. See Fig. 3.
If no sound or an unusual sound is heard, check
injector circuit (wire or coupler) or injector.
2) Turn ignition switch OFF and disconnect a fuel
injector connector.
3) Check for proper connection to fuel injector at
each terminal.
4) If OK, then check injector resistance.
See Fig. 4.
Injector resistance
11.3 – 13.8 ohm at 20 °C (68 °F)
5) Carry out steps 1) and 3) on each injector.
6) Check each injector for injected fuel volume
referring to Section 6E. See Fig. 5.
Injected fuel volume
43 – 47 cc/15 sec (1.45/1.51 – 1.58/1.65 US/
Imp.oz/15 sec)
7) Check each injector for fuel leakage after injec-
tor closed.
Fuel leakage
Less than 1 drop / min. (1)
Is check result in step 1) and 3) to 7) satisfactory?Go to Step 6. Check injector circuit or
replace fuel injector(s).
6 Check EVAP Canister Purge Valve.
1) Disconnect purge hose (2) from EVAP canister.
2) Place finger against the end of disconnected
hose.
3) Check that vacuum is not felt there when
engine is cool and running at idle. See Fig. 6.
Is vacuum felt?Check EVAP control
system (See Section
6E).Go to Step 7.
7 Check intake manifold absolute pressure sensor for
performance (See step 4) of DTC P0105 (No.11)
Diag. Flow Table).
Is it in good condition?Go to Step 8. Repair or replace.
8 Check engine coolant temp. sensor for perfor-
mance (See Section 6E).
Is it in good condition?Go to Step 9. Replace engine coolant
temp. sensor.
9 Check intake air temp. sensor for performance
(See Section 6E).
Is it in good condition?Go to Step 10. Replace intake air temp.
sensor.
10 Check throttle position sensor for performance
(See step 5) of DTC P0121 Diag. Flow Table).
Is it in good condition?Go to Step 11. Replace throttle position
sensor.
11 Check PCV valve for valve clogging
(See Section 6E).
Is it good condition?Substitute a known-
good ECM and recheck.Replace PCV valve. Step Action Yes No
Page 431 of 687

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 6-74 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS
3 Check Ignition System.
1) Remove spark plugs and check them for;
Air gap : 1.0 – 1.1 mm (0.040 – 0.043 in.) See Fig. 1.
Carbon deposits / Insulator damage / Plug type
If abnormality is found, adjust, clean or replace by
referring to Section 6F. (See CAUTION)
2) Disconnect all injector connectors. See Fig. 2.
3) Connect spark plugs to high tension cords and then
ground spark plugs.
4) Crank engine and check that each spark plug sparks.
Are above check results satisfactory?Go to Step 4. Check ignition sys-
tem parts (Refer to
Section 6F).
4 Check Fuel Pressure (Refer to Section 6E for details).
1) Release fuel pressure from fuel feed line.
2) Install fuel pressure gauge. See Fig. 3.
3) Check fuel pressure.
Fuel pressure specification
With fuel pump operating and engine at stop :
270 – 310 kPa, 2.7 – 3.1 kg/cm
2, 38.4 – 44.0 psi.
At specified idle speed :
210 – 260 kPa, 2.1 – 2.6 kg/cm
2, 29.8 – 37.0 psi.
Is measured value as specified?Go to Step 5. Go to Diag. Flow
Table B-3 fuel pres-
sure check.
5 Check Fuel Injectors and Circuit.
1) sing sound scope (1) or such, check operating sound
of each injector (2) when engine is running. Cycle of
operating sound should very according to engine
speed. See Fig 4.
If no sound or an unusual sound is heard, check
injector circuit (wire or coupler) or injector.
2) Turn ignition switch OFF and disconnect a fuel injec-
tor connector.
3) Check for proper connection to fuel injector at each
terminal.
4) If OK, then check injector resistance. See Fig. 5.
Injector resistance
11.3 – 13.8 ohm at 20 °C (68 °F)
5) Carry out steps 1) and 3) on each injector.
6) Check each injector for injected fuel volume referring
to Section 6E. See Fig. 6.
Injected fuel volume
43 – 47 cc/15 sec (1.45/1.51 – 1.58/1.65 US/Imp. oz/
15 sec)
7) Check each injector for fuel leakage after injector
closed.
Fuel leakage
Less than 1 drop/min.
Is check result in step 1) and 3) to 7) satisfactory?Go to Step 6. Check injector cir-
cuit or replace fuel
injector(s).
6 Check PCV valve for clogging (See Section 6E).
Is it in good condition?Go to Step 7. Replace PCV
valve. Step Action Yes No
Page 434 of 687
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS 6-77
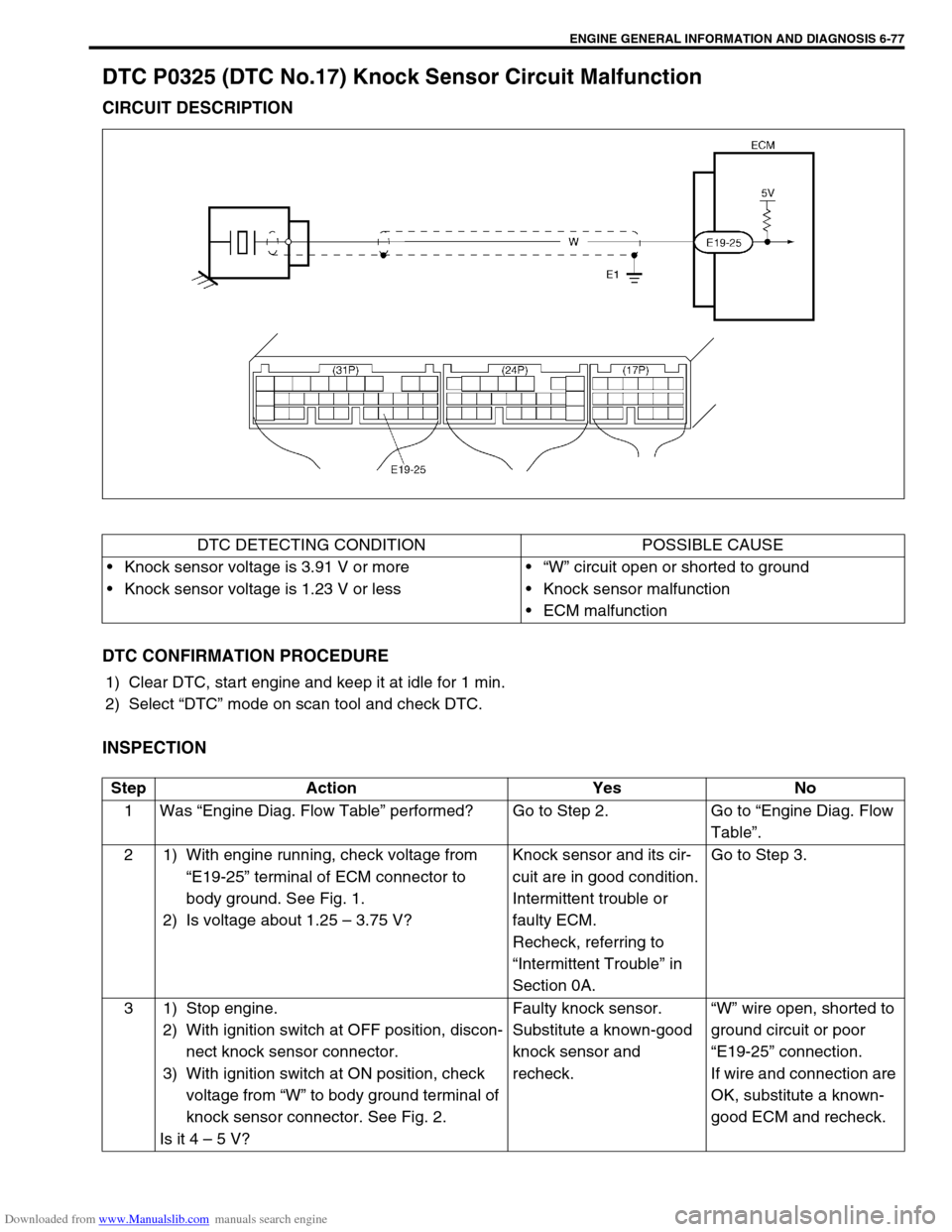
DTC P0325 (DTC No.17) Knock Sensor Circuit Malfunction
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
DTC CONFIRMATION PROCEDURE
1) Clear DTC, start engine and keep it at idle for 1 min.
2) Select “DTC” mode on scan tool and check DTC.
INSPECTION
DTC DETECTING CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE
Knock sensor voltage is 3.91 V or more
Knock sensor voltage is 1.23 V or less“W” circuit open or shorted to ground
Knock sensor malfunction
ECM malfunction
Step Action Yes No
1Was “Engine Diag. Flow Table” performed? Go to Step 2. Go to “Engine Diag. Flow
Table”.
2 1) With engine running, check voltage from
“E19-25” terminal of ECM connector to
body ground. See Fig. 1.
2) Is voltage about 1.25 – 3.75 V?Knock sensor and its cir-
cuit are in good condition.
Intermittent trouble or
faulty ECM.
Recheck, referring to
“Intermittent Trouble” in
Section 0A.Go to Step 3.
3 1) Stop engine.
2) With ignition switch at OFF position, discon-
nect knock sensor connector.
3) With ignition switch at ON position, check
voltage from “W” to body ground terminal of
knock sensor connector. See Fig. 2.
Is it 4 – 5 V?Faulty knock sensor.
Substitute a known-good
knock sensor and
recheck.“W” wire open, shorted to
ground circuit or poor
“E19-25” connection.
If wire and connection are
OK, substitute a known-
good ECM and recheck.
Page 436 of 687

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS 6-79
DTC P0335 (DTC No.23) Crankshaft Position (CKP) Sensor Circuit Malfunction
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
REFERENCE
Connect oscilloscope between terminals E19-23 of ECM connector connected to ECM and body ground and
check CKP sensor signal.
DTC CONFIRMATION PROCEDURE
1) Clear DTC and crank engine for 2 sec.
2) Select “DTC” mode on scan tool and check DTC.
DTC DETECTING CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE
NO CKP sensor signal for 2 seconds at engine crank-
ing.CKP sensor circuit open or short.
Signal teeth damaged.
CKP sensor malfunction, foreign material being
attached or improper installation.
ECM malfunction.
1. 10° signal [A] : Oscilloscope Waveforms [C] : Waveforms at 2000 rpm
2. 30° signal [B] : Waveforms at idle speed
Page 437 of 687
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 6-80 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS
INSPECTION
Step Action Yes No
1Was “Engine Diag. Flow Table” performed? Go to Step 2. Go to “Engine Diag.
Flow Table”.
2 Check CKP Sensor and connector for proper
installation.
Is CKP sensor installed properly and connector
connected securely?Go to Step 3. Correct.
3 Check Wire Harness and Connection.
1) Disconnect connector from CKP sensor.
2) Check for proper connection to CKP sensor at
each terminal.
3) If OK, turn ignition switch ON and check for
voltage at each terminal of sensor connector
disconnected. See Fig. 1.
Terminal “B+” : 10 – 14 V
Terminal “Vout” : 4 – 5 V
Terminal “GND” : 0 V
Is check result satisfactory?Go to Step 5. Go to Step 4.
4 Was terminal “Vout” voltage out of specification in
Step 3 check?“G/R” wire open, short or
poor connection.
If wire and connection are
OK, substitute a known-
good ECM and recheck.“Bl/B” or “B/R” wire
open, short or poor
connection.
5 Check Ground Circuit for Open.
1) Turn ignition switch OFF.
2) Check for continuity between “GND” terminal
of CKP sensor connector and engine ground.
Is continuity indicated?Go to Step 6.“B/R” wire open or
poor ground connec-
tion.
6 Check CKP Sensor for Operation.
1) Remove CKP sensor from sensor case.
2) Remove metal particles on end face of CKP
sensor, if any.
3) Connect each connector to ECM and CKP
sensor.
4) Turn ignition switch ON.
5) Check for voltage at terminal E19-23 of con-
nector connected to ECM by passing magnetic
substance (iron) (1) while keeping approxi-
mately 1 mm (0.03 in.) gap with respect to end
face of CKP sensor. See Fig. 2 and 3.
Does voltage vary from low (0 – 1 V) to high (4 – 5
V) or from high to low?Go to Step 7. Replace CKP sensor.
7 Check signal rotor for the following. See Fig. 4.
Damage
No foreign material attached
Is it in good condition?Intermittent trouble or
faulty ECM.
Check for intermittent
referring to “Intermittent
and Poor Connection” in
Section 0A.Clean rotor teeth or
replace CKP sensor.
Page 439 of 687

Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine 6-82 ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS
DTC P0340 (DTC No.15) Camshaft Position (CMP) Sensor Circuit Malfunction
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
REFERENCE
Connect oscilloscope between terminals E19-11 of ECM connector connected to ECM and body ground and
check CMP sensor signal.
DTC CONFIRMATION PROCEDURE
1) Clear DTC.
2) Start engine and keep it at idle for 1 min.
3) Select “DTC” mode on scan tool and check DTC.
DTC DETECTING CONDITION POSSIBLE CAUSE
The number of CMP sensor signal pulses is incor-
rect during 8 revolution of crankshaft.CMP sensor circuit open or short.
Signal rotor teeth damaged.
CMP sensor malfunction, foreign material being
attached or improper installation.
ECM malfunction.
CMP sensor phase lag.
1. No.1 cylinder 3. No.3 cylinder [A] : Oscilloscope Waveforms [C] : CKP sensor waveform
2. No.2 cylinder 4. No.4 cylinder [B] : Waveforms at specified idle speed [D] : CMP sensor waveform
Page 440 of 687
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS 6-83
INSPECTION
Step Action Yes No
1Was “Engine Diag. Flow Table” performed? Go to Step 2. Go to “Engine Diag.
Flow Table”.
2 Check CMP Sensor and connector for proper installa-
tion.
Is CMP sensor installed properly and connector con-
nected securely?Go to Step 3. Correct.
3 Check Wire Harness and Connection.
1) Disconnect connector from CMP sensor.
2) Check for proper connection to CMP sensor at
each terminal.
3) If OK, turn ignition switch ON and check for volt-
age at each terminal of sensor connector discon-
nected. See Fig. 1.
Terminal “B+” : 10 – 14 V
Terminal “Vout” : 4 – 5 V
Terminal “GND” : 0 V
Is check result satisfactory?Go to Step 5. Go to Step 4.
4 Was terminal “Vout” voltage out of specification in
Step 3 check?“W” wire open, short or
poor connection.
If wire and connection
are OK, substitute a
known-good ECM and
recheck.“Bl/B” or “B/R” wire
open, short or poor
connection.
5 Check Ground Circuit for Open.
1) Turn ignition switch OFF.
2) Check for continuity between “GND” terminal of
CMP sensor connector and engine ground.
Is continuity indicated?Go to Step 6.“B/R” wire open or
poor ground connec-
tion.
6 Check CMP Sensor for Operation.
1) Remove CMP sensor from sensor case.
2) Remove metal particles on end face of CMP sen-
sor, if any.
3) Connect each connector to ECM and CMP sensor.
4) Turn ignition switch ON.
5) Check for voltage at terminal E19-11 of connector
connected to ECM by passing magnetic sub-
stance (iron) (1) while keeping approximately 1
mm (0.03 in.) gap with respect to end face of CMP
sensor. See Fig. 2 and 3.
Does voltage vary from low (0 – 1 V) to high (4 – 5 V)
or from high to low?Go to Step 7. Replace CMP sen-
sor.
7 Check signal rotor for the following.
See Fig. 4.
Damage
No foreign material attached
Is it in good condition?Intermittent trouble or
faulty ECM.
Check for intermittent
referring to “Intermittent
and Poor Connection” in
Section 0A.Clean rotor teeth or
replace CMP sensor.
Page 444 of 687
![SUZUKI JIMNY 2005 3.G Service Workshop Manual Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS 6-87
[A] Fig. 1 for Step 7 / [B] Fig. 2 for Step 3 and 44 With ignition switch at ON, check voltage
b SUZUKI JIMNY 2005 3.G Service Workshop Manual Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS 6-87
[A] Fig. 1 for Step 7 / [B] Fig. 2 for Step 3 and 44 With ignition switch at ON, check voltage
b](/manual-img/20/7588/w960_7588-443.png)
Downloaded from www.Manualslib.com manuals search engine ENGINE GENERAL INFORMATION AND DIAGNOSIS 6-87
[A] Fig. 1 for Step 7 / [B] Fig. 2 for Step 3 and 44 With ignition switch at ON, check voltage
between E19-28, 17, 29, 18 terminals of ECM
and body ground. See Fig. 2.
Is voltage within 10 – 14 V?Go to Step 5. Go to Step 8.
5 Do you have SUZUKI scan tool? Go to Step 6. Stuck or faulty EGR valve
or clogged EGR gas pas-
sage.
If all above are OK, sub-
stitute a known-good
ECM and recheck.
6 Check EGR system referring to “EGR System”
in Section 6E.
Is check result satisfactory?Substitute a known-good
ECM and recheck.Stuck or faulty EGR valve
or clogged EGR gas pas-
sage.
7 1) Disconnect EGR valve connector with igni-
tion switch OFF.
2) Check voltage between “Bl/B” wire terminal
(2) of EGR valve connector (1) and body
ground with ignition switch ON. See Fig. 1.
3) Are they about 10 – 14 V?Go to Step 3.“Bl/B” wire open or short.
8 Check EGR valve referring to “EGR System” in
Section 6E.
Is it good condition?EGR valve harness
(“Gr/B”, “Gr/Bl”, “Gr/R” or
“Gr” wire) open or short or
poor connector connec-
tion (EGR valve connec-
tor, E19-28, 17, 29, 18) If
wire harness and connec-
tion are OK, substitute a
known-good ECM and
recheck.Faulty EGR valve. Step Action Yes No