2004 ISUZU TF SERIES check engine
[x] Cancel search: check enginePage 2642 of 4264

6E–66 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Vehicle service information (service manual, etc.)
ISUZU field support
Ex perience
Identical vehicle or system for comparison
6. Re-examine the complaint
When you do not successfully find/isolate the problem
after ex ecuting a diagnostic path, you should re-
ex amine the complaint.
What you should do
In this case, you will need to backtrack and review
information accumulated from step 1 through 4 of
Strategy Based Diagnostics. You also should repeat any
procedures that require additional attention.
A previous path may be eliminated from consideration
only if you are certain that all steps were ex ecuted as
directed. You must then select another diagnostic path
(step 5a, 5b, 5c or 5d). If all possible options have been
ex plored, you may call or seek ISUZU field support.
What resources you should use
Whenever possible, you should use the following
resources to facilitate the diagnostic process:
Service manual
Accumulated information form a previous diagnostic
path
Service information and publications
ISUZU field support
7. Repair and Verify Fix
What you should do
After you have located the cause of the problem, you
must ex ecute a repair by following recommended
service manual procedures.
When the repair is completed, you should verify the fix
by performing the system checks under the conditions
listed in the customer complaint.
If applicable, you should carry out preventive measures
to avoid a repeat complaint.
What resources you should use
Whenever possible, you should use the following
resources to facilitate the repair process:
Electrical repair procedures
Service manual information and publications
Page 2643 of 4264

ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–67
GENERAL SERVICE INFORMATION
Aftermarket Electrical and Vacuum
Equipment
Aftermarket (add-on) electrical and vacuum equipment
is defined as any equipment which connects to the
vehicle's electrical or vacuum systems that is installed
on a vehicle after it leaves the factory. No allowances
have been made in the vehicle design for this type of
equipment.
NOTE: No add-on vacuum equipment should be added
to this vehicle.
NOTE: Add-on electrical equipment must only be
connected to the vehicle's electrical system at the
battery (power and ground).
Add-on electrical equipment, even when installed to
these guidelines, may still cause the electric system to
malfunction. This may also include equipment not
connected to the vehicle electrical system such as
portable telephones and radios. Therefore, the first step
in diagnosing any electric problem is to eliminate all
aftermarket electrical equipment from the vehicle. After
this is done, if the problem still ex ists, it may be
diagnosed in the normal manner.
Electrostatic Discharge Damage
Electronic components used in the ECM are often
designed to carry very low voltage. Electronic
components are susceptible to damage caused by
electrostatic discharge. Less than 100 volts of static
electricity can cause damage to some electronic
components. By comparison, it takes as much as 4000
volts for a person to feel even the zap of a static
discharge.
There are several ways for a person to become
statically charged. The most common methods of
charging are by friction and induction.
An ex ample of charging by friction is a person sliding
across a vehicle seat.
Charge by induction occurs when a person with well-
insulated shoes stands near a highly charged object
and momentarily touches ground. Charges of the
same polarity are drained off leaving the person
highly charged with the opposite polarity. Static
charges can cause damage, therefore it is important
to use care when handling and testing electronic
components.Non-OEM Parts
All of the OBD diagnostics have been calibrated to run
with OEM parts. Accordingly, if commercially sold
sensor or switch is installed, it makes a wrong diagnosis
and turns on the check engine lamp.
Aftermarket electronics, such as cellular phones,
stereos, and anti-theft devices, may radiate EMI into the
control system if they are improperly installed. This may
cause a false sensor reading and turn on the check
engine lamp.
Poor Vehicle Maintenance
The sensitivity of OBD diagnostics will cause the check
engine lamp to turn on if the vehicle is not maintained
properly. Restricted oil filters, fuel filters, and crankcase
deposits due to lack of oil changes or improper oil
viscosity can trigger actual vehicle faults that were not
previously monitored prior to OBD. Poor vehicle
maintenance can not be classified as a “non-vehicle
fault”, but with the sensitivity of OBD diagnostics,
vehicle maintenance schedules must be more closely
follow ed.
Related System Faults
Many of the OBD system diagnostics will not run if the
ECM detects a fault on a related system or component.
Visual/Physical Engine Compartment
Inspection
Perform a careful visual and physical engine
compartment inspection when performing any
diagnostic procedure or diagnosing the cause of an
emission test failure. This can often lead to repairing a
problem without further steps. Use the following
guidelines when performing a visual/physical
inspection:
Inspect all vacuum hoses for punches, cuts,
disconnects, and correct routing.
Inspect hoses that are difficult to see behind other
components.
Inspect all wires in the engine compartment for
proper connections, burned or chafed spots, pinched
wires, contact with sharp edges or contact with hot
exhaust manifolds or pipes.
Basic Knowledge of Tools Required
NOTE: Lack of basic knowledge of this powertrain
when performing diagnostic procedures could result in
an incorrect diagnosis or damage to powertrain
components. Do not attempt to diagnose a powertrain
problem without this basic knowledge.
A basic understanding of hand tools is necessary to
effectively use this section of the Service Manual.
Page 2644 of 4264

6E–68 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
On-Board Diagnostic (OBD)
On-Board Diagnostic Tests
A diagnostic test is a series of steps, the result of which
is a pass or fail reported to the diagnostic ex ecutive.
When a diagnostic test reports a pass result, the
diagnostic ex ecutive records the following data:
The diagnostic test has been completed since the
last ignition cycle.
The diagnostic test has passed during the current
ignition cycle.
The fault identified by the diagnostic test is not
currently active.
When a diagnostic test reports a fail result, the
diagnostic ex ecutive records the following data:
The diagnostic test has been completed since the
last ignition cycle.
The fault identified by the diagnostic test is currently
active.
The fault has been active during this ignition cycle.
The operating conditions at the time of the failure.
The Diagnostic Executive
The Diagnostic Executive is a unique segment of
software which is designed to coordinate and prioritize
the diagnostic procedures as well as define the protocol
for recording and displaying their results. The main
responsibilities of the Diagnostic Ex ecutive are listed as
follows:
Commanding the check engine lamp on and off
DTC logging and clearing
Current status information on each diagnostic
Diagnostic Information
The diagnostic charts and functional checks are
designed to locate a faulty circuit or component through
a process of logical decisions. The charts are prepared
with the requirement that the vehicle functioned
correctly at the time of assembly and that there are not
multiple faults present.
There is a continuous self-diagnosis on certain control
functions. This diagnostic capability is complemented
by the diagnostic procedures contained in this manual.
The language of communicating the source of the
malfunction is a system of diagnostic trouble codes.
When a malfunction is detected by the control module, a
diagnostic trouble code is set and the check engine
lamp is illumi nated.
Check Engine Lamp
The check engine lamp looks the same as the check
engine lamp you are already familiar with, the “Check
Engine” lamp.
Basically, the check engine lamp is turned on when the
ECM detects a DTC that will impact the vehicle
emissions.
When the check engine lamp remains “ON” while the
engine is running, or when a malfunction issuspected due to a driveability or emissions problem,
a Powertrain On-Board Diagnostic (OBD) System
Check must be performed. The procedures for these
checks are given in On-Board Diagnostic (OBD)
System Check. These checks will ex pose faults
which may not be detected if other diagnostics are
performed first.
Data Link Connector (DLC)
The provision for communication with the contorl
module is the Data Link Connector (DLC). It is located
behind the lower front instrument panel. The DLC is
used to connect to a Tech 2. Some common uses of the
Tech 2 are listed below:
Identifying stored Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs).
Clearing DTCs.
Reading serial data.
Ver ify in g Veh icle Repair
Verification of vehicle repair will be more
comprehensive for vehicles with OBD system
diagnostic. Following a repair, the technician should
perform the following steps:
1. Review and record the Fail Records for the DTC
which has been diagnosed.
2. Clear DTC(s).
3. Operate the vehicle within conditions noted in the
Fail Records.
4. Monitor the DTC status information for the specific
DTC which has been diagnosed until the diagnostic
test associated with that DTC runs.
Following these steps is very important in verifying
repairs on OBD systems. Failure to follow these steps
could result in unnecessary repairs.
Page 2645 of 4264

ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–69
Reading Diagnostic Trouble Codes Using a
Tech 2
The procedure for reading diagnostic trouble code(s) is
to used a diagnostic Tech 2. When reading DTC(s),
follow instructions supplied by Tech 2 manufacturer.
Clearing Diagnostic Trouble Codes
To clear Diagnostic Trouble Codes (DTCs), use the
Te c h 2 “clear DTCs” or “clear information” function.
When clearing DTCs follow instructions supplied by the
Tech 2 manufacturer.
Diagnosis With Tech 2
If no codes are set:
Refer to F1: Data Display and identify the electrical
faults that are not indicated by trouble code.
Refer to “SYMPTOM DIAGNOSIS”.
If codes are set:
1. Record all trouble codes displayed by Tech 2 and
check id the codes are intermittent.
2. Clear the codes.
3. Drive the vehicle for a test to reproduce the faulty
status.
4. Check trouble codes again using the Tech 2.
5. If no codes is displayed by test driving, the fault is
intermittent. In this case, refer to “DIAGNOSIS
AIDS”.
6. If a code is present, refer to DTC Chart for
diagnosis.
7. Check trouble codes again using the Tech 2.
Tech 2 CONNECTION
Tech 2 scan tool is used to electrically diagnose the
automatic transmission system and to check the
system. The Tech 2 enhances the diagnosis efficiency
though all the troubleshooting can be done without the
Te c h 2 .1. Configuration of Tech 2
Tech 2 scan tool kit (No. 7000086), Tech 2 scan
tool (No. 7000057) and DLC cable (No.
3000095).
SAE 16/19 adapter (No. 3000098) (3), RS232
loop back connector (No. 3000112) (2) and
PCMCIA card (No. 3000117) (1).
2. Tech 2 Connection
Check the key switch is turn OFF.
Insert the PCMCIA card (1) into the Tech 2 (5).
Connect the SAE 16/19 adapter (3) to the DLC
cable (4).
Connect the DLC cable (4) to the Tech 2 (5).
Connect the SAE 16/19 adapter (3) to the data
link connector of the vehicle.
Turn the key switch of the vehicle ON and press
the “PWR” key of the Tech 2.
Check the display of the Tech 2.
NOTE: Be sure to check that the power is not supplied
to the Tech 2 when attaching or removing the PCMCIA
card.
Page 2647 of 4264

ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–71
F0: Diagnostic Trouble Code
The purpose of the “Diagnostic Trouble Codes” mod e i s
to display stored trouble code in the ECM.
When “Clear DTC Information” is selected, a “Clear
DTC Information”, warning screen appears.
This screen informs you that by cleaning DTC's “all
stored DTC information in the ECM will be erased”.
After clearing codes, confirm system operation by test
driving the vehicle.
Use the “DTC Information” mode to search for a specific
type of stored DTC information.
History
This selection will display only DTCs that are stored in
the ECM's history memory. It will not display Type B
DTCs that have not requested the MIL (“Check EngineLamp”). It will display all type A and B DTCs that
requested the MIL and have failed within the last 40
warm-up cycles. In addition, it will display all type C and
D DTCs that have failed within the last 40 warm-up
cycles.
MIL SVC or Message Request
This selection will display only DTCs that are requesting
the MIL. Type C and Type D DTCs cannot be displayed
using the MIL. Type C and D DTCs cannot be displayed
using this option.
This selection will report type B DTCs only after the MIL
has been requested.
Last Test Failed
This selection will display only DTCs that have failed the
last time the test run. The last test may have run during
a previous ignition cycle of a type A or type B DTC is
displayed. For type C and type D DTCs, the last failure
must have occurred during the current ignition cycle to
appear as last test fail.
Test Failed Since Code Cleared
The selection will display all active and history DTCs
that have reported a test failure since the last time
DTCs were cleared. DTCs that last failed more that 40
warm-up cycles before this option is selected will not be
displayed.
No Run Since Code Cleared
This selection will display up to DTCs that have not run
since the DTCs were last cleared. Since any displayed
DTCs have not run, their condition (passing or failing) is
unknown.
Failed This Ignition
This selection will display all DTCs that have failed
during the present ignition cycle.
F1: Data Display
The purpose of the “Data Display” mode is to
continuously monitor data parameters.
The current actual values of all important sensors and
signals in the system are display through F1 mode.
See the “Typical Scan Data” section.
F2: Snapshot
“Snapshot” allows you to focus on making the condition
occur, rather than trying to view all of the data in
anticipation of the fault.
The snapshot will collect parameter information around
a trigger point that you select.
F3: Miscellaneous Test:
The purpose of “Miscellaneous Test” mode is to check
for correct operation of electronic system actuators.
F0: Diagnostic Trouble Code
F0: Read DTC Infor By Priority
F1: Clear DTC Information
F2: DTC Information
F0: History
F1: MIL SVS or Message Requested
F2: Last Test Failed
F3: Test Failed Since Code Cleared
F4: Not Run Since Code Cleared
F5: Failed This Ignition
F1: Data Display
F0: Engine Data
F1: O2 Sensor Data
F2: Snapshot
F3: Miscellaneous Test
F0: Lamps
F0: Malfunction Indicator Lamps
F1: Relays
F0: Fuel Pump Relay
F1: A/C Clutch Relay
F2: EVAP
F0: Purge Solenoid
F3: IAC System
F0: IAC Control
F1: IAC Reset
F4: Injector Balance Test
Page 2648 of 4264
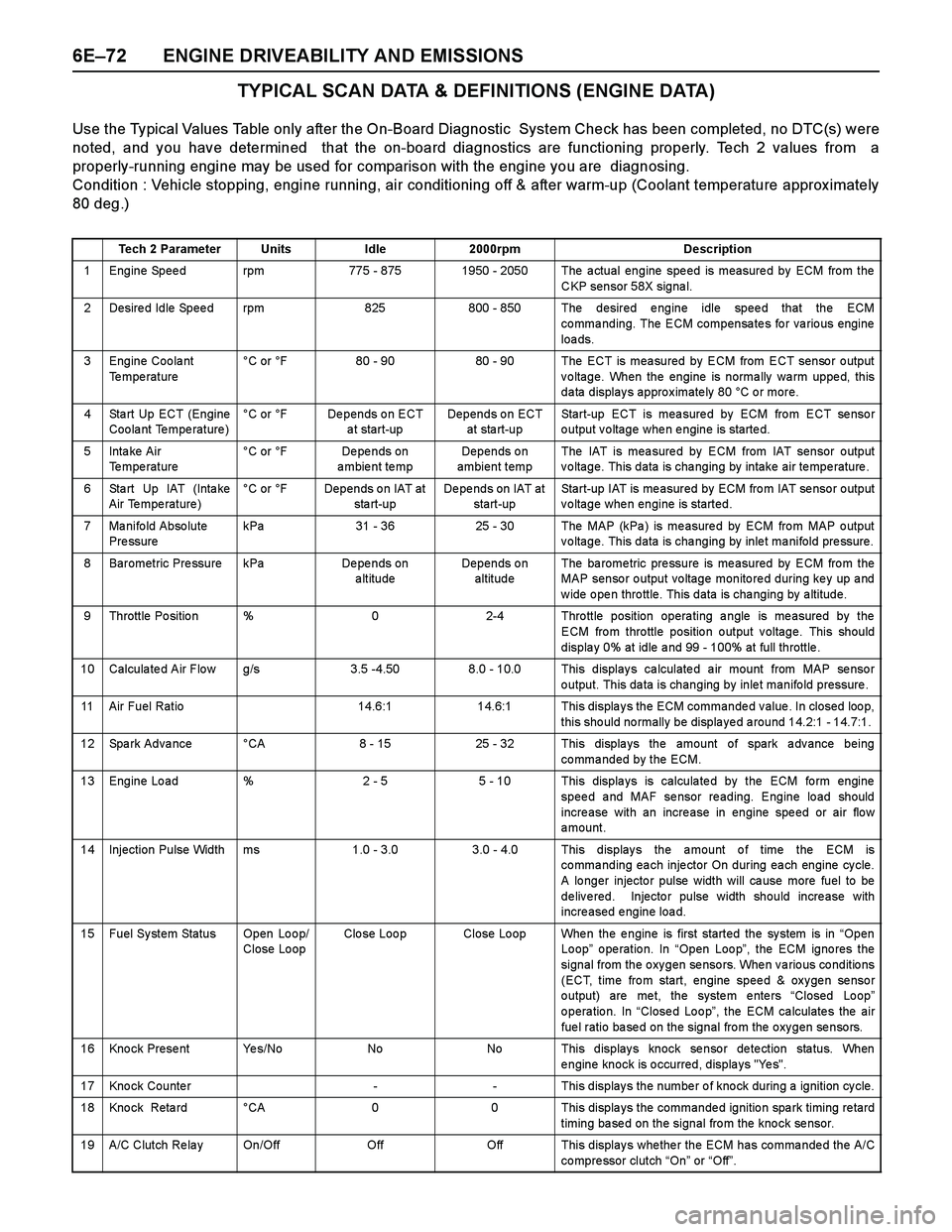
6E–72 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
TYPICAL SCAN DATA & DEFINITIONS (ENGINE DATA)
Use the Typical Values Table only after the On-Board Diagnostic System Check has been completed, no DTC(s) were
noted, and you have determined that the on-board diagnostics are functioning properly. Tech 2 values from a
properly-running engine may be used for comparison with the engine you are diagnosing.
Condition : Vehicle stopping, engine running, air conditioning off & after warm-up (Coolant temperature approx imately
80 deg.)
Tech 2 ParameterUnitsIdle2000rpmDescription
1 Engine Speed rpm775 - 8751950 - 2050 The actual engine speed is measured by ECM from the
CKP sensor 58X signal.
2 Desired Idle Speed rpm825800 - 850 The desired engine idle speed that the ECM
commanding. The ECM compensates for various engine
loa ds.
3 Engine Coolant
Te mpe rature°C or °F80 - 9080 - 90 The ECT is measured by ECM from ECT sensor output
voltage. When the engine is normally warm upped, this
data displays approximately 80 °C or more.
4 Sta rt Up ECT (Engine
Coolant Temperature)°C or °FDepends on ECT
a t start-upDepends on ECT
at sta rt-upStart-up ECT is measured by ECM from ECT sensor
output voltage when engine is started.
5Inta ke Air
Temperature °C or °FDe pe nds on
ambient tempDepends on
ambient tempThe IAT is mea sure d by ECM from IAT sensor o utput
voltage. This data is changing by intake air temperature.
6 Sta rt Up IAT (Inta ke
Air Temperature)°C or °FDepends on IAT at
sta rt-upDepends on IAT at
start-upStart-up IAT is me asured by ECM fro m IAT se nso r o utput
voltage when engine is started.
7 Manifold Absolute
Pre ssurekPa31 - 3625 - 30The MAP (kPa ) is me asure d by ECM fro m MAP o utput
voltage. This data is changing by inlet manifold pressure.
8 Barometric Pressure kPaDe pe nds on
altitudeDepends on
altitudeThe ba rome tric pre ssure is me asured by ECM fro m the
MAP sensor output voltage monitored during key up and
w ide o pe n thro ttle. This data is cha nging by a ltitude.
9 Throttle Position %02-4 Throttle position operating angle is measured by the
ECM from throttle position output voltage. This should
displa y 0% at idle a nd 99 - 100% at full throttle .
10 Calculated Air Flow g/s3.5 -4.508.0 - 10.0 This displays calculated air mount from MAP sensor
output. This data is changing by inlet manifold pressure .
11 Air Fuel Ratio14.6:114.6:1 This displays the ECM commanded value. In closed loop,
this should normally be displayed around 14.2:1 - 14.7:1.
12 Spark Advance °CA8 - 1525 - 32 This displays the amount of spark advance being
commanded by the ECM.
13 Engine Load %2 - 55 - 10 This displays is calculated by the ECM form engine
speed and MAF sensor reading. Engine load should
incre ase with an incre ase in engine spe ed or air flo w
amount.
14 Injection Pulse Width ms1.0 - 3.0 3.0 - 4.0 This displays the amount of time the ECM is
commanding each injector On during each engine cycle.
A lo nger injecto r pulse width will ca use more fuel to be
delivered. Injector pulse width should increase with
increased engine load.
15 Fuel System Status Open Loop/
Close LoopClo se Loo pClose Loop When the engine is first started the system is in “Open
Loop” operation. In “Open Loop”, the ECM ignores the
signal from the oxygen sensors. When various conditions
(ECT, time from start, engine speed & oxygen sensor
o utput) are me t, the syste m e nte rs “Closed Lo op”
o pera tio n. In “Close d Lo o p”, the ECM ca lculate s the air
fuel ratio based on the signal from the oxygen sensors.
16 Knock Present Yes/NoNoNo This displays knock sensor detection status. When
engine knock is occurred, displays "Yes".
17 Knock Counter-- This displays the number of knock during a ignition cycle.
18 Kno ck Reta rd °CA00 This displa ys the commande d ignitio n spa rk timing re tard
timing based on the signal from the knock sensor.
19 A/C Clutch Re la y On/OffOffOff This display s whe the r the ECM has co mma nde d the A/C
co mpre ssor clutch “On” or “Off”.
Page 2649 of 4264
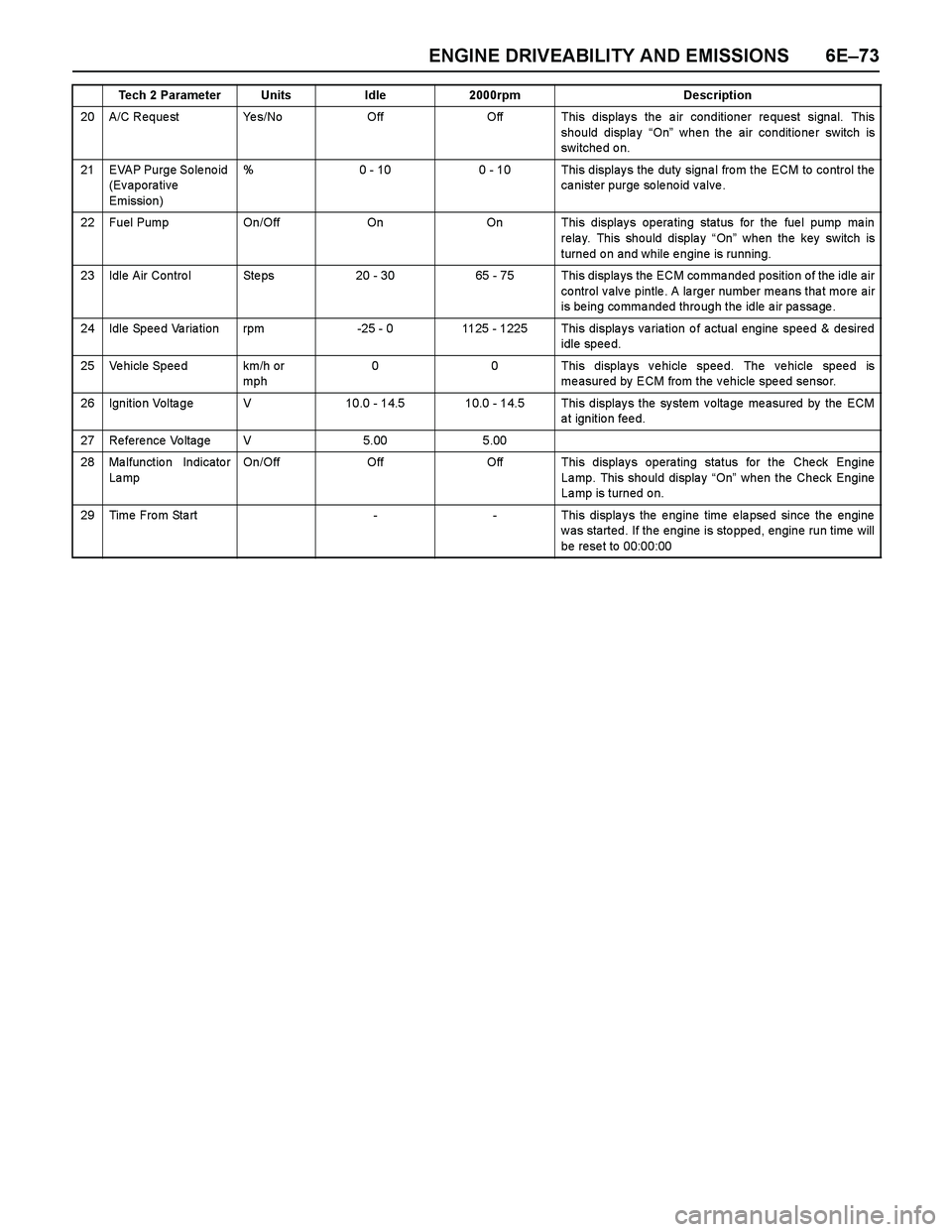
ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–73
20 A/C Reque st Ye s/NoOffOff This displays the air conditioner request signal. This
should display “On” whe n the air conditio ne r switch is
switche d o n.
21 EVAP Purge So le no id
(Evaporative
Emission)%0 - 100 - 10 This display s the duty signa l fro m the ECM to co ntrol the
ca nister purge so le no id v alve .
22 Fuel Pump On/OffOnOn This displays operating status for the fuel pump main
relay. This should display “On” when the key switch is
turned on and while engine is running.
23 Idle Air Contro l Ste ps20 - 3065 - 75 This displays the ECM commanded position of the idle air
control valve pintle. A larger number means that more air
is being commanded through the idle air passage.
24 Idle Speed Variation rpm-25 - 01125 - 1225 This displays variation of actual engine speed & desired
idle speed.
25 Vehicle Speed km/h or
mph00 This displays vehicle speed. The vehicle speed is
me asured by ECM from the v ehicle spe ed senso r.
26 Ignition Voltage V10.0 - 14.510.0 - 14.5 This displays the system voltage measured by the ECM
at ignition feed.
27 Reference Voltage V5.005.00
28 Ma lfunctio n Indicato r
La mpOn/OffOffOff This displays operating status for the Check Engine
La mp. This sho uld displa y “On” when the Check Engine
Lamp is turned on.
29Time From Start--This displays the engine time elapsed since the engine
was started. If the engine is stopped, engine run time will
be rese t to 00:00:00
Tech 2 ParameterUnitsIdle2000rpmDescription
Page 2650 of 4264
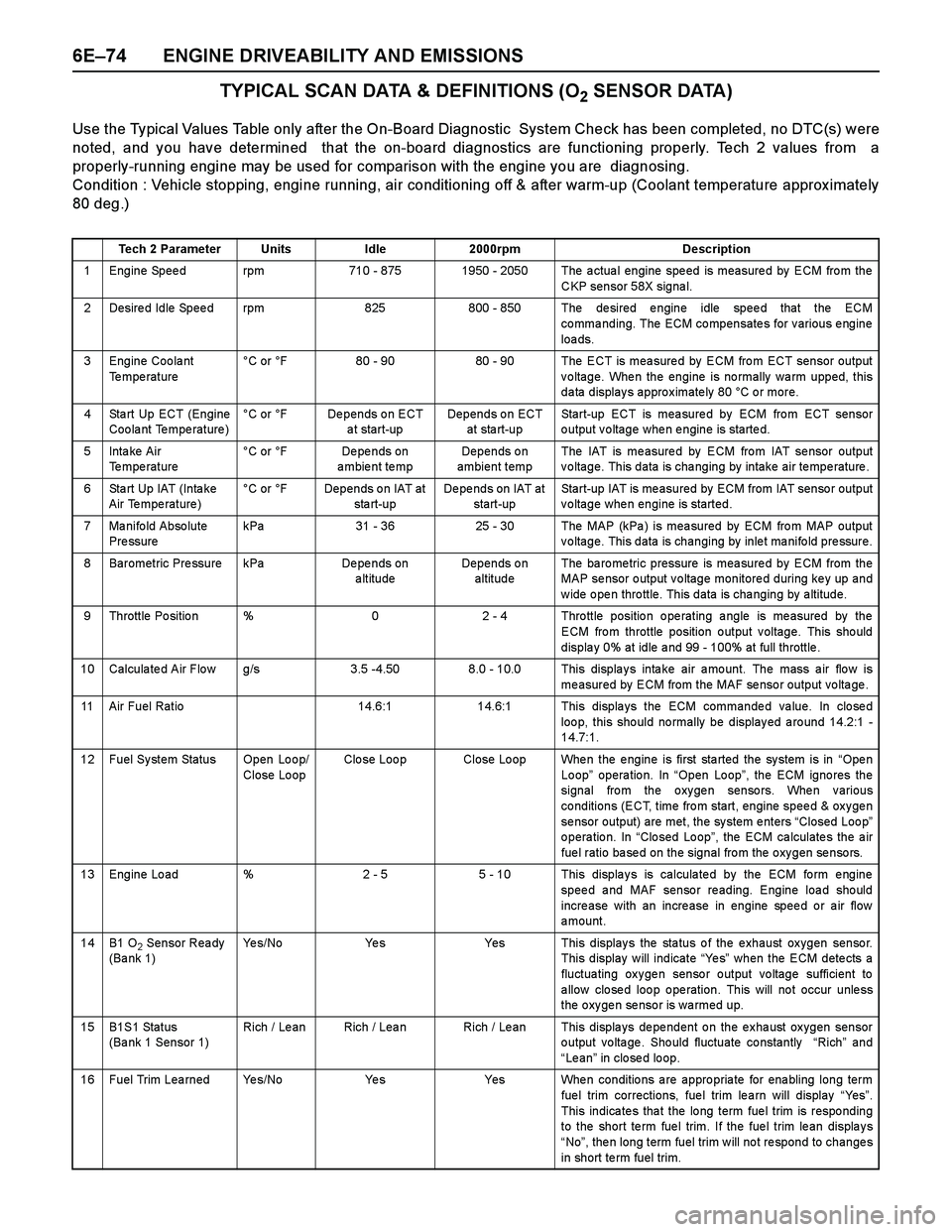
6E–74 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
TYPICAL SCAN DATA & DEFINITIONS (O2 SENSOR DATA)
Use the Typical Values Table only after the On-Board Diagnostic System Check has been completed, no DTC(s) were
noted, and you have determined that the on-board diagnostics are functioning properly. Tech 2 values from a
properly-running engine may be used for comparison with the engine you are diagnosing.
Condition : Vehicle stopping, engine running, air conditioning off & after warm-up (Coolant temperature approx imately
80 deg.)
Tech 2 ParameterUnitsIdle2000rpmDescription
1 Engine Speed rpm710 - 8751950 - 2050 The actual engine speed is measured by ECM from the
CKP sensor 58X signal.
2 Desired Idle Speed rpm825800 - 850 The desired engine idle speed that the ECM
commanding. The ECM compensates for various engine
loa ds.
3 Engine Coolant
Te mpe rature°C or °F80 - 9080 - 90 The ECT is measured by ECM from ECT sensor output
voltage. When the engine is normally warm upped, this
data displays approximately 80 °C or more.
4 Sta rt Up ECT (Engine
Coolant Temperature)°C or °FDepends on ECT
a t start-upDepends on ECT
at sta rt-upStart-up ECT is measured by ECM from ECT sensor
output voltage when engine is started.
5Inta ke Air
Temperature °C or °FDe pe nds on
ambient tempDepends on
ambient tempThe IAT is me asure d by ECM fro m IAT se nsor output
voltage. This data is changing by intake air temperature.
6 Sta rt Up IAT (Inta ke
Air Temperature)°C or °FDepends on IAT at
sta rt-upDepends on IAT at
start-upStart-up IAT is measured by ECM from IAT sensor output
voltage when engine is started.
7 Manifold Absolute
Pre ssurekPa31 - 3625 - 30The MAP (kPa ) is mea sured by ECM fro m MAP output
voltage. This data is changing by inlet manifold pressure.
8 Barometric Pressure kPaDe pe nds on
altitudeDepends on
altitudeThe ba ro me tric pressure is mea sure d by ECM from the
MAP se nsor o utput v o ltage monitore d during ke y up and
w ide o pe n thro ttle. This data is cha nging by a ltitude.
9 Throttle Position %02 - 4 Throttle position operating angle is measured by the
ECM from throttle position output voltage. This should
displa y 0% at idle a nd 99 - 100% at full throttle .
10 Calculated Air Flow g/s3.5 -4.508.0 - 10.0 This displays intake air amount. The mass air flow is
measured by ECM from the MAF sensor output voltage.
11 Air Fuel Ratio14.6:114.6:1 This displays the ECM commanded value. In closed
loo p, this sho uld no rmally be display ed a ro und 14.2:1 -
14.7:1.
12 Fuel System Status Open Loop/
Close LoopClo se Loo pClose Loop When the engine is first started the system is in “Ope n
Loop” operation. In “Open Loop”, the ECM igno res the
signal from the oxygen sensors. When various
conditions (ECT, time from start, engine speed & oxygen
sensor output) are met, the system enters “Closed Loop”
operation. In “Closed Loop”, the ECM calculates the air
fuel ratio based on the signal from the oxygen sensors.
13 Engine Load %2 - 55 - 10 This displays is calculated by the ECM form engine
speed and MAF sensor reading. Engine load should
increase with an increase in engine speed or air flow
amount.
14B1 O2 Sensor Ready
(Ba nk 1)Ye s / N oYe sYes This displays the status of the exhaust oxygen sensor.
This display will indicate “Ye s” when the ECM detects a
fluctuating oxygen sensor output voltage sufficient to
a llow clo se d loo p o pe ration. This will no t occur unle ss
the oxygen sensor is warmed up.
15B1S1 Status
(Bank 1 Sensor 1)Rich / Le anRich / LeanRich / Lean This displays dependent on the exhaust oxygen sensor
output voltage. Should fluctuate constantly “Rich” and
“Le an” in closed loop.
16 Fuel Trim Learned Yes/NoYe sYes When conditions are appropriate for enabling long term
fue l trim corrections, fue l trim le a rn will display “Ye s”.
This indica te s tha t the lo ng term fue l trim is respo nding
to the short te rm fue l trim. If the fue l trim le an displa y s
“No”, then long term fuel trim will not respond to changes
in short te rm fuel trim.