2004 ISUZU TF SERIES check engine
[x] Cancel search: check enginePage 2624 of 4264
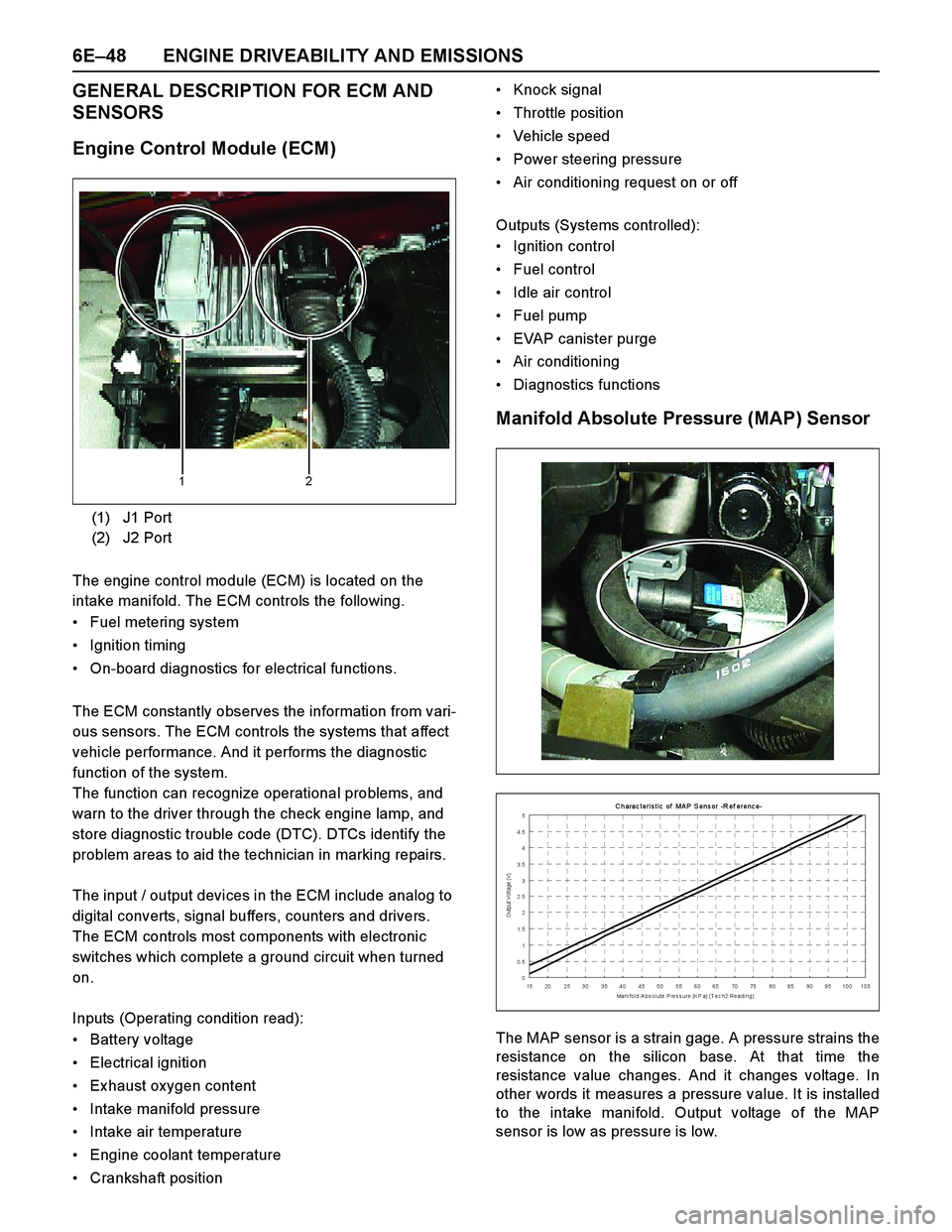
6E–48 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
GENERAL DESCRIPTION FOR ECM AND
SENSORS
Engine Control Module (ECM)
The engine control module (ECM) is located on the
intake manifold. The ECM controls the following.
Fuel metering system
Ignition timing
On-board diagnostics for electrical functions.
The ECM constantly observes the information from vari-
ous sensors. The ECM controls the systems that affect
vehicle performance. And it performs the diagnostic
function of the system.
The function can recognize operational problems, and
warn to the driver through the check engine lamp, and
store diagnostic trouble code (DTC). DTCs identify the
problem areas to aid the technician in marking repairs.
The input / output devices in the ECM include analog to
digital converts, signal buffers, counters and drivers.
The ECM controls most components with electronic
switches which complete a ground circuit when turned
on.
Inputs (Operating condition read):
Battery voltage
Electrical ignition
Ex haust oxygen content
Intake manifold pressure
Intake air temperature
Engine coolant temperature
Crankshaft positionKnock signal
Throttle position
Vehicle speed
Power steering pressure
Air conditioning request on or off
Outputs (Systems controlled):
Ignition control
Fuel control
Idle air control
Fuel pump
EVAP canister purge
Air conditioning
Diagnostics functions
Manifold Absolute Pressure (MAP) Sensor
The MAP sensor is a strain gage. A pressure strains the
resistance on the silicon base. At that time the
resistance value changes. And it changes voltage. In
other words it measures a pressure value. It is installed
to the intake manifold. Output voltage of the MAP
sensor is low as pressure is low. (1) J1 Port
(2) J2 Port
12
C h arac teris tic of MA P S ens or -R ef erenc e-
0 0.51 1.52 2.53 3.54 4.55
15 20 25 30 35 40 45 50 55 60 65 70 75 80 85 90 95 100 105
Mani fold A bs olute P res s ure (K P a) (T ec h2 Reading)
Output Voltage (V)
Page 2628 of 4264

6E–52 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
GENERAL DESCRIPTION FOR FUEL
METERING
The fuel metering system starts with the fuel in the fuel
tank. An electric fuel pump, located in the fuel tank,
pumps fuel to the fuel rail through an in-line fuel filter.
The pump is designed to provide fuel at a pressure
above the pressure needed by the injectors.
A fuel pressure regulator in the fuel rail keeps fuel
available to the fuel injectors at a constant pressure.
A return line delivers unused fuel back to the fuel tank.
The basic function of the air/fuel metering system is to
control the air/fuel delivery to the engine. Fuel is
delivered to the engine by individual fuel injectors
mounted in the intake manifold.
The main control sensor is the heated ox ygen sensor
located in the ex haust system. The heated ox ygen
sensor reports to the ECM how much oxygen is in the
ex haust gas. The ECM changes the air/fuel ratio to the
engine by controlling the amount of time that fuel
injector is “On”.
The best mix ture to minimize exhaust emissions is 14.7
parts of air to 1 part of gasoline by weight, which allows
the catalytic converter to operate most efficiently.
Because of the constant measuring and adjusting of the
air/fuel ratio, the fuel injection system is called a “closed
loop” system.
The ECM monitors signals from several sensors in
order to determine the fuel needs of the engine. Fuel is
delivered under one of several conditions called “mode”.
All modes are controlled by the ECM.
Battery Voltage Correction Mode
When battery voltage is low, the ECM will compensate
for the weak spark by increasing the following:
The amount of fuel delivered.
The idle RPM.
Clear Flood Mode
Clear a flooded engine by pushing the accelerator pedal
down all the way. The ECM then de-energizes the fuel
injectors. The ECM holds the fuel injectors de-energized
as long as the throttle remains above 75% and the
engine speed is below 800 RPM. If the throttle position
becomes less than 75%, the ECM again begins to pulse
the injectors ON and OFF, allowing fuel into the
cylinders.
Deceleration Fuel Cutoff (DFCO) Mode
The ECM reduces the amount of fuel injected when it
detects a decrease in the throttle position and the air
flow. When deceleration is very fast, the ECM may cut
off fuel completely. Until enable conditions meet the
engine revolution less 1000 rpm or manifold absolute
pressure less than 10 kPa.
Engine Speed/ Vehicle Speed/ Fuel Disable
Mode
The ECM monitors engine speed. It turns off the fuel
injectors when the engine speed increases above 6000
RPM. The fuel injectors are turned back on when
engine speed decreases below 3500 RPM.
Acceleration Mode
The ECM provides ex tra fuel when it detects a rapid
increase in the throttle position and the air flow.
Fuel Cutoff Mode
No fuel is delivered by the fuel injectors when the
ignition is OFF. This prevents engine run-on. In addition,
the ECM suspends fuel delivery if no reference pulses
are detected (engine not running) to prevent engine
flooding.
Starting Mode
When the ignition is first turned ON, the ECM energizes
the fuel pump relay for two seconds to allow the fuel
pump to build up pressure. The ECM then checks the
engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor and the
throttle position sensor to determine the proper air/fuel
ratio for starting.
The ECM controls the amount of fuel delivered in the
starting mode by adjusting how long the fuel injectors
are energized by pulsing the injectors for very short
times.
Run Mode
The run mode has the following two conditions:
Open loop
Closed loop
When the engine is first started, the system is in “open
loop” operation. In “Open Loop,” the ECM ignores the
signal from the heated oxygen sensor (HO2S). It
calculates the air/fuel ratio based on inputs from the TP,
ECT, and MAP sensors.
The system remains in “Open Loop” until the following
conditions are met:
The HO2S has a varying voltage output showing that
it is hot enough to operate properly (this depends on
temperature).
The ECT has reached a specified temperature.
A specific amount of time has elapsed since starting
the engine.
Engine speed has been greater than a specified RPM
since start-up.
The specific values for the above conditions vary with
different engines and are stored in the programmable
read only memory (PROM). When these conditions are
met, the system enters “closed loop” operation. In
“closed loop,” the ECM calculates the air/fuel ratio
(injector on-time) based on the signal from the HO2S.
This allows the air/fuel ratio to stay very close to 14.7:1.
Page 2630 of 4264
6E–54 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
GENERAL DESCRIPTION FOR ELECTRIC
IGNITION SYSTEM
The engine use two ignition coils, one per two cylinders.
A two wire connector provides a battery voltage primary
supply through the ignition fuse.
The ignition control spark timing is the ECM’s method of
controlling the spark advance and the ignition dwell.
The ignition control spark advance and the ignition dwell
are calculated by the ECM using the following inputs.
Engine speed
Crankshaft position (CKP) sensor
Engine coolant temperature (ECT) sensor
Throttle position sensor
Vehicle speed sensor
ECM and ignition system supply voltage
Ignition coil works to generate only the secondary
voltage be receiving the primary voltage from ECM.
The primary voltage is generated at the coil driver
located in the ECM. The coil driver generate the primary
voltage based on the crankshaft position signal. In
accordance with the crankshaft position signal, ignition
coil driver determines the adequate ignition timing and
also cylinder number to ignite.
Ignition timing is determined the coolant temperature,
intake air temperature, engine speed, engine load,
knock sensor signal, etc.
Spark Plug
Although worn or dirty spark plugs may give satisfactory
operation at idling speed, they frequently fail at higher
engine speeds. Faulty spark plugs may cause poor fuel
economy, power loss, loss of speed, hard starting and
generally poor engine performance. Follow the
scheduled maintenance service recommendations to
ensure satisfactory spark plug performance. Refer to
Maintenance and Lubrication.
Normal spark plug operation will result in brown to
grayish-tan deposits appearing on the insulator portion
of the spark plug. A small amount of red-brown, yellow,
and white powdery material may also be present on the
insulator tip around the center electrode. These
deposits are normal combustion by-products of fuels
and lubricating oils with additives. Some electrode wear
will also occur. Engines which are not running properly
are often referred to as “misfiring.” This means the
ignition spark is not igniting the air/fuel mix ture at the
proper time. While other ignition and fuel system causes
must also be considered, possible causes include
ignition system conditions which allow the spark voltage
to reach ground in some other manner than by jumping
across the air gap at the tip of the spark plug, leaving
the air/fuel mix ture unburned. Misfiring may also occur
when the tip of the spark plug becomes overheated and
ignites the mixture before the spark jumps. This is
referred to as “pre-ignition.”
Spark plugs may also misfire due to fouling, ex cessive
gap, or a cracked or broken insulator. If misfiring occursbefore the recommended replacement interval, locate
and correct the cause.
Carbon fouling of the spark plug is indicated by dry,
black carbon (soot) deposits on the portion of the spark
plug in the cylinder. Ex cessive idling and slow speeds
under light engine loads can keep the spark plug
temperatures so low that these deposits are not burned
off. Very rich fuel mix tures or poor ignition system output
may also be the cause. Refer to DTC P1167.
Oil fouling of the spark plug is indicated by wet oily
deposits on the portion of the spark plug in the cylinder,
usually with little electrode wear. This may be caused by
oil during break-in of new or newly overhauled engines.
Deposit fouling of the spark plug occurs when the
normal red-brown, yellow or white deposits of
combustion by-products become sufficient to cause
misfiring. In some cases, these deposits may melt and
form a shiny glaze on the insulator around the center
electrode. If the fouling is found in only one or two
cylinders, valve stem clearances or intake valve seals
may be allowing ex cess lubricating oil to enter the
cylinder, particularly if the deposits are heavier on the
side of the spark plug facing the intake valve.
Ex cessive gap means that the air space between the
center and the side electrodes at the bottom of the
spark plug is too wide for consistent firing. This may be
due to improper gap adjustment or to ex cessive wear of
the electrode during use. A check of the gap size and
comparison to the gap specified for the vehicle in
Maintenance and Lubrication will tell if the gap is too
wide. A spark plug gap that is too small may cause an
unstable idle condition. Ex cessive gap wear can be an
indication of continuous operation at high speeds or
with engine loads, causing the spark to run too hot.
Another possible cause is an ex cessively lean fuel
mixture.
Page 2634 of 4264

6E–58 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Damaged EVAP canister
Leaking fuel sender assembly O-ring
Leaking fuel tank or fuel filler neck
The ECM supplies a ground to energize the purge
control solenoid valve (purge “ON” ). The EVAP purge
control is turned “ON” and “OFF,” several times a
second. The duty cycle (pulse width) is determined by
engine operating conditions including load, throttle
position, coolant temperature and ambient temperature.
The duty cycle is calculated by the ECM and the output
is commanded when the appropriate conditions have
been met.
The system checks for conditions that cause the EVAP
system to purge continuously by commanding the EVAP
purge solenoid “OFF”, EVAP purge solenoid duty ratio
“0%”. If fuel tank vacuum level increases during the test,
a continuous purge flow condition is indicated. This can
be caused by the following conditions:
EVAP purge solenoid leaking
EVAP purge and engine vacuum lines switched at the
EVAP purge control solenoid valve
EVAP purge control solenoid valve driver circuit
grounded
Page 2638 of 4264

6E–62 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
Diagnostic Thought Process
As you follow a diagnostic plan, every box on the
Strategy Based Diagnostics chart requires you to use
the diagnostic thought process. This method of thinking
optimizes your diagnosis in the following ways:
Improves your understanding and definition of the
customer complaint
Saves time by avoiding testing and/or replacing good
parts
Allows you to look at the problem from different
perspectives
Guides you to determine what level of understanding
about system operation is needed:
–Owner’s manual level
–Service manual level
–In-depth (engineering) level
–Owner’s manual level
–Service manual level
–In-depth (engineering) level
1. Verify the Complaint
What you should do
To verify the customer complaint, you need to know the
correct (normal) operating behavior of the system and
verify that the customer complaint is a valid failure of the
system.
The following information will help you verify the
complaint:
WHAT the vehicle model/options are
WHAT aftermarket and dealer-installed accessories
exist
WHAT related system(s) operate properly
WHEN the problem occurs
WHERE the problem occurs
HOW the problem occurs
HOW LONG the condition has ex isted (and if the
system ever worked correctly)
HOW OFTEN the problem occurs
Whether the severity of the problem has increased,
decreased or stayed the same
What resources you should use
Whenever possible, you should use the following
resources to assist you in verifying the complaint:
Service manual Theory or Circuit Description
sections
Service manual “System Performance Check”
Owner manual operational description
Technician ex perience
Identical vehicle for comparisonCircuit testing tools
Vehicle road tests
Complaint check sheet
Contact with the customer
2. Perform Preliminary Checks
NOTE: An estimated 10 percent of successful vehicle
repairs are diagnosed with this step!
What you should do
You perform preliminary checks for several reasons:
To detect if the cause of the complaint is VISUALLY
OBVIOUS
To identify parts of the system that work correctly
To accumulate enough data to correctly and
accurately search for a ISUZU Service Bulletin on
ISUZU Web site.
The initial checks may vary depending on the
complex ity of the system and may include the following
actions:
Operate the suspect system
Make a visual inspection of harness routing and
accessible/visible power and ground circuits
Check for blown fuses
Make a visual inspection for separated connectors
Make a visual inspection of connectors (includes
checking terminals for damage and tightness)
Check for any DTCs stored by the on-board
computers
Sense unusual noises, smells, vibrations or
mov ements
Investigate the vehicle service history (call other
dealerships, if appropriate)
What resources you should use
Whenever appropriate, you should use the following
resources for assistance in performing preliminary
checks:
Tech II or other technical equipment for viewing DTCs
Service manual information:
–Component locations
–Harness routing
–Wiring schematics
–Procedures for viewing DTCs
Dealership service history file
Vehicle road test
Identical vehicle or system for comparison
Page 2639 of 4264

ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–63
3. Check Bulletins and
Troubleshooting Hints
NOTE: As estimated 30 percent of successful vehicle
repairs are diagnosed with this step!
What you should do
You should have enough information gained from
preliminary checks to accurately search for a bulletin
and other related service information. Some service
manual sections provide troubleshooting hints that
match symptoms with specific complaints.
What resources you should use
You should use the following resources for assistance in
checking for bulletins and troubleshooting hints:
Printed bulletins
Access ISUZU Bulletin Web site.
Videotapes
Service manual
4. Perform Service Manual
Diagnostic Checks
What you should do
The “System Checks” in most service manual sections
and in most cells of section 8A (electrical) provide you
with:
A systematic approach to narrowing down the
possible causes of a system fault
Direction to specific diagnostic procedures in the
service manual
Assistance to identify what systems work correctly
What resources you should use
Whenever possible, you should use the following
resources to perform service manual checks:
Service manual
Technical equipment (for viewing DTCs and
analyzing data)
Digital multimeter and circuit testing tools
Other tools as needed
5a and 5b. Perform Service Manual
Diagnostic Procedures
NOTE: An estimated 40 percent of successful vehicle
repairs are diagnosed with these steps!
What you should do
When directed by service manual diagnostic checks,
you must then carefully and accurately perform the
steps of diagnostic procedures to locate the fault relatedto the customer complaint.
What resources you should use
Whenever appropriate, you should use the following
resources to perform service manual diagnostic
procedures:
Service manual
Technical equipment (for analyzing diagnostic data)
Digital multimeter and circuit testing tools
Essential and special tools
5c. Technician Self Diagnoses
When there is no DTC stored and no matching
symptom for the condition identified in the service
manual, you must begin with a thorough understanding
of how the system(s) operates. Efficient use of the
service manual combined with you ex perience and a
good process of elimination will result in accurate
diagnosis of the condition.
What you should do
Step 1: Identify and understand the suspect
circuit(s)
Having completed steps 1 through 4 of the Strategy
Based Diagnostics chart, you should have enough
information to identify the system(s) or sub-system(s)
involved. Using the service manual, you should
determine and investigate the following circuit
characteristics:
Electrical:
–How is the circuit powered (power distribution
charts and/or fuse block details)?
–How is the circuit grounded (ground distribution
charts)?
–How is the circuit controlled or sensed (theory of
operation):
–If it is a switched circuit, is it normally open or
normally closed?
–Is the power switched or is the ground
switched?
–Is it a variable resistance circuit (ECT sensor
or TP sensor, for ex ample)?
–Is it a signal generating device (MAF sensor of
VSS, for example)?
–Does it rely on some mechanical/vacuum
device to operate?
Physical:
–Where are the circuit components (component
locators and wire harness routing diagrams):
–Are there areas where wires could be chafed
or pinched (brackets or frames)?
–Are there areas subjected to ex treme
temperatures?
Page 2640 of 4264

6E–64 ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS
–Are there areas subjected to vibration or
movement (engine, transmission or
suspension)?
–Are there areas ex posed to moisture, road salt
or other corrosives (battery acid, oil or other
fluids)?
–Are there common mounting areas with other
systems/components?
–Have previous repairs been performed to wiring,
connectors, components or mounting areas
(causing pinched wires between panels and
drivetrain or suspension components without
causing and immediate problem)?
–Does the vehicle have aftermarket or dealer-
installed equipment (radios, telephone, etc.)
Step 2: Isolate the problem
At this point, you should have a good idea of what could
cause the present condition, as well as could not cause
the condition. Actions to take include the following:
Divide (and separate, where possible) the system or
circuit into smaller sections
Confine the problem to a smaller area of the vehicle
(start with main harness connections while removing
panels and trim as necessary in order to eliminate
large vehicle sections from further investigation)
For two or more circuits that do not share a common
power or ground, concentrate on areas where
harnesses are routed together or connectors are
shared (refer to the following hints)
Hints
Though the symptoms may vary, basic electrical failures
are generally caused by:
Loose connections:
–Open/high resistance in terminals, splices,
connectors or grounds
Incorrect connector/harness routing (usually in new
vehicles or after a repair has been made):
–Open/high resistance in terminals, splices,
connectors of grounds
Corrosion and wire damage:
–Open/high resistance in terminals, splices,
connectors of grounds
Component failure:
–Opens/short and high resistance in relays,
modules, switches or loads
Aftermarket equipment affecting normal operation of
other systems
You may isolate circuits by:
Unplugging connectors or removing a fuse to
separate one part of the circuit from another part
Operating shared circuits and eliminating those that
function normally from the suspect circuit
If only one component fails to operate, begin testingat the component
If a number of components do no operate, begin tests
at the area of commonality (such as power sources,
ground circuits, switches or major connectors)
What resources you should use
Whenever appropriate, you should use the following
resources to assist in the diagnostic process:
Service manual
Technical equipment (for data analysis)
Ex perience
Technical Assistance
Circuit testing tools
5d. Intermittent Diagnosis
By definition, an intermittent problem is one that does
not occur continuously and will occur when certain
conditions are met. All these conditions, however, may
not be obvious or currently known. Generally,
intermittents are caused by:
Faulty electrical connections and wiring
Malfunctioning components (such as sticking relays,
solenoids, etc.)
EMI/RFI (Electromagnetic/radio frequency
interference)
Aftermarket equipment
Intermittent diagnosis requires careful analysis of
suspected systems to help prevent replacing good
parts. This may involve using creativity and ingenuity to
interpret customer complaints and simulating all
ex ternal and internal system conditions to duplicate the
problem.
What you should do
Step 1: A cquire information
A thorough and comprehensive customer check sheet
is critical to intermittent problem diagnosis. You should
require this, since it will dictate the diagnostic starting
point. The vehicle service history file is another
source for accumulating information about the
complaint.
Step 2: A nalyze the intermittent problem
Analyze the customer check sheet and service history
file to determine conditions relevant to the suspect
system(s).
Using service manual information, you must identify,
trace and locate all electrical circuits related to the
malfunctioning system(s). If there is more than one
system failure, you should identify, trace and locate
areas of commonality shared by the suspect circuits.
Page 2641 of 4264

ENGINE DRIVEABILITY AND EMISSIONS 6E–65
Step 3: Simulate the symptom and isolate the
problem
Simulate the symptom and isolate the system by
reproducing all possible conditions suggested in Step 1
while monitoring suspected circuits/components/
systems to isolate the problem symptom. Begin with the
most logical circuit/component.
Isolate the circuit by dividing the suspect system into
simpler circuits. Nex t, confine the problem into a smaller
area of the system. Begin at the most logical point (or
point of easiest access) and thoroughly check the
isolated circuit for the fault, using basic circuit tests.
Hints
You can isolate a circuit by:
Unplugging connectors or removing a fuse to
separate one part of the circuit from another
If only component fails to operate, begin testing the
component
If a number of components do not operate, begin test
at areas of commonality (such as power sources,
ground circuits, switches, main connectors or major
components)
Substitute a known good part from the parts
department or the vehicle system
Try the suspect part in a known good vehicle
See Symptom Simulation Tests on the nex t page for
problem simulation procedures. Refer to service manual
sections 6E and 8A for information about intermittent
diagnosis. Follow procedures for basic circuit testing in
service manual section 8A.
What resources you should use
Whenever appropriate, you should use the following
resources to assist in the diagnostic process:
Service manual
Bulletins
Digital multimeter (with a MIN/MAX feature)
Tech II and Tech II upload function
Circuit testing tools (including connector kits/
harnesses and jumper wires)
Ex perience
Intermittent problem solving simulation methods
Customer complaint check sheet
Symptom Simulation Tests
1. Vibration
This method is useful when the customer complaint
analysis indicates that the problem occurs when the
vehicle/system undergoes some form of vibration.
For connectors and wire harness, slightly shake
vertically and horizontally. Inspect the connector joint
and body for damage. Also, tapping lightly along a
suspected circuit may be helpful.For parts and sensors, apply slight vibration to the part
with a light tap of the finger while monitoring the system
for a malfunction.
2. Heat
This method is important when the complaint suggests
that the problem occurs in a heated environment. Apply
moderate heat to the component with a hair drier or
similar tool while monitoring the system for a
malfunction.
CA UTION: Care must be take to avoid overheating
the component.
3. Water and Moisture
This method may be used when the complaint suggests
that the malfunction occurs on a rainy day or under
conditions of high humidity. In this case, apply water in a
light spray on the vehicle to duplicate the problem.
CA UTION: Care must be take to avoid directly
exposing electrical connections to water.
4. Electrical loads
This method involves turning systems ON (such as the
blower, lights or rear window defogger) to create a load
on the vehicle electrical system at the same time you
are monitoring the suspect circuit/component.
5e. Vehicle Operates as Designed
This condition refers to instances where a system
operating as designed is perceived to be unsatisfactory
or undesirable. In general, this is due to:
A lack of understanding by the customer
A conflict between customer ex pectations and
vehicle design intent
A system performance that is unacceptable to the
customer
What you should do
You can verify that a system is operating as designed
by:
Reviewing service manual functional/diagnostic
checks
Ex amining bulletins and other service information for
supplementary information
Compare system operation to an identical vehicle
If the condition is due to a customer misunderstanding
or a conflict between customer ex pectation and system
operation, you should ex plain the system operation to
the customer.
If the complaint is due to a case of unsatisfactory
system performance, you should contact Technical
Assistance for the latest information.
What resources you should use
Whenever possible, you should use the following
resources to facilitate the diagnostic process: