Page 435 of 4264

BRAKES 5C-9
MAIN DATA AND SPECIFICATIONS
FRONT DISC BRAKE mm(in.) 4 �
2 4 �
4, 4 �
2 HIGH RIDE
Caliper type Pin slide
Disc outside diameter 256(10.079) 280 (11.023)
Disc thickness 26(1.024) 27 (1.063)
Piston diameter 42.8 (1.685) �
2 45.5 (1.79)
Adjustment method Self-adjusting
REAR DRUM BRAKE mm(in.) 4 �
2 4 �
4
Type Leading and Trailing
Drum inside diameter 254(10.008) 295 (11.614)
Brake lining dimension 244 �
50 �
5 283 �
45 �
5
(Length � Width � Thickness) (9.57 � 1.97 � 0.20) (11.14 � 1.77 � 0.20)
Adjustment method Self-adjusting
WHEEL CYLINDER mm(in.)
Inside diameter : rear 25.4 (1.000) 23.8 (0.937)
MASTER CYLINDER mm(in.)
Type Split
Bore diameter 25.4 (1.000)
Piston stroke (Primary + Secondary) 21.8 + 12 (0.86 + 0.47)
VACUUM SERVO mm(in.) 6VE1/C24NE 4JA1-T/4JA1-TC/4JH1-TC
Diaphragm diameter 205(8.077) + 230(9.055) 180(7.087) + 205(8.077)
4JA1-T
Power cylinder stroke 35 (1.378)
PEDAL RATIO 3.7
BALANCE EBD (with ABS)
Type Load sensing proportioning valve (without ABS)
Blend valve (without ABS)
Page 436 of 4264
5C-10 BRAKES
TORQUE SPECIFICATIONS
FRONT WHEEL BRAKE N�m(kgf�m/lb�ft)
E05R300016
Page 437 of 4264
BRAKES 5C-11
REAR WHEEL DRUM BRAKE N�
m(kgf�
m/lb�
in)
E05R300014-1
Page 446 of 4264

5C-20 BRAKES
�
�� � Operation
The operation of the P-valve by the master cylinde
r
pressure is unchanged up to the brake points
A and B.
If master cylinder fluid pressure penetrates into the second
break point
B, the fluid pressure pressing against the seal
2, (which isolated route 4 and route 5), passing the route
4of the master cylinder side, overcomes the operating
force of the spring
3 + fluid pressure affecting the seal 2of
the wheel cylinder, and presses the piston
1to the right
side, resulting in the opening of the routes
4 and 5, and
canceling of the P-valve operation.
Then, because the master cylinder fluid pressure and the
wheel cylinder fluid pressure, up to the point
C, operate on
the identical surface of the seal
2, both have identical
ascending ratio.
However, because of the operation of spring
3 in the wheel
cylinder side, wheel cylinder fluid pressure operate to
preserve the balance against the master cylinder fluid
pressure on the lower level with the difference in pressure
resulting from this spring.
03260002-2
Valve Maintenance
In the case of fluid leak or other abnormalities, faulty valve
should be replaced.
The valve is set up at the engine room.
Note:
The blend proportioning valve is not repairable and must
be replaced as a complete assembly.
Page 448 of 4264
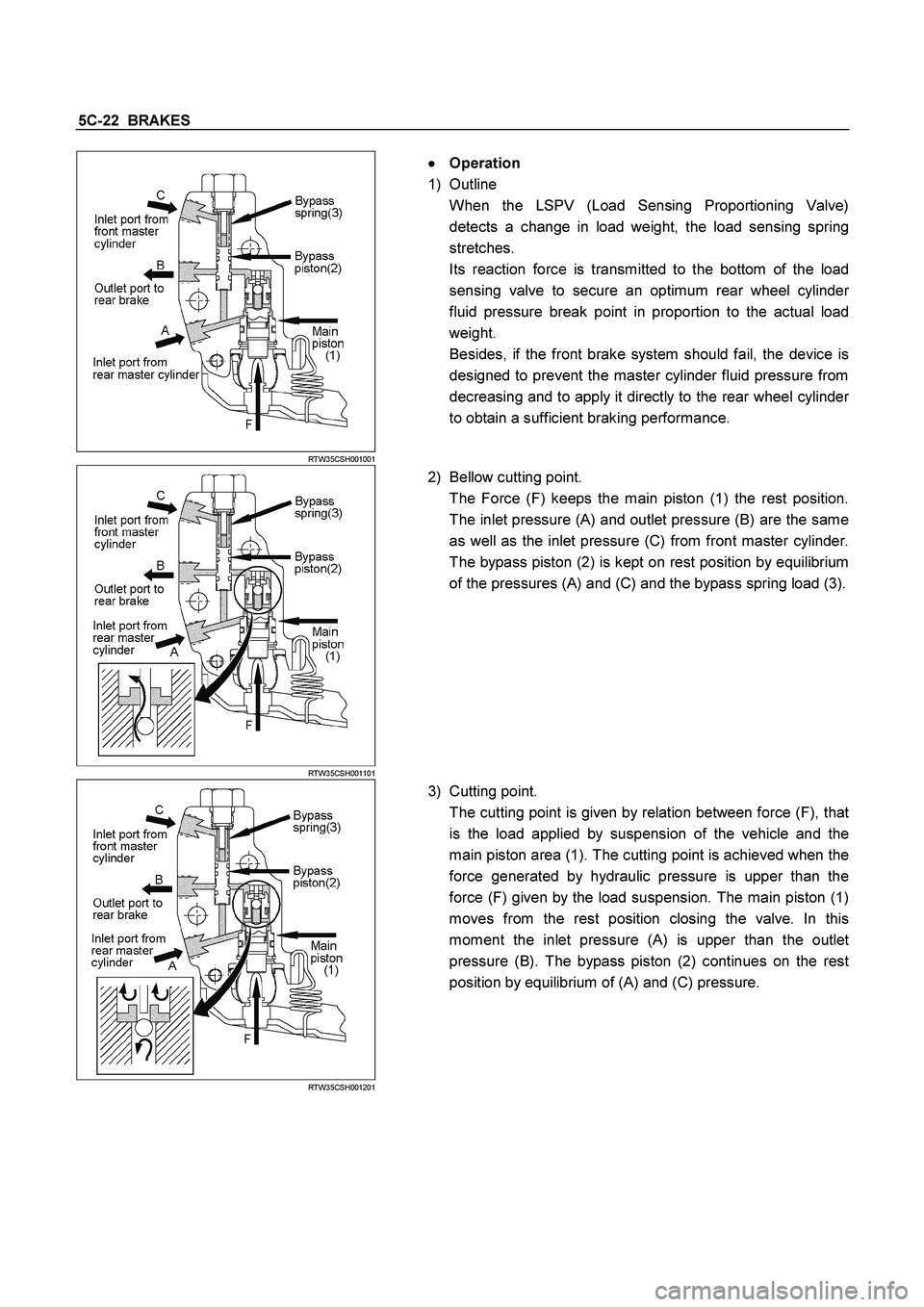
5C-22 BRAKES
RTW35CSH001001
�
�� � Operation
1) Outline
When the LSPV (Load Sensing Proportioning Valve)
detects a change in load weight, the load sensing spring
stretches.
Its reaction force is transmitted to the bottom of the load
sensing valve to secure an optimum rear wheel cylinde
r
fluid pressure break point in proportion to the actual load
weight.
Besides, if the front brake system should fail, the device is
designed to prevent the master cylinder fluid pressure from
decreasing and to apply it directly to the rear wheel cylinde
r
to obtain a sufficient braking performance.
RTW35CSH001101
2) Bellow cutting point.
The Force (F) keeps the main piston (1) the rest position.
The inlet pressure (A) and outlet pressure (B) are the same
as well as the inlet pressure (C) from front master cylinder.
The bypass piston (2) is kept on rest position by equilibrium
of the pressures (A) and (C) and the bypass spring load (3).
RTW35CSH001201
3) Cutting point.
The cutting point is given by relation between force (F), tha
t
is the load applied by suspension of the vehicle and the
main piston area (1). The cutting point is achieved when the
force generated by hydraulic pressure is upper than the
force (F) given by the load suspension. The main piston (1)
moves from the rest position closing the valve. In this
moment the inlet pressure (A) is upper than the outle
t
pressure (B). The bypass piston (2) continues on the res
t
position by equilibrium of (A) and (C) pressure.
Page 449 of 4264

BRAKES 5C-23
RTW35CSH001301
4) Failure on front master cylinder.
In case of failure on front master cylinder the pressure on
the inlet port (C) drop to zero. The pressure from inlet por
t
(A) acts on the bypass piston (2) and move it by comprising
of bypass spring (3). It makes possible the communication
between the inlet port (A) to outlet port (B) through the
bypass system. The outlet pressure (B) reaches the inle
t
pressure (A) and the LSPV is bypassed.
Valve Maintenance
In the case to fluid lead or other a abnormalities, faulty valve
should be replaced.
Note:
The load sensing proportioning valve is not repairable and
must be replaced as a completed assembly.
LOAD SENSING PROPORTIONING
VALVE (LSPV) ADJUSTMENT
RTW35CSH000301
1. Fluid Pressure Measurement
1) Rear axle weight adjustment
With an axle eight meter, adjust the rear axle weight with
a person sitting in the driver’s seat and a weight loaded
in the rear body.
N (kg/lb)
MODEL Adjustment value
4 �
2 7845 (800/1764)
4 � 2 HIGH RIDE
4 �
4 9316 (950/2095)
RTW35CSH000101
2) Installation of a fluid pressure gauge
Remove the air bleeder of the left hand wheel front and
rear brakes. Bleed air out of the fluid pressure gauge
with the measurement hose of the fluid pressure gauge
installed.
Pressure Tester: Brake oil (Fluid pressure gauge)
5-8840-2190-0
Page 450 of 4264

5C-24 BRAKES
RTW35CSH000201
3) Rear wheel cylinder fluid pressure measurement
Step on the brake pedal until the fluid pressure of the
front wheel cylinder gets to 9.8Mpa (100kg/cm
2), and
check the rear wheel cylinder fluid pressure. (Read the
value of the front wheel cylinder fluid pressure 2
seconds after the measurement. When measuring the
L.S.V fluid pressure, keep the brake pedal pressed
down without stepping it down twice or releasing it.)
Rear Wheel Cylinder Fluid Pressure MPa (kg/cm
2)
2WD 6.77�0.83 (69.0�8.5)
2WD (With High Ride
Suspension), 4WD 6.77�
0.83 (69.0�
8.5)
RTW35CSH000401
2. Oil Pressure Adjustment
1) LSPV spring length adjustment
Loosen the adjust nut of the LSPV spring joint, and
adjust the length of the LSPV spring.
When the oil pressure is insufficient, turn the adjust nu
t
clockwise to extend the span “A”. When the oil pressure
is too high, turn the adjust nut counterclockwise to
reduce the span “A”.
2) After adjustment, tighten the lock nut securely.
Lock Nut Torque N�m (kg�m/lb in)
11-20 (1.1-2.0/95-174)
Page 451 of 4264

BRAKES 5C-25
Filling Master Cylinder Reservoir
CAUTION :
Use only specified brake fluid. Do not use any fluid which
contains a petroleum base. Do not use a container which
has been used for petroleum based fluids or a container
which is wet with water. Petroleum based fluid will cause
swelling and distortion of rubber parts in the hydraulic
brake system. Water mixed with brake fluid lowers the
fluid boiling point. Keep all fluid containers capped to
prevent contamination.
Always fill the master cylinder reservoir when the engine
is cold.
Never allow the brake fluid to come in contact with the
painted surfaces.
The master cylinder reservoir must be kept properly filled
to ensure adequate reserve and to prevent air and
moisture from entering the hydraulic system. However,
because of expansion due to heat absorbed from the
brakes and the engine, the reservoir must not be
overfilled. Thoroughly clean reservoir cap before removal
to avoid getting dirt into reservoir. Add fluid as required to
bring level to the “MAX” mark on the reservoir tank. Use
“DOT 3” Hydraulic Brake Fluid.
Leakage of Brake Fluid
With engine idling, set shift lever in the neutral position and
continue to depress brake pedal at a constant pedal
application force.
Should the pedal stroke become deeper gradually, leakage
from the hydraulic pressure system is possible.
Make sure by visual check that there is no leak.
BLEEDING OF THE BRAKE HYDRAULIC
CIRCUIT
If air enters the bake lines, it will cause poor brake action.
Therefore, bleeding should be performed if the brakes have
been used with the level of brake fluid in the reservoir
excessively low or if brake pipes have been disconnected in
the course of brake servicing.
Bleeding operation calls for co-operative action of 2 persons.
�
Set the parking brake firmly while bleeding.
�
Perform bleeding operation with ENGINE RUNNING, to
prevent damage to push rod seal.
Make sure exhaust is suitably ventilated.
�
Bleed the hydraulic system with the fluid reservoir filled to
the specified level.
�
Bleed the system starting with the rear wheel cylinde
r
farthest from the master cylinder.