Page 2783 of 4500
Fig. 100: Inspecting Shift Solenoid Valve (S1)
Courtesy of TOYOTA MOTOR SALES, U.S.A., INC.
NG: REPLACE SHIFT SOLENOID VALVE (S1)
OK: Go to next step
3.INSPECT TRANSMISSION VALVE BODY ASSY (See chapter 2 in PROBLEM SYMPTOMS
TABLE )
OK:
There are no foreign objects on each valve and they operate smoothly.
NG: REPAIR OR REPLACE TRANSMISSION VALVE BODY ASSY (See step 6 on
REPLACEMENT
)
OK: Go to next step
4.INSPECT TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH ASSY (See INSPECTION
)
Page 2784 of 4500
OK:
The torque converter clutch operates normally.
NG: REPLACE TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH ASSY
OK: REPAIR OR REPLACE AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION ASSY (See COMPONENTS
)
DTC P0756: SHIFT SOLENOID "B" PERFORMANCE (SHIFT SOLENOID VALVE S2)
SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
The ECM uses signals from the output shaft speed sensor and input speed sensor to detect the actual gear
position (1st, 2nd, 3rd, 4th, 5th or 6th gear).
Then the ECM compares the actual gear with the shift schedule in the ECM memory to detect mechanical
problems of the shift solenoid valves and valve body.
Fig. 101: DTC Reference Chart
Courtesy of TOYOTA MOTOR SALES, U.S.A., INC.
HINT:
Gear positions in the event of a solenoid valve mechanical problem:
Page 2791 of 4500
TABLE )
OK:
There are no foreign objects on each valve and they operate smoothly.
NG: REPAIR OR REPLACE TRANSMISSION VALVE BODY ASSY (See step 6 on
REPLACEMENT
)
OK: Go to next step
4.INSPECT TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH ASSY (See INSPECTION
)
OK:
The torque converter clutch operates normally.
NG: REPLACE TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH ASSY
OK: REPAIR OR REPLACE AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION ASSY (See COMPONENTS
)
DTC P0761: SHIFT SOLENOID "C" PERFORMANCE (SHIFT SOLENOID VALVE S3)
SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
The ECM uses signals from the output shaft speed sensor and input speed sensor to detect the actual gear
position (1st, 2nd, 3rd, 4th, 5th or 6th gear).
Then the ECM compares the actual gear with the shift schedule in the ECM memory to detect mechanical
problems of the shift solenoid valves and valve body.
Page 2801 of 4500
There are no foreign objects on each valve and they operate smoothly.
NG: REPAIR OR REPLACE TRANSMISSION VALVE BODY ASSY (See step 6 on
REPLACEMENT
)
OK: Go to next step
5.INSPECT TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH ASSY (See INSPECTION
)
OK:
The torque converter clutch operates normally.
NG: REPLACE TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH ASSY
OK: REPAIR OR REPLACE AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION ASSY (See COMPONENTS
)
DTC P0766: SHIFT SOLENOID "D" PERFORMANCE (SHIFT SOLENOID VALVE S4)
SYSTEM DESCRIPTION
The ECM uses signals from the output shaft speed sensor and input speed sensor to detect the actual gear
position (1st, 2nd, 3rd, 4th, 5th or 6th gear).
Then the ECM compares the actual gear with the shift schedule in the ECM memory to detect mechanical
problems of the shift solenoid valves and valve body.
Fig. 112: DTC Reference Chart
Courtesy of TOYOTA MOTOR SALES, U.S.A., INC.
HINT:
Gear positions in the event of a solenoid valve mechanical problem:
Page 2811 of 4500

NG: REPLACE SHIFT SOLENOID VALVE (SL2)
OK: Go to next step
5.INSPECT TRANSMISSION VALVE BODY ASSY (See chapter 2 in PROBLEM SYMPTOMS
TABLE )
OK:
There are no foreign objects on each valve and they operate smoothly.
NG: REPAIR OR REPLACE TRANSMISSION VALVE BODY ASSY (See step 6 on
REPLACEMENT
)
OK: Go to next step
6.INSPECT TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH ASSY (See INSPECTION
)
OK:
The torque converter clutch operates normally.
NG: REPLACE TORQUE CONVERTER CLUTCH ASSY
OK: REPAIR OR REPLACE AUTOMATIC TRANSMISSION ASSY (See COMPONENTS
)
DTC P0778: PRESSURE CONTROL SOLENOID "B" ELECTRICAL (SHIFT SOLENOID VALVE
SL2)
CIRCUIT DESCRIPTION
Shifting from 1st to 6th is performed in combination with "ON" and "OFF" operation of the shift solenoid
valves SL1, SL2, S1, S2, S3, S4 and SR which is controlled by the ECM. If an open or short circuit occurs in
either of the shift solenoid valves, the ECM controls the remaining normal shift solenoid valve to allow the
vehicle to be operated smoothly (see FAIL
-SAFE CHART ).
Fig. 119: DTC Reference Chart
Courtesy of TOYOTA MOTOR SALES, U.S.A., INC.
MONITOR DESCRIPTION
Page 2820 of 4500
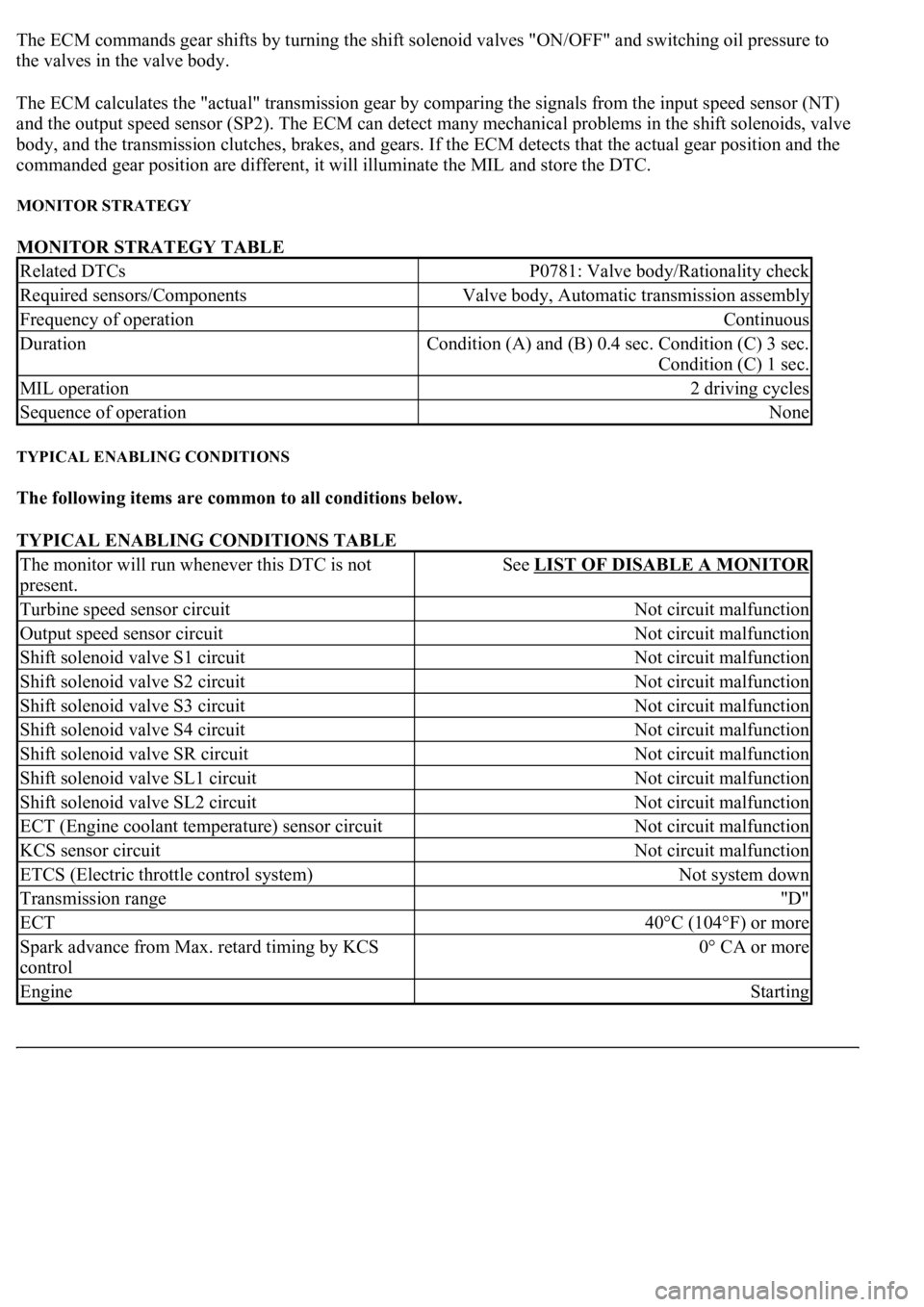
The ECM commands gear shifts by turning the shift solenoid valves "ON/OFF" and switching oil pressure to
the valves in the valve body.
The ECM calculates the "actual" transmission gear by comparing the signals from the input speed sensor (NT)
and the output speed sensor (SP2). The ECM can detect many mechanical problems in the shift solenoids, valve
body, and the transmission clutches, brakes, and gears. If the ECM detects that the actual gear position and the
commanded gear position are different, it will illuminate the MIL and store the DTC.
MONITOR STRATEGY
MONITOR STRATEGY TABLE
TYPICAL ENABLING CONDITIONS
The following items are common to all conditions below.
TYPICAL ENABLING CONDITIONS TABLE
Related DTCsP0781: Valve body/Rationality check
Required sensors/ComponentsValve body, Automatic transmission assembly
Frequency of operationContinuous
Duration<0026005200510047004c0057004c005200510003000b0024000c00030044005100470003000b0025000c00030013001100170003005600480046001100030026005200510047004c0057004c005200510003000b0026000c00030016000300560048004600
110003[
Condition (C) 1 sec.
MIL operation2 driving cycles
Sequence of operationNone
The monitor will run whenever this DTC is not
present.See LIST OF DISABLE A MONITOR
Turbine speed sensor circuitNot circuit malfunction
Output speed sensor circuitNot circuit malfunction
Shift solenoid valve S1 circuitNot circuit malfunction
Shift solenoid valve S2 circuitNot circuit malfunction
Shift solenoid valve S3 circuitNot circuit malfunction
Shift solenoid valve S4 circuitNot circuit malfunction
Shift solenoid valve SR circuitNot circuit malfunction
Shift solenoid valve SL1 circuitNot circuit malfunction
Shift solenoid valve SL2 circuitNot circuit malfunction
ECT (Engine coolant temperature) sensor circuitNot circuit malfunction
KCS sensor circuitNot circuit malfunction
ETCS (Electric throttle control system)Not system down
Transmission range"D"
ECT40°C (104°F) or more
Spark advance from Max. retard timing by KCS
control0° CA or more
EngineStarting
Page 2857 of 4500
Fig. 161: DTC Reference Chart
Courtesy of TOYOTA MOTOR SALES, U.S.A., INC.
MONITOR DESCRIPTION
The ECM calculates the amount of heat absorbed by the friction material based on the difference in revolution
(clutch slippage) between the turbine and output shaft. The ECM turns on the MIL and outputs this DTC when
the amount of heat absorption exceeds the specified value.
When the shift solenoid valve SLT remains on, oil pressure goes down and clutch engagement force decreases.
MONITOR STRATEGY
MONITOR STRATEGY TABLE
TYPICAL ENABLING CONDITIONS
ON malfunction
Related DTCsP2714: Shift solenoid valve SLT/ON malfunction
Required sensors/ComponentsShift solenoid valve SLT
Frequency of operationContinuous
DurationBetween starting in the 1st gear and stopping in the
4th gear
MIL operation2 driving cycles
Sequence of operationNone
Page 2858 of 4500
Fig. 162: Typical Enabling Conditions Chart
Courtesy of TOYOTA MOTOR SALES, U.S.A., INC.
TYPICAL MALFUNCTION THRESHOLDS
ON malfunction
TYPICAL MALFUNCTION THRESHOLDS TABLE
WIRING DIAGRAM
Summation of C1 clutch heat generations = -->
(Turbine speed - Output speed x Temporary gear
ratio) xKSpecified value