Page 380 of 486
All-Wheel Drive
If you have an all-wheel-drive vehicle, be sure to
perform the lubricant checks described in this section.
However, they have two additional systems that
need lubrication.
Transfer Case (Power Transfer Unit)
When to Check Lubricant
Refer to the Maintenance Schedule to determine how
often to check the lubricant. SeePart C: Periodic
MaintenanceInspections on page 6-15.
How to Check Lubricant
To get an accurate reading, the vehicle should be on a
level surface.
If the level is below the bottom of the ®ller plug hole,
you'll need to add some lubricant. Add enough lubricant
to raise the level to the bottom of the ®ller plug hole.
What to Use
Refer to the Maintenance Schedule to determine what
kind of lubricant to use. SeePart D: Recommended
Fluids and Lubricants on page 6-17.
5-50
Page 392 of 486
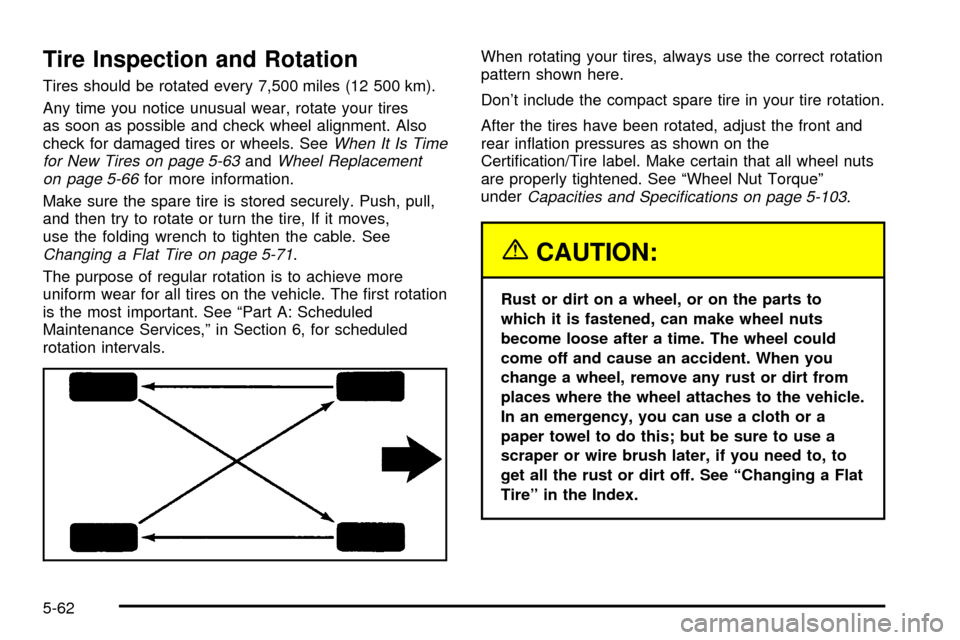
Tire Inspection and Rotation
Tires should be rotated every 7,500 miles (12 500 km).
Any time you notice unusual wear, rotate your tires
as soon as possible and check wheel alignment. Also
check for damaged tires or wheels. See
When It Is Time
for New Tires on page 5-63andWheel Replacement
on page 5-66for more information.
Make sure the spare tire is stored securely. Push, pull,
and then try to rotate or turn the tire, If it moves,
use the folding wrench to tighten the cable. See
Changing a Flat Tire on page 5-71.
The purpose of regular rotation is to achieve more
uniform wear for all tires on the vehicle. The ®rst rotation
is the most important. See ªPart A: Scheduled
Maintenance Services,º in Section 6, for scheduled
rotation intervals.When rotating your tires, always use the correct rotation
pattern shown here.
Don't include the compact spare tire in your tire rotation.
After the tires have been rotated, adjust the front and
rear in¯ation pressures as shown on the
Certi®cation/Tire label. Make certain that all wheel nuts
are properly tightened. See ªWheel Nut Torqueº
under
Capacities and Speci®cations on page 5-103.
{CAUTION:
Rust or dirt on a wheel, or on the parts to
which it is fastened, can make wheel nuts
become loose after a time. The wheel could
come off and cause an accident. When you
change a wheel, remove any rust or dirt from
places where the wheel attaches to the vehicle.
In an emergency, you can use a cloth or a
paper towel to do this; but be sure to use a
scraper or wire brush later, if you need to, to
get all the rust or dirt off. See ªChanging a Flat
Tireº in the Index.
5-62
Page 394 of 486

Buying New Tires
To ®nd out what kind and size of tires you need, look at
the Certi®cation/Tire label.
The tires installed on your vehicle when it was new had
a Tire Performance Criteria Speci®cation (TPC Spec)
number on each tire's sidewall. When you get new tires,
get ones with that same TPC Spec number. That way
your vehicle will continue to have tires that are designed
to give proper endurance, handling, speed rating,
traction, ride and other things during normal service on
your vehicle. If your tires have an all-season tread
design, the TPC number will be followed by an ªMSº (for
mud and snow).
If you ever replace your tires with those not having a
TPC Spec number, make sure they are the same size,
load range, speed rating and construction type (bias,
bias-belted or radial) as your original tires.{CAUTION:
Mixing tires could cause you to lose control
while driving. If you mix tires of different sizes
or types (radial and bias-belted tires), the
vehicle may not handle properly, and you
could have a crash. Using tires of different
sizes may also cause damage to your vehicle.
Be sure to use the same size and type tires on
all wheels. It's all right to drive with your
compact spare temporarily, it was developed
for use on your vehicle. See ªCompact Spare
Tireº in the index.
{CAUTION:
If you use bias-ply tires on your vehicle, the
wheel rim ¯anges could develop cracks after
many miles of driving. A tire and/or wheel
could fail suddenly, causing a crash. Use only
radial-ply tires with the wheels on your vehicle.
5-64
Page 396 of 486

Temperature ± A, B, C
The temperature grades are A (the highest), B, and C,
representing the tire's resistance to the generation
of heat and its ability to dissipate heat when tested
under controlled conditions on a speci®ed indoor
laboratory test wheel. Sustained high temperature can
cause the material of the tire to degenerate and
reduce tire life, and excessive temperature can lead to
sudden tire failure. The grade C corresponds to a
level of performance which all passenger car tires must
meet under the Federal Motor Vehicle Safety Standard
No. 109. Grades B and A represent higher levels of
performance on the laboratory test wheel than the
minimum required by law.
Warning: The temperature grade for this tire is
established for a tire that is properly in¯ated and not
overloaded. Excessive speed, underin¯ation, or
excessive loading, either separately or in combination,
can cause heat buildup and possible tire failure.
Wheel Alignment and Tire Balance
The wheels on your vehicle were aligned and balanced
carefully at the factory to give you the longest tire life
and best overall performance.Scheduled wheel alignment and wheel balancing are
not needed. However, if you notice unusual tire wear or
your vehicle pulling one way or the other, the alignment
may need to be reset. If you notice your vehicle
vibrating when driving on a smooth road, your wheels
may need to be rebalanced.
Wheel Replacement
Replace any wheel that is bent, cracked or badly rusted
or corroded. If wheel nuts keep coming loose, the
wheel, wheel bolts and wheel nuts should be replaced.
If the wheel leaks air, replace it (except some
aluminum wheels, which can sometimes be repaired).
See your dealer if any of these conditions exist.
Your dealer will know the kind of wheel you need.
Each new wheel should have the same load-carrying
capacity, diameter, width, offset and be mounted
the same way as the one it replaces.
If you need to replace any of your wheels, wheel bolts
or wheel nuts, replace them only with new GM
original equipment parts. This way, you will be sure to
have the right wheel, wheel bolts and wheel nuts
for your vehicle.
5-66
Page 397 of 486
{CAUTION:
Using the wrong replacement wheels, wheel
bolts or wheel nuts on your vehicle can be
dangerous. It could affect the braking and
handling of your vehicle, make your tires lose
air and make you lose control. You could have
a collision in which you or others could be
injured. Always use the correct wheel, wheel
bolts and wheel nuts for replacement.
Notice:The wrong wheel can also cause problems
with bearing life, brake cooling, speedometer or
odometer calibration, headlamp aim, bumper height,
vehicle ground clearance and tire or tire chain
clearance to the body and chassis.
See
Changing a Flat Tire on page 5-71for more
information.
Used Replacement Wheels
{CAUTION:
Putting a used wheel on your vehicle is
dangerous. You can't know how it's been used
or how far it's been driven. It could fail
suddenly and cause a crash. If you have to
replace a wheel, use a new GM original
equipment wheel.
Tire Chains
Notice:Use tire chains only where legal and only
when you must. Use only SAE Class ªSº type chains
that are the proper size for your tires. Install them
on the front tires and tighten them as tightly as
possible with the ends securely fastened. Drive
slowly and follow the chain manufacturer's
instructions. If you can hear the chains contacting
your vehicle, stop and retighten them. If the contact
continues, slow down until it stops. Driving too
fast or spinning the wheels with chains on will
damage your vehicle.
5-67
Page 400 of 486

If a Tire Goes Flat
It's unusual for a tire to ªblowoutº while you're driving,
especially if you maintain your tires properly. If air goes
out of a tire, it's much more likely to leak out slowly.
But if you should ever have a ªblowout,º here are a few
tips about what to expect and what to do:
If a front tire fails, the ¯at tire will create a drag that
pulls the vehicle toward that side. Take your foot off the
accelerator pedal and grip the steering wheel ®rmly.
Steer to maintain lane position, and then gently brake to
a stop well out of the traffic lane.
A rear blowout, particularly on a curve, acts much like a
skid and may require the same correction you'd use
in a skid. In any rear blowout, remove your foot from the
accelerator pedal. Get the vehicle under control by
steering the way you want the vehicle to go. It may be
very bumpy and noisy, but you can still steer. Gently
brake to a stop, well off the road if possible.{CAUTION:
Lifting a vehicle and getting under it to do
maintenance or repairs is dangerous without
the appropriate safety equipment and training.
The jack provided with your vehicle is
designed only for changing a ¯at tire. If it is
used for anything else, you or others could be
badly injured or killed if the vehicle slips off
the jack. Use the jack provided with your
vehicle only for changing a ¯at tire.
If a tire goes ¯at, the next part shows how to use your
jacking equipment to change a ¯at tire safely.
5-70
Page 401 of 486
Changing a Flat Tire
If a tire goes ¯at, avoid further tire and wheel damage
by driving slowly to a level place. Turn on your
hazard warning ¯ashers.
{CAUTION:
Changing a tire can cause an injury. The
vehicle can slip off the jack and roll over you
or other people. You and they could be badly
injured. Find a level place to change your tire.
To help prevent the vehicle from moving:
1. Set the parking brake ®rmly.
2. Put the shift lever in PARK (P).
3. Turn off the engine.
To be even more certain the vehicle won't
move, you can put blocks at the front and rear
of the tire farthest away from the one being
changed. That would be the tire on the other
side of the vehicle, at the opposite end.The following steps will tell you how to use the jack and
change a tire.
5-71
Page 404 of 486

3. To remove the compact spare tire from the cable,
tilt the retainer at the end of the cable so it can be
pulled up through the wheel opening.4. If your vehicle is an all-wheel-drive vehicle, after
removing the compact spare tire turn the wrench
clockwise to raise the cable back up.
On an AWD vehicle, you can not store a full-size
tire under the vehicle. It should be stowed inside the
vehicle by the cable provided. See ªStoring the
Flat Tire on an All-Wheel-Drive Vehicleº later in this
section.
If you have a front-wheel-drive vehicle, the hoist is
used to store a full-size or a ¯at road tire under
the vehicle. See ªStoring the Spare Tire and Toolsº
and ªStoring the Flat Tire on a Front-Wheel Drive
Vehicleº later in this section.
If the compact spare tire will not lower, check under the
vehicle to see if the tire is hanging loose and the
cable end and spring under the wheel plate are missing.
If so, the secondary latch system is engaged. See
ªSecondary Latch Systemº later in this section.
To continue changing the ¯at tire see ªRemoving the
Flat Tire and Installing the Spare Tireº later in this
section.
5-74